

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 334.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180523
王志鹏, 牛珠珠, 班丽君, 郝全爱, 张鸿喜, 李海涛( ), 赵永祥(
), 赵永祥( )
)
收稿日期:2018-07-24
出版日期:2019-02-10
发布日期:2018-12-05
作者简介:联系人简介: 赵永祥, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事多相催化方面的研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
WANG Zhipeng, NIU Zhuzhu, BAN Lijun, HAO Quanai, ZHANG Hongxi, LI Haitao*( ), ZHAO Yongxiang*(
), ZHAO Yongxiang*( )
)
Received:2018-07-24
Online:2019-02-10
Published:2018-12-05
Contact:
LI Haitao,ZHAO Yongxiang
E-mail:htli@sxu.edu.cn;yxzhao@sxu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
分别以金红石相和锐钛矿相TiO2为载体, 采用液相还原-沉积法制备了Cu2O/TiO2催化剂. 采用氮气物理吸附-脱附(N2-physisorption)实验、 氢气程序升温还原(H2-TPR)、 X射线衍射(XRD)、 X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、 CO红外光谱(CO-IR)及高分辨透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)等技术, 研究了不同晶相TiO2载体对Cu2O/TiO2结构及其催化甲醛乙炔化反应性能的影响. 结果表明, 以金红石相TiO2为载体的催化剂炔化活性明显高于以锐钛矿相TiO2为载体的催化剂, 原因在于金红石相TiO2主要暴露(110)晶面, 其与铜物种的配位环境及较高的空位密度形成了更多的Cu—O—Ti结构物种, 表现为Cu2O与TiO2之间强的相互作用. 这导致Cu2O高效转变为乙炔亚铜活性物种, 并保持了较高的分散度与稳定性, 抑制了过度还原物种金属Cu的生成, 进而使催化剂表现出较高的催化性能.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
王志鹏, 牛珠珠, 班丽君, 郝全爱, 张鸿喜, 李海涛, 赵永祥. 不同晶相TiO2负载Cu2O催化甲醛乙炔化反应. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(2): 334.
WANG Zhipeng,NIU Zhuzhu,BAN Lijun,HAO Quanai,ZHANG Hongxi,LI Haitao,ZHAO Yongxiang. Formaldehyde Ethynylation Reaction over Cu2O Supported on TiO2 with Different Phases†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 334.
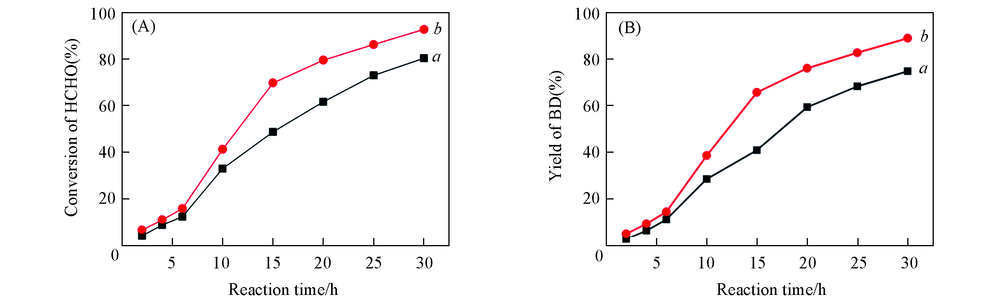
Fig.1 Effects of reaction time on conversion of HCHO(A) and yield of BD(B) over different catalystsa. Cu2O/A-TiO2; b. Cu2O/R-TiO2. Reaction conditions: catalyst amount, 2.5 g; reaction temperature, 90 ℃.
