

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 456.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160633
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Yanlong, FENG Xiaojuan*( ), WANG Suiqian, FENG Chunchun
), WANG Suiqian, FENG Chunchun
Received:2016-09-12
Online:2017-03-10
Published:2017-02-22
Contact:
FENG Xiaojuan
E-mail:cherry-820@163.com
Supported by:TrendMD:
SHI Yanlong, FENG Xiaojuan, WANG Suiqian, FENG Chunchun. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Film of Co(OH)2CO3 Nanowires and Its Anticorrosion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 456.
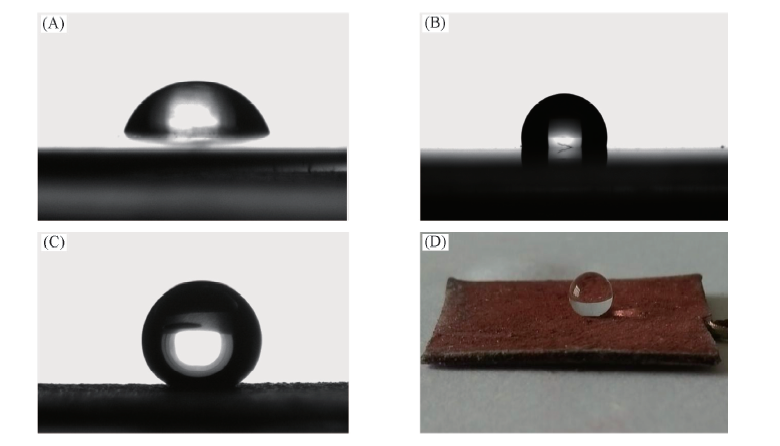
Fig.2 Images of water droplet on pristine nickel(A), pristine nickel modified by DDT(B), superhydrophobic nickel treated by hydrothermal and DDT modification(C, D)
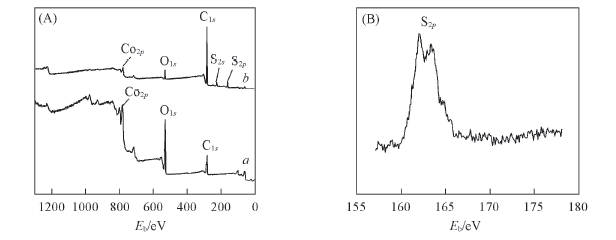
Fig.3 XPS spectra of Co(OH)2CO3 film on nickel substrate before(a) and after(b) DDT modification(A) and the characteristic peak of S2p of DDT modified Co(OH)2CO3 film(B)
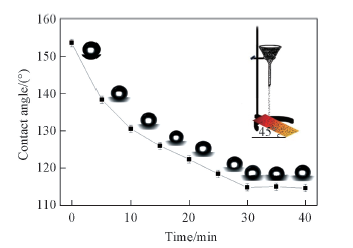
Fig.5 Relationship of water contact angles and friction times of superhydrophobic nickel The inset is a simulation device for the friction measurement.
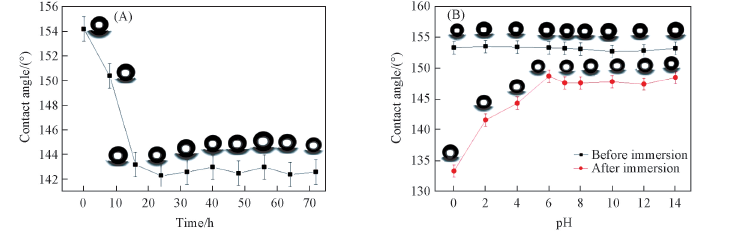
Fig.6 Relationship of contact angles of superhydrophobic nickel with immersion time(A) and pH value(B) (A) In 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution;(B) in acidic and basic solution.
