

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 20240013.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240013
白蓉1,2, 李尚伟1( ), 陈全1,2, 孙昭艳1,2, 徐文生1,2(
), 陈全1,2, 孙昭艳1,2, 徐文生1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-08
出版日期:2024-06-10
发布日期:2024-04-10
通讯作者:
李尚伟,徐文生
E-mail:swli@ciac.ac.cn;wsxu@ciac.ac.cn
基金资助:
BAI Rong1,2, LI Shangwei1( ), CHEN Quan1,2, SUN Zhaoyan1,2, XU Wensheng1,2(
), CHEN Quan1,2, SUN Zhaoyan1,2, XU Wensheng1,2( )
)
Received:2024-01-08
Online:2024-06-10
Published:2024-04-10
Contact:
LI Shangwei, XU Wensheng
E-mail:swli@ciac.ac.cn;wsxu@ciac.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
性能优异的聚合物电解质需要兼具较高的离子电导率和良好的机械性能. 深入理解聚合物的结构和分子动力学及其与材料宏观性能之间的关系, 对于从分子尺度设计高性能聚合物电解质至关重要. 本文选取玻璃化转变温度低、 氢键缔合基团位于链端的非晶遥爪型聚丙二醇模型体系, 通过化学修饰端基合成了分子量为1000, 2000和4000的两端端基均为烯丙基的聚丙二醇, 并利用宽频介电谱研究了链端基团相互作用强度及分子量对聚丙二醇多尺度动力行为的影响. 实验结果表明, 具有两种不同端基的聚丙二醇均出现了对应链段尺度的α松弛和对应整链尺度的Normal Mode松弛. 在相同温度下, 端基相互作用会同时影响两个松弛过程, 相互作用越强, 松弛时间越长. 由于端基含量随分子量减小而增加, 分子量越小, 缔合端基对高分子动力学的影响越明显. 此外, 利用高分子玻璃化熵理论研究了端基缔合强度和分子量对遥爪型高分子熔体链段动力学的影响, 理论预测与实验结果定性一致. 研究结果为聚合物电解质的分子设计提供了指导.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
