

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (12): 20250184.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250184
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XING Yuhang, WANG Li, ZHAO Jiruo, SHAO Huafeng( ), HE Aihua(
), HE Aihua( )
)
Received:2025-07-04
Online:2025-12-10
Published:2025-10-14
Contact:
SHAO Huafeng, HE Aihua
E-mail:hfshao@qust.edu.cn;ahhe@qust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XING Yuhang, WANG Li, ZHAO Jiruo, SHAO Huafeng, HE Aihua. Structure Regulation of Chlorinated Trans-1,4-butadiene-co-isoprene Rubber[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(12): 20250184.
| Initial reaction temperature/℃ | Time/s | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) | Molar fraction of double bond(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 60 | 12.1 | 29.8 |
| 24 | 60 | 9.0 | 52.3 |
| 100 | 60 | 7.7 | 54.6 |
| 24 | 70 | 11.8 | 51.4 |
Table 1 Content of double bond in CTBIR with different initial reaction temperature
| Initial reaction temperature/℃ | Time/s | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) | Molar fraction of double bond(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 60 | 12.1 | 29.8 |
| 24 | 60 | 9.0 | 52.3 |
| 100 | 60 | 7.7 | 54.6 |
| 24 | 70 | 11.8 | 51.4 |
| Chlorine passing mode | Reaction temperaturemax/℃ | Molar fraction of double bond(%) | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic | 28 | 18.8 | 35.4 |
| Continuous | 72 | 9.15 | 35.8 |
Table 2 Effect of different ways of passing chlorine gas on double bond content
| Chlorine passing mode | Reaction temperaturemax/℃ | Molar fraction of double bond(%) | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic | 28 | 18.8 | 35.4 |
| Continuous | 72 | 9.15 | 35.8 |
| m(TEMPO)/m(TBIR) | Molar fraction of double bond(%) | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) | Reaction temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 9.15 | 35.8 | 72 |
| 1.25∶1 | 31.5 | 36.4 | 78 |
Table 3 Effect of TEMPO on double bonds and chlorine content of TBIR
| m(TEMPO)/m(TBIR) | Molar fraction of double bond(%) | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) | Reaction temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 9.15 | 35.8 | 72 |
| 1.25∶1 | 31.5 | 36.4 | 78 |
| UV light | Reaction time/min | Molar fraction of double bond(%) | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) | Rection temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 1 | 54.7 | 5.51 | 28 |
| + | 1 | 52.3 | 6.08 | 30 |
| - | 5 | 9.2 | 24.70 | 45 |
| + | 5 | 31.5 | 32.20 | 41 |
Table 4 Influence of ultraviolet light on double bond in molecular chain of CTBIR
| UV light | Reaction time/min | Molar fraction of double bond(%) | Mass fraction of chlorine(%) | Rection temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 1 | 54.7 | 5.51 | 28 |
| + | 1 | 52.3 | 6.08 | 30 |
| - | 5 | 9.2 | 24.70 | 45 |
| + | 5 | 31.5 | 32.20 | 41 |
| Main structure | 1H NMR, δ | Time/min | Molar content of allyl chlorine(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 ℃ | 24 ℃ | 100 ℃ | |||
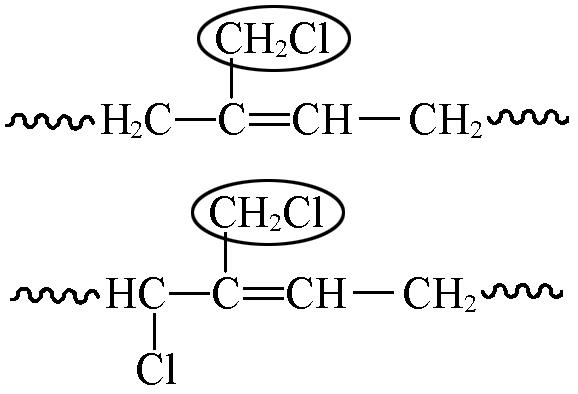 | 4.01—4.03 | 1 5 | 3.9 9.8 | 4.5 4.9 | 2.3 2.7 |
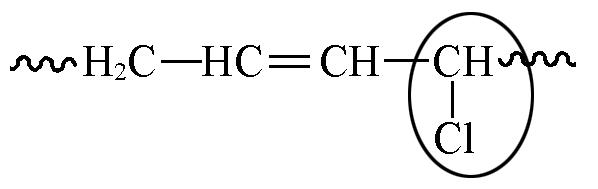 | 5.45—5.93 | 1 5 | 2.9 3.9 | 3.2 4.3 | 4.2 5.7 |
Table 5 Chemical shifts and contents of allyl chlorine in CTBIR at different initial temperatures
| Main structure | 1H NMR, δ | Time/min | Molar content of allyl chlorine(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 ℃ | 24 ℃ | 100 ℃ | |||
 | 4.01—4.03 | 1 5 | 3.9 9.8 | 4.5 4.9 | 2.3 2.7 |
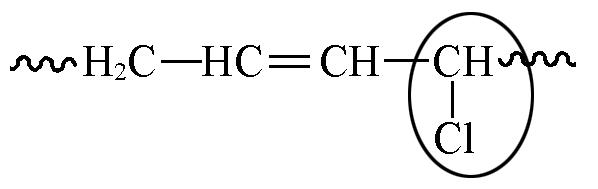 | 5.45—5.93 | 1 5 | 2.9 3.9 | 3.2 4.3 | 4.2 5.7 |
