

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 806.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160911
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Luyuan, LIU Shuxue, LI Huimin, HUANG Yaodong*( )
)
Received:2016-12-19
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-04-20
Contact:
HUANG Yaodong
E-mail:huangyaodong@tju.edu.cn
Supported by:TrendMD:
WANG Luyuan, LIU Shuxue, LI Huimin, HUANG Yaodong. Preparation and Properties of the Two-component Hydrogels Based on Pyrazine Dicarboxylic Acid and Melamine†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 806.
| Organic-water mixture | Gelation property | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0b | 10%b | 20%b | 40%b | 50%b | 60%b | 80%b | 90%b | 100%b | |
| Ethanol-water | P | P | PG | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| Methanol-water | P | P | PG | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| Acetone-water | P | P | PG | PG | PG | G | G | G | G |
| Acetonitrile-water | P | P | PG | PG | PG | G | G | G | G |
| THF-water | P | P | PG | PG | G | G | G | G | G |
| DMF-water | P | P | PG | PG | G | G | G | G | G |
| DMSO-water | P | P | PG | PG | G | G | G | G | G |
Table 1 Gelation properties of PM12 in different solventsa
| Organic-water mixture | Gelation property | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0b | 10%b | 20%b | 40%b | 50%b | 60%b | 80%b | 90%b | 100%b | |
| Ethanol-water | P | P | PG | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| Methanol-water | P | P | PG | G | G | G | G | G | G |
| Acetone-water | P | P | PG | PG | PG | G | G | G | G |
| Acetonitrile-water | P | P | PG | PG | PG | G | G | G | G |
| THF-water | P | P | PG | PG | G | G | G | G | G |
| DMF-water | P | P | PG | PG | G | G | G | G | G |
| DMSO-water | P | P | PG | PG | G | G | G | G | G |
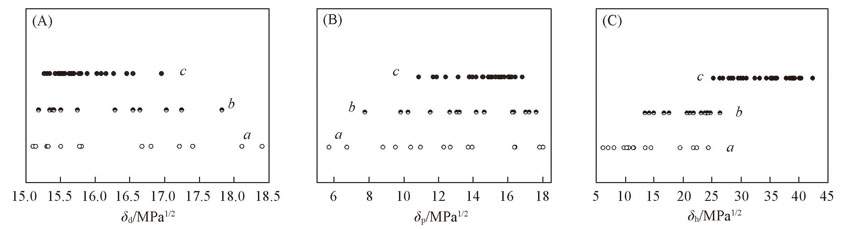
Fig.10 Plots of the Hansen solubility parameters correlated with the gelling behavior of PM12 in the mixed solvents(A) δd; (B) δp; (C) δh. a. P; b. PG; c. G.
| [1] | Ahmed E. M., J. Adv. Res., 2015, 6(2), 105—121 |
| [2] | Loos M. D., Feringa B. L., Esch J. H. V., Cheminform, 2005, 36(47), 3615—3631 |
| [3] | Yu F., Cao X., Du J., Wang G., Chen X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(43), 24023—24031 |
| [4] | Mckay C. A., Pomrenke R. D., Mclane J. S., Schaub N. J., Desimone E. K., Ligon L. A., Gilbert R. J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(3), 1424—1438 |
| [5] | Ziane S., Schlaubitz S., Miraux S., Patwa A., Lalande C., Bilem I., Lepreux S., Rousseau B., Meins J. F. L., Latxague L., European Cells & Materials, 2012, 23(2), 147—160 |
| [6] | Skilling K. J., Citossi F., Bradshaw T. D., Ashford M., Kellam B., Marlow M., Soft Matter, 2014, 10(10), 237—256 |
| [7] | Almeida H., Amaral M. H., Lobao P., Sousa Lobo J. M., J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 2012, 15(4), 592—605 |
| [8] | Bhattacharya C., Kumar N., Sagiri S. S., Pal K., Ray S. S., J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci., 2012, 4(2), 155—163 |
| [9] | Liu Y., Xu Y., Zhao Y., Jia Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(2), 302—310 |
| [10] | Vemula P. K., John G., Chem. Commun., 2006, 42(21), 2218—2220 |