白蓉, 李尚伟, 陈全, 孙昭艳, 徐文生. 遥爪型聚丙二醇熔体动力学的宽频介电谱研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(6): 20240013.
BAI Rong, LI Shangwei, CHEN Quan, SUN Zhaoyan, XU Wensheng. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy Study of Dynamics of Telechelic Polypropylene Glycol Melts. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(6): 20240013.
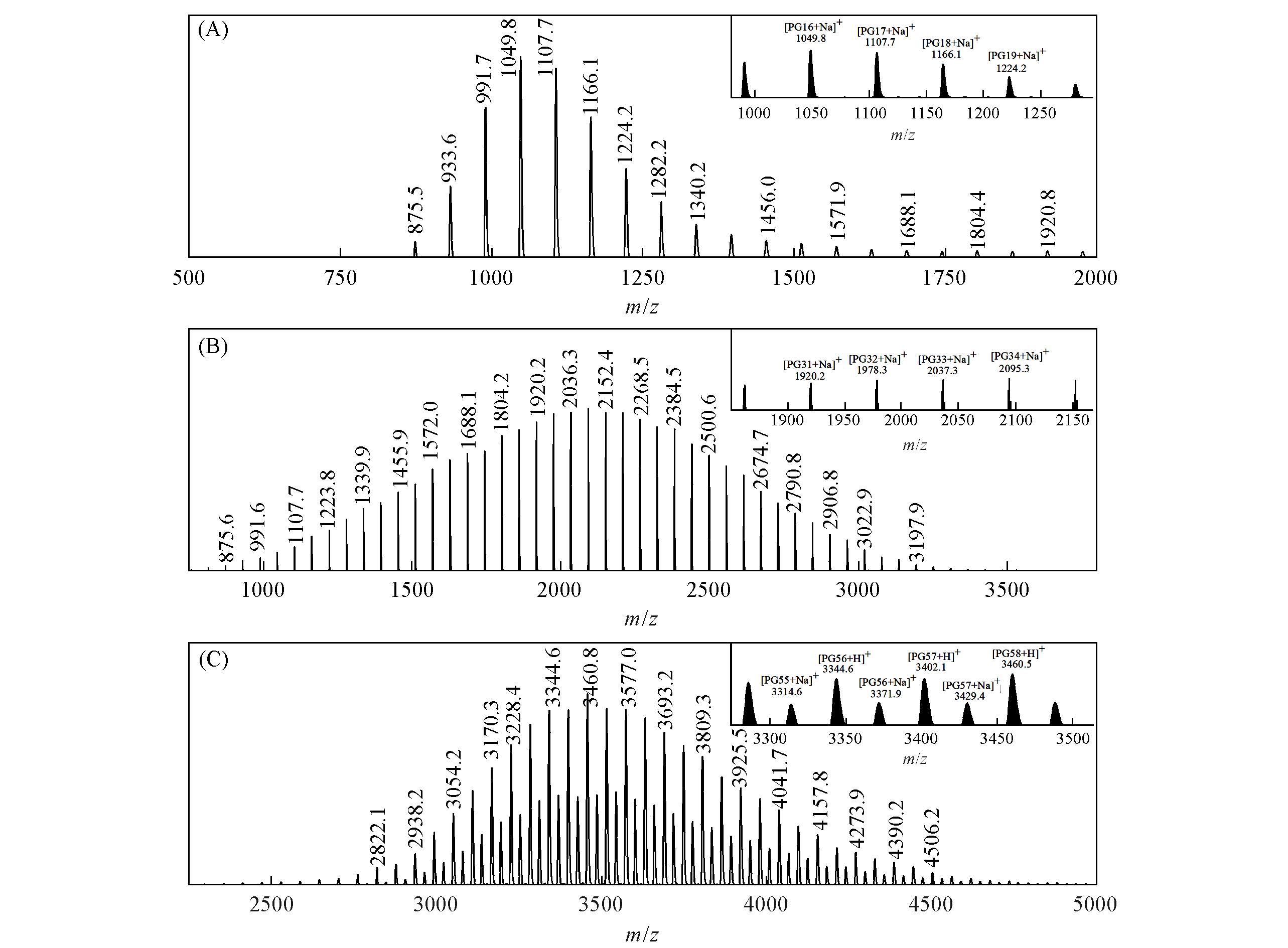
Fig.2 MALDI⁃TOF⁃MS spectra of 1k⁃PPG⁃C=C(A), 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C(B) and 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C(C)The insets highlight the spectra in the particular range where the characteristics of m/z are most evident.
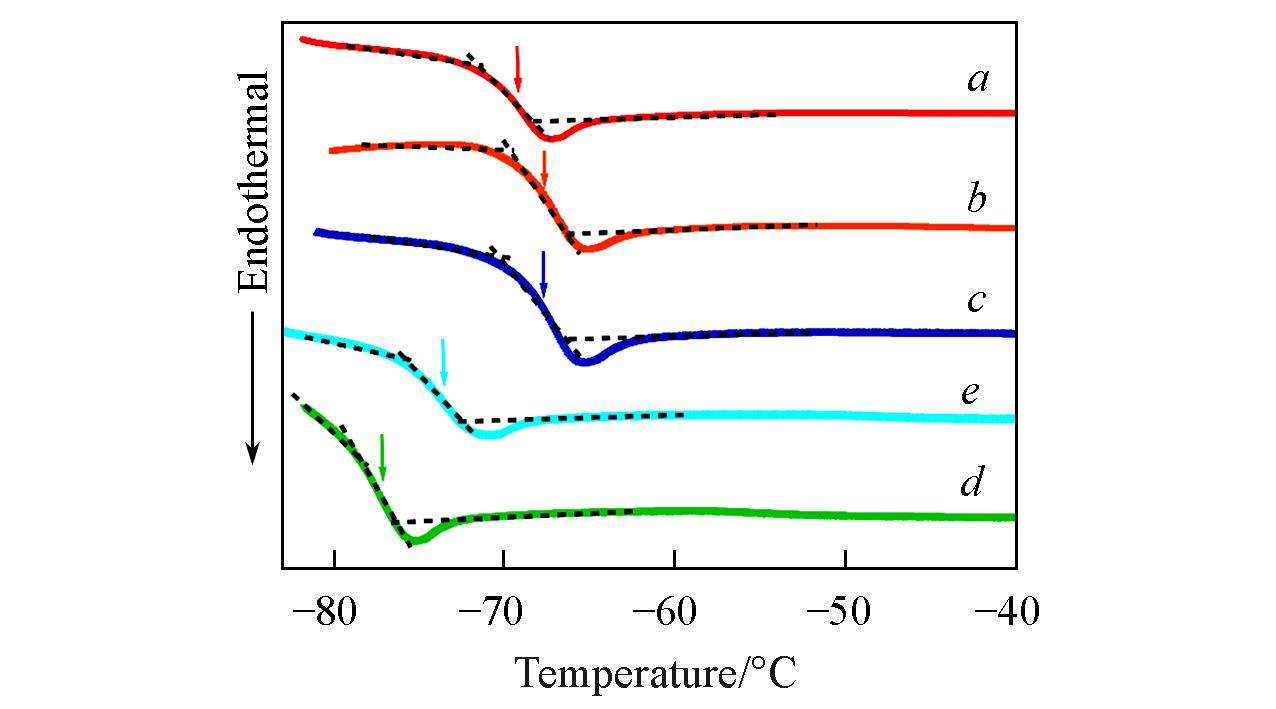
Fig.3 DSC trace of 1k⁃PPG⁃OH(a), 2k⁃PPG⁃OH(b), 4k⁃PPG⁃OH(c), 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C(d) and 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C(e)Arrows indicate the locations of the glass transition temperatures(Tg).
