

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (9): 1975.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140185
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Dandan, LIU Junbo*( ), CHANG Haibo, TANG Shanshan
), CHANG Haibo, TANG Shanshan
Received:2014-03-06
Online:2014-09-10
Published:2019-08-01
Contact:
LIU Junbo
E-mail:liujb@mail.ccut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Dandan, LIU Junbo, CHANG Haibo, TANG Shanshan. Visible Photocatalytic Degradation of Polyvinyl Chloride Film by AgNbO3 Photocatalyst†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 1975.
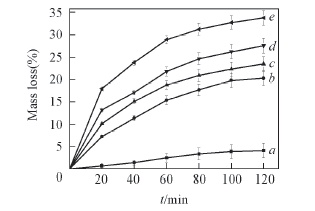
Fig.4 Mass loss of the pure film and PVC-AgNbO3 composite films under visible light irradiation a. Pure PVC; b. PVC-3%AgNbO3; c. PVC-6%AgNbO3; d. PVC-9%AgNbO3; e. PVC-15%AgNbO3.
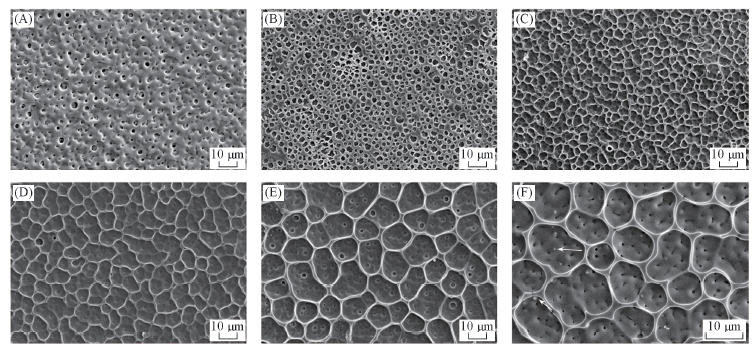
Fig.5 SEM images of the pure PVC film before(A) and after(B) photocatalytic degradation and PVC-AgNbO3 composite films after photocatalytic degradation(C—F) (C) PVC-3%AgNbO3; (D) PVC-6%AgNbO3; (E) PVC-9%AgNbO3; (F) PVC-15%AgNbO3.
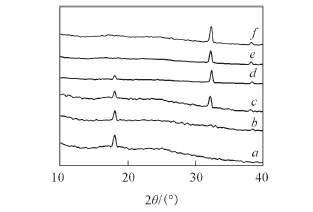
Fig.6 XRD patterns of the pure PVC film before(a) and after(b) photocatalytic degradation and of PVC-AgNbO3 composite films after photocatalytic degradation(c—f) c. PVC-3%AgNbO3; d. PVC-6%AgNbO3; e. PVC-9%AgNbO3; f. PVC-15%AgNbO3.
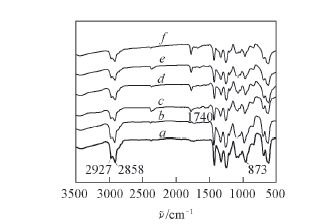
Fig.7 FTIR spectra of the pure PVC film before(a) and after(b) photocatalytic degradation and of PVC-AgNbO3 composite films after photocatalytic degradation(c—f) c. PVC-3%AgNbO3; d. PVC-6%AgNbO3; e. PVC-9%AgNbO3; f. PVC-15%AgNbO3.
