

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 1146.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150055
收稿日期:2015-01-19
出版日期:2015-06-10
发布日期:2015-05-15
作者简介:联系人简介: 黄旭日, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事功能材料设计研究和化学微观反应机理研究. E-mail:基金资助:
LI Shaochen, YU Guangtao*( ), CHEN Wei, ZHOU Zhongjun, HUANG Xuri*(
), CHEN Wei, ZHOU Zhongjun, HUANG Xuri*( )
)
Received:2015-01-19
Online:2015-06-10
Published:2015-05-15
Contact:
YU Guangtao,HUANG Xuri
E-mail:yugt@jlu.edu.cn;huangxr@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用密度泛函理论(DFT)方法系统研究了碱金属Li原子吸附亚苯基-1,2-亚乙烯基(Phenylenevinylene)聚合物(PPV)及其衍生物(具有给受体基团修饰的)体系的结构和非线性光学性质. Li原子能稳定地吸附在PPV及其衍生物的表面, 吸附能高达62.3 ~ 78.2 kJ/mol. 当碱金属Li原子吸附在[PPV]n(n=2~4)表面时, 锂盐效应导致了Li原子和[PPV]n之间发生了明显的电荷转移过程, 使体系的一阶超极化率β0从249 ~ 756 a.u.明显增加到1.16×104 ~ 1.37×105 a.u.. 当碱金属Li原子吸附在只有给体(—NH2)或只有受体(—CN)基团修饰的PPV衍生物{[NH2-(PPV)n]/[(PPV)n-CN]}时, 体系的一阶超极化率值进一步提升, 分别高达1.61×105 a.u.(n=4)和2.85×105 a.u.(n=4). 这主要源于锂盐效应和Donor-π-Acceptor之间的协同作用导致跃迁能进一步降低所致. 在Li原子吸附的具有给受体基团同时修饰的PPV衍生物 (Li@[NH2-(PPV)n-CN])体系中, 这种协同作用得到进一步加强, 显著改善了体系的一阶超极化率(高达3.56×105 a.u., n=4).
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李绍晨, 于广涛, 陈巍, 周中军, 黄旭日. 碱金属原子吸附PPV及其衍生物体系的结构和非线性光学性质的理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(6): 1146.
LI Shaochen, YU Guangtao, CHEN Wei, ZHOU Zhongjun, HUANG Xuri. Investigation on Structures and Nonlinear Optical Properties of PPV and Its Derivatives Systems with Adsorbing Alkali Metal Atom†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(6): 1146.
| Method | MP2 6-311++G(3df,3pd) | MP2 6-31+G(d) | M06-2x 6-31+G(d) | B3LYP 6-31+G(d) | HF 6-31+G(d) | CAM-B3LYP 6-31+G(d) | LC-BLYP 6-31+G(d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0/a.u. | 11258 | 11922 | 11566 | 11735 | 12200 | 13618 | 13872 |
| Error(%) | 5.9 | 2.7 | 4.2 | 8.4 | 21.0 | 23.2 |
Table 1 Static first hyperpolarizability(β0) and the corresponding error*
| Method | MP2 6-311++G(3df,3pd) | MP2 6-31+G(d) | M06-2x 6-31+G(d) | B3LYP 6-31+G(d) | HF 6-31+G(d) | CAM-B3LYP 6-31+G(d) | LC-BLYP 6-31+G(d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0/a.u. | 11258 | 11922 | 11566 | 11735 | 12200 | 13618 | 13872 |
| Error(%) | 5.9 | 2.7 | 4.2 | 8.4 | 21.0 | 23.2 |
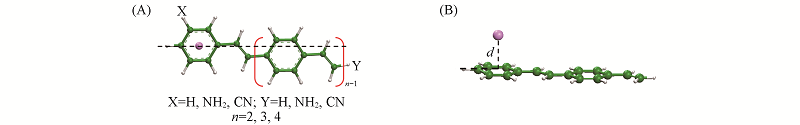
Fig.1 Optimized geometries of Li@[PPV]2 [the top(A) and side(B) views] and the general formula of Li@[X-(PPV)n-Y](n=2—4; X, Y=H, —NH2, —CN) systemsThe d value is the vertical distance between the Li atom and benzene ring of [X-(PPV)n-Y].
