

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 85.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160477
收稿日期:2016-07-06
出版日期:2017-01-10
发布日期:2016-12-20
作者简介:联系人简介: 崔正刚, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事胶体与表面活性剂方面的研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
LIU Kaihong, LIN Qi, CUI Zhenggang*( ), PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong
), PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong
Received:2016-07-06
Online:2017-01-10
Published:2016-12-20
Contact:
CUI Zhenggang
E-mail:cuizhenggang@hotmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
用纳米SiO2颗粒与微量氨基酸型两性表面活性剂十二烷基氨基丙酸钠作复合乳化剂, 以正癸烷为油相, 制备了pH响应性O/W型Pickering乳状液. 室温下该乳状液在pH≤4.0 时稳定, 在pH≥6.0时不稳定, 因此, 可以通过改变水相的pH值使乳状液在稳定和破乳之间多次循环. 在酸性水介质中, 氨基酸型两性表面活性剂分子呈阳离子状态, 可通过静电作用吸附到带负电荷的SiO2颗粒表面, 产生原位疏水化作用, 使其转变为表面活性颗粒; 而在中性和碱性水介质中, 氨基酸型两性表面活性剂呈两性或阴离子状态, 不能产生原位疏水化作用, 因而导致乳状液破乳. 相关作用机理通过吸附量、 Zeta电位及接触角等实验数据得以论证. 该刺激-响应性Pickering乳状液在乳液聚合、 油品输送以及燃料生产等领域具有重要的应用价值.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
刘凯鸿, 林琪, 崔正刚, 裴晓梅, 蒋建中. 纳米SiO2/十二烷基氨基丙酸钠协同稳定的pH响应性Pickering乳状液. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(1): 85.
LIU Kaihong, LIN Qi, CUI Zhenggang, PEI Xiaomei, JIANG Jianzhong. pH-Responsive Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles in Combination with N-Dodecyl-β-aminopropionate†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 85.

Fig.1 Photographs of n-decane-in-water(volume ratio 1:1) emulsions stabilized by 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles solely(A), DPA solely at different concentrations(B) and their mixtures(C, D)DPA concentration(from left to right)/(mmol·L-1): (B) 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1, 3; (C), (D) 0.003, 0.006, 0.01, 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1. Taken 24 h after preparation; (D) 1 week after preparation.
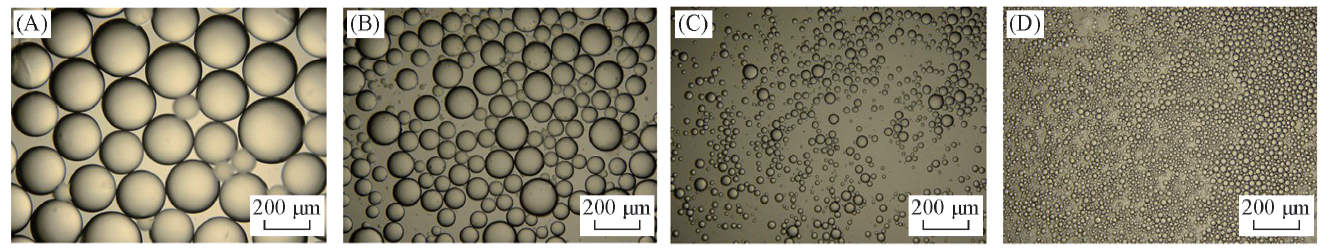
Fig.2 Optical micrographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles and DAP at different concentrations(A—C) and by DAP solely(D) taken 24 h after preparationSurfactant concentration/(mmol·L-1): (A) 0.006; (B) 0.3; (C) 0.6; (D) 1.
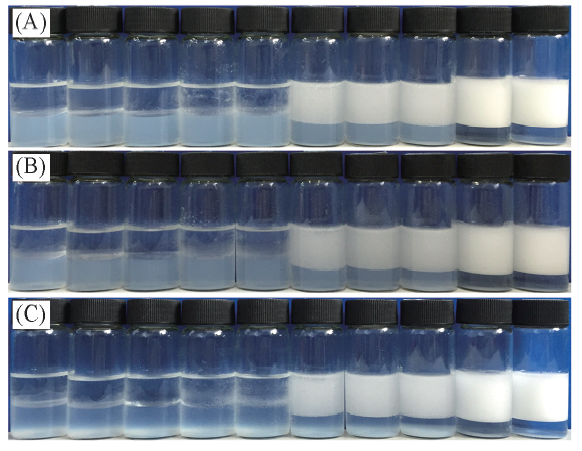

Fig.3 Photographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles and 0.06 mmol/L DAP with different aqueous pH value, taken 24 h(A), 1 week(B) and 2 months(C) after preparationAqueous pH value(from left to right): 6.77, 6.03, 5.65, 5.32, 5.14, 4.99, 4.58, 4.18, 3.63, 3.30.
