

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 1031.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200620
收稿日期:2020-08-31
出版日期:2021-04-10
发布日期:2020-12-15
通讯作者:
汪大洋
E-mail:wangdayang@jlu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2020-08-31
Online:2021-04-10
Published:2020-12-15
Contact:
WANG Dayang
E-mail:wangdayang@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
立足于分子自组装单层膜的制备及结构, 讨论了分子自组装单层膜的头基基团与基底的作用机理、 主链与环境的温度依赖关系, 特别是其端基基团的化学性质及构象对表面浸润行为的影响. 重点讨论了分子自组装单层膜的端甲基基团对表面能的贡献、 极性端基基团与水分子之间的相互作用以及自组装单层膜表面的分子尺寸粗糙度对表面浸润的影响. 最后, 基于理论和实验基础对以上问题提出新的认知与看法, 并对未来该领域发展的机遇与挑战进行了展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
马卓远, 汪大洋. 分子自组装单层膜的表面浸润性研究现状和展望. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1031.
MA Zhuoyuan, WANG Dayang. Status and Prospect of Surface Wettability of Molecular Self-assembled Monolayers. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1031.
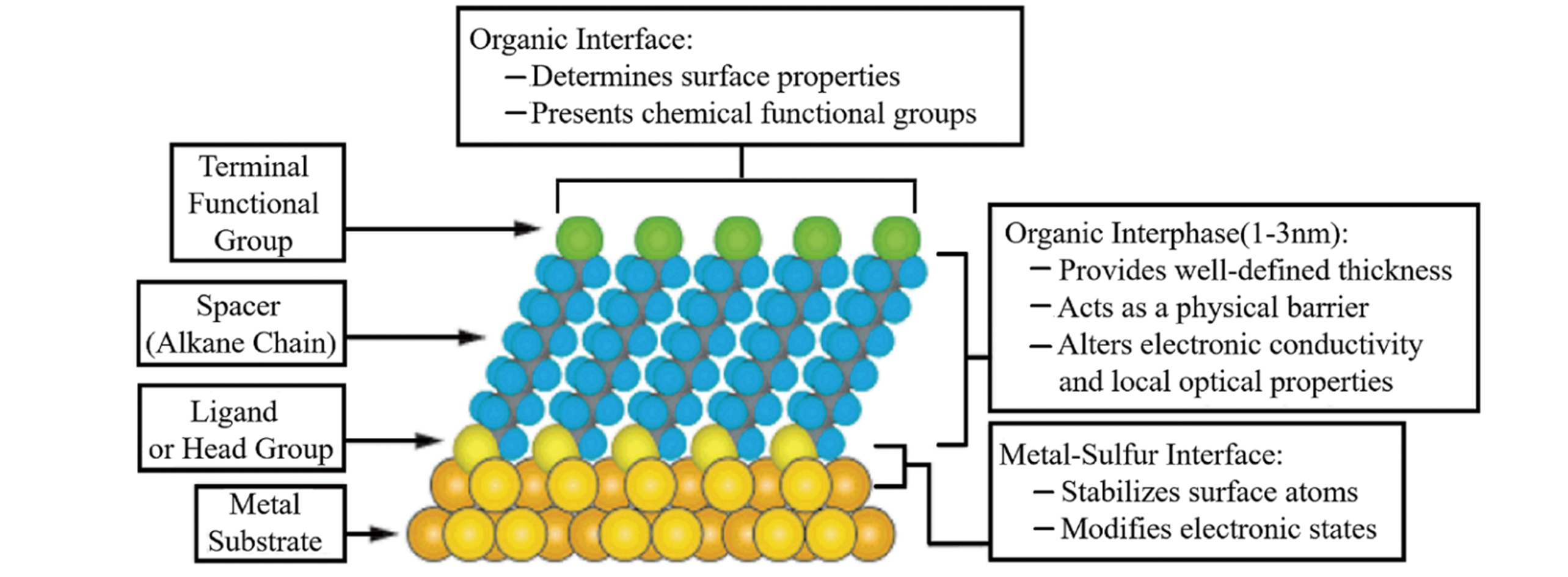
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of an ideal, single?crystalline SAM of alkanethiolates supported on a gold surface with a (111) texture[13]Copyright 2005, American Chemical Society.
