

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 1156.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150050
张法达1,2, 刘轶2,3( ), 徐京城2, 李生娟2, 汪秀南1,2, 孙玥2, 赵新洛3
), 徐京城2, 李生娟2, 汪秀南1,2, 孙玥2, 赵新洛3
收稿日期:2015-01-16
出版日期:2015-06-10
发布日期:2015-05-22
作者简介:联系人简介: 刘 轶, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事计算物理化学研究. E-mail:基金资助:
ZHANG Fada1,2, LIU Yi2,3,*( ), XU Jingcheng2, LI Shengjuan2, WANG Xiunan1,2, SUN Yue2, ZHAO Xinluo3
), XU Jingcheng2, LI Shengjuan2, WANG Xiunan1,2, SUN Yue2, ZHAO Xinluo3
Received:2015-01-16
Online:2015-06-10
Published:2015-05-22
Contact:
LIU Yi
E-mail:yiliu@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用全原子分子动力学方法系统研究了聚酰胺(PAMAM)型树形大分子非共价搭载4种抗癌药物分子(CE6, DOX, MTX及SN38)的药物传输复合体系. 考察了药物分子种类、 数量及树形大分子的代数和聚乙二醇化表面修饰对复合体系的结合强度、 尺寸及溶剂中扩散行为的影响. 研究发现, PAMAM自身变形能对药物-PAMAM间的结合有重要影响. 搭载较多的药物分子可以使PAMAM自身增大, 但同样搭载条件下经过聚乙二醇化修饰过的PAMAM变化并不明显. PAMAM分子表面的聚乙二醇化可以更高的强度结合更多的药物分子, 并减缓其扩散速度, 因而提高药物分子的搭载效率和体内滞留时间. 为新型树形大分子基药物传输体系的设计提供理论依据.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
张法达, 刘轶, 徐京城, 李生娟, 汪秀南, 孙玥, 赵新洛. 树形大分子基药物传输系统结合强度及构型的分子动力学研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(6): 1156.
ZHANG Fada, LIU Yi, XU Jingcheng, LI Shengjuan, WANG Xiunan, SUN Yue, ZHAO Xinluo. Molecular Dynamics Study on Binding Strength and Conformation of Dendrimer-based Drug Delivery Systems†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(6): 1156.
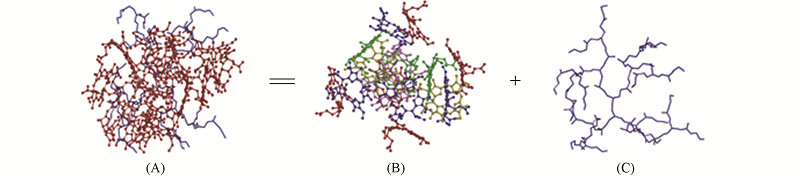
Fig.1 Atomic structures of CE616@G2(A) snapshot and the structures of the CE616(B) and G2(C) separated from the CE616@G2, respectivelyThe various colors in (B) denote the different drug molecules. All the H atoms are omitted for clarity.
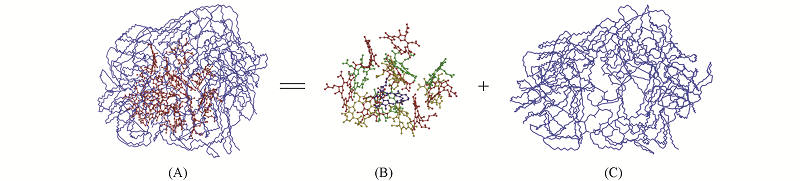
Fig.2 Atomic structures of CE616@G2-PEG(A) snapshot and the structures of the CE616(B) and G2-PEG(C) separated from the CE616@G2-PEG, respectivelyThe various colors in (B) denote the different drug molecules. All the H atoms are omitted for clarity.
