

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 2089.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180006
收稿日期:2018-01-03
出版日期:2018-07-30
发布日期:2018-07-30
作者简介:联系人简介: 黄汉雄, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事高分子材料加工设备与工程研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
HAN Jiahui, HUANG Hanxiong*( ), HUANG Yuxiao
), HUANG Yuxiao
Received:2018-01-03
Online:2018-07-30
Published:2018-07-30
Contact:
HUANG Hanxiong
E-mail:mmhuang@scut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用混沌混炼单螺杆挤出机, 制备马来酸酐接枝聚乳酸(PLA-g-MAH), 进而制备PLA/滑石粉(5%, 10%和20%, 质量分数)和PLA/滑石粉(20%)/PLA-g-MAH(5%和10%)复合材料. 复合材料样品中滑石粉的分散状态良好, 滑石粉含量高达20%时未发生团聚. 20%滑石粉和10% PLA-g-MAH使复合材料中PLA的α晶含量明显增加, 结晶度提高至31.6%. 在175 ℃下, PLA样品的熔体强度仅为3.6 mN, 20%滑石粉明显提高了PLA的熔体强度(11.6 mN), 这是由于分散较均匀的片状滑石粉对PLA熔体起增强效应并可提高PLA结晶速率, 对PLA结晶有促进效应. 与PLA样品对比, PLA/滑石粉(20%)/PLA-g-MAH(5%)复合材料的杨氏模量和冲击强度分别提高了51.7%和16.9%.
TrendMD:
韩嘉晖, 黄汉雄, 黄宇霄. 滑石粉和PLA-g-MAH对聚乳酸结晶性能和熔体强度的改善. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(9): 2089.
HAN Jiahui,HUANG Hanxiong,HUANG Yuxiao. Improving Crystallization Behavior and Melt Strength of Poly(lactic acid) via Adding Talc and PLA-g-MAH†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2089.
| Sample | w(PLA)(%) | w(Talc)(%) | w(PLA-g-MAH)(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| PLA/T5 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| PLA/T10 | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| PLA/T20 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| PLA/T20/M5 | 75 | 20 | 5 |
| PLA/T20/M10 | 70 | 20 | 10 |
Table 1 Mass fraction of samples
| Sample | w(PLA)(%) | w(Talc)(%) | w(PLA-g-MAH)(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| PLA/T5 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| PLA/T10 | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| PLA/T20 | 80 | 20 | 0 |
| PLA/T20/M5 | 75 | 20 | 5 |
| PLA/T20/M10 | 70 | 20 | 10 |
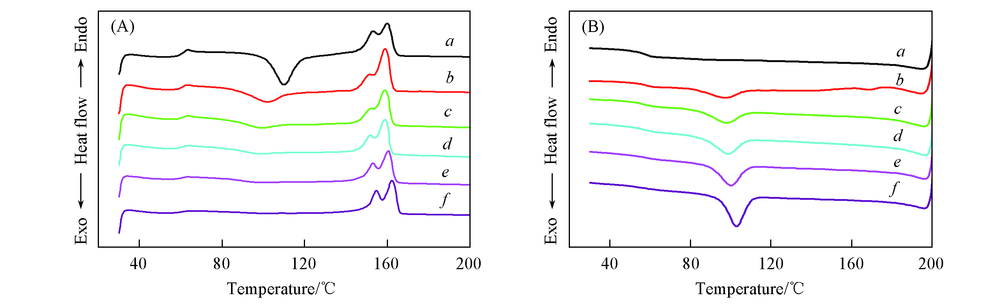
Fig.4 DSC curves of PLA and PLA/talc composite samples (A) Second heating scans; (B) cooling scans. a. PLA; b. PLA/T5; c. PLA/T10; d. PLA/T20; e. PLA/T20/M5; f. PLA/T20/M10.