| Polymer | Structureal formula | γc/(mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinylidene chloride) | —(CH2CCl2)n— | 40 |
| Poly(vinyl chloride) | —(CH2CHCl)n— | 39 |
| Polyethylene | —(CH2)n— | 31 |
| Poly(vinyl fluoride) | —(CH2CHF)n— | 28 |
| Poly(vinylidene fluoride) | —(CH2CF2)n— | 25 |
| Polytrifluoroethylene | —(CH2CHF)n— | 22 |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | —(CF2)n— | 18 |
| —CH3(crystal) | —CH3 | 22 |
| —CH3(monolayer) | —CH3 | 24 |
| —CF3(monolayer) | —CF3 | 6 |
| Polystyrene | —(CH2CHC6H6)n— | 33 |
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) | —(CH2CH3COOCCH3)n— | 39 |
Table 1 Relationship between wettability and surface structure[59]*
| Polymer | Structureal formula | γc/(mJ·m-2) |
|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinylidene chloride) | —(CH2CCl2)n— | 40 |
| Poly(vinyl chloride) | —(CH2CHCl)n— | 39 |
| Polyethylene | —(CH2)n— | 31 |
| Poly(vinyl fluoride) | —(CH2CHF)n— | 28 |
| Poly(vinylidene fluoride) | —(CH2CF2)n— | 25 |
| Polytrifluoroethylene | —(CH2CHF)n— | 22 |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | —(CF2)n— | 18 |
| —CH3(crystal) | —CH3 | 22 |
| —CH3(monolayer) | —CH3 | 24 |
| —CF3(monolayer) | —CF3 | 6 |
| Polystyrene | —(CH2CHC6H6)n— | 33 |
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) | —(CH2CH3COOCCH3)n— | 39 |
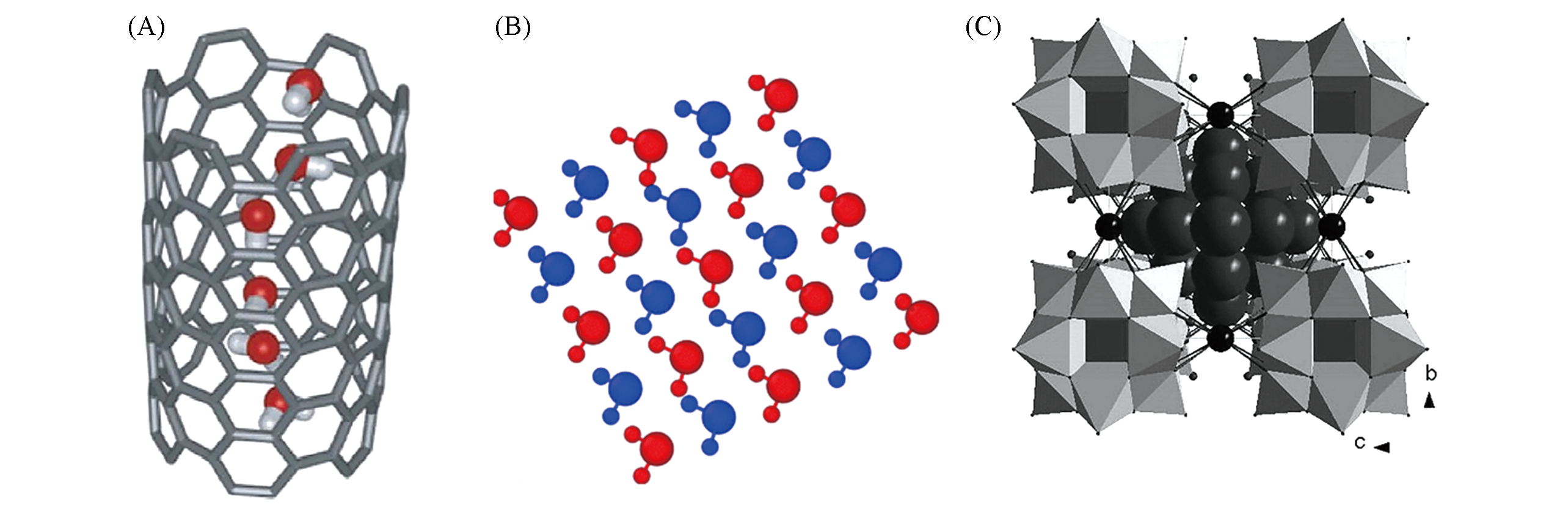
Fig.2 A strip of one?dimensional water chain in carbon nano tube(A)[74]; a layer of two?dimension “ice?like” water on graphene surface(B)[78]; a ball of three?dimensional water in inorganic cage material(C)[79](A) Copyright 2010, American Physical Society; (B) Copyright 2016, Elsevier; (C) Copyright 2012, Wiley-VCH.
