

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 2205.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190187
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2019-03-29
Online:2019-10-08
Published:2019-06-01
Contact:
DONG Yongchun
E-mail:dye@tjpu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GAN Lu,DONG Yongchun. Photocatalytic Performance of Fe-complexes Prepared Using Cotton Fiber Modified with Different Dicarboxylic Acids †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2205.
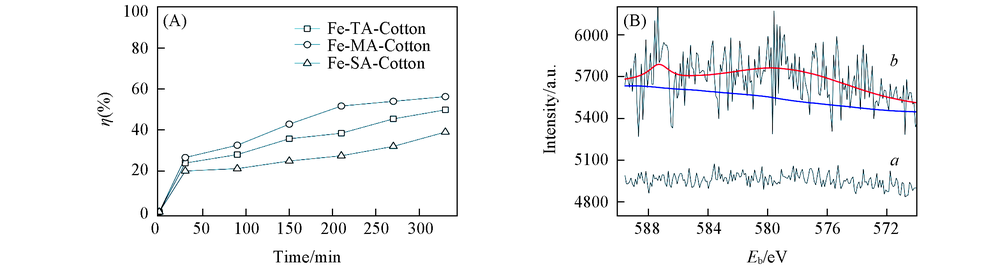
Fig.10 Cr species removal performance of three Fe-DCA-Cotton samples(A) and XPS spectra of Cr2p on Fe-MA-Cotton before(a) and after(b) removal test(B)
| [1] | Jiang Z. Y., Liu Y. Y., Jing T., Huang B. B., Wang Z. Y., Zhang X. Y., Qin X. Y., Dai Y. , Appl. Catal. B:Environ., 2017,200(1), 230— 236 |
| [2] | Jiang Z. Y., Zhang X. H., Yuan Z. M., Chen J. C., Huang B. B., Dionysiou D. D., Yang G. H. , Chem. Eng. J., 2018,348, 592— 598 |
| [3] | Wang P., Dong Y. C., Li B., Li Z. Q., Bian L. R. , Ind. Crops Prod., 2018,123, 197— 207 |
| [4] | Jiang Z. Y., Liang X. Z., Zheng H. L., Liu Y. Y., Wang Z. Y., Wang P., Zhang X. Y., Q X. Y., Dai Y., Whangbo M., Huang B. B. , Appl. Catal. B:Environ., 2017,219, 209— 215 |
| [5] | Yang G. H., Miao W. K., Yuan Z. M., Jiang Z. Y., Huang B. B., Wang P., Chen J. C. , Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2018,237(12), 302— 308 |
| [6] | Yip C K., Lam L. Y., Hu X. J., Chem. Eng. Sci., 2007,62(18), 5150— 5153 |
| [7] | Bozzi A., Yuranova T., Mielczarski E., Mielczarski J., Buffat P. A., Lais P., Kiwi J., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2003,42(3), 289— 303 |
| [8] | Ji H. W., Song W. J., Chen C. C., Yuan H., Ma W. H., Zhao J. C., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007,41(14), 5103— 5107 |
| [9] | Liu X. H., Tang R., He Q., Liao X. P., Shi B., J. Hazard. Mater., 2010,174(1), 687— 693 |
| [10] | Dong Y. C., Bian L. R., Wang P. , Chem. Eng. J., 2019,358, 1489— 1498 |
| [11] | Song X. X., Wang C. C., Xu X. Y., Jing H. P., Wang P., Gao S. J., Transition Met. Chem., 2017,42(2), 181— 191 |
| [12] | Wang Z. N., Wang X., Wei S. Y., Wang J. X., Bai F. Y., Xing Y. H., Sun L. X., New J. Chem., 2015,39(5), 4168— 4177 |
| [13] | Ruskov T., Turmanova S., Kostov G., Eur. Polym. J., 1997,33(8), 1285— 1288 |
| [14] | Cutsanu V., Luca C., Neagu V., Shofransky V., Turta C., React. Funct. Polym., 1999,40(2), 123— 128 |
| [15] | El-Sawy N M., Ali Z. I., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2007,103(6), 4065— 4071 |
| [16] | El-Sawy N. M., Sagheer F. A. , Eur. Polym. J., 2001,37(1), 161— 166 |
| [17] | Du M., Liu C. S., Li C. P., Fang S. M., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2013,257(7/8), 1282— 1305 |
| [18] | Wang X. L., Luan J., Sui F. F., Lin H. Y., Liu G. C., Xu C., Cryst. Growth Des., 2013,13(8), 3561— 3576 |
| [19] | Liu G. Z., Dong Y. C., Wang P., Bian L. R.. , Carbohydr. Polym., 2018,181, 103— 110 |
