

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 1615.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140457
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Min, LIU Xiaoyang, ZHAO Xudong, LI Benxian, WANG Xiaofeng*( )
)
Received:2014-05-14
Online:2014-08-10
Published:2014-06-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Min, LIU Xiaoyang, ZHAO Xudong, LI Benxian, WANG Xiaofeng*. Acetone Sensing Characteristics of γ-Fe2O3 Nanofibers†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1615.
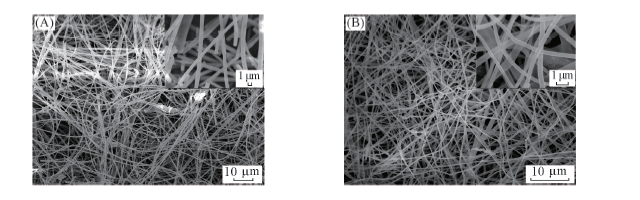
Fig.3 SEM images of PVP/FeC6H5O7 composite nanofibers(A) and γ-Fe2O3 nanofibers after calcinations(B) Insets are the magnified SEM images of the samples.
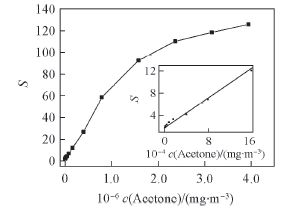
Fig.6 Gas response of the γ-Fe2O3 sensors vs. concentration of acetone Inset shows the calibration curve in an acetone concentration range of 7.88×102—1.58×105 mg/m3.
| Material | Prepare method | S, Ra/Rg | Response time/s | Recovery time/s | Work temperature/℃ | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Fe2O3 nanopowder | Solvent method | ≈27(7.88×105 mg/m3) | 20 | 100 | 240 | [ |
| γ-Fe2O3 film | Screen printing method | ≈2(7.88×104 mg/m3) | 330 | [ | ||
| γ-Fe2O3 nanopowder | Solid phase reaction | ≈5(7.88×105 mg/m3) | 335 | [ | ||
| γ-Fe2O3 nanofiber | Electrospinning method | 6.9(7.88×104 mg/m3) | 24 | 38 | 230 | This work |
| γ-Fe2O3 nanofiber | Electrospinning method | 58.5(7.88×105 mg/m3) | 25 | 41 | 230 | This work |
Table 1 γ-Fe2O3 nanomaterials prepared by different methods and the acetone sensing properties
| Material | Prepare method | S, Ra/Rg | Response time/s | Recovery time/s | Work temperature/℃ | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Fe2O3 nanopowder | Solvent method | ≈27(7.88×105 mg/m3) | 20 | 100 | 240 | [ |
| γ-Fe2O3 film | Screen printing method | ≈2(7.88×104 mg/m3) | 330 | [ | ||
| γ-Fe2O3 nanopowder | Solid phase reaction | ≈5(7.88×105 mg/m3) | 335 | [ | ||
| γ-Fe2O3 nanofiber | Electrospinning method | 6.9(7.88×104 mg/m3) | 24 | 38 | 230 | This work |
| γ-Fe2O3 nanofiber | Electrospinning method | 58.5(7.88×105 mg/m3) | 25 | 41 | 230 | This work |
| [1] | Tu J. C., Huang W., Liu Z. X., Wang X. H., Wen F., Cao Y., Chem. Engineer, 2012, 8, 1—3 |
| (涂进春, 黄玮, 刘钟馨, 王小红, 文峰, 曹阳. 化学工程师, 2012, 8, 1—3) | |
| [2] | Mani G. K., Rayappan J. B. B., Sensor Actuat. B-Chem., 2014, 198, 125—133 |
| [3] | Pan C., Dong L., Qiu J. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(5), 1031—1035 |
| (潘超, 董丽, 邱介山. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(5), 1031—1035) | |
| [4] | Liu S., Wang Z. Y., Zhao H. R., Fei T., Zhang T., Sensor Actuat. B—Chem., 2014, 197, 342—349 |
| [5] | Jing Z. H., Mater. Lett., 2006, 60, 3315—3318 |
| [6] | Patil S. B., Patil P. P., More M. A., Sensor Actuat. B-Chem., 2007, 125, 126—130 |
| [7] | Dong W. J., Zhao H.X., Li C. R., Mei J., Chen B. Y., Tang W. H., Shi Z., Feng S. H., Sci. China-Chem., 2011, 54, 865—875 |
| [8] | Jing Z. H., Wu S. H., Mater. Lett., 2006, 60, 952—956 |
| [9] | Ming J., Wu Y. Q., Wang L. Y., Yu Y. C., Zhao F. Y., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 17776—17782 |
| [10] | Kind H., Yan H. Q., Messer B. J., Law M., Yang P. D., Adv. Mater., 2002, 14, 158—160 |
| [11] | Zhang Y., He X. L., Li J. P., Miao Z. J., Huang F., Sensor Actuat. B—Chem., 2008, 132(1), 67—73 |
| [12] | Dong W. J., Huang H. D., Zhu Y. J., Li X. Y., Wang X. B., Li C. R., Chen B. Y., Wang G., Shi Z., Nanotechnology, 2012, 23, 425602—425609 |
| [13] | Chuangchote S., Sagawa T., Yoshikawa S., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 93, 033310-1—033310-3 |
| [14] | Atsunori M., Yoshinori K., Toshihiro K., Masahiro T., Tsutomu M., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2000, 83(1), 229—231 |
| [15] | Choi K. J., Jang H. W., Sensors, 2010, 10(4), 4083—4099 |
| [16] | Huang H. M., Li Z. Y., Yang F., Wang W., Wang C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6), 1200—1202 |