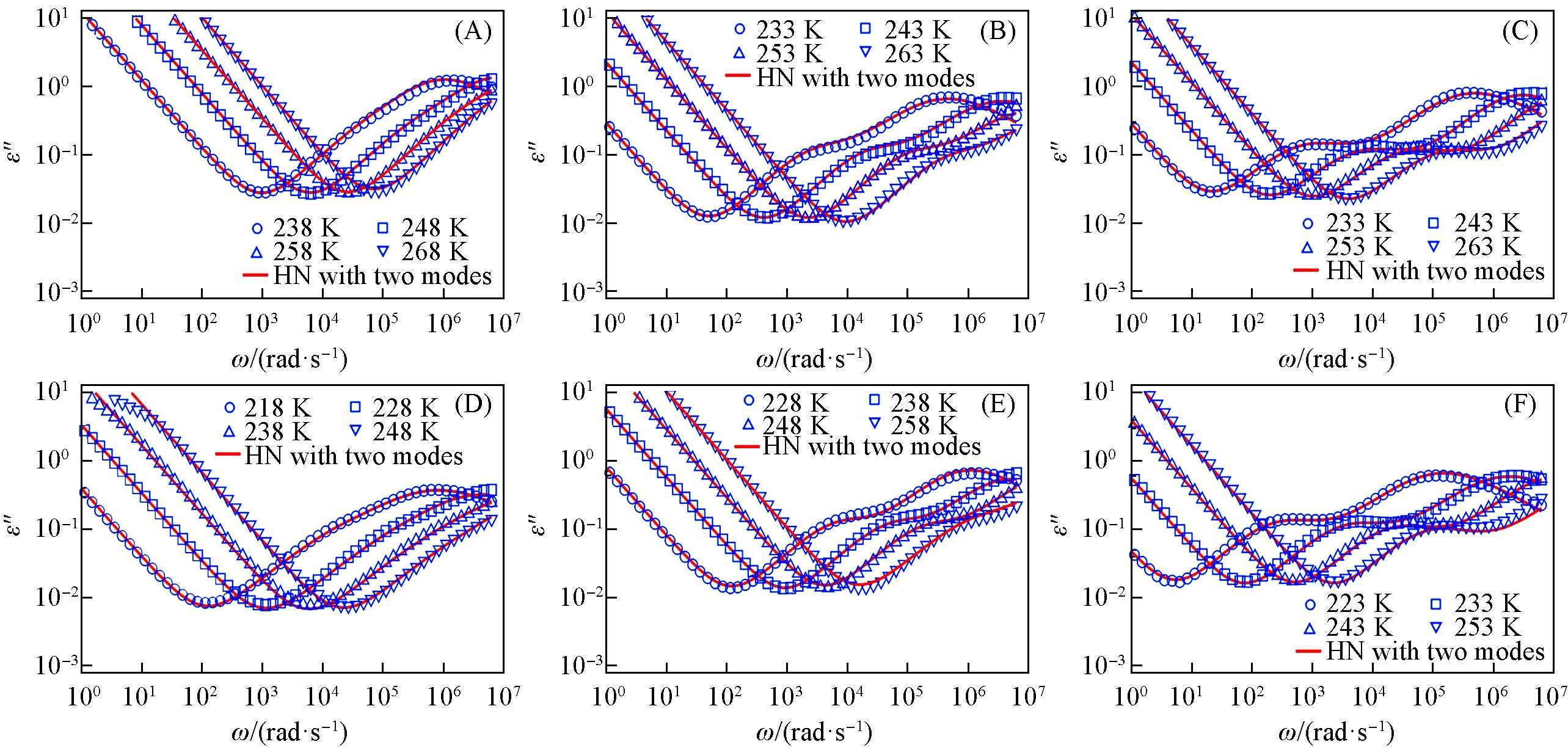
Fig.4 Dielectric loss spectra measured of 1k⁃PPG⁃OH(A), 2k⁃PPG⁃OH(B), 4k⁃PPG⁃OH(C), 1k⁃PPG⁃C=C(D), 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C(E) and 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C(F)Symbols correspond to experimental measurements. Solid lines correspond to the fits based on the Havriliak-Negami(HN) equation.