| Sample | w(Cu)a(%) | T | H2 consumptione/ (μmol·g-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/A-TiO2 | 19.7 | 39.5(53.6) | 24 | 15.6 | 1588(1539) |
| C/R-TiO2 | 19.3 | 35.7(44.6) | 19 | 28.3 | 1567(1508) |
Table 1 Structural and textural data of supported catalysts
| Sample | w(Cu)a(%) | T | H2 consumptione/ (μmol·g-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/A-TiO2 | 19.7 | 39.5(53.6) | 24 | 15.6 | 1588(1539) |
| C/R-TiO2 | 19.3 | 35.7(44.6) | 19 | 28.3 | 1567(1508) |
| [1] | Zhong C. R., Lu A., Oilfield Chem.,2000, 17(3), 285-288 |
| (钟传蓉, 卢艾. 油田化学, 2000, 17(3), 285-288) | |
| [2] | Li H. T., Zhao Y. X., Gao C. G., Wang Y. Z., Sun Z. J., Liang X. Y., Chem. Eng. J.,2012, 181/182, 501-507 |
| [3] | Nadgeri J. M., Telkar M. M., Rode C. V., Catal. Commun.,2008, 9(3), 441-446 |
| [4] | Zhang Q., Zhang Y., Li H. T., Gao C. G., Zhao Y. X., Appl. Catal. A,2013, 466, 233-239 |
| [5] | Haas T., Jaeger B., Weber R., Mitchell S. F., King C. F., Appl. Catal. A,2005, 280(1), 83-88 |
| 6 | [6] Cheng J. S., Jiang H. F., Zhang Q. J., Ouyang X. Y., Guangzhou Chemistry,2003, 28(1), 1-4 |
| (程金生, 江焕峰, 张群健, 欧阳小月. 广州化学, 2003, 28(1), 1-4) | |
| [7] | Yang G. H., Xu Y. B., Su X. T., Xie Y. H., Yang C., Dong Z. J., Wang J. D., Ceram. Int.,2014, 40(3), 3969-3973 |
| [8] | Luo P., Zhao X. M., Li H. X., Zhang H., Li Y. H., Lv X. W., Li X. D., Chem. Eng. Design Commun.,2012, 38(5), 87-93 |
| (罗平, 赵新明, 李海侠, 张浩, 李耀会, 吕小婉, 李小定. 化工设计通讯, 2012, 38(5), 87-93) | |
| [9] | Wang J. Y., Jiang Y., Xie J. C., Chen J. H., Zhang X. X., Jiang W., Chin. J. Synth. Chem., 2010, 18(B09), 26-29 |
| (王娟芸, 蒋毅, 谢建川, 陈君和, 张小霞, 蒋伟. 合成化学, 2010, 18(B09), 26-29) | |
| [10] | Zheng Y., Sun Z. J., Wang Y. Z., Li H. T., Wang S. A., Luo M., Zhao J. L., Zhao Y. X., J. Mol. Catal.,2012, 26(3), 233-238 |
| (郑艳, 孙自瑾, 王永钊, 李海涛, 王韶安, 罗敏, 赵吉龙, 赵永祥. 分子催化, 2012, 26(3), 233-238) | |
| [11] | Wang J. J., Li H. T., Ma Z. Q., Wang Z. P., Guo J. Y., Zhao Y. X., J. Chem. Ind. Eng.,2015, 66(6), 2098-2104 |
| (王俊俊, 李海涛, 马志强, 王志鹏, 郭江渊, 赵永祥. 化工学报, 2015, 66(6), 2098-2104) | |
| [12] | Ma Z. Q., Zhang H. X., Li H. T., Wu R. F., Wang J. J., Guo J. Y., Wang Z. P., Zhao Y. X., Ind. Catal.,2015, 23(5), 344-348 |
| (马志强, 张鸿喜, 李海涛, 吴瑞芳, 王俊俊, 郭江渊, 王志鹏, 赵永祥. 工业催化, 2015, 23(5), 344-348) | |
| [13] | Yang G. F., Li H. T., Zhang H. X., Wang Z. P., Liu L. L., Zhao Y. X., J. Mol. Catal.,2016, 30(6), 540-546 |
| (杨国峰, 李海涛, 张鸿喜, 王志鹏, 刘琳丽, 赵永祥. 分子催化, 2016, 30(6), 540-546) | |
| [14] | Li H. T., Niu Z. Z., Yang G. F., Zhang H. X., Wang Z. P., Zhao Y. X., J. Chem. Ind. Eng.,2018, 69(6), 2512-2518 |
| (李海涛, 牛珠珠, 杨国锋, 张鸿喜, 王志鹏, 赵永祥. 化工学报, 2018, 69(6), 2512-2518) | |