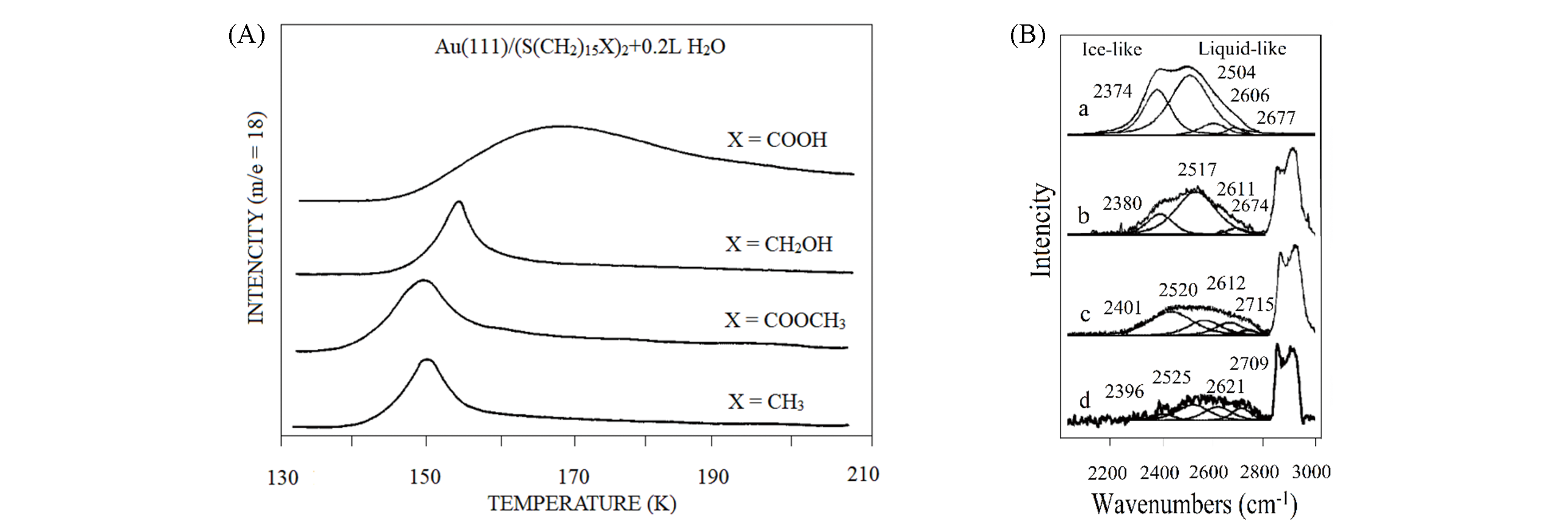
Fig.3 Desorption experiment of surface water with different tail groups(A)[82] and residual interface water after external dehydration with different tail groups(B)[83](A) Copyright 2008, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
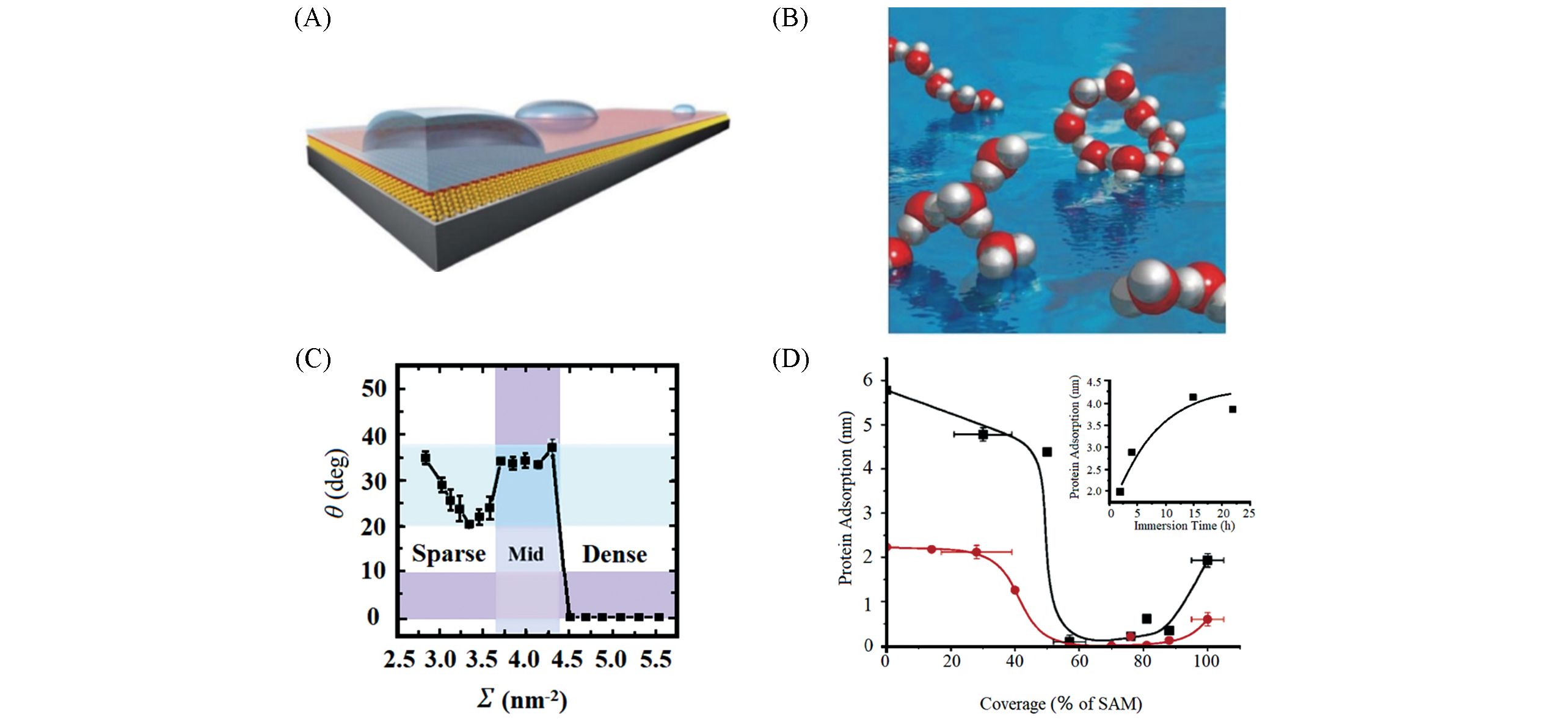
Fig.4 Composite structure of carboxyl self?assembled monolayers(A)[85]; the strong hydrogen bonding between water molecules(B)[86]; the relationgship of contact Angle and chain density on carboxyl self?assembled monolayers(C)[87]; surface plasmon resonance absorption of fibrous protein(black) and bovine serum albumin(red) with chain density curves(D)[92](A) Copyright 2011, Royal Society of Chemistry; (B) Copyright 2004, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (C) Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society; (D) Copyright 2004, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Kusano H., Kimura S., Kitabuwa M., Kobayashi H., Thin Solid Films, 1997, 295, 53—59 |
| 2 | Susannah C. C., Paul F. N., Langmuir, 2001, 17( 3), 720—732 |
| 3 | Decher G., Hong G. D., Schmitt J., Thin Solid Films, 1992, 210, 831—835 |
| 4 | New Scientist, 1983, 98, 20 |
| 5 | Ulman A., Chem. Rev., 1996, 96(4), 1533—1554 |
| 6 | Schwartz D. K., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2001, 52(1), 107—137 |
| 7 | Bain C. D., Evall J., Whitesides G. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111(18), 7155—7164 |
| 8 | Capadona J. R., Collard D. M., García A. J., Langmuir, 2003, 19(5), 1847—1852 |
| 9 | Hirata I., Hioki Y., Toda M., Kitazawa T., Murakami Y., Kitano E., Kitamura H., Ikada Y., Iwata H., J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A., 2003, 66(3), 669—676 |
| 10 | Riepl M., Ostblom M., Lundstrom I., Svensson S. C. T., van der Gon A. W. D., Schaferling M., Liedberg B., Langmuir, 2005, 21(3), 1042—1050 |
| 11 | Martinsa M. C. L., Rodrigues S. N., Gonc⁃alves I. C., Barbosa M. A., Ratner B. D., Biomaterials, 2006, 27(31), 5357—5367 |
| 12 | Arima Y., Iwata H., Biomaterials, 2007, 28(20), 3074—3082 |
| 13 | Nuzzo R. G., Whitesides G. M., Chem. Rev., 2005, 105, 1103—1169 |
| 14 | Dubois L. H., Nuzzo R. G., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 1992, 43(1), 437—463 |
| 15 | Bigelow W. C., Pickett D. L., Zisman W. A., J. Colloid Sci., 1946,1(6), 513—538 |
| 16 | Bigelow W. C., Glass E., Zisman W. A., J. Colloid Sci., 1947, 2(6), 563—591 |