| Sample | Segmental(α) relaxation | NM relaxation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lg[τ0(s)] | D | T0/K | m | lg[τ0(s)] | D | T0/K | m | |
| 1k⁃PPG⁃OH | -11.2 | 4.5 | 174 | 102 | -12.1 | 7.7 | 161 | 63 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃OH | -12.0 | 5.0 | 174 | 103 | -11.5 | 9.4 | 155 | 58 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃OH | -11.8 | 4.6 | 176 | 109 | -10.0 | 6.6 | 166 | 63 |
| 1k⁃PPG⁃C=C | -18.2 | 16.6 | 136 | 77 | -11.7 | 8.9 | 142 | 63 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C | -14.4 | 8.8 | 156 | 87 | -11.9 | 10.5 | 146 | 56 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C | -13.9 | 7.6 | 162 | 93 | -9.8 | 6.0 | 163 | 65 |
Table 1 Vogel-Fulcher-Tamman(VFT) parameters and fragility index m for the dielectric relaxations of PPGs
| Sample | Segmental(α) relaxation | NM relaxation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lg[τ0(s)] | D | T0/K | m | lg[τ0(s)] | D | T0/K | m | |
| 1k⁃PPG⁃OH | -11.2 | 4.5 | 174 | 102 | -12.1 | 7.7 | 161 | 63 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃OH | -12.0 | 5.0 | 174 | 103 | -11.5 | 9.4 | 155 | 58 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃OH | -11.8 | 4.6 | 176 | 109 | -10.0 | 6.6 | 166 | 63 |
| 1k⁃PPG⁃C=C | -18.2 | 16.6 | 136 | 77 | -11.7 | 8.9 | 142 | 63 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C | -14.4 | 8.8 | 156 | 87 | -11.9 | 10.5 | 146 | 56 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C | -13.9 | 7.6 | 162 | 93 | -9.8 | 6.0 | 163 | 65 |
| Sample | Mn | Tg,cal/K | Tg,diel/K |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1k⁃PPG⁃OH | 1000 | 204.4 | 199.8 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃OH | 2000 | 206.3 | 200.9 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃OH | 4000 | 206.3 | 201.7 |
| 1k⁃PPG⁃C=C | 1080 | — | 184.3 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C | 2080 | 195.9 | 191.8 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C | 4080 | 199.8 | 195.4 |
Table 2 Basic properties of PPGs
| Sample | Mn | Tg,cal/K | Tg,diel/K |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1k⁃PPG⁃OH | 1000 | 204.4 | 199.8 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃OH | 2000 | 206.3 | 200.9 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃OH | 4000 | 206.3 | 201.7 |
| 1k⁃PPG⁃C=C | 1080 | — | 184.3 |
| 2k⁃PPG⁃C=C | 2080 | 195.9 | 191.8 |
| 4k⁃PPG⁃C=C | 4080 | 199.8 | 195.4 |
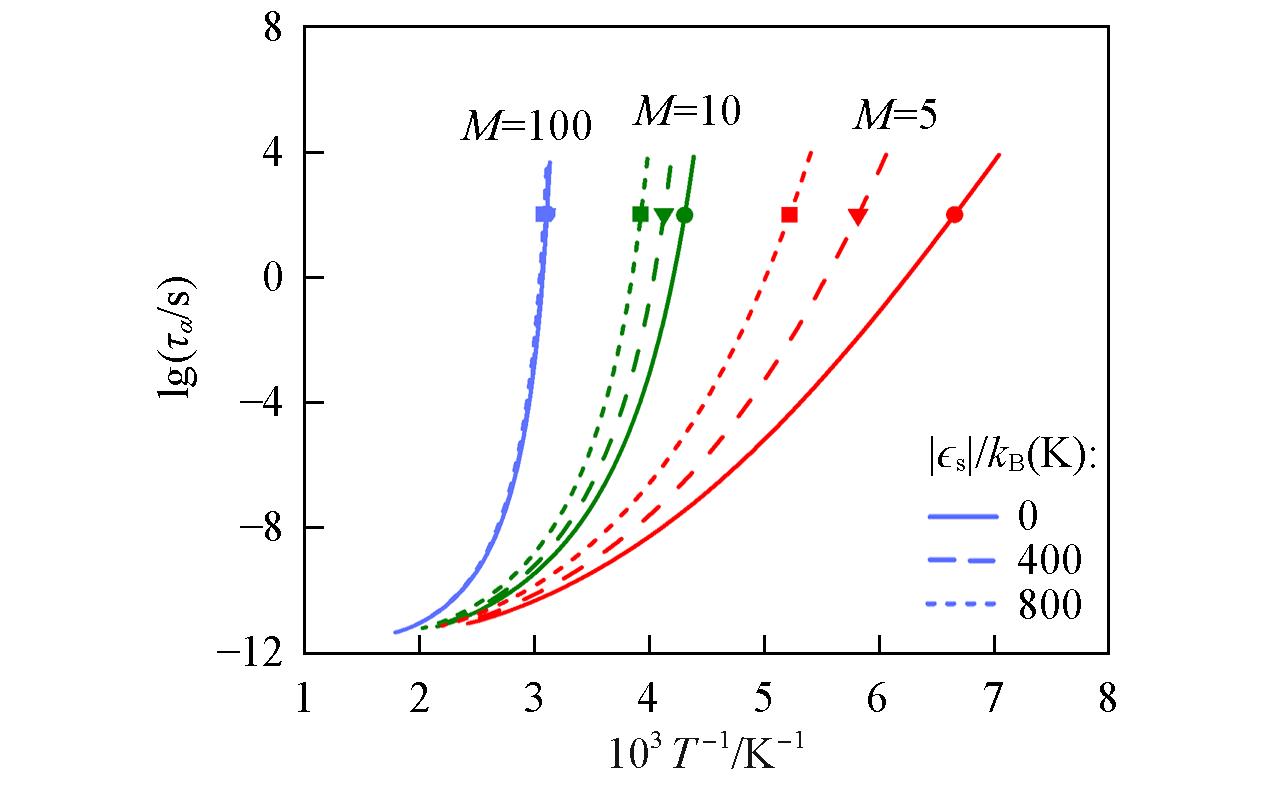
Fig.7 Predictions from the generalized entropy theory(GET) of the Arrhenius plot of α relaxation time for telechelic polymer melts having variable molecular mass and sticky interaction strengthSymbols indicate the positions of Tg.