| Sample | Tg/℃ | Tcc/℃ | Xcc(%) | Tm1/℃ | Tm2/℃ | Xc(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 59.6 | 109.8 | 27.9 | 152.9 | 159.7 | — |
| PLA/T5 | 60.0 | 101.7 | 15.0 | 151.5 | 158.7 | 15.2 |
| PLA/T10 | 59.8 | 99.1 | 7.6 | 152.2 | 158.7 | 19.8 |
| PLA/T20 | 59.8 | 96.6 | 4.5 | 151.7 | 158.7 | 25.1 |
| PLA/T20/M5 | 59.6 | 96.5 | 2.8 | 152.9 | 160.3 | 27.2 |
| PLA/T20/M10 | 59.8 | — | — | 154.4 | 162.1 | 31.6 |
Table 2 Thermal analysis data for PLA and PLA/talc composite samples
| Sample | Tg/℃ | Tcc/℃ | Xcc(%) | Tm1/℃ | Tm2/℃ | Xc(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 59.6 | 109.8 | 27.9 | 152.9 | 159.7 | — |
| PLA/T5 | 60.0 | 101.7 | 15.0 | 151.5 | 158.7 | 15.2 |
| PLA/T10 | 59.8 | 99.1 | 7.6 | 152.2 | 158.7 | 19.8 |
| PLA/T20 | 59.8 | 96.6 | 4.5 | 151.7 | 158.7 | 25.1 |
| PLA/T20/M5 | 59.6 | 96.5 | 2.8 | 152.9 | 160.3 | 27.2 |
| PLA/T20/M10 | 59.8 | — | — | 154.4 | 162.1 | 31.6 |
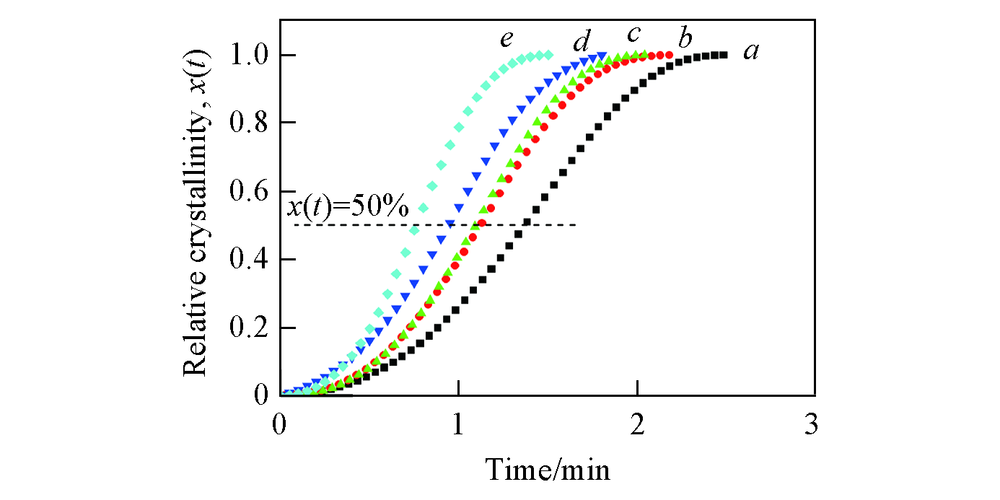
Fig.5 Relative crystallinity versus crystallization time curves for PLA/talc composite samples a. PLA/T5; b. PLA/T10; c. PLA/T20; d. PLA/T20/M5; e. PLA/T20/M10.