| 17 | Nuzzo R. G., Allara R. G., D. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105(13), 4481—4483 |
| 18 | Porter M. D., Bright T. B., Allara D. L., Chidsey C. E. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109(12), 3559—5368 |
| 19 | Peterlinz K. A., Georgiadis R., Langmuir, 1996, 12(20), 4731—4740 |
| 20 | Dannenberger O., Wolff J. J., Buck M., Langmuir, 1998, 14(17), 4679—4682 |
| 21 | Sun L., Crooks R. M. J., Electrochem. Soc., 1991, 138, 123—125 |
| 22 | Terrill R. H., Tanzer T. A., Bohn P. W., Langmuir, 1998, 14(4), 845—854 |
| 23 | Kawasaki M., Sato T., Tanaka T., Takao K., Langmuir, 2000,16(4), 1719—1728 |
| 24 | Yamada R., Wano H., Uosaki K., Langmuir, 2000, 16(13), 5523—5525 |
| 25 | Bain C. D., Troughton E. B., Tao Y. T., Evall J., Whitesides G. M., Nuzzo R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111(1), 321—335 |
| 26 | Love J. C., Wolfe D. B., Haasch R., Chabinyc M. L., Paul K. E., Whitesides G. M., Nuzzo R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003,125(9), 2597—2609 |
| 27 | Dubois L. H., Nuzzo R. G., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 1992, 43(1), 437—463 |
| 28 | Whitesides G. M., Laibinis P. E., Langmuir, 1990, 6(1), 87—96 |
| 29 | Pyun J., Kowalewski T., Matyjazewski K., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2003, 24(18), 1043—1059 |
| 30 | Edmondson S., Osbome V. L., Huck W. T. S., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2004, 33(1), 14—22 |
| 31 | Boyes S. G., Granville A. M., Baum M., Adv. Polym. Sci., 2006, 197, 1—45 |
| 32 | Tsujii Y., Ohno K., Yamamoto S., Goto A., Fukuda T., Adv. Polym. Sci., 2006, 197,1—45 |
| 33 | Senaratne W., Andruzzi L., Ober C. K., Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6(5), 2427—2448 |
| 34 | Flink S., van Veggel F. C. J. M., Reinhoudt D. N., Adv. Mater., 2000, 12(18), 1315—1328 |
| 35 | van der Veen N. J., Flink S., Deij M. A., Egberink R. J. M., van Veggel F. C. J. M., Reinhoudt D. N., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122, 6112—6113 |
| 36 | Potochnik S. J., Pehrsson P. E., Hsu D. S. Y., Calvert J. M., Langmuir, 1995, 11(6), 1841—1845 |
| 37 | Steinberg S., Tor Y., Sabatani E., Rubinstein I., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113(14), 5176—5182 |
| 38 | Gilardi G., Fantuzzi A., Sadeghi S. J., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2001, 11(4), 491—499 |
| 39 | Castner D. G., Ratner B. D., Surf. Sci., 2002, 500, 28—60 |
| 40 | Harder P., Grunze M., Dahint R., Whitesides G. M., Laibinis P. E., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(2), 426—436 |