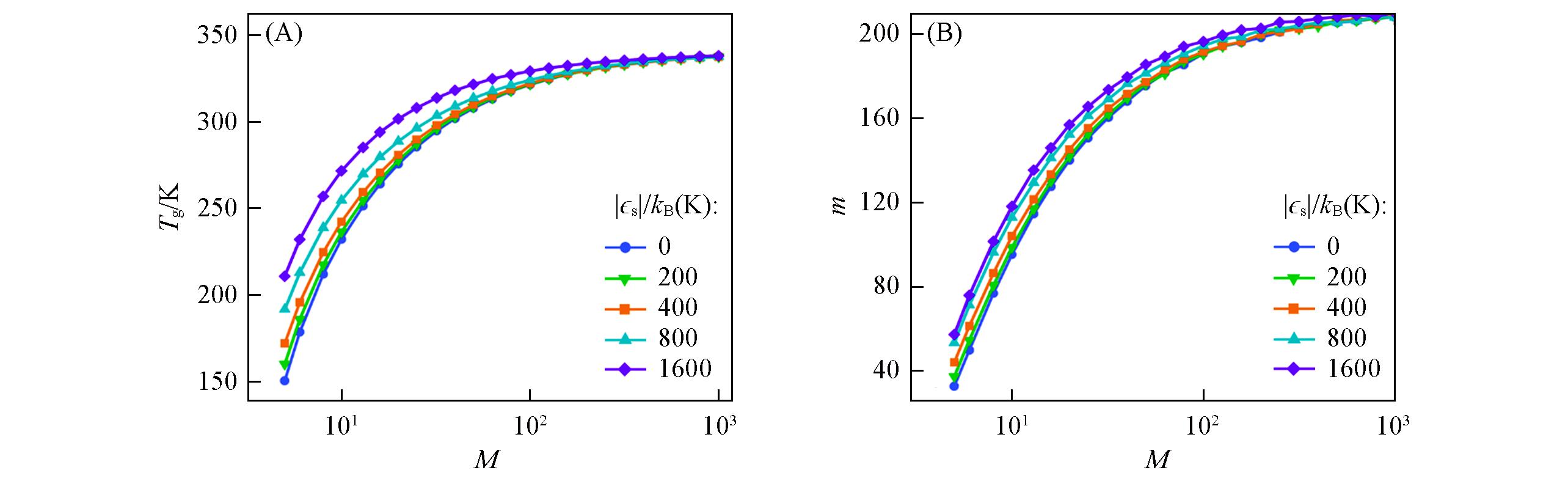
Fig.8 Predictions from the GET of the molecular mass dependence of Tg(A) and m(B) for telechelic polymer melts having variable sticky interaction strength
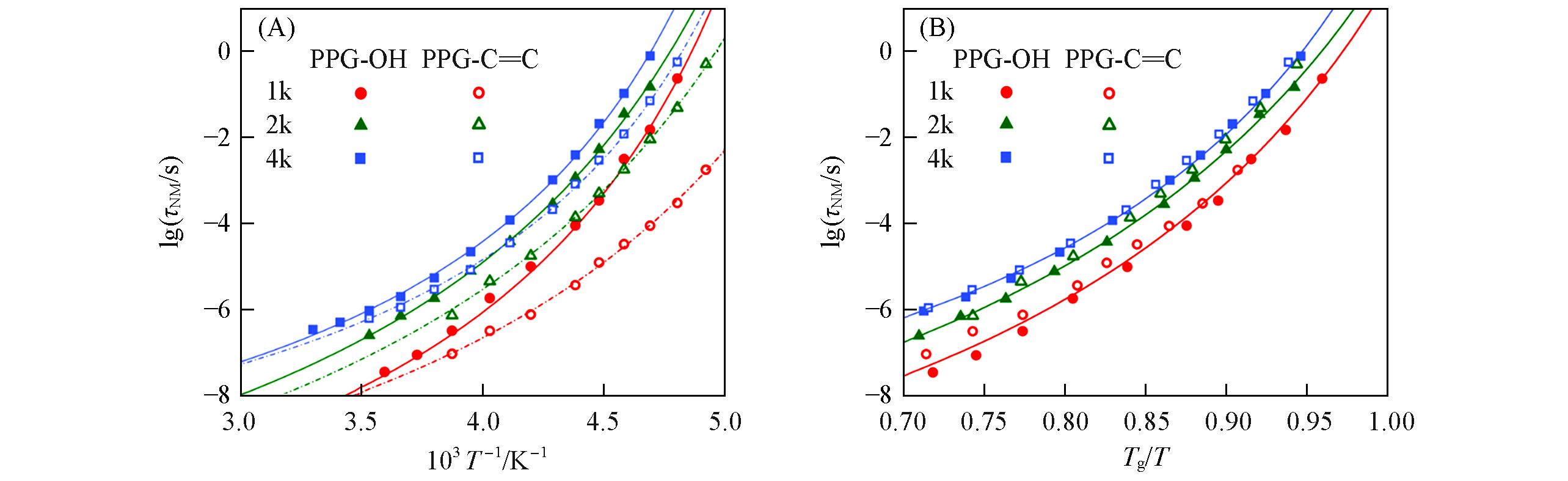
Fig.9 Arrhenius plots(A) and Angell plots(B) of NM relaxation time for PPGs having variable molecular weightSymbols correspond to experimental measurements. Solid and dashed lines are fits to the VFT equation.
| 1 | Ramesh S., Lu S. C., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 126(S2), E484—E492 |
| 2 | Vincent C. A., Prog. Solid State Chem., 1987, 17(3), 145—261 |
| 3 | Sa’adun N. N., Subramaniam R., Kasi R., Sci. World J., 2014, 2014, 254215 |
| 4 | Susan M. A. B. H., Kaneko T., Noda A., Watanabe M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(13), 4976—4983 |
| 5 | Ngai K. S., Ramesh S., Ramesh K., Juan J. C., Ionics, 2016, 22(8), 1259—1279 |
| 6 | Arya A., Sharma A. L., Ionics, 2017, 23(3), 497—540 |
| 7 | Aziz S. B., Brza M. A., Nofal M. M., Abdulwahid R. T., Hussen S. A., Hussein A. M., Karim W. O., Materials, 2020, 13(17), 3675 |
| 8 | Wang H. C., Li S., Ghulam Y., Li W., Xu H., He X. M., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 33, 188—215 |
| 9 | Meabe L., Aldalur I., Lindberg S., Arrese⁃Igor M., Armand M., Martinez⁃Ibañez M., Zhang H., Materials Futures, 2023, 2(3), 033501 |
| 10 | Tong B., Song Z. Y., Wu H., Wang X. X., Feng W. F., Zhou Z. B., Zhang H., Materials Futures, 2022, 1(4), 042103 |
| 11 | Vashishta P., Mundy J. N., Shenoy G. K., Fast Ion Transport in Solids: Electrodes and Electrolytes, Amsterdam, North Holland, 1979 |
| 12 | Ferry A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1997, 101(2), 150—157 |
| 13 | Ferry A., Jacobsson P., Stevens J. R., J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(30), 12574—12582 |
| 14 | Fan F., Wang Y. Y., Sokolov A. P., Macromolecules, 2013, 46(23), 9380—9389 |
| 15 | Schantz S., Torell L. M., Stevens J. R., J. Chem. Phys., 1991, 94(10), 6862—6867 |
| 16 | Xing K. Y., Tress M., Cao P. F., Fan F., Cheng S. W., Saito T., Sokolov A. P., Macromolecules, 2018, 51(21), 8561—8573 |
| 17 | Novikov V. N., Sokolov A. P., Entropy⁃Switz, 2022, 24(8), 1101 |
| 18 | Ngai K. L., Capaccioli S., Paluch M., Wang L., Philos. Mag., 2020, 100(20), 2596—2613 |
| 19 | Ngai K. L., Grzybowska K., Grzybowski A., Kaminska E., Kaminski K., Paluch M., Capaccioli S., J. Non⁃Cryst. Solids, 2008, 354(47), 5085—5088 |
| 20 | Ngai K. L., Paluch M., J. Chem. Phys., 2004, 120(2), 857—873 |