| [15] | Oishi T., Katayama T., Yamaguchi K., Mizuno N., Chem. Eur. J.,2009, 15, 7539-7542 |
| [16] | A S., Zheng J. W., Liu J. M., Bai J., Yang J. C., Zhang Q. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(8), 1450-1457 |
| (阿山, 郑家威, 刘聚明, 白杰, 杨桔材, 张前程. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(8), 1450-1457) | |
| [17] | Meng Z. Y., Zhang Y., Zhao L. L., Zhang H. X., Zhao Y. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(9), 1779-1785 |
| (孟志宇, 张因, 赵丽丽, 张鸿喜, 赵永祥. 高等学校化学学报. 2015, 36(9), 1779-1785) | |
| [18] | Wang Y., Widmann D., Heenemann M., Diemant T., Biskupek J., Schlögl R., Behm R. J., J. Catal.,2017, 354, 46-60 |
| [19] | Shah P., Bhange D. S., Deshpande A. S., Chem. Phys.,2009, 117, 399-407 |
| [20] | Widchaya R., Araya T., Ratchaneekorn W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2014, 30(1), 149-156 |
| [21] | Saadi A., Merabti R., Rassoul Z., Bettahar M. M., J. Mol. Catal.,2006, 253(1/2), 79-85 |
| [22] | Xie G. Q., Liu X. J., Tao L. P., Lu J. Q., Luo M. F., Li X. N., Chinese J. Catal.,2009, 30(6), 543-548 |
| (谢冠群, 刘西敬, 陶丽萍, 鲁继青, 罗孟飞, 李小年. 催化学报, 2009, 30(6), 543-548) | |
| [23] | Li Y. Z., Xu B. L., Fan Y. N., Feng N. Y., Qiu A. D., Miao J. W., He J., Yang H. P., Chen Y., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem.,2004, 216, 107-114 |
| [24] | Chen J. S., Tan Y. L., Li C. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2010, 132, 6124-6130 |
| [25] | Li Y. Z., Xu B. L., Fan Y. N., Chen Y., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem.,2004, 216, 107-114 |
| [26] | Zhu H. Y., Dong L., Chen Y., J. Colloid Interface Sci.,2011, 357, 497-503 |
| [27] | Zhu Y. F., Zhu Y. L., Ding G. Q., Zhu S. H., Zheng H. Y., Li Y. H., Appl. Catal. A,2013, 468, 296-304 |
| [28] | Liu Y. X., Wang Z. L., Huang W. X., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2016, 389, 760-767 |
| [29] | Wang Z. L., Liu Q. S., Yu J. F., Wu T. H., Wang G. J., Appl. Catal. A,2003, 239, 87-94 |
| [30] | Platzman I., Brener R., Haick H., Tannenbaum P., J. Phys. Chem. C,2008, 112, 1101-1108 |
| [31] | Lu Y., Zhang X., Chu Y. C., Yu H. B., Huo M. X., Qu J., Huo H. L., Yuan X., Appl. Catal. B,2018, 224, 239-248 |
| [32] | Hensel J., Wang G., Li Y., Zhang J. Z., Nano Lett.,2010, 10, 478-483 |
| [33] | Park S. M., Razzaq A., Park Y. H., Sorcar S., Park Y., Grimes C. A., ACS Omega,2016, 1, 868-875 |
| [34] | Chen Y., Zhang L. F., Catal. Lett.,1992, 12, 51-62 |
| [35] | Zhu H. Y., Wu Y., Zhao X., Wan H. Q., Yang L. J., Hong J. M., Yu Q., Dong L., Chen Y., Jian C., Wei J., Xu P. H., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem.,2006, 243, 24-30 |
| [36] | Giordano L., Pacchioni G., Bredow T., Sanz J. F., Surf. Sci.,2001, 471, 21-31 |