| [1] | Sun G. Y., Xu S. H., Miao J. J., Gao X. F., Wang Z. Z., Polymer Mater. Sci. Engin., 2013, 29(5), 117—124 |
| (孙光耀, 徐少洪, 苗嘉俊, 高楔峰, 王正洲. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2013, 29(5), 117—124) | |
| [2] | Chen A. Z., Yin J. P., Wu D. Z., China Plastics,2013, 27(4), 25—29 |
| (陈安珍, 尹建平, 武德珍. 中国塑料, 2013, 27(4), 25—29) | |
| [3] | Zhang Z. F., Liu H. R., Zhang H., Liu X. G., Jia H. S., Xu B. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(12), 2827—2833 |
| (张振飞, 刘海瑞, 张华, 刘旭光, 贾虎生, 许并社. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(12), 2827—2833) | |
| [4] | Jaka N., Is F., Inter. J. Chem. Anal. Sci., 2013, 4(2), 125—130 |
| [5] | Yang C.J., Tian L. H., Ye L. Q., Zan L., Peng T. Y., J. Appl. Poly. Sci., 2011, 120, 2048—2053 |
| [6] | Lin H. L., Toshihiro I., Hong L., Kiyoshi O., Akira N., Mater. Res. Bull., 2011, 46, 175—184 |
| [7] | Wang M., Liu Q., Wang X. D., J. Funct. Mater., 2013, 9(44), 1315—1319 |
| (王敏, 刘琼, 王晓冬. 功能材料, 2013, 9(44), 1315—1319) | |
| [8] | Xu P. C., Liu Y., Wei J. H., Xiong R., Pan C. X., Shi J., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica,2010, 26(8), 2261—2266 |
| (许平昌, 柳阳, 魏建红, 熊锐, 潘春旭, 石兢. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26(8), 2261—2266) | |
| [9] | Lu Y. G., Yang Y. C., Ye Z. X., Liu S. Y., J. Inorg. Mater., 2012, 27(6), 643—648 |
| [10] | Liu W. K., Zhou W. C., Zhang Q. L., Pan A. L., Zhuang X. J., Wan Q., J. Inorg. Mater., 2013, 28(8), 875—879 |
| (刘文魁, 周伟昌, 张清林, 潘安练, 庄秀娟, 万强. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(8), 875—879) | |
| [11] | Liu Y., Yu L., Wei Z. G., Pan Z. C., Zou Y. D., Xie Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(2), 434—440 |
| (刘月, 余林, 魏志钢, 潘湛昌, 邹燕娣, 谢英豪. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(2), 434—440) | |
| [12] | Wang Y., Shao X., Wang B., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica,2013, 29(7), 1363—1369 |
| (王阳, 邵翔, 王兵. 物理化学学报, 2013, 29(7), 1363—1369) | |
| [13] | Hari B., Guo J. Y., A R. N., Yuan G. Y., Zhang Z. Y., Liu Z. R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(12), 2716—2721 |
| (哈日巴拉, 郭金毓, 阿茹娜, 原光瑜, 张战营, 刘宗瑞. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(12), 2716—2721) | |
| [14] | Maeda K., Teramura K., Lu D L., Nature,2006, 440, 295—297 |
| [15] | Li G. Q., Bai Y., Liu X. Y., Zhang W. F., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2009, 42, 1—4 |
| [16] | Shu H. M., Xie J. M., Xu H., Li H. M., Xu Y. G., Gu Z., J. Inorg. Mater., 2012, 25(9), 935—941 |
| (舒火明, 谢吉民, 许晖, 李华明, 徐远国, 顾正. 无机材料学报, 2012, 25(9), 935—941) | |
| [17] | Kato H., Kobayashik H., Kudo A., J. Phys. Chem. B,2002, 106, 12441—12447 |
| [18] | Li G.Q., Yan S. C., Wang Z. Q., Wang X. Y., Li Z. S., Ye J. H., Zou Z. J.,Roy. Soc. Chem., 2009, (40), 8519—8524 |
| [19] | Chang H. B., Shang M. Y., Zhang C. Y., Yuan H. M., Feng S. H., Am. Ceram. Soc,2012, 95, 3408—3414 |
| [20] | Masatomo Y., Shota M., Rikiya S., Mitsuru I., Kenji T., Fu D. S., Chem. Mater., 2011, 23, 1643—1645 |
| [21] | Xiong Y. H., Li F. Y., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica,2005, 21(6), 607—611 |
| (熊裕华, 李凤仪. 物理化学学报, 2005, 21(6), 607—611) | |
| [22] | Yang C. J., Ye L. Q., Tian L. H., Peng T. Y., Deng K. J., Zan L., J. Colloid Inter. Sci., 2011, 353, 537—541 |
| [23] | Ranby B., Rabek J.F., Photodegration Photo-Oxidation and Photostabilization of Polymers, John Wiley and Sons, Sweden, 1975 |