| 21 | Ngai K. L., Pawlus S., Grzybowska K., Kaminski K., Capaccioli S., Paluch M., Macromolecules, 2015, 48(12), 4151—4157 |
| 22 | Ngai K. L., Relaxation and Diffusion in Complex Systems, Springer, New York, 2011, 49—638 |
| 23 | Gainaru C., Hiller W., Böhmer R., Macromolecules, 2010, 43(4), 1907—1914 |
| 24 | Talik A., Tarnacka M., Dzienia A., Kaminska E., Kaminski K., Paluch M., Macromolecules, 2019, 52(15), 5658—5669 |
| 25 | Tarnacka M., Kaminski K., Mapesa E. U., Kaminska E., Paluch M., Macromolecules, 2016, 49(17), 6678—6686 |
| 26 | Hofmann M., Gainaru C., Cetinkaya B., Valiullin R., Fatkullin N., Rössler E. A., Macromolecules, 2015, 48(20), 7521—7534 |
| 27 | Kaminski K., Kipnusu W. K., Adrjanowicz K., Mapesa E. U., Iacob C., Jasiurkowska M., Wlodarczyk P., Grzybowska K., Paluch M., Kremer F., Macromolecules, 2013, 46(5), 1973—1980 |
| 28 | Ge S., Tress M., Xing K., Cao P. F., Saito T., Sokolov A. P., Soft Matter, 2020, 16(2), 390—401 |
| 29 | Diogo H. P., Moura R. J. J., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2021, 61(6), 1638—1649 |
| 30 | Baker D. L., Reynolds M., Masurel R., Olmsted P. D., Mattsson J., Phys. Rev. X, 2022, 12(2), 021047 |
| 31 | Liu S., Zhang Z. J., Chen Q., Matsumiya Y., Watanabe H., Macromolecules, 2021, 54(20), 9724—9738 |
| 32 | He Q. B., Zhang Y. J., Li H. L., Chen Q., Macromolecules, 2020, 53(24), 10927—10941 |
| 33 | Liu S., Wu S. L., Chen Q., ACS Macro Lett., 2020, 9(7), 917—923 |
| 34 | Zhang Z. J., Chen Q., Colby R. H., Soft Matter, 2018, 14(16), 2961—2977 |
| 35 | Ghosh A., Samanta S., Ge S., Sokolov A. P., Schweizer K. S., Macromolecules, 2022, 55(6), 2345—2357 |
| 36 | Fontanella J. J., Wintersgill M. C., Smith M. K., Semancik J., Andeen C. G., J. Appl. Phys., 1986, 60(8), 2665—2671 |
| 37 | Aziz S. B., Woo T. J., Kadir M. F. Z., Ahmed H. M., J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices, 2018, 3(1), 1—17 |
| 38 | Fu Y., Pathmanathan K., Stevens J. R., J. Chem. Phys., 1991, 94(9), 6323—6329 |
| 39 | Dou S. C., Zhang S. H., Klein R. J., Runt J., Colby R. H., Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(18), 4288—4295 |
| 40 | Xu W. S., Freed K. F., J. Chem. Phys., 2015, 143(2), 024901 |
| 41 | Xu W. S., Freed K. F., J. Chem. Phys., 2015, 143(2), 024902 |
| 42 | Xu W. S., Freed K. F., J. Chem. Phys., 2016, 144(21), 214903 |
| 43 | Freed K. F., Dudowicz J., Influence of Monomer Molecular Structure on the Miscibility of Polymer Blends, Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005, 63—126 |
