

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 1661.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150301
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Chuting, WU Xiaofeng, LI Guanghua, GAO Lu*( ), FENG Shouhua
), FENG Shouhua
Received:2015-04-15
Online:2015-09-10
Published:2015-07-24
Contact:
GAO Lu
E-mail:gaolu@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Chuting, WU Xiaofeng, LI Guanghua, GAO Lu, FENG Shouhua. Synthesis, Structure and Luminescence Propreties of 3D Interpenetrating Metal-organic Frameworks Built by Zn(Ⅱ) and Mixed Ligands†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1661.
| Empirical formula | C26H16N2O8Zn2 | Z | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula weight | 615.15 | Dc/(Mg·m-3) | 1.688 |
| T/K | 293(2) | F(000) | 620 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Rint | 0.0699 |
| Space group | P21/c | Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.106 |
| a/nm | 0.64963(13) | Final R indices[I>2σ(I)] | R1=0.0518 |
| b/nm | 1.7952(4) | wR2=0.1214 | |
| c/nm | 1.1054(2) | R indices(all data) | R1=0.0760 |
| β/(°) | 110.13(3) | wR2=0.1408 | |
| V/nm3 | 1.2103(4) | Largest diff. peak and hole/(e·nm-3) | 820 , -927 |
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for Zn2(BPDC)(IN)2
| Empirical formula | C26H16N2O8Zn2 | Z | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formula weight | 615.15 | Dc/(Mg·m-3) | 1.688 |
| T/K | 293(2) | F(000) | 620 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Rint | 0.0699 |
| Space group | P21/c | Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.106 |
| a/nm | 0.64963(13) | Final R indices[I>2σ(I)] | R1=0.0518 |
| b/nm | 1.7952(4) | wR2=0.1214 | |
| c/nm | 1.1054(2) | R indices(all data) | R1=0.0760 |
| β/(°) | 110.13(3) | wR2=0.1408 | |
| V/nm3 | 1.2103(4) | Largest diff. peak and hole/(e·nm-3) | 820 , -927 |
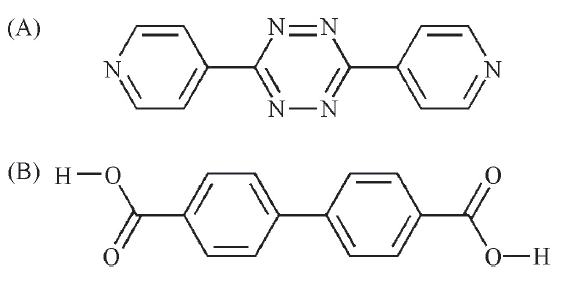
Fig.1 Structures of the rigid dipyridyl bridging ligand 3,6-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4,5-tetra-zine(A) and aromatic dicarboxylate ligand biphenyl-4,4'-dicarboxylic acid(B)
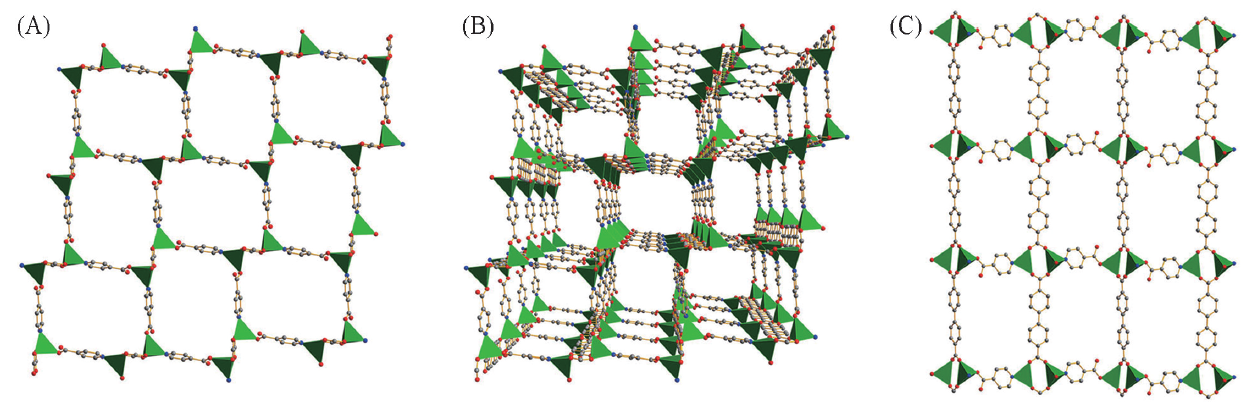
Fig.3 Views of the infinite two-dimensional layer constructed from dinuclear Zn2+ coordinated to IN ligands with the quadrangular channels of 1.205 nm×1.022 nm(A), the three-dimensional framework of [Zn2(BPDC)(IN)2] formed by [Zn2(—CO2)2(IN)2]∞ and BPDC ligands(B)and two-dimensional network of [Zn2(BPDC)(IN)2] with the quadrangular channels of 1.125 nm×1.462 nm(C)
| [1] | Wang X. Y., Wang L., Wang Z. M., Gao S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 674—675 |
| [2] | Sun T., Ying J. Y., Nature, 1997, 389, 704—706 |
| [3] | Baur W. H., Nature Materrials, 2003, 2, 17—18 |
| [4] | Wirnsberger G., Yang P., Scott B.J., Chmelka B. F., Stucky G. D., Spectro-chim. Acta A, 2001, 57, 2049—2060 |
| [5] | Mathiowitz E., Jacob J. S., Jong Y. S., Carino G. P., Chickering D. E., Chaturved P., Santos C. A., Vijayaraghavan K., Montgomery S., Bassett M., Morrell C., Nature, 1997, 386, 410—414 |