| System | d/nm | Ead/ (kJ·mol-1) | NBO/e | α/a.u. | β0/a.u. | f0 | ΔE/eV | Δμ/a.u. | (Δμ·f0/ ΔE3)/a.u. | CT* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[(PPV)2] | 0.171 | 62.3 | 0.834 | 310 | 1.16×104 | 0.6020 | 2.907 | 1.083 | 534 | H→L+9H→L+11 |
| Li@[(PPV)3] | 0.172 | 66.0 | 0.837 | 549 | 6.29×104 | 0.7236 | 2.591 | 2.054 | 1720 | H→L+1 H→L+5 |
| Li@[(PPV)4] | 0.172 | 66.9 | 0.838 | 783 | 1.37×105 | 0.4791 | 2.360 | 2.627 | 1927 | H→L+1 H→L+6 |
| [(PPV)2] | 223 | 249 | 1.2516 | 3.835 | 0.219 | 98 | H→L | |||
| [(PPV)3] | 382 | 518 | 2.1335 | 3.351 | 0.175 | 200 | H-1→L+1 H→L | |||
| [(PPV)4] | 555 | 756 | 3.0035 | 3.109 | 0.147 | 296 | H-1→L+1 H→L |
Table 2 Vertical distance(d) between the Li atom and Li@[PPV]n(n=2—4) systems, the adsorption energies(Ead), NBO charges of doped Li atoms, the polarizability(α), the first hyperpolarizability(β0), the oscillator strength(f0), the transition energy(ΔE), the dipole moment(Δμ) between the crucial excited state and ground state, the estimated values under the two-level approach(Δμ·f0/ΔE3), and the compositions of the crucial transition(CT) state for Li@[PPV]n and [PPV]n
| System | d/nm | Ead/ (kJ·mol-1) | NBO/e | α/a.u. | β0/a.u. | f0 | ΔE/eV | Δμ/a.u. | (Δμ·f0/ ΔE3)/a.u. | CT* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[(PPV)2] | 0.171 | 62.3 | 0.834 | 310 | 1.16×104 | 0.6020 | 2.907 | 1.083 | 534 | H→L+9H→L+11 |
| Li@[(PPV)3] | 0.172 | 66.0 | 0.837 | 549 | 6.29×104 | 0.7236 | 2.591 | 2.054 | 1720 | H→L+1 H→L+5 |
| Li@[(PPV)4] | 0.172 | 66.9 | 0.838 | 783 | 1.37×105 | 0.4791 | 2.360 | 2.627 | 1927 | H→L+1 H→L+6 |
| [(PPV)2] | 223 | 249 | 1.2516 | 3.835 | 0.219 | 98 | H→L | |||
| [(PPV)3] | 382 | 518 | 2.1335 | 3.351 | 0.175 | 200 | H-1→L+1 H→L | |||
| [(PPV)4] | 555 | 756 | 3.0035 | 3.109 | 0.147 | 296 | H-1→L+1 H→L |
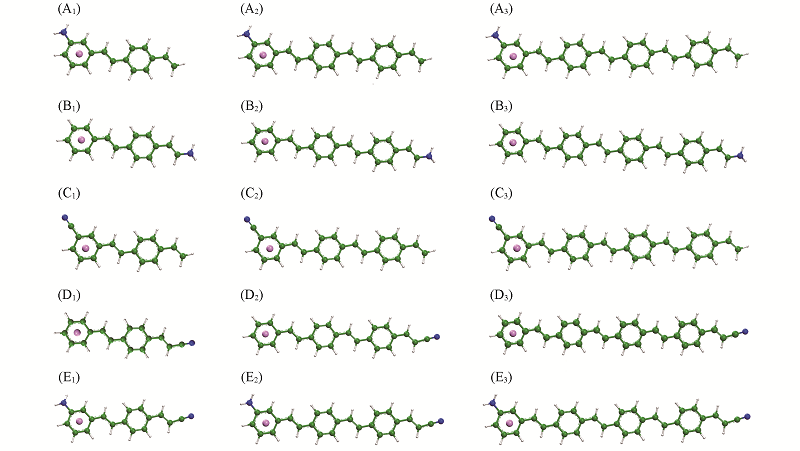
Fig.5 Optimized geometries of Li@[NH2-(PPV)n](A1—A3), Li@[(PPV)n-NH2](B1—B3), Li@[CN-(PPV)n](C1—C3], Li@[(PPV)n-CN](D1—D3), Li@[NH2-(PPV)n-CN](E1—E3)n=2—4.