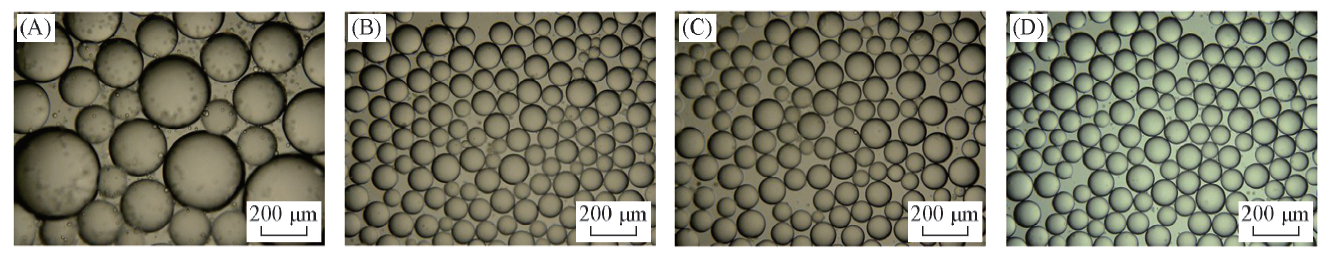
Fig.4 Optical micrographs of n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles and 0.06 mmol/L DAP with different pH values taken 24 h(A—C) and 2 months(D) after preparationpH value: (A) 4.58; (B) 3.63; (C) 3.30; (D) 3.63.
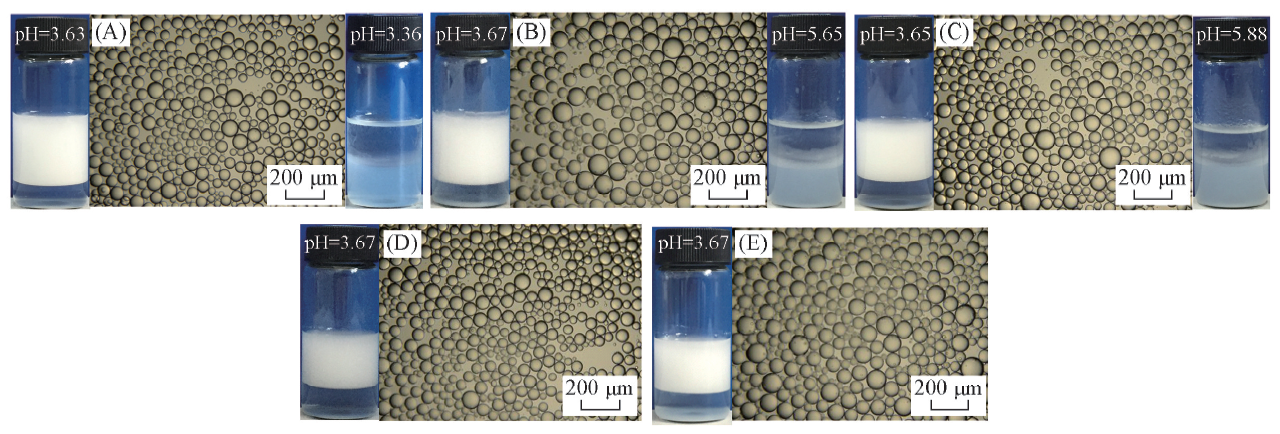

Fig.5 Photographs and micrographs(at low pH) of the n-decane-in-water emulsions stabilized by a mixture of 0.5%(mass fraction) silica nanoparticles in combination with 0.06 mmol/L DAP following pH alternation cycling, taken 24 h[cycle 1(A), cycle 2(B), cycle 4(C), cycle 6(D)] and 2 months(cycle 6 only, E) after homogenization(for stable emulsions) and 20 min after dropping NaOH solution with agitation(for unstable emulsions)
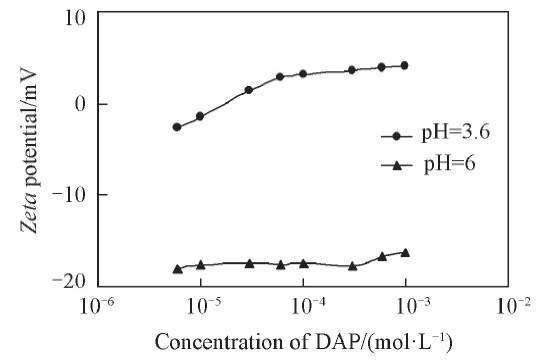
Fig.8 Zeta potential of silica nanoparticles(0.1%) dispersed in DAP aqueous solution with different pH values as a function of initial DAP concentration(25 ℃)
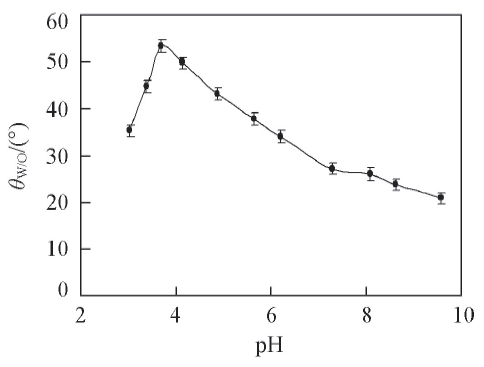
Fig.9 Contact angle of DAP aqueous solution(0.06 mmol/L) on negatively charged quartz slide as a function of pH measured by captured oil(n-decane) drop method(25 ℃)
| [1] | Aveyard R., Binks B. P., Clint J. H., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, 100, 503—546 |
| [2] | Jiang J. Z., Zhu Y., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(47), 12373—12376 |
| [3] | Li T., Zhang L., Chen Y., Guo Y. J., Du X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(4), 772—780 |
| (李涛, 张龙, 陈颖, 郭亚军, 杜雪岩. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4), 772—780) | |
| [4] | Gao Y. J., Zhang L., Hou J. J., Ma Y. B., Qiu H., Zhang W. J., Du X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(6), 1202—1207 |
| (郭亚军, 张龙, 后洁琼, 马泳波, 秋虎, 张文娟, 杜雪岩. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6), 1202—1207) | |
| [5] | Tang J. T., Quinlan P. J., Tam K. C., Soft Matter,2015, 11(18), 3512—3529 |
| [6] | Binks B. P., Murakami R., Armes S. P., Fujii S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(30), 4795—4798 |
| [7] | Zoppe J. O., Venditti R. A., Rojas O. J., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 369, 202—209 |
| [8] | Saigal T., Dong H. C., Matyjaszewski K., Tilton R. D., Langmuir,2010, 26(19), 15200—15209 |
| [9] | Tan T. T. Y., Ahsan A., Reithofer M. R., Tay S. W., Tan S. Y., Hor T. S. A., Chin J. M., Chew B. K. J., Wang X. B., Langmuir,2014, 30(12), 3448—3454 |
| [10] | Anwar N., Williams T., Grimme B., Kuehne A. J. C., ACS Macro Lett., 2013, 2(9), 766—769 |