| [11] | Qian C., Cao K. Y., Liu X. L., Zhang X. F., Xu D. F., Xue P. C., Lu R., Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(33), 4264—4271 |
| [12] | Zheng B. Y., Ji F. Y., Hou Z. S., Sun S. M., Sun Y. L., Yang R. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(4), 715—722 |
| (郑博元, 纪锋颖, 侯智善, 孙思明, 孙允陆, 杨蕊竹.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(4), 715—722) | |
| [13] | Roy B., Saha A., Esterrani A., Nandi A. K., Soft Matter, 2010, 6(14), 3337—3345 |
| [14] | Zhang Y., Xue P., Yao B., Sun J., New J. Chem., 2014, 38(12), 5747—5753 |
| [15] | Ohsedo Y., Oono M., Saruhashi K., Watanabe H., RSC Adv., 2014, 4(82), 43560—43563 |
| [16] | Yan L., Li G., Ye Z., Tian F., Zhang S., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(94), 14839—14842 |
| [17] | Schmuck C., Samanta K., Ehlers M., Chemistry, 2016, 22(43), 15242—15247 |
| [18] | Ye Y., Wang Y., Feng C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(5), 872—876 |
| [19] | Llanespallas A., Palma C. A., Piot L., Belbakra A., Listorti A., Prato M., Samori P., Armaroli N., Bonifazi D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(2), 509—520 |
| [20] | Mahesh S., Thirumalai R., Yagai S., Kitamura A., Ajayaghosh A., Chem. Commun., 2009, 40(40), 5984—5986 |
| [21] | Yagai S., Aonuma H., Kikkawa Y., Kubota S., Karatsu T., Kitamura A., Mashesh S., Ajayaghosh A., Chemistry, 2010, 16(29), 8652—8661 |
| [22] | Roy B., Bairi P., Nandi A. K., RSC Adv., 2013, 4(4), 1708—1734 |
| [23] | Manna S., Saha A., Nandi A. K., Chem. Commun., 2006, 41(41), 4285—4287 |
| [24] | Saha A., Roy B., Garai A., Nandi A. K., Langmuir, 2009, 25(15), 8457—8461 |
| [25] | Yadav P., Ballabh A., Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2012, 414(46), 333—338 |
| [26] | Liu X.L., Synthesis, Characterizations and Biological Activities of Coordination Compounds with Pyrazine Derivatives as Ligands, Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu, 2014 |
| (刘晓蕾. 吡嗪衍生物及其配合物的合成与性质及生物活性研究, 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014) | |
| [27] | Huang Y. D., Tu W., Yuan Y. Q., Fan D. L., Tetrahedron, 2014, 70(6), 1274—1282 |
| [28] | Huang Y. D., Yuan Y., Tu W., Zhang Y., Zhang M. J., Qu H. M., Tetrahedron, 2015, 71(21), 3221—3230 |
| [29] | Fan D. L., Zhai Y., Zhang Y., Tu W., Huang Y. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11), 2447—2454 |
| (樊冬丽, 翟岩, 张妍, 涂伟, 黄耀东.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(11), 2447—2454) | |
| [30] | Shen L. Y., Chen X. Z., Yu H. T., Liang G., Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2009, 29(3), 321—333 |
| (沈利英, 陈肖卓, 于海涛, 梁刚.有机化学, 2009,29(3), 321—333) | |
| [31] | Zhu P., Yan X., Su Y., Yang Y., Li J., Chemistry, 2010, 16(10), 3176—3183 |
| [32] | Huang Y. D., Li H. M., Li Z. Y., Zhang Y., Cao W. W., Wang L. Y., Liu S. X., Langmuir, 2017, 33(1), 311—321 |
| [33] | Zhang M. J., Cao W. W., Li Z. Y., Huang Y. D., Fine Chemicals, 2016, 33(6), 601—607 |
| (张梅杰, 曹雯雯, 李紫烟, 黄耀东.精细化工, 2016,33(6), 601—607) | |
| [34] | Barton A. F. M., Chem. Rev., 1975, 75(9), 731—753 |
| [1] | CHU Yao, WANG Shuo, ZHANG Zinuo, WANG Yibo, CAI Yibing. Preparation and Properties of Cu Particles Loaded Foam-based Phase Change Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210619. |