| 44 | Adam G., Gibbs J. H., J. Chem. Phys., 1965, 43(1), 139—146 |
| 45 | Yuan Q. L., Yang Z. Y., Xu W. S., Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2023, 53(4), 616—627 |
| 袁琦璐, 杨镇岳, 徐文生. 中国科学: 化学, 2023, 53(4), 616—627 | |
| 46 | Xu W. S., Sun Z. Y., Chin. J. Polym. Sci., 2023, 41(9), 1329—1341 |
| 47 | Xu W. S., Douglas J. F., Sun Z. Y., Macromolecules, 2021, 54(7), 3001—3033 |
| 48 | Gainaru C., Böhmer R., Macromolecules, 2009, 42(20), 7616—7618 |
| 49 | Jang K., Miura K., Koyama Y., Takata T., Org. Lett., 2012, 14(12), 3088—3091 |
| 50 | Woodward W. H. H., Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy—A Practical Guide, American Chemical Society, Washington DC, 2021, 3—59 |
| 51 | Zhao K. S., Dielectric Spectroscopy Methods and Applications, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2008, 1—5 |
| 赵孔双. 介电谱方法及应用, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008, 1—5 | |
| 52 | Kremer F., Schohals A., Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy, Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002, 1—33 |
| 53 | Xu W. S., Freed K. F., J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 141(4), 044909 |
| 54 | Dudowicz J., Douglas J. F., Freed K. F., J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 141(23), 234903 |
| 55 | Angell C. A., J. Non⁃Cryst. Solids, 1991, 131, 13—31 |
| 56 | Angell C. A., Science, 1995, 267(5206), 1924—1935 |
| 57 | Boersma A., van Turnhout J., Wübbenhorst M., Macromolecules, 1998, 31(21), 7453—7460 |
| 58 | Vogel H., Phys. Z, 1921, 22(1), 645—646 |
| 59 | Tammann G., Hesse W., Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1926, 156(1), 245—257 |
| 60 | Fulcher G. S., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1925, 8(6), 339—355 |
| 61 | Dudowicz J., Freed K. F., Douglas J. F., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109(45), 21285—21292 |
| 62 | Dudowicz J., Freed K. F., Douglas J. F., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109(45), 21350—21356 |
| 63 | Angell C. A., J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol., 1997, 102(2), 171—185 |
| 64 | Angell C. A., Polymer, 1997, 38(26), 6261—6266 |
| 65 | Stickel F., Fischer E. W., Richert R., J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 102(15), 6251—6257 |
| 66 | Stickel F., Fischer E. W., Richert R., J. Chem. Phys., 1996, 104(5), 2043—2055 |
| 67 | Roggero A., Caussé N., Pébère N., Dantras E., Polymer, 2022, 241, 124542 |