| 41 | Ball P., Designing the Molecular World, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1994 |
| 42 | Schierbaum K. D., Weiss T., Thoden van Velzen J. F. J., Reinhoudt D. N., Goepel W., Science, 1994, 265, 1413—1415 |
| 43 | Duan C. M., Meyerhoff M. E., Anal. Chem., 1994, 66(9), 1369—1377 |
| 44 | Angst D. L., Simmons G. W., Langmuir, 1991, 7(10), 2236—2242 |
| 45 | Zhuravlev L. T., Langmuir, 1987, 3(3), 316—318 |
| 46 | Sagiv J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102(1), 92—98 |
| 47 | Vericat C., Vela M. E., Benitez G., Carrob P., Salvarezza R. C., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39(5), 1805—1834 |
| 48 | Inkpen M. S. , Liu Z. F., Li H. S., Campos L. M., Neaton J. B., Venkataraman L., Nat. Chem., 2019, 11(4), 351—358 |
| 49 | Silberzan P., Leger L., Ausserre D., Benattar J. J., Langmuir, 1991, 7(8), 1647—1651 |
| 50 | Badia A., Back R., Lennox R. B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 1994, 33(22), 2332—2335 |
| 51 | Bensebaa F., Ellis T. H., Badia A., Lennox R. B., J. Vac.Sci. Technol. A,1995, 13(3), 1331—1336 |
| 52 | Bhatia R., Garrison B. J., Langmuir, 1997, 13(4), 765—769 |
| 53 | The Collected Works of Irving Langmuir, Pergamon Press, New York, 1960 |
| 54 | Langmuir I., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1916, 38(11), 2221—2295 |
| 55 | Langmuir I., J. Franklin Inst., 1934, 218(2), 143—171 |
| 56 | Langmuir I., Science, 1938, 87(2266), 493—500 |
| 57 | Langmuir I., Trans. Faraday Soc., 1920, 15, 62—74 |
| 58 | Chaudhury M. K., Mat, Sci. Eng. R., 1996, 16(3), 97—159 |
| 59 | Zisman W. A., Adv. Chem. Ser., 1964, 43, 1—50 |
| 60 | Shafrin E. G., Zisman W. A., J. Chem. Phys., 1960, 64(5), 519—524 |
| 61 | Price A. H., Hill N. E., Vaughan W. E., Davies M., Dielectric Properties and Molecular Behouiour, Van Nostrand Rcinhold Company, London, 1969 |
| 62 | Adam N. K., Adv. Chem. Ser., 1964, 43, 52—56 |
| 63 | Liu G. Y., Paul R., Giacinto S., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 91(7), 4421—4423 |
| 64 | Liu G. Y., Nicholas C., Christopher E. D. C., Putvinski T. M., Giacinta S., J. Chem. Phys., 1991, 94(5), 8493—8502 |
| 65 | Liu G. Y., Giacinta S., Nicholas C., Nicholas C., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 3503—3511 |
| 66 | Bigelow W. C., Brockway L. O., J. Colloid Sci., 1956, 11(1), 60—68 |
| 67 | Colin D., Whitesides G. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111(1), 321—335 |