| Main structure | 1H NMR, δ | Molar content of allyl chlorine(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With TEMPO | Without TEMPO | ||
 | 4.01—4.03 | 14.8 | 15.4 |
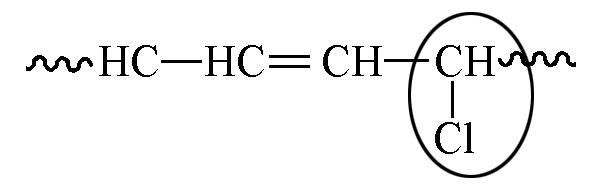 | 5.93 | 9.4 | 6.7 |
Table 6 Chemical shift and content of allyl chlorine in 1H NMR spectra with or without TEMPO
| Main structure | 1H NMR, δ | Molar content of allyl chlorine(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With TEMPO | Without TEMPO | ||
 | 4.01—4.03 | 14.8 | 15.4 |
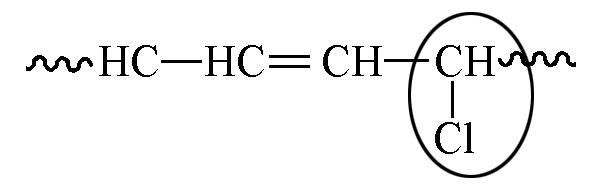 | 5.93 | 9.4 | 6.7 |
| Main structure | 1H NMR, δ | Molar content of allyl chlorine(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTBIR⁃1 | CTBIR⁃5 | ||
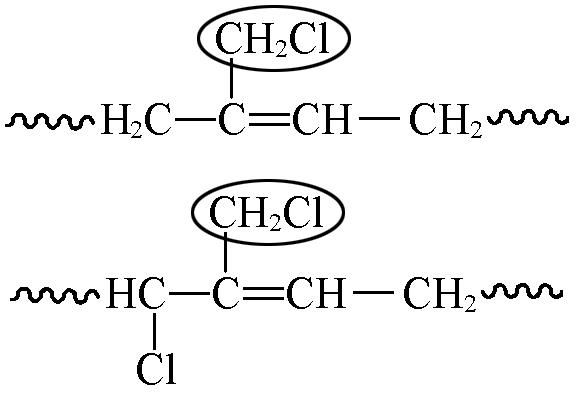 | 4.01—4.03 | 1.82 | 15.48 |
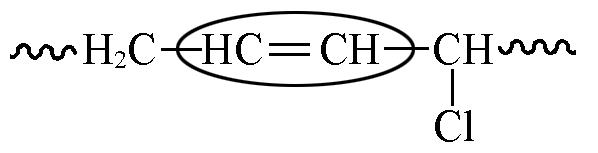 | 5.45 | 4.03 | 2.23 |
Table 7 Chemical shifts and contents of CTBIR in 1H NMR spectra
| Main structure | 1H NMR, δ | Molar content of allyl chlorine(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTBIR⁃1 | CTBIR⁃5 | ||
 | 4.01—4.03 | 1.82 | 15.48 |
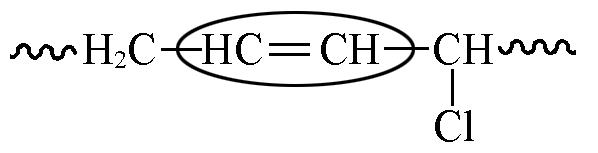 | 5.45 | 4.03 | 2.23 |
| [1] | Shao H. F., Ren S. T., Wang R. G., He A. H., Polymer, 2020, 186, 122015 |
| [2] | Li W. T., Nie H. R., Shao H. F., Ren H. C., He A. H., Polymer, 2018, 156, 148—161 |
| [3] | Liu X. Y., Li W. T., Niu Q. T., Wang R. G., He A. H., Polymer, 2018, 140, 255—268 |
| [4] | Qian Z. H., Wang S., Zong X., Cai L., He A. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(8), 20230023 |
| 钱浙濠, 王硕, 宗鑫, 蔡磊, 贺爱华. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8), 20230023 | |
| [5] | Wu Y. F., Li H. Y., Cai L., He A. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3), 565—571 |
| 武营飞,李洪昱,蔡磊,贺爱华. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(3), 565—571 | |
| [6] | Guo Q. R., Shao H. F., He A. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4), 789—794 |
| 国钦瑞, 邵华锋, 贺爱华. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4), 789—794 | |
| [7] | Wang H., Zhang X. P., Nie H. R., Wang R. G., He A. H., Compos. Part A⁃Appl. S., 2019, 116, 197—205 |
| [8] | Wang H., Song L. Y., Ma Y. S., Wang R. G., He A. H., Acta Polym. Sin., 2018, 3, 419—428 |
| [9] | Wang H., Zou C., He A. H., Acta Polym. Sin., 2015, 12, 1387—1395 |
| [10] | Luo S. F., Zhao Y. J., Wang S., Zhou R. C., Yang X., He A. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(8), 20250067 |
| 罗淑芳, 赵远进, 王硕, 周润川, 杨霞, 贺爱华. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(8), 20250067 | |
| [11] | Radabutra S., Thanawan S., Amornsakchai T., Eur. Polym. J., 2009, 45(7), 2017—2022 |
| [12] | Cao R. W., Zhao X. Y., Zhao X. Y., Wu X. H., Li X. L., Zhang L. Q., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58(36), 16645—16653 |
| [13] | Xue X. H., Liu Y. F., Han X. P., Li G., Wang Z. Y., J. Wuhan Univ. Technol., 2019, 34(1), 201—206 |
| [14] | Vitiello R., Tesser R., Turco R., Santacesaria E., Compagnone G., Di Serio M., Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact., 2017, 22(4), 348—360 |
| [15] | Nihmath A., Ramesan M.T., Polym. Adv. Technol., 2018, 29(8), 2165—2173 |
| [16] | Yang L., Wang J. C., Luo L. Z., Li S. F., Zhao J. R., Feng Y., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2018, 135(48), 46880 |
| [17] | Tuampoemsab S., Nimpaiboon A., Sakdapipanich J. T., Polym. Test., 2015, 43, 21—26 |
| [18] | Eskina M. V., Khachaturov A. S., Krentsel L. B., Litmanovich A. D., Eur. Polym. J., 1990, 26(2), 181—188 |
| [19] | Lenko D., Schlogl S., Kramer R., Kern W., Schaller R., Holzner A., Macromolecular Symposia, 2012, 311(1), 9—17 |
| [20] | Song X. P., Wang L., Shao H. F., Zhao J. R., He A. H., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2025, 65(3), 1530—1539 |