| [20] | Wang C. C., Zhang Y. Q., Zhu T., Zhang X. Y., Wang P., Gao S. J., Polyhedron, 2015,90, 58— 68 |
| [21] | Xie F. T. , Studies on the Syntheses, Structures and Performances of Transition Metal-Hydroxyl Polycarboxylate Coordination Polymers , Jilin University,Changchun, 2005 |
| ( 谢凤桐 . 过渡金属-羟基多羧酸配位聚合物的合成、 结构与性能研究 , 长春: 吉林大学, 2005) | |
| [22] | Guo Y. Q. , Syntheses, Structural Characterization, Properties Studies of Complex Constructed from Transition Metals and Hydroxyl Carboxy-lic Acial, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 2005 |
| ( 郭亚勤 . 过渡金属与羟基羧酸构筑的化合物的合成、 表征及性能研究, 长春: 东北师范大学, 2005) | |
| [23] | Yang C Q., Wang X., J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem., 1997,35, 557— 564 |
| [24] | Yang C. Q., Wang X. L., Kang I. , Text. Res. J., 1997,67(5), 334— 342 |
| [25] | Li B., Dong Y C., Li L., Cellulose, 2015,22(2), 1295— 1309 |
| [26] | Clesceri L. S., Greenberg A. E., Eaton A. D. , Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Ed., American Public Health Association, Washington D. C., 1998, 366— 368 |
| [27] | Wang J. T., Zhang B. S., Wang Y. M., Hu Q. M., Organic Chemistry, 2nd Ed., Nankai University Press, Tianjin, 2004, 476— 477 |
| ( 王积涛, 张宝申, 王永梅, 胡青眉. 有机化学, 天津:南开大学出版社, 2004, 476— 477) | |
| [28] | Li B., Dong Y. C., Zou C., Xu Y. M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014,53(11), 4199— 4206 |
| [29] | Zhang H. , Coordination Chemistry:Principle and Application, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2008, 164— 165 |
| ( 章慧 . 配位化学原理与应用, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008, 164— 165) | |
| [30] | Leng Y. Q., Guo W. L., Shi X., Li Y. Y., Wang A. Q., Hao F. F., Xing L. T. , Chem. Eng. J., 2014,240, 338— 343 |
| [31] | Li Y., Yang Z. Q., Zhang H. G., Tong X. W., Feng J. N. , Colloids Surf. A, 2017,529, 856— 863 |
| [32] | Zhang C. C., Dong Y. C., Li B., Li F. J. , Clean. Prod., 2018,177, 245— 253 |
| [33] | Pan C. Y. , Functional Polymers, Science Press, Beijing, 2006, 55— 56 |
| ( 潘才元 . 功能高分子, 北京: 科学出版社, 2006, 55— 56) | |
| [34] | Yip A C., Lam F. L., Hu, X. J., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2005,44(21), 7983— 7990 |
| [35] | Li B., Dong Y C., Ding Z. Z., Color. Technol., 2013,129, 403— 411 |
| [1] | SONG Yingying, HUANG Lin, LI Qingsen, CHEN Limiao. Preparation of CuO/BiVO4 Photocatalyst and Research on Carbon Dioxide Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220126. |
| [2] | WANG Jin, SHI Wenjie, JIN Linyu, MA Pengtao, WANG Jingping, NIU Jingyang. Synthesis, Structure, and Allochroic Property of Two Hetro-arsenomolybdates Hybrid Polyoxometalates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210600. |
| [3] | CHANG Shuqing, XIN Xu, HUANG Yaqi, ZHANG Xincong, FU Yanghe, ZHU Weidong, ZHANG Fumin, LI Xiaona. Pyroelectrically-induced Catalytic Performance of Zr-based MOF Under Cold-hot Alternation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2558. |