| 68 | Bain C. D., Evall J., Whitesides G. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111(18), 7155—7164 |
| 69 | Bakker H. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(49), 15540—15544 |
| 70 | Ball P., Chem. Rev., 2008, 108(1), 74—108 |
| 71 | Holt J. K., Park H. G., Wang Y., Science, 2006, 312(5776), 1034—1037 |
| 72 | Koga K., Zeng C. X., Tanaka H., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1997, 79(26), 5262—5265 |
| 73 | Hummer G., Rasaiah J. C., Noworyta J. P., Nature, 2001, 414(6860), 188—190 |
| 74 | CambréS., Schoeters B., Luyckx S., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 104(20), 207401—207405 |
| 75 | Ghosh S., Sood A. K., Kumar N., Science, 2003, 299(5609), 1042—1044 |
| 76 | Hu J., Xiao X. D., Ogletree D. F., Science,1995, 268(5208), 267—269 |
| 77 | Sun Y. R., Yu F., Ma J., Acta Phys.⁃Chim. Sin., 2017, 33(11), 2173—2183 |
| 78 | Zhu Y., Wang F., Bai J., Zeng X. C., Wu H., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18 (32), 22039—22046 |
| 79 | Xu K. M., Liu Y. J., Liu H. S., Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2012, 638 (6), 1018—1022 |
| 80 | Wang D., Liu X., Leng C., Yu L., He K., Brown L., Chen Z., Cho J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(16), 4851—4856 |
| 81 | Dubois L. H., Zegarski B. R., Nuzzo R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112(2), 570—579 |
| 82 | Tiani D. J., Yoo H., Mudalige A., Pemberton J. E., Langmuir, 2008, 24(23), 13483—13489 |
| 83 | Whitney A. F., Jason W. D., Jeffrey E. D., Logan M. W., Katie L. B., Mathieu D., James F. B., Lauren J. W., Langmuir, 2019, 35(16), 5647—5662 |
| 84 | Wang C. L., Lu H. J., Wang Z. G., Xiu P., Zhou B., Zuo G. H., Wan R. Z., Hu J. Z., Fang H. P., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 103, 137801 |
| 85 | James M., Darwish T. A., Ciampi S., Sylvester S. O., Zhang Z. M., Ng A., Gooding J. J., Hanley T. L., Soft Matter, 2011, 7(11), 5309—5318 |
| 86 | Zubavicus Y., Grunze M., Science, 2004, 304(5673), 974—976 |
| 87 | Guo P., Tu Y. S., Yang J. R., Wang C. L., Sheng N., Fang H. P., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 115, 18610—18611 |
| 88 | Desai N. P., Hubbell J. A., Biomaterials, 1991, 12, 144—158 |
| 89 | Herrwerth S., Eck W., Reinhardt S., Grunze M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(31), 9359—9366 |
| 90 | Vanderah D. J., Valincius G., Meuse C. W., Langmuir, 2002, 18(12), 4674—4680 |