| [37] | Wu G., Guan N., Li L., Catal. Sci. Technol.,2011, 1, 601-608 |
| [38] | Chen C. S., Chen T. C., Chen C. C., Langmuir,2012, 28, 9996-10006 |
| [39] | Trotuş I. T., Zimmermann T., Schüth F., Chem. Rev.,2014, 114, 1761-1782 |
| [40] | Hornes A., Bera P., Camara A. L., Gamarra D., Munuera G., Martinez-Arias A., J. Catal., 2009, 268, 367-375 |
| [41] | Manzoli M., Monte R. D., Boccuzzi F., Coluccia S., Kašpar J., Appl. Catal. B,2005, 61, 192-205 |
| [42] | Boccuzzi F., Ghiotti G., Chiorino A., Surf. Sci.,1985, 162, 361-367 |
| [43] | Scarano D., Bordiga S., Lamberti C., Spoto G., Ricchiardi G., Zecchina A., Otero A. C., Surf. Sci.,1998, 411, 272-285 |
| [44] | Guo X. L., Zhou R. X., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6, 3862-3871 |
| [45] | Kalies H., Pinto N., Pajonk G. M., Bianchi D., Appl. Catal. A,2000, 202, 197-205 |
| [46] | Sun C. Z., Zhu J., Lv Y. Y., Qi L., Liu B., Gao F., Sun K. Q., Dong L., Chen Y., Appl. Catal. B,2011, 103, 206-220 |
| [1] | 郭彪, 赵晨灿, 刘芯辛, 于洲, 周丽景, 袁宏明, 赵震. 表面水热碳层对磁性NiFe2O4八面体光催化活性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220472. |
| [2] | 董妍红, 鲁新环, 杨璐, 孙凡棋, 段金贵, 郭昊天, 张钦峻, 周丹, 夏清华. 双功能金属有机骨架材料的制备及催化烯烃环氧化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [3] | 王祖民, 孟程, 于然波. 过渡金属磷化物析氢催化剂的掺杂调控[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [4] | 何建云 蒋云波 张爱敏 唐振艳 李鸿鹏. 新型卟啉基多孔有机聚合物COP-180负载钯催化剂的制备及应用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220535. |
| [5] | 夏文文 于洪晶 王时野 姚丽 李象远. 燃烧反应机理构建的极小反应网络方法—芳香烃燃烧[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220616. |
| [6] | 李怀科 岳贵初 谢海韵 刘静 高松伟 侯兰兰 李帅 苗贝贝 王女 白杰 崔志民 赵勇. 静电纺丝中空纳米纤维在催化领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220625. |
| [7] | 匡华艺 陈晨. 贵金属纳米框架催化剂的设计合成及电催化性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220586. |
| [8] | 王雅芝 贾显枝 张宏港 刘璐 赵彬然. 介质阻挡放电等离子制备5Ni-5La/SiO2催化剂用于甲烷干重整反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220503. |
| [9] | 朱佶鹏 刘润辉 宋恭华. 双噁唑啉接枝的氨基酸聚合物作为手性催化中心在不对称Henry 反应中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220569. |
| [10] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [11] | 李学宇, 王朝, 陈雅, 李可可, 李建全, 金顺敬, 陈丽华, 苏宝连. 等离激元共振光转热增强负载纳米金对丁二烯选择性加氢的催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220174. |
| [12] | 孙金时, 陈鹏, 景丽萍, 孙福兴, 刘佳. 多级孔芳香骨架材料的合成及固载硫脲催化剂的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220171. |
| [13] | 宋佳欣, 崔静, 范晓强, 孔莲, 肖霞, 解则安, 赵震. 介孔二氧化硅负载高分散钒催化剂的制备及乙烷选择氧化性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220532. |
| [14] | 唐全骏, 刘颖馨, 孟蓉炜, 张若天, 凌国维, 张辰. 单原子催化在海洋能源领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220324. |
| [15] | 林治, 彭志明, 贺韦清, 沈少华. 单原子与团簇光催化: 竞争与协同[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||