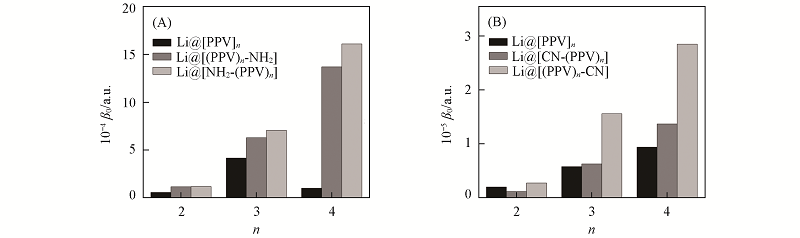
Fig.6 Comparison of the first hyperpolarizability β0 values for Li@[PPV]n, Li@[NH2-(PPV)n] and Li@[(PPV)n-NH2] systems(A) and Li@[PPV]n, Li@[CN-(PPV)n] and Li@[(PPV)n-CN] systems(B)
| System | d/nm | Ead/(kJ·mol-1) | NBO/e | α/a.u. | β0/a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)2] | 0.173 | 67.3 | 0.846 | 329 | 1.18×104 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)3] | 0.173 | 71.9 | 0.849 | 582 | 7.06×104 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)4] | 0.174 | 68.6 | 0.832 | 831 | 1.61×105 |
| Li@[(PPV)2-NH2] | 0.171 | 54.3 | 0.831 | 323 | 5.69×103 |
| Li@[(PPV)3-NH2] | 0.172 | 62.3 | 0.835 | 555 | 4.16×104 |
| Li@[(PPV)4-NH2] | 0.172 | 65.5 | 0.837 | 789 | 1.01×105 |
| Li@[CN-(PPV)2] | 0.171 | 70.2 | 0.852 | 354 | 2.01×104 |
| Li@[CN-(PPV)3] | 0.171 | 71.1 | 0.853 | 578 | 5.79×104 |
| Li@[CN-(PPV)4] | 0.171 | 71.5 | 0.854 | 788 | 9.41×104 |
| Li@[(PPV)2-CN] | 0.173 | 78.2 | 0.841 | 393 | 2.73×104 |
| Li@[(PPV)3-CN] | 0.172 | 73.6 | 0.841 | 683 | 1.56×105 |
| Li@[(PPV)4-CN] | 0.172 | 70.6 | 0.840 | 913 | 2.85×105 |
Table 3 Vertical distance(d) between the Li atom and Li@[PPV]n(n=2—4) systems, the adsorption energies(Ead), NBO charges of doped Li atoms, the polarizability(α), the first hyperpolari-zability(β0) for Li@[NH2-(PPV)n], Li@[(PPV)n-NH2], Li@[CN-(PPV)n] and Li@[(PPV)n-CN] systems, respectively
| System | d/nm | Ead/(kJ·mol-1) | NBO/e | α/a.u. | β0/a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)2] | 0.173 | 67.3 | 0.846 | 329 | 1.18×104 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)3] | 0.173 | 71.9 | 0.849 | 582 | 7.06×104 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)4] | 0.174 | 68.6 | 0.832 | 831 | 1.61×105 |
| Li@[(PPV)2-NH2] | 0.171 | 54.3 | 0.831 | 323 | 5.69×103 |
| Li@[(PPV)3-NH2] | 0.172 | 62.3 | 0.835 | 555 | 4.16×104 |
| Li@[(PPV)4-NH2] | 0.172 | 65.5 | 0.837 | 789 | 1.01×105 |
| Li@[CN-(PPV)2] | 0.171 | 70.2 | 0.852 | 354 | 2.01×104 |