| [21] | Brame E. G., J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem., 1971, 9(7), 2051—2061 |
| [22] | Novak I., Harrison L. J., J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69(22), 7628—7634 |
| [1] | LUO Shufang, ZHAO Yuanjin, WANG Shuo, ZHOU Runchaun, YANG Xia, HE Aihua. Preparation of Amine-capped Functionalized Trans-1,4-poly(butadiene-co-isoprene) Rubber and Coordination Chain Transfer Mechanism [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(8): 20250067. |
| [2] | QIAN Zhehao, WANG Shuo, ZONG Xin, CAI Lei, HE Aihua. Regulation of TBIR on the Structure and Properties of Natural Rubber Based Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(8): 20230023. |
| [3] | SONG Xinyue, WEI Yue, SHEN Jie, SHI Dean, YANG Huawei, LUAN Shifang. Impact Resistance Mechanism of Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene Molded Sheet [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(4): 20220641. |
| [4] | LI Jiangtao, ZHAO Xinxin, GU Fang, WANG Haijun. Statistical Properties of Ring-based Polymers Formed in Polycondensation Systems [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(4): 20220561. |
| [5] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [6] | XU Xiaozhou, LIU Yi, HE Minhui, MO Song, LAN Bangwei, ZHAI Lei, FAN Lin. Effect of Copolymerization Structure and Molecular Weight on Melt Fluidity and Thermal Properties of Thermoplastic Polyimide Resins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 919. |
| [7] | DU Xinyao, WANG Wei, LIN Yu, WU Guozhang. Synthesis and Optical Properties of Polycarbonates Copolymerized with Bisphenol Fluorene Moiety [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3765. |
| [8] | GUO Qinrui, SHAO Huafeng, HE Aihua. Thermal-oxidative Aging Performance of TBIR Modified NR/BR Vulcanizates in Aircraft Tire Sidewall † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 789. |
| [9] | WANG Xia, LIU Yanji, JIA Yongfeng, JI Lei, HU Quanli, DUAN Limei, LIU Jinghai. Preparative Chemistry of N-containing Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Capacity Improvement in Lithium-sulfur Battery † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 829. |
| [10] | WU Yingfei,LI Hongyu,CAI Lei,HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of NBR/TBIR Composites with High Abrasion Resistance and Low Heat Built-up † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 565. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yuefa, SHAO Huafeng, WANG Riguo, HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of Sidewall Compounds for Aircraft Tyre Modified by TBIR [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1733. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xinping, ZHANG Jianping, CAI Lei, ZONG Xin, HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of Damping Materials with Super Fatigue Resistance Based on Chloroprene Rubber† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1571. |
| [13] | WANG Qianqian,YIN Luping,GU Fang,WANG Haijun. Monte Carlo Simulation on the Semi-batch Process in the Self-condensing Vinyl Polymerization System in the Presence of Core Initiators † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2241. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jianping, SONG Liyuan, WANG Hao, WANG Riguo, HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of Brominated Butyl Rubber/Nature Rubber(BIIR/NR) Blends Modified with TBIR† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1334. |
| [15] | REN Huicheng,WU Yingfei,LIU Dandan,NIE Huarong,HE Aihua. Crystallization, Nucleation and Kinetics of TPI in SSBR/TPI Blends† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 1091. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||