| [4] | YANG Xiaomei, WU Qiang, GUO Ru, YE Kaibo, XUE Ping, WANG Xiaozhong, LAI Xiaoyong. Ordered Mesoporous NiS-loaded CdS with Ultrathin Frameworks for Efficient Photocatalytic H2 Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1581. |
| [5] | GAO Xia,PAN Huibin,QIAO Chengfang,CHEN Fengying,ZHOU Yuan,YANG Wenhua. Construction of HRP Immobilized Enzyme Reactor Based on Hierarchically Porous Metal-organic Framework and Its Dye Degradation Application† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1591. |
| [6] | MA Xiangying, LIAO Yanjun, QIN Fanghong, YIN Yuanhao, HUANG Zaiyin, CHEN Qifeng. Study on the Photocatalytic Performance of Carbon Doped g-C3N4 Based on in situ Photomicrocalorimeter-fluorescence Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2526. |
| [7] | ZHAO Mengxin, MENG Zhe, LI Heping, MA Zongqin, ZHAN Haijuan, LIU Wanyi. Photodegradation of Antibiotic in Environmental Water by Graphene Oxide Modulation Bismuth Molybdate Under Visible Light Irradiation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2479. |
| [8] | HE Pengchen,ZHOU Jian,ZHOU Awu,DOU Yibo,LI Jianrong. MOFs-Based Materials for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 855. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jing,DONG Yuming,LIU Xiang,LI Hexing. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Z-Scheme Photocatalyst Sb2WO6/g-C3N4 † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 123. |
| [10] | WEI Liangchen, HU Weikang, ZHOU Shixiong, SHU Jun, ZHOU Huidong, HU Xucheng, JIANG Yi, TONG Bihai, ZHANG Qianfeng. Iridium Complex Containing Phosphite and Bipyridine Carboxylate Ligands and Their Aggregation Induced Enhanced Emission and Electroluminescent Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1371. |
| [11] | CONG Rimin, YU Huaiqing, LUO Yunjun, LI Jiao, WANG Weiwei, LI Qiuhong, SUN Wuzhu, SI Weimeng, ZHANG Hua. Synthesis and Properties of Bi25FeO40/α-Fe2O3 Composite Nanoparticle Photocatalysts† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 629. |
| [12] | LI Fu, DONG Yongchun, CHENG Bowen, KANG Weimin. Application of Hybrid Modified PAN Nanofibrous Membrane Fe Complexes with Adsorption-photocatalysis Bifunctions for Removal of Organic Dye from Water† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 115. |
| [13] | WANG Qiushuang, ZHENG Xiaoli, QU Xianglong, LI Rui, LI Xia. Synthesis, Structure and Luminescence Property of Transition Metal Complexes with 1,3-Di(4-pyridyl)-propane and 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic Acid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1125. |
| [14] | GAO Xiaoming, DAI Yuan, FEI Jiao, ZHANG Yu, FU Feng. Synthesis of n-p Heterojunction BiOBr/CdS Composites with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1249. |
| [15] | WANG Luyuan, LIU Shuxue, LI Huimin, HUANG Yaodong. Preparation and Properties of the Two-component Hydrogels Based on Pyrazine Dicarboxylic Acid and Melamine† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 806. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