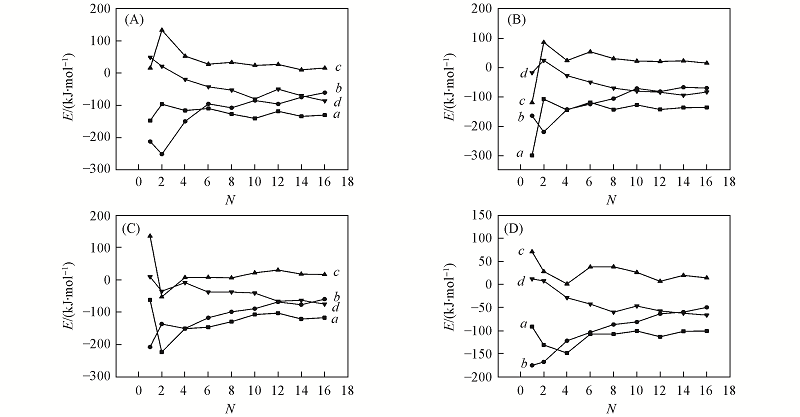
Fig.4 Instantaneous binding energies(Eb-PD, a), interaction energies(Ei-PD, b), deformation energies(Ed-P, c), and deformation-and-interaction energies(Edi-D, d) of the DN@G2 complexes with CE6(A), DOX(B), MTX(C) and SN38(D) as the functions of the number of drug molecules N
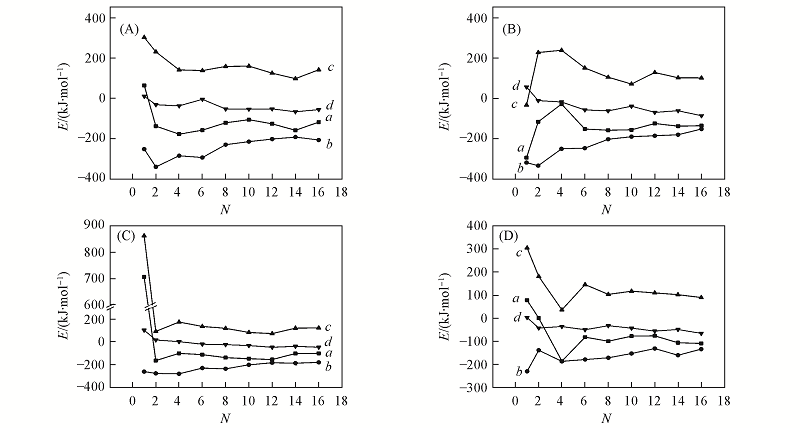
Fig.5 Instantaneous binding energies(Eb-PD, a), interaction energies(Ei-PD, b), deformation energies(Ed-P, c), and deformation-and-interaction(Edi-D, d) energies of the DN@G2-PEG complexes with CE6(A), DOX(B), MTX(C) and SN38(D) as the functions of the number of drug molecules N
| Drug | D1 | D1(D16@G2) | G2 | G2(D16@G2) | D16@G2 | D1(D16@ G2-PEG) | G2-PEG | G2-PEG(D16@ G2-PEG) | D16@G2-PEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 0.896 | 1.965 | |||||||
| CE6 | 0.465 | 0.469±0.05 | 1.294(44.4%) | 1.351(50.8%) | 0.467±0.05 | 2.411(22.7%) | 2.242(14.1%) | ||
| DOX | 0.479 | 0.484±0.07 | 1.314(46.7%) | 1.227(67.0%) | 0.484±0.07 | 2.475(26.0%) | 2.318(18.0%) | ||
| MTX | 0.525 | 0.541±0.42 | 1.228(37.1%) | 1.211(35.2%) | 0.542±0.45 | 2.315(17.8%) | 2.167(10.3%) | ||
| SN38 | 0.434 | 0.434±0.01 | 1.14(27.2%) | 1.189(32.7%) | 0.435±0.01 | 2.36(20.1%) | 2.254(14.7%) |
Table 1 Rg(nm) of drug molecules(D1), dendrimers(G2 or G2-PEG) and drug-dendrimer complexes(DN@G2 or DN@G2-PEG)
| Drug | D1 | D1(D16@G2) | G2 | G2(D16@G2) | D16@G2 | D1(D16@ G2-PEG) | G2-PEG | G2-PEG(D16@ G2-PEG) | D16@G2-PEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 0.896 | 1.965 | |||||||
| CE6 | 0.465 | 0.469±0.05 | 1.294(44.4%) | 1.351(50.8%) | 0.467±0.05 | 2.411(22.7%) | 2.242(14.1%) | ||
| DOX | 0.479 | 0.484±0.07 | 1.314(46.7%) | 1.227(67.0%) | 0.484±0.07 | 2.475(26.0%) | 2.318(18.0%) | ||
| MTX | 0.525 | 0.541±0.42 | 1.228(37.1%) | 1.211(35.2%) | 0.542±0.45 | 2.315(17.8%) | 2.167(10.3%) | ||
| SN38 | 0.434 | 0.434±0.01 | 1.14(27.2%) | 1.189(32.7%) | 0.435±0.01 | 2.36(20.1%) | 2.254(14.7%) |
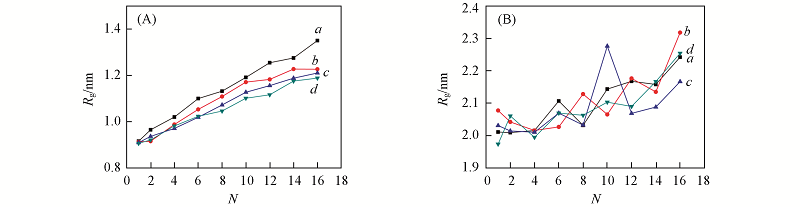
Fig.6 Radius of gyration(Rg) as functions of number of drug molecules in DN@G2(A) and DN@G2-PEG(B) with CE6(a), DOX(b), MTX(c) and SN38(d), respectively
| DN@Gn | Eb(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eb(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | DN@Gn-PEG | Eb(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eb(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE68@G0 | -218.572 | -98.157 | CE68@G0-PEG | 154.808 | -138.951 |
| DOX8@G0 | -201.418 | -111.587 | DOX8@G0-PEG | 118.407 | -146.900 |
| MTX8@G0 | -205.476 | -82.299 | MTX8@G0-PEG | 166.900 | -145.478 |
| SN388@G0 | -137.277 | -84.224 | SN388@G0-PEG | 212.464 | -125.813 |
| CE610@G1 | -254.136 | -109.412 | CE612@G1-PEG | 224.555 | -144.766 |
| DOX10@G1 | -148.699 | -125.478 | DOX12@G1-PEG | 364.719 | -129.160 |