| [11] | Liu P. W., Lu W. Q., Wang W. J., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Langmuir,2014, 30(34), 10248—10255 |
| [12] | Liang C., Liu Q. X., Xu Z. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2014, 6(9), 6898—6904 |
| [13] | Zhang Q., Yu G. Q., Wang W. J., Yuan H. M., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Langmuir,2012, 28(14), 5940—5946 |
| [14] | Su X., Jessop P. G., Cunningham M. F., Macromol., 2012, 45(2), 666—670 |
| [15] | Pinaud J., Kowal E., Cunningham M. F., Jessop P. G., ACS Macro Lett., 2012, 1(9), 1103—1107 |
| [16] | Zhang Q., Wang W. J., Lu Y. Y., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Macromol., 2011, 44(16), 6539—6545 |
| [17] | Lin S. J., Theato P., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2013, 34(14), 1118—1133 |
| [18] | Zhang Q., Yu G. Q., Wang W. J., Yuan H. M., Li B. G., Zhu S. P., Macromol., 2013, 46(4), 1261—1267 |
| [19] | Quesada M., Muniesa C., Botella P., Quesada M., Muniesa C., Botella P., Chem. Mater., 2013, 25(13), 2597—2602 |
| [20] | Lam S., Blanco E., Smoukov S. K., Velikov K. P., Velev O. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(35), 13856—13859 |
| [21] | Blanco E., Lam S., Smoukov S. K., Velikov K. P., Khan S. A., Velev O. D., Langmuir,2013, 29(32), 10019—10027 |
| [22] | Morse A. J., Armes S. P., Thompson K. L., Dupin D., Fielding L. A., Mills P., Swart R., Langmuir,2013, 29(18), 5466—5475 |
| [23] | Liu H., Wang C. Y., Zou S. W., Wei Z. J., Tong Z., Langmuir,2012, 28(30), 11017—11024 |
| [24] | Fujii S., Suzaki M., Armes S. P., Dupin D., Hamasaki S., Aono K., Nakamura Y., Langmuir,2011, 27(13), 8067—8074 |
| [25] | Binks B. P., Murakami R., Armes S. P., Fujii S., Schmid A., Langmuir,2007, 23(17), 8691—8694 |
| [26] | Yi C. L., Yang Y. Q., Zhu Y., Liu N., Liu X. Y., Luo J., Jiang M., Langmuir,2012, 28(25), 9211—9222 |
| [27] | Fujii S., Okada M., Furuzone T., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 315(1), 287—292 |
| [28] | Yu D., Lin Z., Li Y., Colloid Surface A,2013, 422, 100—109 |
| [29] | Yang H., Zhou T., Zhang W., Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(29), 7455—7459 |
| [30] | Motornov M., Sheparovych R., Lupitskyy R., MacWillianms E., Hoy O., Luzinov I., Minko S., Adv. Func. Mater., 2007, 17(14), 2307—2314 |
| [31] | Yang F., Niu Q., Lan Q., Sun D., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 306(2), 285—295 |