| [2] | CHEN Shaoyun, ZHANG Xingying, LIU Ben, TIAN Du, LI Qi, CHEN Fang, HU Chenglong, CHEN Jian. Controllable Growth of Silver Nanoparticles on TiO2 Tetragonal Prism Nanarrays and Its SERS Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2381. |
| [3] | WANG Xiaoru,ZHANG Na,XING Jun. Preparation and Application of Melamine Imprinted Material Using Itaconic Acid as Multidentate Functional Monomer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1521. |
| [4] | LIU Shuaizhuo,ZHANG Qian,LIU Ning,XIAO Wenyan,FAN Leiyi,ZHOU Ying. One-step Synergistic Hydrophobic Modification of Melamine Sponge and Its Application † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 521. |
| [5] | QIU Lijuan,ZHANG Ying,LIU Shuaizhuo,ZHANG Qian,ZHOU Ying. Preparation and Application of Superhydrophobic and Robust Graphene Composites Oil/Water Separation Material† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2758. |
| [6] | WANG Huijie, YU Haiyang, ZHANG Dawei, TANG Zhaohui, CAO Qi. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(E,K) and Poly(E,R)† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 165. |
| [7] | ZHUANG Qianfen, CAO Wei, WU Qi, NI Yongnian. Fluorescence Detection of Au(Ⅲ) Based on Carbon Nitride Nanoparticles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1611. |
| [8] | LIU Yajie, ZHANG Peng, DU Jianwei, WANG Youxiang. pH-Responsive PEGylated Gene Delivery System† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 1003. |
| [9] | WANG Xiao, YANG Xinguo, SHEN Qili. Synthesis and Gel Properties of a Novel Amide Gelator with Melamine Moieties and Rationalizing Gelation Behavior by Hansen Solubility Parameters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2068. |
| [10] | LIU Ruiqing, LIANG Shuang, JIANG Cun, XU Zushun, XU Haibo. Synthesis and Proporties of Temperature and pH-sensitive and Gadolinium Contained Polymeric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 155. |
| [11] | WANG Yan, LIU Junbo, TANG Shanshan, JIN Ruifa, CHANG Haibo. Preparation of Melamine Molecular Imprinted Polymer by Computer Aided Design† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 945. |
| [12] | JIANG Guangce, LIN Xiongchao, ZHANG Shengjuan, WANG Zhongqi, WANG Yonggang, CHEN Qiang, ZHU Yufei. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Direct Coal Liquefaction Residue Basing on Hansen Solubility Parameters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(3): 544. |
| [13] | YANG Yongan, XU Shuping, WANG Yuyang, QI Guohua, XU Weiqing. Facile Fabrication of SERS-based Microchannel Device for Hazardous Chemical Analysis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(2): 254. |
| [14] | WANG Zitao, XIAO Changfa, ZHAO Jian, HU Xiao, XU Naiku. Preparation of Reduced Graphene Oxide-based Melamine Sponge and Its Absorption Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11): 2410. |
| [15] | DING Li-Wei, YANG Xin-Guo, ZHONG Wen-Bin, LIU Cun, LIU Zhen-Hui, ZHANG Feng-Ju. Synthesis of a New Perylene Bisimide Dye Containing Melamine Moieties and Construction of Well-defined Nano-fiber [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5): 1277. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||