

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 2500.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180450
收稿日期:2018-06-22
出版日期:2018-11-10
发布日期:2018-09-10
作者简介:联系人简介: 李伟光, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事高级氧化技术研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
YU Xiaodan1,2, LIN Xinchen3, FENG Wei2,3, LI Weiguang1,*( )
)
Received:2018-06-22
Online:2018-11-10
Published:2018-09-10
Contact:
LI Weiguang
E-mail:hitliwg@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
以玉米秸秆为生物模板, 经铁盐和钛盐溶液浸渍后煅烧, 制备了新型Fe3O4/TiO2分层介孔玉米秸秆碳骨架复合材料(Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC), 并研究了其多相UV-Fenton体系降解四环素的效能. 利用X射线衍射(XRD)、 X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、 N2吸附-脱附、 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)对合成的催化剂进行了表征. 结果表明, Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC保留了玉米秸秆的分级多孔形态, 纳米Fe3O4和TiO2在MSC表面生长, 秸秆碳作为骨架提高了纳米Fe3O4的分散性, 防止其团聚, 提高了催化剂的稳定性, 并且能够增加材料的比表面积和活性点位, 进而增强对UV-Fenton体系的催化活性. TiO2光催化和多相Fenton体系的协同作用促进了Fe(Ⅲ)向Fe(Ⅱ)转化. 催化性能研究结果表明, 在相同条件下, Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC催化的多相UV-Fenton体系盐酸四环素(TCH)降解效率在反应40 min后达到99.8%, 远高于Fe3O4@MSC+H2O2(30%), UV+H2O2(73%)、 UV+Fe3O4@MSC+H2O2(89.1%)和UV+Fe3O4/TiO2+H2O2(89.2%)体系, 并且该体系在中性甚至碱性条件下均能达到满意的TCH去除效果.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
于晓丹, 林鑫辰, 冯威, 李伟光. Fe3O4/TiO2@生物碳骨架复合材料的一步法制备及UV-Fenton催化性能. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2500.
YU Xiaodan, LIN Xinchen, FENG Wei, LI Weiguang. One-step Preparation and UV-Fenton Properties of Fe3O4/TiO2@Bio-carbon Composities†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2500.
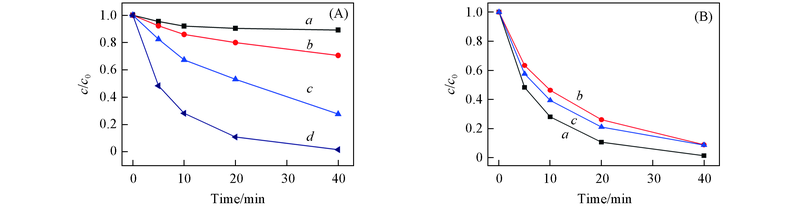
Fig.7 Degradation efficiency of TCH in different systems(A) and with different catalysts(B)Experimental conditions: [catalyst]0=0.3 g/L, [H2O2]0=10 mmol/L, [TC]0=50 mg/L, temperature=(23±1) ℃, initial pH=7; (A) a. Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC; b. Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC+H2O2; c. UV+H2O2; d. UV+Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC+H2O2.(B) a. Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC; b. Fe3O4@MSC; c. Fe3O4/TiO2.
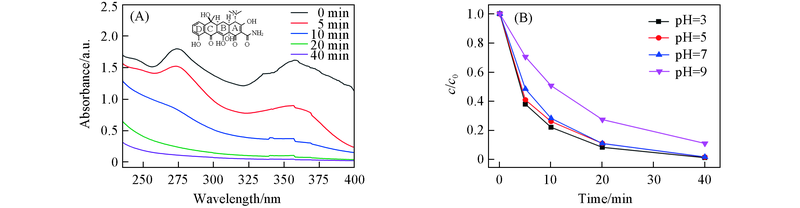
Fig.8 UV-Vis spectra of UV-Fenton system with Fe3O4/TiO2@MSC at different time(A) and at different pH(B)Experimental conditions: [catalyst]0=0.3 g/L, [H2O2]0=10 mmol/L, [TC]0=50 mg/L, temperature=(23±1) ℃. (A) Illustration is the structure of TCH; initial pH=7.