| (黄绘敏, 李振宇, 杨帆, 王威, 王策. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(6), 1200—1202) | |
| [17] | Nie G. D., Li S. K., Lu X. F., Wang C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(1), 15—29 |
| (乜广弟, 力尚昆, 卢晓峰, 王策. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(1, 15—29) | |
| [18] | Wang Y. H., Wang J. X., Dong X. T., Yu W. S., Liu G. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(8), 1657—1662 |
| (王莹熇, 王进贤, 董相廷, 于文生, 刘桂霞. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(8), 1657—1662) | |
| [19] | Li W. Y., Xu L. N., Chen J., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2005, 15, 851—857 |
| [20] | Mou F. Z., Xu L. L., Ma H. R., Guan J. G., Chen D. R., Wang S. H., Nanoscale, 2012, 4, 4650—4657 |
| [21] | Drits V., Srodon J., Eberl D. D., Clays Clay Miner., 1997, 45(3), 461—475 |
| [22] | Peng K. Q., Wang X., Lee S. T., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 95, 243112-1—243112-3 |
| [23] | Rezlescu E., Doroftei C., Rezlescu N., Popa P. D., Phys. Stat. Sol.(a), 2008, 205, 1790—1793 |
| [24] | Jing Z. H., Wu S. H., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2006, 22, 483—487 |
| [25] | Zhang R., Tian Y., Lu C., Liu L. Q., Liu X. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universites, 2014, 30(3), 343—346 |
| [1] | WU Yu, LI Xuan, YANG Hengpan, HE Chuanxin. Construction of Cobalt Single Atoms via Double-confinement Strategy for High-performance Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [2] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [3] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [4] | HE Beibei, YANG Kuihua, LYU Rui. Construction of Mn-Cu Bimetal Containing Phyllosilicate Nanozyme and Evaluation of the Enzyme-like Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220150. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhicai, WANG Yuge, GU Qianqian, LYU Yongpeng, XIAO Jianshu, YIN Yuan, SUN Hongguo, ZHENG Yafang, SUN Zhaoyan. Flocculation of Fillers in Isoprene Rubber and Its Effects on Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220155. |
| [6] | YAO Yiting, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Yu, LI Xiaoyun, SU Baolian, CHEN Lihua. Preparation of Hierarchical Microporous-mesoporous Fe2O3/ZSM-5 Hollow Molecular Sieve Catalytic Materials and Their Catalytic Properties for Benzylation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220090. |
| [7] | LI Yulong, XIE Fating, GUAN Yan, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Guiqun, YAO Chao, YANG Tong, YANG Yunhui, HU Rong. A Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Ion Interaction with DNA for the Detection of Silver Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| [8] | JIA Yanggang, SHAO Xia, CHENG Jie, WANG Pengpeng, MAO Aiqin. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of Pseudocapacitance-controlled Perovskite High-entropy Oxide La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| [9] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [10] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [11] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [12] | WANG Zhengwen, GAO Fengxiang, CAO Han, LIU Shunjie, WANG Xianhong, WANG Fosong. Synthesis and Property of CO2 Copolymer⁃based UV-curable Polymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220236. |
| [13] | SHI Naike, ZHANG Ya, SANSON Andrea, WANG Lei, CHEN Jun. Uniaxial Negative Thermal Expansion and Mechanism in Zn(NCN) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [14] | HUANG Mingxin, ZHOU Lei, WANG Xuezhong. Measurement of Particle Size Distribution of Battery Slurries Using Ultrasonic Attenuation Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220040. |
| [15] | GAO Wenxiu, LYU Jieqiong, GAO Yongping, KONG Changjian, WANG Xueping, GUO Shengnan, LOU Dawei. Preparation of Ethyl α⁃Cyanocinnamate Catalyzed by Nitrogen-rich Porous Organic Polymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220078. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||