| 91 | Harder P., Grunze M., Dahint R., Whitesides G., Laibinis P., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(2), 426—436 |
| 92 | Vanderah D. J., La H., Naff J., Silin V., Rubinson K. A,. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(42), 13639—13641 |
| 93 | Li L., Chen S., Zheng J., Ratner B. D., Jiang S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 2934—2941 |
| 94 | Schröter A., Franzka S., Hartmann N., Langmuir, 2014, 30(49), 14841—14848 |
| 95 | Wang C., Bo Z., Tu Y., Scientific Reports, 2012, 2(4), 282—286 |
| 96 | Coridan R. H., Schmidt N. W., Lai G. H., Phys. Rev. E, 2012, 85(3), 031501 |
| 97 | Zhu C., Li H., Huang Y., Phys. Rev. Lett.,2013, 110(12), 336—337 |
| 98 | Riess J. G., Artificial Cells, Blood Substitutes, and Biotechnology, 2005, 33(1), 47—63 |
| 99 | Riess J. G., Artificial Cells, Blood Substitutes, and Biotechnology, 2006, 34(6), 567—580 |
| 100 | Gallardo I. F., Webb L. J., Langmuir, 2012, 28(7), 3510—3515 |
| 101 | Mrksich M., Acta Biomatter, 2009, 5(3), 832—841 |
| 102 | Wenzel R. N., Ind. Eng. Chem., 1936, 28(8), 988—994 |
| 103 | Wenzel R. N., J. Phys. Colloid. Chem., 1949, 53(9), 1466—1467 |
| 104 | Cassie A. B. D., Baxter S., Trans. Faraday Soc., 1944, 40, 546—551 |
| 105 | Kumar A., Whitesides G. M., Appl. Phys. Lett., 1993, 63(14), 2002—2004 |
| 106 | Lea A. S., Pungor A., Hlady V., Andrade J. D., Herron J. N., Voss E. W. Jr., Langmuir, 1992, 8(1), 68—73 |
| 107 | Kumar A., Whitesides G. M., Science, 1994, 263(5143), 60—62 |
| 108 | Prime K. L., Whitesides G. M., Science, 1991, 252(5010), 1164—1167 |
| 109 | Singhvi R., Kumar A., Lopez G. P., Stephanopouos G. N., Wang D. I. C., Whitesides G. M., Ingber D. E., Science, 1994, 264(5159), 696—698 |
| 110 | Horton R. C. Jr., Herne T. M., Myles D. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119(52), 12980—12981 |
| 111 | Liu Z., Amiridis M. D., Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces, 2004, 35(3-4), 197—203 |
| 112 | Gu T., Whitesell J. K., Fox M. A., J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69(12), 4075—4080 |
| 113 | Peelen D., Smith L. M., Langmuir, 2005, 21(1), 266—271 |
| 114 | Brüning C., Grobe J., J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1995, 297, 2323—2324 |
| 115 | Zammatteo N., Jeanmart L., Hamels S., Courtois S., Louette P., Hevesi L., Remacle J., Anal. Biochem., 2000, 280(1), 143—150 |
| 116 | Hozumi A., Inagaki M., Shirahata N., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2006, 252(18), 6111—6114 |