| MTX10@G1 | -210.079 | -101.546 | MTX12@G1-PEG | 301.834 | -112.089 |
| SN3810@G1 | -90.709 | -96.650 | SN3812@G1-PEG | 346.017 | -142.047 |
| CE616@G2 | -213.761 | -122.089 | CE616@G2-PEG | 378.610 | -141.126 |
| DOX16@G2 | -195.351 | -137.612 | DOX16@G2-PEG | 533.251 | -119.077 |
| MTX16@G2 | 114.683 | -115.060 | MTX16@G2-PEG | 486.265 | -136.608 |
| SN3816@G2 | -109.746 | -103.721 | SN3816@G2-PEG | -632.788 | -88.408 |
Table 2 Binding energy(Eb) of DN@PAMAM complexes with(or without) water
| DN@Gn | Eb(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eb(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | DN@Gn-PEG | Eb(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eb(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE68@G0 | -218.572 | -98.157 | CE68@G0-PEG | 154.808 | -138.951 |
| DOX8@G0 | -201.418 | -111.587 | DOX8@G0-PEG | 118.407 | -146.900 |
| MTX8@G0 | -205.476 | -82.299 | MTX8@G0-PEG | 166.900 | -145.478 |
| SN388@G0 | -137.277 | -84.224 | SN388@G0-PEG | 212.464 | -125.813 |
| CE610@G1 | -254.136 | -109.412 | CE612@G1-PEG | 224.555 | -144.766 |
| DOX10@G1 | -148.699 | -125.478 | DOX12@G1-PEG | 364.719 | -129.160 |
| MTX10@G1 | -210.079 | -101.546 | MTX12@G1-PEG | 301.834 | -112.089 |
| SN3810@G1 | -90.709 | -96.650 | SN3812@G1-PEG | 346.017 | -142.047 |
| CE616@G2 | -213.761 | -122.089 | CE616@G2-PEG | 378.610 | -141.126 |
| DOX16@G2 | -195.351 | -137.612 | DOX16@G2-PEG | 533.251 | -119.077 |
| MTX16@G2 | 114.683 | -115.060 | MTX16@G2-PEG | 486.265 | -136.608 |
| SN3816@G2 | -109.746 | -103.721 | SN3816@G2-PEG | -632.788 | -88.408 |
| DN@Gn | Ei-PD(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Ei-PD(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | DN@Gn-PEG | Ei-PD(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eb(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE68@G0 | -161.126 | -37.447 | CE68@G0-PEG | -204.137 | -106.734 |
| DOX8@G0 | -174.389 | -20.209 | DOX8@G0-PEG | -253.969 | -133.260 |
| MTX8@G0 | -175.770 | -29.079 | MTX8@G0-PEG | -195.184 | -161.377 |
| SN388@G0 | -122.591 | -21.255 | SN388@G0-PEG | -167.862 | -130.708 |
| CE610@G1 | -164.640 | -54.057 | CE612@G1-PEG | -193.970 | -153.929 |
| DOX10@G1 | -182.841 | -54.099 | DOX12@G1-PEG | -192.087 | -165.184 |
| MTX10@G1 | -157.151 | -42.802 | MTX12@G1-PEG | -177.694 | -153.595 |
| SN3810@G1 | -121.545 | -40.417 | SN3812@G1-PEG | -120.792 | -93.430 |
| CE616@G2 | -153.678 | -60.250 | CE616@G2-PEG | -230.204 | -205.476 |
| DOX16@G2 | -173.887 | -69.036 | DOX16@G2-PEG | -212.589 | -151.586 |
| MTX16@G2 | -194.472 | -59.329 | MTX16@G2-PEG | -192.004 | -178.950 |
| SN3816@G2 | -121.503 | -49.162 | SN3816@G2-PEG | -162.088 | -133.553 |
Table 3 Interaction energies(Ei-PD) of DN@PAMAM complexes with(or without) water