| 68 | Hansen C., Stickel F., Berger T., Richert R., Fischer E. W., J. Chem. Phys., 1997, 107(4), 1086—1093 |
| 69 | Struik L., Polymer, 1997, 38(6), 1477—1479 |
| 70 | Schmidtke B., Hofmann M., Lichtinger A., Rössler E. A., Macromolecules, 2015, 48(9), 3005—3013 |
| 71 | Cohen M. H., Turnbull D., J. Chem. Phys., 1959, 31(5), 1164—1169 |
| 72 | Turnbull D., Cohen M. H., J. Chem. Phys., 1961, 34(1), 120—125 |
| 73 | Turnbull D., Cohen M. H., J. Chem. Phys., 1970, 52(6), 3038—3041 |
| 74 | Kashiwagi Y., Urakawa O., Zhao S., Takashima Y., Harada A., Inoue T., Macromolecules, 2021, 54(7), 3321—3333 |
| [1] | 矫龙, 代学民, 牟建新, 杜志军, 王汉夫, 董志鑫, 邱雪鹏. 柔性OLED用高耐热聚酰亚胺薄膜的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220390. |
| [2] | 赵宝东, 刘亚静, 潘永飞, 刘卫孝, 高福磊, 汪营磊. 含能增塑剂2, 2-偕二硝基丙基三氟丙酸酯的合成及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2815. |
| [3] | 黄聪聪, 张宝庆, 刘琛阳. 聚酰亚胺玻璃化转变温度预测: 基团贡献加和法与未知基团赋值[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2617. |
| [4] | 吴红枚, 李惠婷, 李永成, 王宏青, 王孟. 基于基团贡献法和分子动力学预测聚间苯二甲酰对苯二胺的玻璃化转变温度[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 180. |
| [5] | 路莹, 杨雪, 杨霞, 朱遂一, 范伟, 耿直. 侧链含卤素基团聚芳醚酮的合成及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(9): 1819. |
| [6] | 张玥, 张洪生, 郭卫红, 吴驰飞. 热处理条件对R-PET/LLDPE-g-MA共混物中PET玻璃化转变行为的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(5): 1024. |
| [7] | 陆晴, 赵孔双, 赵方, 贾京津. 聚吡咯/聚苯乙烯混合膜/电解质溶液体系的介电谱解析电解质种类和浓度对膜透过性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(1): 113. |
| [8] | 麦亦勇, 周永丰, 颜德岳. 超支化聚醚的支化度对玻璃化转变温度的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(7): 1373. |
| [9] | 边界, 叶胜荣, 封麟先. PET类共聚酯的玻璃化转变[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2003, 24(1): 155. |
| [10] | 张肇英, 黄玉惠, 廖兵, 丛广民. 对-氨基苯甲酸改性环氧树脂的性能表征及乳化性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 23(5): 974. |
| [11] | 单国荣, 翁志学, 黄志明, 潘祖仁. 乙烯基单体-N-取代马来酰亚胺共聚物玻璃化温度研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2000, 21(10): 1603. |
| [12] | 张海潮, 潘才元. 聚甲基丙烯酸-对-甲氧基偶氮苯氧己基酯的液晶及光响应行为[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1999, 20(7): 1152. |
| [13] | 杜淼, 翁志学, 单国荣, 黄志明, 潘祖仁. 氯乙烯/N-苯基马来酰亚胺共聚物的玻璃化温度研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1999, 20(10): 1656. |
| [14] | 陈平, 杜惠, 刘凤歧, 李铁津, 汤心颐. 包覆Fe2O3超微粒的苯乙烯/丙烯酸/丙烯酸丁酯核-壳型复合共聚物的性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1998, 19(1): 148. |
| [15] | 柯杨船, 郑玉斌, 吴忠文, 张善举, 那辉, 王军佐, 姬相玲. 主链芳香型刚性链聚醚酮(砜)分子结构与其热性能的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1996, 17(6): 978. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||