| [32] | Amalvy J. I., Unali G. F., Li Y., Granger-Bevan S., Armes S. P., Binks B. P., Rodrigues J. A., Whiteby C. P., Langmuir,2004, 20(11), 4345—4354 |
| [33] | Morse A. J., Madsen J., Growney D. J., Armes S. P., Mills P., Swart R., Langmuir,2014, 30(42), 12509—12519 |
| [34] | Wang Z. P., Floris P. J. T. R., van Hest J. C. M., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(93), 14550—14553 |
| [35] | Nguyen B. T., Wang W. K., Saunders B. R., Benyahia L., Nicolai T., Langmuir,2015, 31(12), 3605—3611 |
| [36] | Lu J., Zhou W., Chen J., Jin Y. L., Walters K. B., Ding S. J., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(13), 9416—9424 |
| [37] | Richtering W., Langmuir, 2012, 28(50), 17218—17229 |
| [38] | Yamagami T., Kitayama Y., Okubo M., Langmuir,2014, 30(26), 7823—7832 |
| [39] | Tang J., Lee M. F. X., Zhang W., Zhao B. X., Berry R. M., Tam K. C., Biomacromolecules,2014, 15(8), 3052—3062 |
| [40] | Fujii S., Akiyama K., Nakayama S., Hamasaki S., Yusa S., Nakamura Y., Soft Matter,2015, 11(3), 572—579 |
| [41] | Rahman M. M., Chehimi M. M., Fessi H., Elaissari A., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 360(2), 556—564 |
| [42] | Brugger B., Richtering W., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19(19), 2973—2978 |
| [43] | Fameau A. L., Lam S., Velev O. D., Chem. Sci., 2013, 4(10), 3874—3881 |
| [44] | Zhou P., Liu B., Yang F. X., Wang Q., Qu X. Z., Yang Z. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(7), 1431—1436 |
| (周鹏, 刘宝, 杨福鑫, 王倩, 屈小中, 杨振忠. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(7), 1431—1436) | |
| [45] | Yan H. Q., Chen X. Q., Li J. C., Feng Y. H., Wu J. B., Ling Q., Shi Z. F., Wang X. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(5), 1018—1024 |
| (颜慧琼, 陈秀琼, 李嘉诚, 冯玉红, 伍剑博, 林强, 史载峰, 王向辉. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(5), 1018—1024) | |
| [46] | Cui Z. G., Yang L. L., Cui Y. Z., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2010, 26(7), 4717—4724 |
| [47] | Binks B. P., Rodrigues J. A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46(28), 5389—5392 |
| [48] | Cui Z. G., Cui C. F., Zhu Y., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2012, 28(1), 314—320 |
| [49] | Chen Z., Cui C. F., Cui Z. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(11), 2246—2253 |
| (陈钊, 崔晨芳, 崔正刚. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(11), 2246—2253) | |
| [50] | Zhu Y., Jiang J. Z., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Soft Matter,2014, 10(48), 9739—9745 |
