

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 447.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190545
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
RONG Hua1,2,WANG Chungang2,*,ZHOU Ming2,*
Received:2019-10-21
Online:2020-03-10
Published:2020-01-10
Contact:
Chungang WANG,Ming ZHOU
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
RONG Hua, WANG Chungang, ZHOU Ming. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of FeS2 Microspheres as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 447.
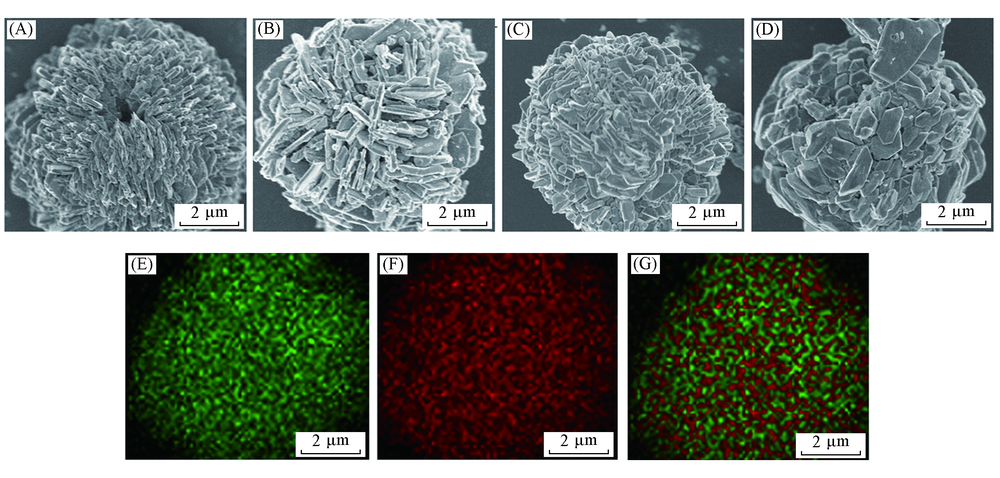
Fig.3 SEM images of single particle reacting for 5 h(A), 10 h(B), 15 h(C) and 20 h(D) and elemental mapping of Fe(E), S(F) and the overlap of Fe and S for the single particle(G)
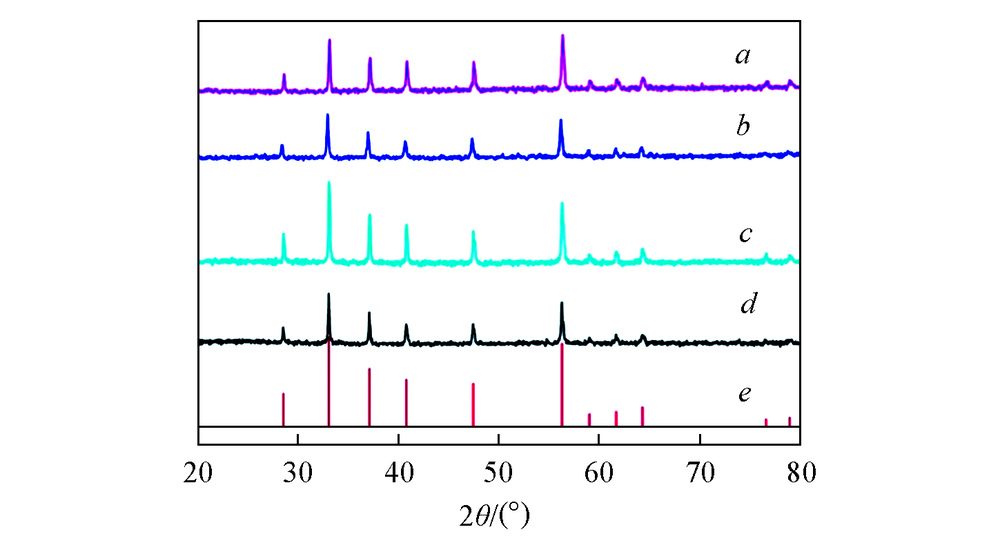
Fig.6 XRD patterns of samples with different FeCl2/Na2S3O4 molar contents FeCl2/Na2S3O4 molar content: a. 1.5/1.5; b. 1/1; c. 0.5/0.5; d. 0.25/0.25; e. FeS2, JCPDS No.71-1680.