| DN@Gn | Ei-PD(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Ei-PD(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | DN@Gn-PEG | Ei-PD(H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eb(no H2O)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE68@G0 | -161.126 | -37.447 | CE68@G0-PEG | -204.137 | -106.734 |
| DOX8@G0 | -174.389 | -20.209 | DOX8@G0-PEG | -253.969 | -133.260 |
| MTX8@G0 | -175.770 | -29.079 | MTX8@G0-PEG | -195.184 | -161.377 |
| SN388@G0 | -122.591 | -21.255 | SN388@G0-PEG | -167.862 | -130.708 |
| CE610@G1 | -164.640 | -54.057 | CE612@G1-PEG | -193.970 | -153.929 |
| DOX10@G1 | -182.841 | -54.099 | DOX12@G1-PEG | -192.087 | -165.184 |
| MTX10@G1 | -157.151 | -42.802 | MTX12@G1-PEG | -177.694 | -153.595 |
| SN3810@G1 | -121.545 | -40.417 | SN3812@G1-PEG | -120.792 | -93.430 |
| CE616@G2 | -153.678 | -60.250 | CE616@G2-PEG | -230.204 | -205.476 |
| DOX16@G2 | -173.887 | -69.036 | DOX16@G2-PEG | -212.589 | -151.586 |
| MTX16@G2 | -194.472 | -59.329 | MTX16@G2-PEG | -192.004 | -178.950 |
| SN3816@G2 | -121.503 | -49.162 | SN3816@G2-PEG | -162.088 | -133.553 |
| DN@Gn | D/(nm2·ps-1) | DN@Gn-PEG | D/(nm2·ps-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE68@G0 | 1.1×10-3 | CE68@G0-PEG | 6.4×10-4 |
| DOX8@G0 | 1.0×10-3 | DOX8@G0-PEG | 8.1×10-4 |
| MTX8@G0 | 1.0×10-3 | MTX8@G0-PEG | 8.8×10-4 |
| SN388@G0 | 9.6×10-4 | SN388@G0-PEG | 7.5×10-4 |
| CE610@G1 | 7.8×10-4 | CE612@G1-PEG | 7.0×10-4 |
| DOX10@G1 | 8.7×10-4 | DOX12@G1-PEG | 7.0×10-4 |
| MTX10@G1 | 1.2×10-3 | MTX12@G1-PEG | 7.9×10-4 |
| SN3810@G1 | 1.2×10-3 | SN3812@G1-PEG | 5.7×10-4 |
| CE616@G2 | 8.8×10-4 | CE616@G2-PEG | 5.0×10-4 |
| DOX16@G2 | 7.1×10-4 | DOX16@G2-PEG | 5.1×10-4 |
| MTX16@G2 | 6.6×10-4 | MTX16@G2-PEG | 5.5×10-4 |
| SN3816@G2 | 7.7×10-4 | SN3816@G2-PEG | 3.2×10-4 |
Table 4 Diffusion coefficients(D) of the DN@Gn and DN@Gn-PEG complexes in water
| DN@Gn | D/(nm2·ps-1) | DN@Gn-PEG | D/(nm2·ps-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE68@G0 | 1.1×10-3 | CE68@G0-PEG | 6.4×10-4 |
| DOX8@G0 | 1.0×10-3 | DOX8@G0-PEG | 8.1×10-4 |
| MTX8@G0 | 1.0×10-3 | MTX8@G0-PEG | 8.8×10-4 |
| SN388@G0 | 9.6×10-4 | SN388@G0-PEG | 7.5×10-4 |
| CE610@G1 | 7.8×10-4 | CE612@G1-PEG | 7.0×10-4 |
| DOX10@G1 | 8.7×10-4 | DOX12@G1-PEG | 7.0×10-4 |
| MTX10@G1 | 1.2×10-3 | MTX12@G1-PEG | 7.9×10-4 |
| SN3810@G1 | 1.2×10-3 | SN3812@G1-PEG | 5.7×10-4 |
| CE616@G2 | 8.8×10-4 | CE616@G2-PEG | 5.0×10-4 |
| DOX16@G2 | 7.1×10-4 | DOX16@G2-PEG | 5.1×10-4 |
| MTX16@G2 | 6.6×10-4 | MTX16@G2-PEG | 5.5×10-4 |
| SN3816@G2 | 7.7×10-4 | SN3816@G2-PEG | 3.2×10-4 |
| [1] | Kavyani S., Amjad-Iranagh S., Modarress H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118, 3257—3266 |
| [2] | Tomalia D. A., Baker H., Dewald J., Hall M. E., Kallos G., Martin S., Roeck J., Ryder J., Smith P., Polym. J., 1985, 17, 117—132 |