| [51] | Zhu Y., Jiang J. Z., Liu K. H., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2015, 31(11), 3301—3307 |
| [52] | Zhu Y., Pei X. M., Jiang J. Z., Cui Z. G., Binks B. P., Langmuir,2015, 31(47), 12937—12943 |
| [53] | Bettayeb B., Descoteaux C., Benoit F., Chapados C., Bérubé G., J. Surfact. Deterg., 2009, 12(3), 237—247 |
| [54] | Xu H.J., Liu X. M., Cao H. X., Ma D. G., 1999, (Suppl.), 47—49 |
| (许虎君, 刘学民, 曹红霞, 马德广. 日用化学品科学, 1999, (增刊), 47—49 | |
| [55] | Worthen A. J., Foster L. M., Dong J., Bollinger J. A., Peterman A. H., Pastora L. E., Bryant S. L.,Truskett T. M., Bielawski C. W., Johnston K. P., Langmuir,2014, 30(4), 984—994 |
| [1] | 姜宏斌, 代文臣, 张娆, 徐晓晨, 陈捷, 杨光, 杨凤林. Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3陶瓷膜对VOCs废气的分离催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [2] | 戴卫, 侯华, 王宝山. 七氟异丁腈负离子结构与反应活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220044. |
| [3] | 郝宏蕾, 孟繁雨, 李若钰, 李迎秋, 贾明君, 张文祥, 袁晓玲. 生物质基氮掺杂多孔炭材料的制备及对水中亚甲基蓝的吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [4] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 蒋伟, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 香蒲基生物炭的活化及对VOCs吸附的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [5] | 孟祥龙, 杨歌, 郭海玲, 刘晨光, 柴永明, 王纯正, 郭永梅. 纳米分子筛的合成及硫化氢吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [6] | 陈潇禄, 袁珍闫, 仲迎春, 任浩. 机械球磨制备三苯胺基PAF-106s及C2烃吸附性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [7] | 靳科研, 白璞, 李小龙, 张佳楠, 闫文付. 新型Mg-Al吸附剂去除压水堆核电厂废水中高浓度硼[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210516. |
| [8] | 谭乐见, 仲宣树, 王锦, 刘宗建, 张爱英, 叶霖, 冯增国. β-环糊精的低临界溶解温度现象及其在有序纳米孔道片晶制备中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [9] | 郑美琪, 毛方琪, 孔祥贵, 段雪. 类水滑石材料在核废水处理领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [10] | 田晓康, 张青松, 杨舒淋, 白洁, 陈冰洁, 潘杰, 陈莉, 危岩. 微生物发酵诱导多孔材料: 制备方法和应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [11] | 马鉴新, 刘晓东, 徐娜, 刘国成, 王秀丽. 一种具有发光传感、 安培传感和染料吸附性能的多功能Zn(II)配位聚合物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| [12] | 张弛, 孙福兴, 朱广山. 双金属同构金属-有机框架材料CAU-21-Al/M的合成、 氮气吸附及复合膜性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [13] | 刘昌辉, 梁国俊, 李妍璐, 程秀凤, 赵显. NH3在硼纳米管表面吸附的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [14] | 刘云鸿, 彭新艳. 新型蛋白结合类毒素血液灌流吸附剂的制备及吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1952. |
| [15] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 宋夫交, 朱婷, 黄维秋, 钟璟, 陈若愚. 中空碳纳米球的制备及VOCs吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1704. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||