| [1] | Lopez A., Pagano M., Volpe A., Pinto A., Chemosphere, 2004, 54(7), 1005—1010 |
| [2] | Kuan C. C., Chang S. Y., Schroeder S. L. M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2015, 54(33), 8122—8129 |
| [3] | Kavitha V., Palanivelu K., Water Res., 2005, 39(13), 3062—3072 |
| [4] | Ma Z. C., Li J. S., Xing S. T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4), 636—641 |
| (马子川, 李俊淑, 邢胜涛. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(4), 636—641) | |
| [5] | Qiu B. C., Li Q. Y., Shen B., Xing M. Y., Zhang J. L., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2016, 183, 216—223 |
| [6] | Xu T. Y., Zhu R. L., Zhu G. Q., Zhu J. X., Liang X. L., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2017, 212, 50—58 |
| [7] | Huang M. J., Zhou T., Wu X. H., Mao J., Water Res., 2017, 119, 47—56 |
| [8] | Kim H. E., Lee J., Lee H. S., Lee C. H., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2012, 115/116, 219—224 |
| [9] | Zhao B. X., Li X., Li W. J., Yang L, Li J. C., Xia W. X., Zhou L., Wang F., Zhao C. L., Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 273, 527—533 |
| [10] | Deng Y. X., Xing M. Y., Zhang J. L., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2017, 211, 157—166 |
| [11] | Yang J. P., Zhao Y. C., Ma S. M., Zhu B. B., Zhang J. Y., Zheng C. G., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2016, 50(21), 12040—12047 |
| [12] | Li S., Wang M. Y., Luo Y., Huang J. G., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2016, 8(27), 17343—17351 |
| [13] | Zhang X. M., Dong Z. J., Liu S. R., Shi Y., Dong Y. H., Feng W., Sensor. Actuat. B: Chem., 2017, 243, 1224—1230 |
| [14] | Zhang Z. Y., Kong J. L., J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 193, 325—329 |
| [15] | Jia X. H., Dai R. R., Lian D. D., Han S., Wu X. Y., Song H. J., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 392, 268—276 |
| [16] | Li D., Guo X. L., Song H. R., Sun T. Y., Wan J. F., J. Hazard. Mater., 2018, 351, 250—259 |
| [17] | Wang Y., Zhang H., Chen L., Catal. Today, 2011, 175(1), 283—292 |
| [18] | Zhang Y. Y., He C., Sharma V. K., Li X. Z., Tian S. H., Xiong Y., Sep. Purif. Technology, 2011, 80(1), 45—51 |
| [19] | Du D., Shi W., Wang L. Z., Zhang J. L., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2017, 200, 484—492 |
| [1] | 郭彪, 赵晨灿, 刘芯辛, 于洲, 周丽景, 袁宏明, 赵震. 表面水热碳层对磁性NiFe2O4八面体光催化活性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220472. |
| [2] | 董妍红, 鲁新环, 杨璐, 孙凡棋, 段金贵, 郭昊天, 张钦峻, 周丹, 夏清华. 双功能金属有机骨架材料的制备及催化烯烃环氧化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [3] | 王祖民, 孟程, 于然波. 过渡金属磷化物析氢催化剂的掺杂调控[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [4] | 何建云 蒋云波 张爱敏 唐振艳 李鸿鹏. 新型卟啉基多孔有机聚合物COP-180负载钯催化剂的制备及应用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220535. |
| [5] | 夏文文 于洪晶 王时野 姚丽 李象远. 燃烧反应机理构建的极小反应网络方法—芳香烃燃烧[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220616. |
| [6] | 李怀科 岳贵初 谢海韵 刘静 高松伟 侯兰兰 李帅 苗贝贝 王女 白杰 崔志民 赵勇. 静电纺丝中空纳米纤维在催化领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220625. |
| [7] | 匡华艺 陈晨. 贵金属纳米框架催化剂的设计合成及电催化性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220586. |
| [8] | 王雅芝 贾显枝 张宏港 刘璐 赵彬然. 介质阻挡放电等离子制备5Ni-5La/SiO2催化剂用于甲烷干重整反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220503. |
| [9] | 朱佶鹏 刘润辉 宋恭华. 双噁唑啉接枝的氨基酸聚合物作为手性催化中心在不对称Henry 反应中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220569. |
| [10] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [11] | 李学宇, 王朝, 陈雅, 李可可, 李建全, 金顺敬, 陈丽华, 苏宝连. 等离激元共振光转热增强负载纳米金对丁二烯选择性加氢的催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220174. |
| [12] | 孙金时, 陈鹏, 景丽萍, 孙福兴, 刘佳. 多级孔芳香骨架材料的合成及固载硫脲催化剂的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220171. |
| [13] | 宋佳欣, 崔静, 范晓强, 孔莲, 肖霞, 解则安, 赵震. 介孔二氧化硅负载高分散钒催化剂的制备及乙烷选择氧化性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220532. |
| [14] | 唐全骏, 刘颖馨, 孟蓉炜, 张若天, 凌国维, 张辰. 单原子催化在海洋能源领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220324. |
| [15] | 林治, 彭志明, 贺韦清, 沈少华. 单原子与团簇光催化: 竞争与协同[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||