| [3] | Mignani S., Kazzouli S. E., Bousmina M., Majoral J. P., Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev., 2013, 65, 1316—1330 |
| [4] | Wu L. P., Zhang Z. P., Guo Y., Wang Y., Lu W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(6), 1436—1444 |
| (吴丽平, 张政朴, 郭义, 王勇, 陆伟.高等学校化学学报, 2011,32(6), 1436—1444) | |
| [5] | Zhang Y., Thomas T. P., Lee K. H., Li M., Zong H., Desai A. M., Kotlyar A., Huang B. H., Banaszak Holl M. M., Baker J. R. Jr., Bioorgan. Med. Chem., 2011, 19, 2557—2564 |
| [6] | Cai J., Ai S. Y., Yin H. S., Shi W. J., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2009, 67(19), 2227—2232 |
| (蔡军, 艾仕云, 殷焕顺, 时伟杰.化学学报, 2009,67(19), 2227—2232) | |
| [7] | Esfand R., Tomalia D. A., Drug. Discov. Today, 2001, 6(8), 427—436 |
| [8] | Svenson S., Tomalia D. A., Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev., 2012, 64, 102—115 |
| [9] | Tomalia D. A., Naylor A. M., Goddard III W. A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 1990, 29, 138—175 |
| [10] | Han Q. R., Wang B. X., He X. M., Ding M. T., Xia H. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(3), 629—631 |
| (韩巧荣, 王炳祥, 何旭敏, 丁马太, 夏海平.高等学校化学学报, 2009,30(3), 629—631) | |
| [11] | Lu W. T., Li G. P., Luo Y. J., Jin Y. J., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2008, 66(20), 2258—2262 |
| (卢文婷, 李国平, 罗运军, 靳玉娟.化学学报, 2008,66(20), 2258—2262) | |
| [12] | Lee C. C., MacKay J. A., Frechet J. M. J., Szoka F. C., Nat. Biotechnol., 2005, 23(12), 1517—1526 |
| [13] | Wiener E. C., Brechbiel M. W., Brothers H., Magin R. L., Gansow O. A., Tomalia D. A., Lauterbur P. C., Magn. Reson. Med., 1994, 31, 1—8 |
| [14] | Radu Daniela R., Lai C. Y., Jeftinija K., Rowe E. W., Jeftinija S., Lin V. S. Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(41), 13216—13217 |
| [15] | Domanski D. M., Klajnert B., Bryszewska M., Bioelectrochemistry, 2004, 63, 189—191 |
| [16] | Wang W., Xiong W., Zhu Y., Xu H., Yang X., J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2010, 93B, 59—64 |
| [17] | He H., Li Y., Jia X. R., Du J., Ying X., Lu W. L., Lou J. N., Wei Y., Biomaterials.2011, 32, 478—487 |
| [18] | Sideratou Z., Kontoyianni C., Drossopoulou G. I., Paleos C. M., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.2010, 20, 6513—6517 |
| [19] | Singh P., Gupta U., Asthana A., Jain N. K., Bioconjugate. Chem., 2008, 19, 2239—2252 |
| [20] | Yu H. Y., Tang Z. H., Song W. T., Deng M. X., Chen X. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5), 903—916 |
| (于海洋, 汤朝晖, 宋万通, 邓明虓, 陈学思.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(5), 903—916) | |
| [21] | Goldberg D. S., Vijayalakshmi N., Swaan P. W., Ghandehari H., J. Control. Release., 2011, 150, 318—325 |
| [22] | Allen T. M., Cullis P. R., Science, 2004, 303(19), 1818—1822 |
| [23] | Tian W. D., Ma Y. Q., Soft. Matter., 2012, 8, 2627—2632 |