| [1] | Zhang D., Tu J. P., Xiang J. Y., Qiao Y. Q., Xia X. H., Wang X. L., Gu C. D ., Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, 9980— 9985 |
| [2] | Takeuchi T., Kageyama H., Nakanishi K., Inada Y., Katayama M., Ohta T., Senoh H., Sakaebe H., Sakai T., Tatsumi K., Kobayashi H ., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2012, 159, A75— A84 |
| [3] | Hu Z., Zhang K., Zhu Z., Tao Z., Chen J ., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 12898— 12904 |
| [4] | Xiao Z., Xin N., Song L., Li L., Cao Z., Zhu H ., J. Electron. Mater., 2018, 47, 6311— 6318 |
| [5] | Xiao Z., Xin N., Song L., Li L., Cao Z., Zhu H ., Ionics, 2019, 1— 11 |
| [6] | Meng W., Bai X., Wang B., Liu Z., Lu S., Yang B ., Energy Environ. Mater., 2019, 2, 172— 192 |
| [7] | Lu S., Mi W., Jin G., Zeng Q., Feng X., Feng T., Liu H., Meng S., Redfern S. A. T, Yang B ., Sci. China Chem., 2018, 61, 437— 443 |
| [8] | Zhu Q., Liu C., Zhou L., Wu L., Bian K., Zeng J., Wang J., Feng Z., Yin Y., Cao Z ., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 140, 111356 |
| [9] | Du Y., Yin Z., Zhu J., Huang X., Wu X. J., Zeng Z ., Nat. Commun., 2012, 3, 1177— 1183 |
| [10] | Tao Y., Rui K., Wen Z., Wang Q. S., Jin J., Zhang T ., Solid State Ionics, 2016, 290, 47— 52 |
| [11] | Tan R., Yang J., Hu J., Wang K., Zhao Y., Pan F ., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52( 5), 986— 989 |
| [12] | Zhu X., Li J., Ali R. N., Huang M., Liu P., Xiang B ., Mater. Des., 2018, 160, 636— 641 |
| [13] | Liang K., Marcus K., Zhang S., Zhou L ., Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7( 22), 1— 6 |
| [14] | Khateeb S. A., Sparks T. D ., J. Mater. Sci., 2019, 54( 5), 4089— 4104 |
| [15] | Liu J., Wen Y., Wang Y., Aken P. A. V., Maier J ., Adv. Mater., 2014, 26( 34), 6025— 6030 |
| [16] | Huang S. Y., Liu X. Y., Li Q. Y., Chen J ., J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 472( 1/2), 9— 12 |
| [17] | Samad L., Cabán-Acevedo., Miguel., Shearer M. J., Park K., Hamers R. J., Jin S ., Chem. Mater., 2015, 27( 8), 3108— 3114 |
| [18] | Ma Q., Song H., Zhuang Q., Liu J., Chen K ., Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 338, 726— 733 |
| [19] | Ma W. Q., Liu X. Z., Lei X. F., Yuan Z. H., Ding Y ., Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 334, 725— 731 |
| [20] | Son S. B., Yersak T. A., Piper D. M., Kim S. C., Lee S. H ., Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 4( 3), 1— 5 |
| [21] | Lv J. W., Qu Y. P., Feng Y. J., Liu J. F ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37( 1), 142— 148 |
| ( 吕江维, 曲有鹏, 冯玉杰, 刘峻峰 . 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37( 1), 142— 148) |
| [1] | JIA Yanggang, SHAO Xia, CHENG Jie, WANG Pengpeng, MAO Aiqin. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of Pseudocapacitance-controlled Perovskite High-entropy Oxide La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| [2] | LI Xiaohui, WEI Aijia, MU Jinping, HE Rui, ZHANG Lihui, WANG Jun, LIU Zhenfa. Effects of SmPO4 Coatingon Electrochemical Performance of High-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210546. |
| [3] | TIAN Runsai, LU Qian, ZHANG Hongbin, ZHANG Bo, FENG Yuanyuan, WEI Jinxiang, FENG Jijun. Design and Construction of N-Doping Carbon in⁃situ Coated Cu2O/Co3O4@C Heterostructured Composite Material for Highly Efficient Lithium-ion Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2592. |
| [4] | WU Zhuoyan, LI Zhi, ZHAO Xudong, WANG Qian, CHEN Shunpeng, CHANG Xinghua, LIU Zhiliang. A Highly Efficient One-step Preparation Method of Nano-silicon and Carbon Composite for High-performance Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2500. |
| [5] | HAN Muyao, ZHAO Lina, SUN Jie. Advances in Silicon and Silicon-based Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3547. |
| [6] | YE Yihua, BA Deliang, LIU Shuailei, CHEN Yinglin, LI Yuanyuan, LIU Jinping. Recent Progress on High⁃rate Niobium-based Oxides Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3005. |
| [7] | HUANG He, LI Chunguang, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Microwave-assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon Dots Based on Tyrosine and Their Application in Ion Detection and Bioimaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1579. |
| [8] | FANG Liang,DING Xiaoli,SONG Yun,LIU Dongming,LI Yongtao,ZHANG Qingan. Effect of Morphological Tuning on Electrochemical Performance of Perovskite LaCoO3 Anodes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1456. |
| [9] | DONG Xiangyang,NIU Xiaoqing,WEI Jishi,XIONG Huanming. One-step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application in White Light Devices† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1288. |
| [10] | LIN Weiguo,SUN Weihang,QU Zongkai,FENG Xiaolei,RONG Junfeng,CHEN Xu,YANG Wensheng. Preparation and Performance of Nano-porous Si/Graphite/C Composite Microspheres as Anode Material for Li-ion Batteries† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1216. |
| [11] | JIA Hongliang,ZHAO Jianwei,QIN Lirong,ZHAO Min. Uric Acid Biosensor Based on Ni Wire Modified with NiO Nanosheets† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 240. |
| [12] | SUN Dawei,LI Yuejun,CAO Tieping,ZHAO Yanhui,YANG Diankai. Preparation of Dy 3+-doped YVO4/TiO2 Composite Nanofibers with Three-dimensional Net-like Structure and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2348. |
| [13] | WANG Qiuxian,LI Kai,YANG Beining,YUE Hongyun,YANG Shuting. Sodium Alginate Directed Synthesis of ZnFe2O4 with Micro-nano Structure and Its Performance in Lithium Ion Batteries† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2039. |
| [14] | PAN Shuai, HU Xiaobing, SONG Runmin, XIE Lili, ZHU Zhigang, ZHENG Liaoying. Ionic Liquid Assisted Synthesis of α-Fe2O3 Nanospheres Based on Potassium Acetate Solution and Their Gas-sensing Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1631. |
| [15] | KANG Yuanyuan, GUO Zeqing, ZHOU Jianping. Hydrothermal Preparation and Adsorption Property of MoS2/Na2Fe2Ti6O16† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1364. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||