| Sample | t1/2/min | n | K/mi | Kc/mi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/T5 | 1.38 | 2.60 | 0.3217 | 0.8928 |
| PLA/T10 | 1.13 | 2.64 | 0.5284 | 0.9382 |
| PLA/T20 | 1.09 | 2.76 | 0.5672 | 0.9449 |
| PLA/T20/M5 | 0.92 | 2.37 | 0.8831 | 0.9876 |
| PLA/T20/M10 | 0.76 | 2.67 | 1.4421 | 1.0373 |
Table 3 Crystallization half-time(t1/2) and Jeziorny-modified-Avrami crystallization kinetic parameters for PLA/talc composite samples
| Sample | t1/2/min | n | K/mi | Kc/mi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/T5 | 1.38 | 2.60 | 0.3217 | 0.8928 |
| PLA/T10 | 1.13 | 2.64 | 0.5284 | 0.9382 |
| PLA/T20 | 1.09 | 2.76 | 0.5672 | 0.9449 |
| PLA/T20/M5 | 0.92 | 2.37 | 0.8831 | 0.9876 |
| PLA/T20/M10 | 0.76 | 2.67 | 1.4421 | 1.0373 |
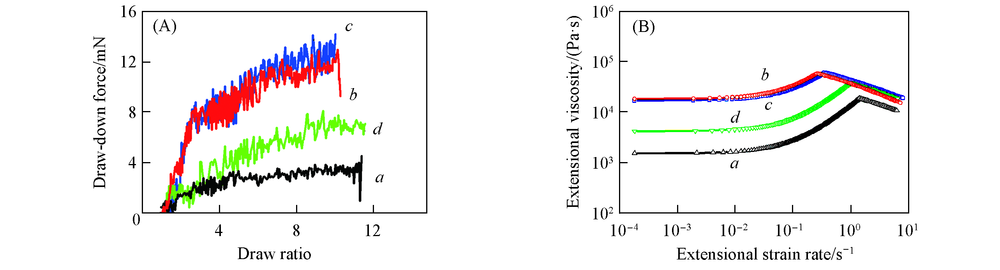
Fig.7 Draw-down force versus draw ratio(A) and extensional viscosity versus extensional strain rate curves(B) for PLA and PLA/talc composite samples a. PLA; b. PLA/T20; c. PLA/T20/M5; d. PLA/T20/M10.
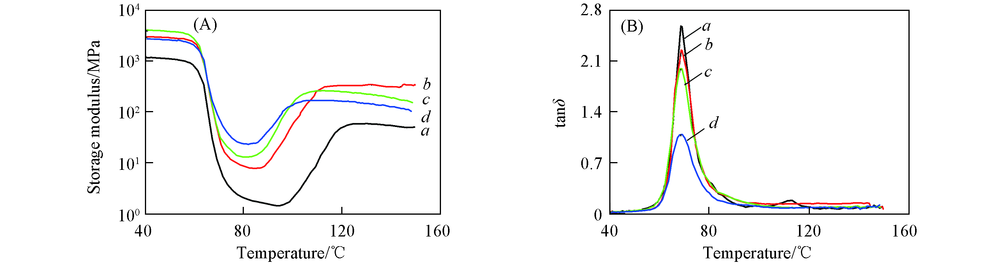
Fig.8 Storage modulus(A) and tanδ versus temperature curves(B) for PLA and PLA/talc composite samples a. PLA; b. PLA/T20; c. PLA/T20/M5; d. PLA/T20/M10.
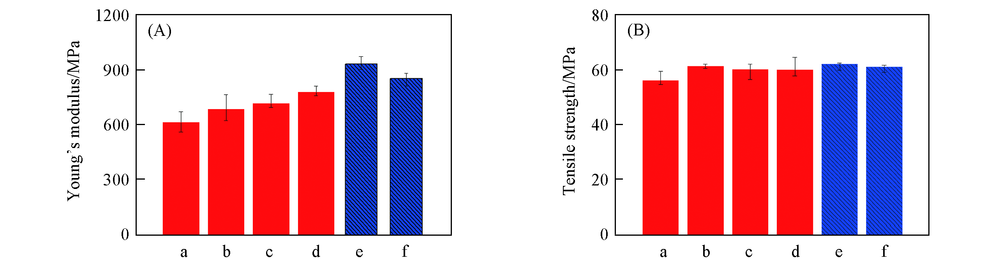
Fig.9 Young’s moduli(A) and tensile strengths(B) of PLA and PLA/talc composite samples a. PLA; b. PLA/T5; c. PLA/T10; d. PLA/T20; e. PLA/T20/M5; f. PLA/T20/M10.