| [6] | Wigley T. M. L., Richels R., Edmonds J. A., Nature, 1996, 379, 240—243 |
| [7] | Janiak C.,Dalton Trans., 2003, 2781—2804 |
| [8] | Collins D. J., Zhou H. C., J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17, 3154—3160 |
| [9] | Li Z. Q., Wang A., Guo C. Y., Hu W. N., Tai Y. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(11), 2470—2477 |
| (李宗群, 汪艾, 郭春燕, 胡文娜, 邰艳芳. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(11), 2470—2477) | |
| [10] | Zhang Y., Yang X. G., Wang Q. Y., Yao J., Hu J., Wang G. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3), 613—618 |
| (张毅, 杨先贵, 王庆印, 姚洁, 胡静, 王公应. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(3), 613—618) | |
| [11] | Subramanian S., Zaworotk M. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 1995, 34(19), 2127—2129 |
| [12] | Yaghi O. M., Li H. L., Groy T. L. Inorg. Chem., 1997, 36, 4292—4293 |
| [13] | Yaghi O. M., O’Keeffe M., Ockwig N. W., Chse H. K., Eddaoudi M., Kim J., Nature, 2003, 423, 705—714 |
| [14] | Xue M., Chen S. R., Guo L. J., Qiu S. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(9), 1889—1894 |
| (薛铭, 陈思如, 郭莉佳, 裘式纶. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(9), 1889—1894) | |
| [15] | Hu B., Feng M. L., Li J. R., Lin Q. P., Huang X. Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 8110—8113 |
| [16] | Zheng S. T., Wu T., Chou C., Fuhr A., Feng P. Y., Bu X. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 4517—4520 |
| [17] | Pramanik S., Zheng C., Zhang X., Emge T. J., Li J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 4153—4155 |
| [18] | Takashima Y., Martínez V.M., Furukawa S., Kondo M., Shimomura S., Uehara H., Nakahama M., Sugimoto K., Kitagawa S., Nature Commun., 2010, 1—8 |
| [19] | Dinolfo P. H., Williams M. E., Stern C. L., Hupp J. T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 12989—13001 |
| [20] | Hsu C. J., Tang S. W., Wang J. S., Wang W. J., Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 2006, 456, 201—208 |
| [21] | Hao Z. M., Fang R. Q., Wu H. S., Zhang X. M., Inorg. Chem., 2008, 48(18), 8197—8203 |
| [22] | Zhang X. M., Fang R. Q., Wu H. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 7670—7671 |
| [23] | He Y. K., Han Z. B., Ma Y., Zhang X. D., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2007, 10, 829—832 |
| [24] | Zhu H. B., Ji J. F., Zhang Y. W., Gou S. H., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2009, 12, 240—242 |
| [25] | Zeng M.H., Feng X. L., Zhang W. X., Chen X. M.,Dalton Trans., 2006, 5294—5303 |
| [26] | Evans O. R., Lin W., Cryst. Growth Des., 2001, 1, 9—11 |
| [27] | Li J., Peng Y., Liang H.W., Yu Y., Xin B. J., Li G. H., Shi Z., Feng S. H.,Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2011, 2712—2719 |
| [28] | Qin J. H., Ma L. F., Hu Y., Wang L. Y., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2012, 14, 2891—2898 |
| [29] | Feng W. J., Xu Y., Zhou G. P., Zhang C. L., Zheng X. F., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2007, 10, 49—52 |