| Li@[CN-(PPV)3] | 0.171 | 71.1 | 0.853 | 578 | 5.79×104 |
| Li@[CN-(PPV)4] | 0.171 | 71.5 | 0.854 | 788 | 9.41×104 |
| Li@[(PPV)2-CN] | 0.173 | 78.2 | 0.841 | 393 | 2.73×104 |
| Li@[(PPV)3-CN] | 0.172 | 73.6 | 0.841 | 683 | 1.56×105 |
| Li@[(PPV)4-CN] | 0.172 | 70.6 | 0.840 | 913 | 2.85×105 |
| System | f0 | ΔE/eV | Δμ/a.u. | (Δμ· f0/ΔE3)/a.u. | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)2] | 0.7360 | 2.875 | 1.907 | 1189 | H→L, H→L+1 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)3] | 0.6424 | 2.584 | 2.850 | 2135 | H→L+1, H→L+7 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)4] | 0.5948 | 2.354 | 4.245 | 3895 | H→L+2, H→L+3 |
| Li@[(PPV)2-CN] | 0.6532 | 2.744 | 1.853 | 1179 | H→L+1, H→L+2 |
| Li@[(PPV)3-CN] | 0.7612 | 2.363 | 3.575 | 4150 | H→L, H→L+2 |
| Li@[(PPV)4-CN] | 0.5931 | 1.444 | 9.834 | 38981 | H→L, H→L+2 |
Table 4 Oscillator strength(f0), the transition energy(ΔE), the dipole moment(Δμ) between the crucial excited state and ground state, the estimated values under the two-level approach(Δμ·f0/ΔE3), and the compositions of the crucial transition(CT) state for for Li@[NH2-(PPV)n] and Li@[(PPV)n-CN](n=2—4) systems, respectively
| System | f0 | ΔE/eV | Δμ/a.u. | (Δμ· f0/ΔE3)/a.u. | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)2] | 0.7360 | 2.875 | 1.907 | 1189 | H→L, H→L+1 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)3] | 0.6424 | 2.584 | 2.850 | 2135 | H→L+1, H→L+7 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)4] | 0.5948 | 2.354 | 4.245 | 3895 | H→L+2, H→L+3 |
| Li@[(PPV)2-CN] | 0.6532 | 2.744 | 1.853 | 1179 | H→L+1, H→L+2 |
| Li@[(PPV)3-CN] | 0.7612 | 2.363 | 3.575 | 4150 | H→L, H→L+2 |
| Li@[(PPV)4-CN] | 0.5931 | 1.444 | 9.834 | 38981 | H→L, H→L+2 |
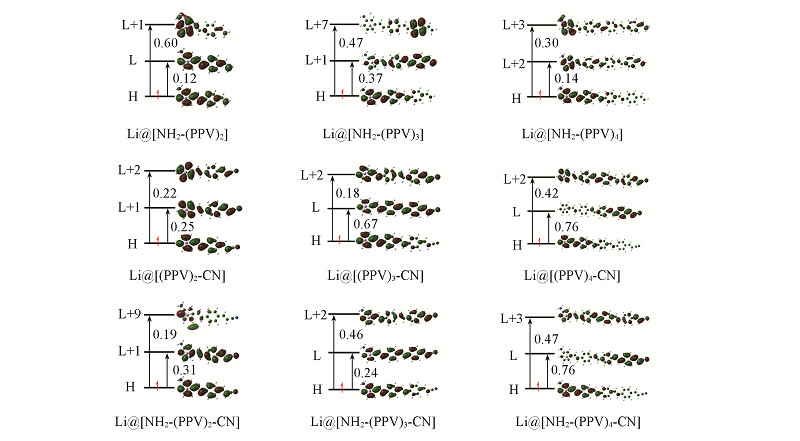
Fig.7 Crucial transition states of the Li@[NH2-(PPV)n], Li@[(PPV)n-CN] and Li@[NH2-(PPV)n-CN] systems(n=2—4) The relatively large component cofficients are marked.