| [1] | Drumright R. E., Gruber P. R., Henton D. E., Adv. Mater., 2000, 12(23), 1841—1846 |
| [2] | Li G. L., Huang J. J., Zhuang H. H., Yuan Z. S., Shao C. G., Ying J., Wang Y. M., Cao W., Liu C. T., Shen C. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9), 1663—1669 |
| (李桂丽, 黄静静, 张欢欢, 袁朝圣, 邵春光, 应进, 王亚明, 曹伟, 刘春太, 申长雨. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(9), 1663—1669) | |
| [3] | Li Y. J., Shimizu. H., Macromol. Biosci., 2007, 7(7), 921—928 |
| [4] | Han J. J., Huang H. X., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2011, 120(6), 3217—3223 |
| [5] | Zhao F., Huang H. X., Zhang S. D., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2015, 132(48), doi/10.1002/app.42511 |
| [6] | Xiong Z. J., Zhang X. Q., Liu G. M., Zhao Y., Wang R., Wang D. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5), 1288—1294 |
| (熊祖江, 张秀芹, 刘国明, 赵莹, 王锐, 王笃金. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(5), 1288—1294) | |
| [7] | Wang Y. Y., Song Y. M., Du J., Xi Z. H., Wang Q. W., Materials, 2017, 10(9), doi/org/10.3390/ma10090999 |
| [8] | Zhou M., Zhou P., Xiong P., Qian X., Zheng H.H., Macromol. Res., 2015, 23(3), 231—236 |
| [9] | Lai X. L., Yang W., Wang Z., Shi D. W., Liu Z. Y., Yang M. B., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2018, 135, doi/10.1002/app.45675 |
| [10] | Nofar M., Mater. Design., 2016, 101, 24—34 |
| [11] | Jain S., Misra M., Mohanty A K., Ghosh A. K., J. Polym. Environ., 2012, 20(4), 1027—1037 |
| [12] | Shakoor A., Thomas N.L., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2014, 54(1), 64—70 |
| [13] | Kaynak C., Erdogan A.R., Polym. Adv. Technol., 2015, 27(6), 812—822 |
| [14] | Zhang S. D., Huang H. X., Jiang G., Polym. Renew. Resour., 2013, 4(4), 153—168 |
| [15] | Zhu R., Liu H. Z., Zhang J. W., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51(22), 7786—7792 |
| [16] | Kaynak C., Meyva Y., Polym. Adv. Technol., 2015, 25(12), 1622—1632 |
| [17] | Ouchiar S., Stoclet G., Cabaret C., Georges E., Smith A., Martias C., Addad A., Gloaguen V., Appl. Clay. Sci., 2015, 116/117, 231—240 |
| [18] | Jiang G., Huang H. X., Chen Z. K., Polym. Plast. Technol., 2011, 50(10), 1035—1039 |
| [19] | Fowlks A. C., Narayan R., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2010, 118(5), 2810—2820 |
| [20] | Barletta M., Pizzi E., Puopolo M., Vesco S., Daneshvar-Fatah F., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2017, 134(32), doi/10.1002/app.45179 |
| [21] | Hua C., Chen F., Wang H., Liu Z., Yang W., Yang M., Acta Polym. Sin., 2016, (8), 1136—1144 |
| (华笋, 陈风, 王捍卿, 刘正英, 杨伟, 杨鸣波. 高分子学报, 2016, (8), 1136—1144) | |
| [22] | Yu T., Jiang N., Li Y.,Compos. Part A: Appl. S., 2014, 64(21), 139—146 |
| [23] | Li M., Hu D., Wang Y. M., Shen C. Y., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2010, 50(12), 2298—2305 |
| [24] | Mo Z.S., Acta Polym. Sin., 2008, (7), 656—661 |
| (莫志深. 高分子学报, 2008, (7), 656—661) | |