| Sample | Ba/(mV·dec-1) | Bc/(mV·dec-1) | 105 Icorr/(A·cm-2 ) | Ecorr /V(vs. SCE) | Corrosion rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 7.116 | 8.806 | 1.26 | -0.517 | |
| b | 6.442 | 10.260 | 0.158 | -0.220 | 87.46 |
| c | 3.350 | 6.638 | 0.0091 | -0.165 | 99.27 |
Table 1 Electrochemical parameters correspond to Fig.7
| Sample | Ba/(mV·dec-1) | Bc/(mV·dec-1) | 105 Icorr/(A·cm-2 ) | Ecorr /V(vs. SCE) | Corrosion rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 7.116 | 8.806 | 1.26 | -0.517 | |
| b | 6.442 | 10.260 | 0.158 | -0.220 | 87.46 |
| c | 3.350 | 6.638 | 0.0091 | -0.165 | 99.27 |
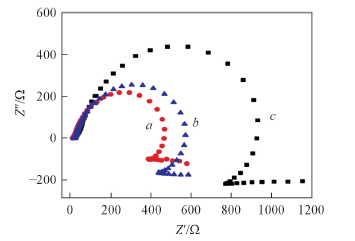
Fig.8 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of the pristine nickel(a), Co(OH)2CO3 film without modification(b) and Co(OH)2CO3treated by DDT modification(c)
| [1] | Wang R., Hashimoto K., Fujishima A., Watanabe T., Adv. Mater., 1998, 10(2), 135—138 |
| [2] | Öner D., McCarthy J. T., Langmuir,2000, 16(20), 7777—7782 |
| [3] | Liu K., Yao X., Jiang L., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 3240—3255 |
| [4] | Xiang M., Wilhelm A., Luo C., Langmuir,2013, 29(25), 7715—7725 |
| [5] | Gao X. F., Jiang L., Nature,2004, 432, 36—36 |
| [6] | Wang Y. S., Shi Y. L., Feng X. J., Yang. W., Yue G. R., Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(4), 1227—1230 |
| (王永生, 石彦龙, 冯晓娟, 杨武, 岳国仁. 科学通报, 2012, 57(4), 1227—1230) | |
| [7] | Zhang F., Chen S. G., Dong L. H., Lei Y. H., Liu T., Yin Y. S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257(7), 2587—2591 |
| [8] | Ou J. F., Hu W. H., Xue M. S., Wang F. J., Li W., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(8), 3101—3107 |
| [9] | Sun Z. Q., Liao T., Liu K. S., Jiang L., Kim J. H., Dou S. X., Small,2014, 10(15), 3001—3006 |
| [10] | Howarter J. A., Youngblood J. P., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2008, 29(6), 455—466 |
| [11] | Meuler A. J., Smith J. D., Varanasi K. K., Mabry J. M., McKinley G. H., Cohen R. E., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2(11), 3100—3110 |
| [12] | Darmanin T., Guittard F., J. Mater. Chem. A., 2014, 2(39), 16319—16359 |
| [13] | Zhang X. X., Wang L., Levänen E., RSC Adv., 2013, 3(30), 12003—12020 |
| [14] | Srinivasan S., Choi W., Park K. C., Chhatre S. S., Cohen R. E., McKinley G. H., Soft Matter, 2013, 9, 5691—5702 |
| [15] | Jiang W., He J., Xiao F., Yuan S. J., Lu H. F., Liang B., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2015, 54, 6874—6883 |
| [16] | Wu J. X., Li J. Y., Wang Z. Q., Yu M., Jiang H. Q., Li L. F., Zhang B. W., RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 27752—27758 |
| [17] | Wang B., Liang W. X., Guo Z. G., Liu W. M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 336—361 |
| [18] | Chu Z. L., Feng Y. J., Seeger S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 2—13 |
| [19] | Shi Y. L., Yang W., Feng X. J., Chem.J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9), 1724—1729 |
| (石彦龙, 杨武, 冯晓娟. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(9), 1724—1729) | |
| [20] | Liu M., Qing Y., Wu Y. Q., Liang J., Luo S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 330, 332—338 |
| [21] | Liu Y., Yin X. M., Zhang J. J., Yu S. R., Han Z. W., Ren L. Q., Electrochim Acta, 2014, 125, 395—403 |
| [22] | Li Y., Liu F., Sun J.Q.,Chem. Commun., 2009, 2730—2732 |
| [23] | Chen Z., Hao L. M, Chen A. Q., Song Q. J., Chen C. L., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 59, 168—171 |
| [24] | Wang H. Y., Zhu Y. X., Hu Z. Y., Zhang X. G., Wu S. Q., Wang R., Zhu Y. J., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 303, 37—47 |
| [25] | Isimjan T. T., Wang T., Rohani S., Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 210, 182—187 |
| [26] | Li H., Yu S. R., Han X. X., Zhao Y., Colloid Sur. A, Physicochem. Eng. Asp., 2016, 503, 43—52 |
| [27] | Liu Y., Cao H. J., Chen S. G., Wang D. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(45), 25449—25456 |
| [28] | Jeong C. Y., Lee J., Sheppard K., Choi C. H., Langmuir,2015, 31(40), 11040—11050 |
| [29] | Wu Z. Z., Wang K. K., Yuan G. Z., Li W., Song C. L., Han G. R., Liu Y., Surf. Coat Tech., 2016, 302, 468—473 |
| [30] | Zheng S. L., Li C., Fu Q. T., Hu W., Xiang T. F., Wang Q., Du M. P., Liu X. C., Chen Z., Mater. Design., 2016, 93, 261—270 |
| [31] | Zhang X., Guo Y. G., Liu Y., Yang X., Pan J. Q., Zhang P. Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 287, 299—303 |
| [32] | Wenzel R. N., Ind. Eng. Chem., 1936, 28 (8), 988—994 |
| [33] | Laibinis P. E., Whitesides G. M., Allara D. L., Tao Y. T., Parikh A. N., Nuzzo R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113(19), 7152—7167 |
| [34] | Cassie A. B. D., Baxter S., Trans. Faraday Soc., 1944, 40, 546—551 |
| [35] | Gao L. C., McCarthy T. J., Langmuir,2006, 22(14), 6234—6237 |