| [24] | Ye L., Jiang X. Z., Yang H., Su J. T., Yun L. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(2), 353—355 |
| (叶玲, 江晓舟, 杨华, 苏健婷, 恽榴红.高等学校化学学报, 2005,26(2), 353—355) | |
| [25] | Liu Y., Bryantsev V. S., Diallo M. S., Goddard III W. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 2798—2799 |
| [26] | Tomalia D. A., Reyna L. A., Svenson S., Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2007, 35, 61—67 |
| [27] | Gurdag S., Khandare J., Stapels S., Matherly L. H., Kannan R. M., Bioconjug. Chem., 2006, 17, 275—283 |
| [28] | Thomas T. P., Majoros I. J., Kotlyar A., Kukowska-Latallo J. F., Bielinska A., Myc A., Baker J. R. Jr., J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48, 3729—3735 |
| [29] | Kwon II. K., Lee S. C., Han B., Park K., J. Control. Release., 2012, 164, 108—114 |
| [30] | Fu Y., Jia G. F., Pang X. Q., Wang R. N., Wang X., Li C. J., Smemo S., Dai Q., Bailey K. A., Nobrega M. A., Han K. L., Cui Q., He C., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1798—1805 |
| [31] | Pang X. Q., Yang M. J., Han K. L., Proteins, 2013, 81, 1399—1410 |
| [32] | Karatasos K., Krystallis M. J., Chem. Phys., 2009, 130, 1—11 |
| [33] | Zhong T. P., Ai P. F., Zhou J., Fluid. Phase. Equilibr., 2011, 302, 43—47 |
| [1] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [3] | 李聪聪, 刘明皓, 韩佳睿, 朱镜璇, 韩葳葳, 李婉南. 基于分子动力学模拟的VmoLac非特异性底物催化活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [4] | 雷晓彤, 金怡卿, 孟烜宇. 基于分子模拟方法预测PIP2在双孔钾通道TREK-1上结合位点的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [5] | 闫婷婷, 张娜, 李强, 李振华, 李春辉, 李雪, 于茹, 王瑞, 王吉华, 曹赞霞. 添加共试剂改善聚酰胺复合反渗透膜的性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2008. |
| [6] | 曾永辉, 言天英. 质子水合结构的振动态密度分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [7] | 刘爱清, 徐文生, 徐晓雷, 陈继忠, 安立佳. 高分子/棒状纳米粒子复合物的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [8] | 齐人睿, 李明昊, 常浩, 付学奇, 高波, 韩葳葳, 韩璐, 李婉南. 基于拉伸分子动力学模拟的黄嘌呤氧化酶抑制剂解离途径的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [9] | 薛旭玲,陈俊,张自由,王萌萌,吕梦迪,郝元元,胡炯圣,葛超,苏志,钱勇,刘红科. 基于萘普生-芳基金属配合物的抗癌及抗炎性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 243. |
| [10] | 瞿思颖, 徐沁. 凝血因子Xa的S4口袋部分关键残基对利伐沙班结合的不同作用机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| [11] | 马玉聪, 樊保民, 王满曼, 杨彪, 郝华, 孙辉, 张慧娟. 曲唑酮的两步法制备及对碳钢的缓蚀机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| [12] | 孙浩帆, 张凌怡, PATRICKNorman, 张维冰. 二芳基乙烯衍生物与DNA结合的分子动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(6): 1229. |
| [13] | 张璋, 王栋, 王晓雷, 徐岩. 华根霉脂肪酶有机相酯合成活性的重塑[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(4): 747. |
| [14] | 马兰, 容婧婧, 朱有亮, 黄以能, 孙昭艳. 软胶体粒子形成束晶的动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 195. |
| [15] | 朱镜璇, 于正飞, 刘野, 詹冬玲, 韩佳睿, 田晓翩, 韩葳葳. 基于分子动力学模拟提高嗜热磷酸三酯酶样内酯酶非特异性底物活力的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 138. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||