| System | d/nm | Ead/ (kJ·mol-1) | NBO/e | α/ a.u. | β0/a.u. | f0 | ΔE/ eV | Δμ/ a.u. | (Δμ· f0/ ΔE3)/a.u. | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)2-CN] | 0.174 | 84.0 | 0.853 | 416 | 2.74×104 | 1.0662 | 2.734 | 1.860 | 1953 | H→L+1, H→L+9 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)3-CN] | 0.174 | 75.2 | 0.836 | 737 | 1.80×105 | 0.5581 | 1.400 | 4.553 | 18635 | H→L, H→L+2 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)4-CN] | 0.174 | 72.7 | 0.835 | 987 | 3.56×105 | 0.6597 | 1.363 | 9.001 | 47190 | H→L, H→L+3 |
Table 5 Vertical distance(d) between the Li atom and Li@[NH2-(PPV)n-CN](n=2—4) systems, the adsorption energies(Ead), NBO charges of doped Li atoms, the polarizability(α), the first hyperpolarizability(β0), the oscillator strength(f0), the transition energy(ΔE), the dipole moment(Δμ) between the crucial excited state and ground state, the estimated values under the two-level approach(Δμ·f0/ΔE3), and the compositions of the crucial transition(CT) state for Li@[NH2-(PPV)n-CN](n=2—4) systems
| System | d/nm | Ead/ (kJ·mol-1) | NBO/e | α/ a.u. | β0/a.u. | f0 | ΔE/ eV | Δμ/ a.u. | (Δμ· f0/ ΔE3)/a.u. | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)2-CN] | 0.174 | 84.0 | 0.853 | 416 | 2.74×104 | 1.0662 | 2.734 | 1.860 | 1953 | H→L+1, H→L+9 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)3-CN] | 0.174 | 75.2 | 0.836 | 737 | 1.80×105 | 0.5581 | 1.400 | 4.553 | 18635 | H→L, H→L+2 |
| Li@[NH2-(PPV)4-CN] | 0.174 | 72.7 | 0.835 | 987 | 3.56×105 | 0.6597 | 1.363 | 9.001 | 47190 | H→L, H→L+3 |
| [1] | Eaton D. F., Science, 1991, 253, 281—287 |
| [2] | Kanis D. R., Ratner M. A., Marks T. J., Chem. Rev., 1994, 94, 195—242 |
| [3] | Yu G. T., Zhao X. G., Niu M., Huang X. R., Zhang H., Chen W., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013, 1, 3833—3841 |
| [4] | Liu C. G., Guan W., Song P., Yan L. K., Su Z. M., Inorg. Chem., 2009, 48, 6548—6554 |
| [5] | Cornelis D., Franz E., Asselberghs I., Clays K., Verbiest T., Koeckelberghs G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 1317—1327 |
| [6] | Maury O., Viau L., Senechal K., Corre B., Guegan J. P., Renouard T., Ledoux I., Zyss J., Bozec L. H., Chem. Eur. J., 2004, 10, 4454—4466 |
| [7] | Lee S. H., Park J. R., Jeong M. Y., Kim H. M., Li S. J., Song J., Ham S., Jeon S. J., Cho B. R., Chem. Phys. Chem., 2006, 7, 206—212 |
| [8] | Chen W., Li Z. R., Wu D., Li Y., Sun C. C., Gu F. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 10977—10981 |
| [9] | Yu G.T., Huang X. R., Chen, W., Sun C. C., J. Comput. Chem., 2011, 32, 2005—2011 |
| [10] | Li S. C, Yu G. T., Chen W., Huang X. R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11), 2390—2396 |
| (李绍晨, 于广涛, 陈巍, 黄旭日.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(11), 2390—2396) | |
| [11] | Zhao X. G., Yu G. T., Huang X. R., Chen W., Niu M., J. Mol. Model., 2013, 19, 5601—5610 |
| [12] | Niu M., Yu G. T., Yang G. H., Chen W., Zhao X. G., Huang X. R., Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 349—358 |
| [13] | Muhammad S., Xu H. L., Liao Y., Kan Y. H., Su Z. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 11833—11840 |
| [14] | Chen W., Li Z. R., Wu D., Li R. Y., Sun C. C., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 601—608 |
| [15] | Xu H. L., Li Z. R., Wu D., Wang B. Q., Li Y., Gu F. L., Aoki Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 2967—2970 |
| [16] | Xu H. L., Li Z. R., Wu D., Ma F., Li Z. J., Gu F. L., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 4984—4986 |
| [17] | Xu H. L., Zhong R. L., Sun S. L., Su Z. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 16340—16346 |