| [36] | Cheng Z. J., Wang J. W., Lai H., Du Y., Hou R., Li C., Zhang N. Q., Sun K. L., Langmuir,2015, 31(4), 1393—1399 |
| [37] | Youngblood J. P., McCarthy T. J., Macromolecules,1999, 32(20), 6800—6806 |
| [38] | Kim J. Y., Kim E. K., Kim S. S., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2013, 392, 376—381 |
| [39] | Schrader M. E., Langmuir, 1995, 11(9), 3585—3589 |
| [40] | Xiu Y. H., Zhu L. B., Hess D. W., Wong C. P., J. Phys. Chem. C., 2008, 112(30), 11403—11407 |
| [41] | Yuan R. X., Wu S. Q., Wang B. H., Liu Z. J., Mu L. W., Ji T., Chen L., Liu B. W., Wang H. Y., Zhu J. H., Polymer,2016, 85, 37—46 |
| [42] | She Z. X., Li Q., Wang Z. W., Li L. Q., Chen F. N., Zhou J. C., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4(8), 4348—4356 |
| [43] | Wang P., Zhang D., Qiu R., Hou B. R., Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(6), 2080—2086 |
| [44] | Liu L., Xu F. Y., Lin M., J. Phys. Chem. C., 2012, 116(35), 18722—18727 |
| [45] | Zhai L., Cebeci F. Ç., Cohen R. E., Rubner M. F., Nano Letters, 2004, 4(7), 1349—1353 |
| [46] | Peng C. W., Chang K. C., Weng C. J., Lai M. C., Hsu C. H., Hsu S. C., Hsu Y. Y., Hung W. L., Wei Y., Yeh J. M., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 95, 192—199 |
| (Ed.:V, Z, K) |
| [1] | XIA Dacheng, ZHOU Rui, TU Bo, CAI Zhiwei, GAO Nan, JI Xiaoxu, CHANG Gang, REN Xiaoming, HE Yunbin. Fabrication of Ag/Au Nanowires Array as a SERS Substrate for High-sensitivity Malachite Green Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210731. |
| [2] | LI Xiaohui, WEI Aijia, MU Jinping, HE Rui, ZHANG Lihui, WANG Jun, LIU Zhenfa. Effects of SmPO4 Coatingon Electrochemical Performance of High-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210546. |
| [3] | REN Wen, ZHANG Guoli, YAN Han, HU Xinghua, LI Kun, WANG Jingfeng, LI Ruiqi. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Polyaniline/Polytetrafluoroethylenethylene Composite Membrane and Its Separation Ability for Oil-Water Emulsion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 846. |
| [4] | LIU Shuaizhuo,ZHANG Qian,LIU Ning,XIAO Wenyan,FAN Leiyi,ZHOU Ying. One-step Synergistic Hydrophobic Modification of Melamine Sponge and Its Application † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 521. |
| [5] | RONG Hua, WANG Chungang, ZHOU Ming. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of FeS2 Microspheres as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 447. |
| [6] | WANG Wu, LAI Hua, CHENG Zhongjun, LIU Yuyan. Reversible Regulation of Droplet Directional/anti-directional Rolling on Superhydrophobic Shape Memory Microarray Surface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2538. |
| [7] | LI Botian,SHAO Wei,XIAO Da,ZHOU Xue,DONG Junwei,TANG Liming. Polypyrrole Nanowire Gels Based on Templating Fabrication and Their Energy Storage and Electrochemical Sensing Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 183. |
| [8] | HUANG He, LI Chunguang, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Microwave-assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon Dots Based on Tyrosine and Their Application in Ion Detection and Bioimaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1579. |
| [9] | DONG Xiangyang,NIU Xiaoqing,WEI Jishi,XIONG Huanming. One-step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application in White Light Devices† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1288. |
| [10] | JIA Hongliang,ZHAO Jianwei,QIN Lirong,ZHAO Min. Uric Acid Biosensor Based on Ni Wire Modified with NiO Nanosheets† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 240. |
| [11] | SUN Dawei,LI Yuejun,CAO Tieping,ZHAO Yanhui,YANG Diankai. Preparation of Dy 3+-doped YVO4/TiO2 Composite Nanofibers with Three-dimensional Net-like Structure and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2348. |
| [12] | PAN Shuai, HU Xiaobing, SONG Runmin, XIE Lili, ZHU Zhigang, ZHENG Liaoying. Ionic Liquid Assisted Synthesis of α-Fe2O3 Nanospheres Based on Potassium Acetate Solution and Their Gas-sensing Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1631. |
| [13] | KANG Yuanyuan, GUO Zeqing, ZHOU Jianping. Hydrothermal Preparation and Adsorption Property of MoS2/Na2Fe2Ti6O16† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1364. |
| [14] | LI Juan, ZHU Linfang, ZHAO Anting, LEI Guoming, GAO Li, XIA Wen, WANG Li. Catalytic Activity of Cucurbit[6]uril Modified Copper Flower Clusters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 422. |
| [15] | LI Ren, ZHAO Jianwei, HOU Jin, HE Yuanyuan, CHENG Na. Effect of the Convex and the Concave Microstructures in the Metallic Nanowires on the Initial Deformation Behavior† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 514. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||