| [24] | Cho S. M., Choi W. Y., J. Photochem. Photobio. A: Chemistry,2001, 143, 221—228 |
| [25] | Chen Y. Y., Yuan S., Shi L. Y., Zhu H. Y., Zhang J. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2008, 29(3), 554—558 |
| (陈怡一, 袁帅, 施利毅, 朱焕扬, 张剑平. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(3), 554—558) | |
| [26] | Zhao X., Li Z. W., Chen Y., Shi L. Y., Zhu Y. F., J. Molecular Catal. A: Chemical,2007, 268(1/2), 101—106 |
| [27] | Yang C.J., Preparation and Solid-phase Photocatalytic Degradation Activity of Photodegradable Polyvinyl Chloride Composite Films, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 2010 |
| (杨昌军. 可光降解聚氯乙烯复合膜的制备及其固相光催化降解活性, 武汉: 武汉大学, 2010) | |
| [28] | Li X. J., Qiao G. J., Chen J. R., Polym. Mater. Sci. Engin., 2008, 24(9), 112—115 |
| (李晓菁, 乔冠军, 陈杰瑢. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2008, 24(9), 112—115) |
| [1] | DONG Yanhong, LU Xinhuan, YANG Lu, SUN Fanqi, DUAN Jingui, GUO Haotian, ZHANG Qinjun, ZHOU Dan, XIA Qinghua. Preparation of Bifunctional Metal-organic Framework Materials and Application in Catalytic Olefins Epoxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [2] | WANG Zumin, MENG Cheng, YU Ranbo. Doping Regulation in Transition Metal Phosphides for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [3] | SONG Jiaxin, CUI Jing, FAN Xiaoqiang, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean, ZHAO Zhen. Preparation of mesoporous silica supported highly dispersed vanadium catalyst and their catalytic performance for selective oxidation of ethane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220532. |
| [4] | TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325. |
| [5] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [6] | LIU Shuanghong, XIA Siyu, LIU Shiqi, LI Min, SUN Jiajie, ZHONG Yong, ZHANG Feng, BAI Feng. Current Advances of Hollow All-solid-state Z-scheme Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220512. |
| [7] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [8] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [9] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [10] | GAO Wenxiu, LYU Jieqiong, GAO Yongping, KONG Changjian, WANG Xueping, GUO Shengnan, LOU Dawei. Preparation of Ethyl α⁃Cyanocinnamate Catalyzed by Nitrogen-rich Porous Organic Polymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220078. |
| [11] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [12] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [13] | HU Huimin, CUI Jing, LIU Dandan, SONG Jiaxin, ZHANG Ning, FAN Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Zhen, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean. Influence of Different Transition Metal Decoration on the Propane Dehydrogenation Performance over Pt/M-DMSN Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210815. |
| [14] | ZHAO Wanjun, LI Xiao, Dang Hui, WANG Yongzhao, ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation of Supported Pd-Cu Catalyst and Its Preferential Oxidation of CO Under Hydrogen-rich Atmosphere [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210754. |
| [15] | ZHOU Ning, TANG Xiaohua, CAO Hong, ZHA Fei, LI Chun, XIE Chunyan, XU Mingping, SUN Yige. Preparation, Characterization and Degradation to BPA of Pomegranate-like Gel Microsphere Entrapmented Laccase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210705. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||