| [18] | Ma F., Zhou Z. J., Li Z. R., Wu D., Li Y., Li Z. S., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2010, 488, 182—186 |
| [19] | Shi Z. M., Chen W., Wan S. Q., Li H., Huang X. R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2), 441—446 |
| (石芝铭, 陈巍, 万素琴, 李辉, 黄旭日.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(2), 441—446) | |
| [20] | Junkers T., Vandenbergh J., Adriaensens P., Lutsen L., Vanderzande D., Polym. Chem., 2012, 3, 275—285 |
| [21] | Burroughes J. H., Bradley D. D. C., Brown A. R., Marks R. N., Friend R. H., Holmes A. B., Nature, 1990, 347, 539—541 |
| [22] | Greenham N. C., Moratti S. C., Bradely D. D. C., Friend R. H., Holmes A. B., Nature, 1993, 365, 628—630 |
| [23] | Gillissen S., Lutsen L., Vanderzande D., Gelan J., Synth. Met., 2001, 119, 137—13 |
| [24] | Yu G. T., Huang X. R., Li S. C., Chen W., Int. J. Quantum. Chem., 2015, 115, 671—679 |
| [25] | Wei W., Bai F. Q., Xia B. H., Chen H. B., Zhang H. X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(5), 962—968 |
| [26] | Zhang S. S., Shi L. L., Su Z. M., Ceng Y., Zhao L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(2), 361—365 |
| [27] | Chen J., Wang J., Bai F. Q., Zheng Q. C., Zhang H. X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2012, 28(4), 696—702 |
| [28] | Wang X. L., Zhang K., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2012, 28(4), 703—706 |
| [29] | Lewis E. J., Larry R. D., Bruce H. R., Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 3258—3265 |
| [30] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A., Peralta J. E. Jr., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision B.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2010 |
| [31] | Oudar J. L., J. Chem. Phys., 1977, 67, 446—457 |
| [1] | 郑雪莲, 杨翠翠, 田维全. 全椅式边含薁缺陷石墨烯纳米片的二阶非线性光学性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [2] | 程效, BORA Debajeet K., Per⁃Anders, GUO Jinghua, 罗毅. 理论研究晶体场效应和电荷转移效应对Co2+的2p电子X射线L2,3吸收边光谱的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2197. |
| [3] | 李欣宇, 李志伟, 张兴元. 硫磺素型聚乳酸/苯磺酸室温磷光体系的构建[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1987. |
| [4] | 常慧, 姚双全, 韩文佳, 康榭娜, 张力, 李新平, 张召. 三联吡啶化合物的溶剂致荧光变色及丁醇异构体鉴别[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 902. |
| [5] | 王琳硕, 李昆杰, 刘玉敏, 赵瑞红, 李青, 钱鑫, 张帆, 薛志伟. 三苯基均三嗪基团调控敏化染料光电性能的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(7): 1653. |
| [6] | 林桂锋,郭景富,何腾飞,任爱民. 供电子基团修饰对NNI-R系列分子光物理性质的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1277. |
| [7] | 康慧敏, 王洪强, 王慧莹, 吴黎歆, 仇永清. 卟啉-碳硼烷-硼亚甲基二吡咯三元化合物二阶非线性光学性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(5): 965. |
| [8] | 吴娟, 王洪强, 刘晓云, 史志圆, 仇永清. D-A-D(D')型邻位碳硼烷三元体系二阶非线性光学性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7): 1490. |
| [9] | 刘翀, 刘丽来, 聂佳慧. 高活性碳球修饰g-C3N4的制备及光催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7): 1511. |
| [10] | 李想, 王慧莹, 王洪强, 叶近婷, 仇永清. 联吡啶RuⅡ/Ⅲ配合物二阶非线性光学性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10): 2221. |
| [11] | 陈德利, 杨鹏勇, 武胜男, 何思慧, 王芳芳. 从头算分子动力学模拟Pd团簇负载UiO-66材料结构及稳定性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(7): 1210. |
| [12] | 李荣荣, 王洪强, 王丽, 吴娟, 仇永清. 二芳基氨(硼)-π-碳硼烷三元化合物的二阶非线性光学性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(10): 1796. |
| [13] | 陈九菊. 有机半导体Terazulene单晶双极电荷传输性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(1): 121. |
| [14] | 张雪莹, 于广涛, 陈巍, 黄旭日. 给/受体基团修饰的含5-9缺陷Zigzag碳纳米条带体系的非线性光学性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(11): 2204. |
| [15] | 庞然, 金曦, 赵刘斌, 丁松园, 吴德印, 田中群. 电化学表面增强拉曼光谱的量子化学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(11): 2087. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||