| 117 | Nishino T., Meguro M., Nakamae K., Matsushita M., Ueda Y., Langmuir, 1999, 15(13), 4321—4323 |
| 118 | Takai O., Hozumi A., Sugimoto N., J. Non⁃Cryst. Solids, 1997, 218, 280—285 |
| 119 | Miwa M., Nakajima A., Fujishima A., Hashimoto K., Watanabe T., Langmuir, 2000, 16, 5754—5760 |
| 120 | Wu Y., Sugimura H., Inoue Y., Takai O., Chem. Vap. Depos., 2002, 8(2), 47—50 |
| 121 | Teshima K., Sugimura H., Inoue Y., Takai O., Takano A., Langmuir, 2003, 19(25), 10624—10627 |
| 122 | Daub C. D., Luzar A., Faraday Discuss, 2010, 146, 67—77 |
| 123 | Chen S., Itoh Y., Okuro K., Aida T., Science, 2015, 348(6234), 555—559 |
| [1] | 于泳博, 刘翠, 宫利东. 从头算和ABEEMσπ/MM对(CH3OH)n(n=3~12)和[Na(CH3OH)n]+(n=3~6)体系的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(8): 1468. |
| [2] | 肖志夏, 朱艳丽, 赵勇, 邢家超, 焦清介. NiCl2晶体生长的数值模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(12): 2497. |
| [3] | 司朋飞, 罗发亮, 海梅. 聚L-乳酸/4,4'-二羟基二苯硫醚共混物的分子间相互作用及结晶和熔融行为[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(1): 188. |
| [4] | 袁伟, 任清江, 孙恒达, 李慧, 程延祥, 马东阁. 外围取代基团对卟啉铂(Ⅱ)配合物发光性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(6): 1229. |
| [5] | 戚克振, 王艳, 付嘉琦, 王贵昌. 花状硫化铟纳米多级结构的液相合成及形貌调控机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(12): 2523. |
| [6] | 侯海云, 黄银蓉, 白博峰, 杨靖. 293.15 K时咪唑醋酸盐-乙醇二元体系的体积性质及分子间相互作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(1): 121. |
| [7] | 钱涛, 汪涓涓, 张庆华, 詹晓力, 陈丰秋. 丙烯酸(N-甲基全氟己烷磺酰胺基)乙酯与MMA梯度共聚物的合成与表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(3): 703. |
| [8] | 孟素慈, 殷秀莲, 马晶, 谢吉民. 有机π共轭配体溶剂化效应与分子间相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(11): 2492. |
| [9] | 梁雪, 孙涛, 王一波. 苯-卤素(X2, X=F, Cl, Br, I)相互作用本质的对称性匹配微扰理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(03): 541. |
| [10] | 魏志钢,张红星,李前树,Lewis James P. . 二氧化钛(TiO2)表面能的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(4): 824. |
| [11] | 赵建新,乔义涛,冯菁,罗昭峰,袁直 . 共聚物-锌与多肽的相互作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(3): 658. |
| [12] | 凌笑梅,刘一,赖先银,张媛,刘晓明,屠鹏飞,赵玉英,,崔景荣 . 采用毛细管电泳方法以凝血酶为靶筛选天然药物提取化合物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(2): 234. |
| [13] | 汪朝旭, 张敬畅, 曹维良 . HCN(HNC)与NH3, H2O和HF分子间相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(2): 320. |
| [14] | 林宪杰,徐为人,王建武,刘成卜 . 对甲氧基苯甲醛肟晶体结构、 红外光谱及分子间相互作用的实验与理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(5): 897. |
| [15] | 张庆华, 刘龙孝, 陈丰秋, 詹晓力. 采用XPS与接触角法研究氟聚合物表面结构与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(4): 790. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