| [25] | Kawai T., Rahman N., Matsuba G., Nishida K., Kanaya T., Nakano M., Okamoto H., Kawada J., Usuki A., Honma N., Nakajima K., Matsuda M., Macromolecules, 2007, 40, 9463—9469 |
| [26] | Xu L. Q., Huang H. X., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(6), 2277—2286 |
| [27] | Shao W. G., Wang Q., Li K. S., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2005, 45(4), 451—457 |
| [28] | Wagner M. H., Bernnat A., Schulze V., J. Rheol., 1997, 42(4), 917—928 |
| [29] | Botta L., Scaffaro R., Mantia F. P. L., Dintcheva N. T., J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys., 2010, 48, 344—355 |
| [30] | Bangarusampath D. S., Ruckdaschel H., Altstadt V., Sandler J. K. W., Garray D., Shaffer M. S. P., Polymer, 2009, 50, 5803—5811 |
| [31] | Wang Q. J., Huang H. X., Polym. Test., 2013, 32, 1400—1407 |
| [32] | Singh V. P., Vimal K. K., Kapur G. S., Sharma S., Choudhary V., J. Polym. Res., 2016, 23(43), 1—17 |
| [33] | Lee S. H., Cho E., Youn R. J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2006, 103, 3506—3515 |
| [1] | 赵盛, 霍志鹏, 钟国强, 张宏, 胡立群. 改性钆/硼/聚乙烯纳米复合材料的制备及对中子和伽马射线的屏蔽性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [2] | 于鹏东, 关兴华, 王冬冬, 辛志荣, 石强, 殷敬华. 新型光、 热双响应形状记忆聚合物的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220085. |
| [3] | 赵君禹, 王春博, 王成杨, 张克, 丛冰, 杨岚, 赵晓刚, 陈春海. 导热膨胀石墨/聚醚酰亚胺复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210800. |
| [4] | 高京, 何文涛, 王欣欣, 向宇姝, 龙丽娟, 秦舒浩. DOPO衍生物改性碳纳米管的制备及对聚乳酸阻燃性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210670. |
| [5] | 储瑶, 王烁, 张子诺, 王艺博, 蔡以兵. 铜粒子负载泡沫基相变复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210619. |
| [6] | 徐欢, 柯律, 唐梦珂, 尚涵, 徐文轩, 张子林, 付亚男, 韩广东, 崔金声, 杨皓然, 高杰峰, 张生辉, 何新建. 液相剪切原位剥离蒙脱土纳米片增强高阻氧聚乳酸[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220316. |
| [7] | 李淑蓉, 王琳, 陈玉贞, 江海龙. 金属-有机框架材料在液相催化化学制氢中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [8] | 高晓乐, 王家信, 李志芳, 李艳春, 杨冬花. 复合材料NiOx-ZSM-5的制备及微生物电解池催化析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2886. |
| [9] | 杨英杰, 张晓蓉, 孙玉雪, 刘军, 谢海明. 一种双锂盐梳状聚合物电解质的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2861. |
| [10] | 李占峰, 刘本学, 刘晓婵, 王新强, 张晶, 于诗摩, 赵新富, 张新恩, 伊希斌. 氧化锆湿凝胶中乙酰丙酮配体的脱除机理及气凝胶复合材料的制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2904. |
| [11] | 赵凌云, 黄汉雄, 罗杜宇, 苏逢春. 复合材料柔软性对倒金字塔微结构阵列传感器性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2953. |
| [12] | 魏敏敏, 袁泽, 闾敏, 马辉, 谢小吉, 黄岭. 稀土掺杂上转换纳米颗粒-金属有机骨架复合材料的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2313. |
| [13] | 李欣宇, 李志伟, 张兴元. 硫磺素型聚乳酸/苯磺酸室温磷光体系的构建[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1987. |
| [14] | 王献伟, 柯红军, 袁航, 鲁戈舞, 李丽英, 孟祥胜, 宋书林, 王震. 耐高温可溶性聚酰亚胺树脂及其复合材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2041. |
| [15] | 杨思娴, 钟文钰, 李超贤, 苏秋瑶, 许炳佳, 何谷平, 孙丰强. 聚苯胺纳米线/SnO2复合光催化材料的光化学制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1942. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||