| [30] | Yuan Q., Liu B., Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2006, 27, 150—152 |
| [31] | Liu B., Xu L., Guo G.C.,J. Solid State Chem., 2006, 883—890 |
| [1] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [2] | LU Cong, LI Zhenhua, LIU Jinlu, HUA Jia, LI Guanghua, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescence Detection Properties of a New Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220037. |
| [3] | TIAN Xueqin, MO Zheng, DING Xin, WU Pengyan, WANG Yu, WANG Jian. A Squaramide-containing Luminescent Metal-organic Framework as a High Selective Sensor for Histidine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210589. |
| [4] | XING Peiqi, LU Tong, LI Guanghua, WANG Liyan. Controllable Syntheses of Two Cd(II) Metal-organic Frameworks Possessing Related Structures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220218. |
| [5] | LIU Xueguang, YANG Xiaoshan, MA Jingjing, LIU Weisheng. Separating Methyl Blue Selectively from the Mixture of Dyes by Europium Metal-organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210715. |
| [6] | HAN Zongsu, YU Xiaoyong, MIN Hui, SHI Wei, CHENG Peng. A Rare Earth Metal-Organic Framework with H6TTAB Ligand [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210342. |
| [7] | MO Zongwen, ZHANG Xuewen, ZHOU Haolong, ZHOU Dongdong, ZHANG Jiepeng. Guest-responses of A Porous Coordination Polymer Based on Synergistic Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210576. |
| [8] | SHI Xiaofan, ZHU Jian, BAI Tianyu, FU Zixuan, ZHANG Jijie, BU Xianhe. Research Status and Progress of MOFs with Application in Photoelectrochemical Water-splitting [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210613. |
| [9] | WU Ji, ZHANG Hao, LUO Yuhui, GENG Wuyue, LAN Yaqian. A Microporous Cationic Ga(III)-MOF with Fluorescence Properties for Selective sensing Fe3+ Ion and Nitroaromatic Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210617. |
| [10] | LI Wen, QIAO Junyi, LIU Xinyao, LIU Yunling. Zirconium-based Metal-Organic Framework with Naphthalene for Fluorescent Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210654. |
| [11] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [12] | WANG Jie, HUO Haiyan, WANG Yang, ZHANG Zhong, LIU Shuxia. General Strategy for In situ Synthesis of NENU-n Series Polyoxometalate-based MOFs on Copper Foil [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210557. |
| [13] | LI Shurong, WANG Lin, CHEN Yuzhen, JIANG Hailong. Research Progress of Metal⁃organic Frameworks on Liquid Phase Catalytic Chemical Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [14] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yangyang, LIU Qiyong, CHEN Boxin, ZHAO Bin, ZHOU Haimei, LI Xinxin, ZHENG Dan, FENG Fei. Silicon-based Micro Gas Chromatographic Column Using Metal-Organic Framework Material ZIF-8 as Stationary Phase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1736. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||