

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 565.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190459
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Yingfei,LI Hongyu,CAI Lei,HE Aihua
Received:2019-08-19
Online:2020-02-26
Published:2020-02-07
Contact:
Aihua HE
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Yingfei,LI Hongyu,CAI Lei,HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of NBR/TBIR Composites with High Abrasion Resistance and Low Heat Built-up †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 565.
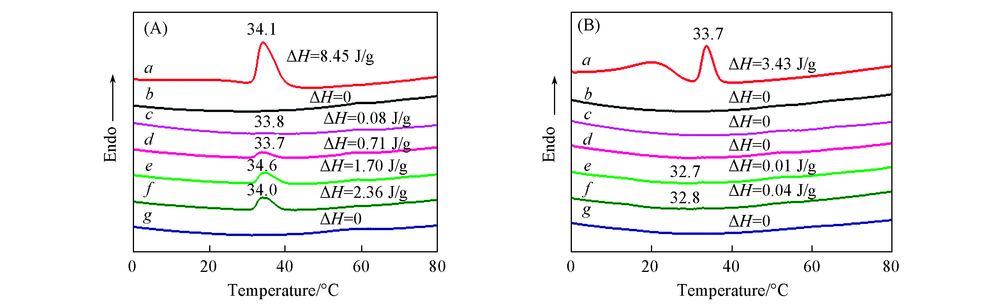
Fig.1 DSC curves of TBIR, NBR, NBR/TBIR and NBR/BR compounds(A) and vulcanizates(B) m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR): a. 0/100/0; b. 100/0/0; c. 95/5/0; d. 90/10/0; e. 85/15/0; f. 80/20/0; g. 80/0/20.
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML/(dN·m) | 1.50 | 1.72 | 1.97 | 2.29 | 2.47 | 2.54 |
| MH/(dN·m) | 15.81 | 16.17 | 17.70 | 18.52 | 19.96 | 20.88 |
| (MH-ML)/(dN·m) | 14.31 | 14.45 | 15.73 | 16.23 | 17.49 | 18.34 |
| t10/min | 2.40 | 2.09 | 1.72 | 1.39 | 1.21 | 1.18 |
| t90/min | 42.58 | 42.26 | 41.35 | 41.41 | 38.83 | 38.57 |
| 104 Crosslink density/(mol·cm-3) | 1.601 | 1.714 | 1.802 | 1.837 | 1.878 | 1.692 |
| Tensile strength/MPa | 27.94 | 23.23 | 24.58 | 22.34 | 20.74 | 20.76 |
| Modulus at 100%/MPa | 1.96 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 2.07 | 2.03 | 2.43 |
| Modulus at 300%/MPa | 6.86 | 6.08 | 6.86 | 6.71 | 6.24 | 8.71 |
| Elongation at break(%) | 735 | 747 | 769 | 651 | 651 | 576 |
| Tear strength/(kN·m-1) | 45.09 | 44.52 | 41.41 | 40.02 | 38.41 | 38.10 |
| Shore A hardness/(°) | 64.5 | 62.7 | 63.8 | 64.6 | 66.0 | 67.2 |
| Rebound(%) | 22.8 | 23.7 | 24.3 | 25.3 | 26.4 | 28.1 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML/(dN·m) | 1.50 | 1.72 | 1.97 | 2.29 | 2.47 | 2.54 |
| MH/(dN·m) | 15.81 | 16.17 | 17.70 | 18.52 | 19.96 | 20.88 |
| (MH-ML)/(dN·m) | 14.31 | 14.45 | 15.73 | 16.23 | 17.49 | 18.34 |
| t10/min | 2.40 | 2.09 | 1.72 | 1.39 | 1.21 | 1.18 |
| t90/min | 42.58 | 42.26 | 41.35 | 41.41 | 38.83 | 38.57 |
| 104 Crosslink density/(mol·cm-3) | 1.601 | 1.714 | 1.802 | 1.837 | 1.878 | 1.692 |
| Tensile strength/MPa | 27.94 | 23.23 | 24.58 | 22.34 | 20.74 | 20.76 |
| Modulus at 100%/MPa | 1.96 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 2.07 | 2.03 | 2.43 |
| Modulus at 300%/MPa | 6.86 | 6.08 | 6.86 | 6.71 | 6.24 | 8.71 |
| Elongation at break(%) | 735 | 747 | 769 | 651 | 651 | 576 |
| Tear strength/(kN·m-1) | 45.09 | 44.52 | 41.41 | 40.02 | 38.41 | 38.10 |
| Shore A hardness/(°) | 64.5 | 62.7 | 63.8 | 64.6 | 66.0 | 67.2 |
| Rebound(%) | 22.8 | 23.7 | 24.3 | 25.3 | 26.4 | 28.1 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength/MPa | 32.30 | 28.51 | 28.23 | 25.32 | 23.13 | 23.31 |
| Modulus at 100%/MPa | 3.24 | 3.25 | 2.88 | 3.17 | 3.06 | 3.98 |
| Modulus at 300%/MPa | 12.59 | 12.14 | 10.97 | 11.35 | 10.37 | 13.80 |
| Elongation at break(%) | 593 | 566 | 569 | 521 | 528 | 459 |
| Ageing coefficient(%) | 93 | 93 | 92 | 91 | 90 | 89 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength/MPa | 32.30 | 28.51 | 28.23 | 25.32 | 23.13 | 23.31 |
| Modulus at 100%/MPa | 3.24 | 3.25 | 2.88 | 3.17 | 3.06 | 3.98 |
| Modulus at 300%/MPa | 12.59 | 12.14 | 10.97 | 11.35 | 10.37 | 13.80 |
| Elongation at break(%) | 593 | 566 | 569 | 521 | 528 | 459 |
| Ageing coefficient(%) | 93 | 93 | 92 | 91 | 90 | 89 |
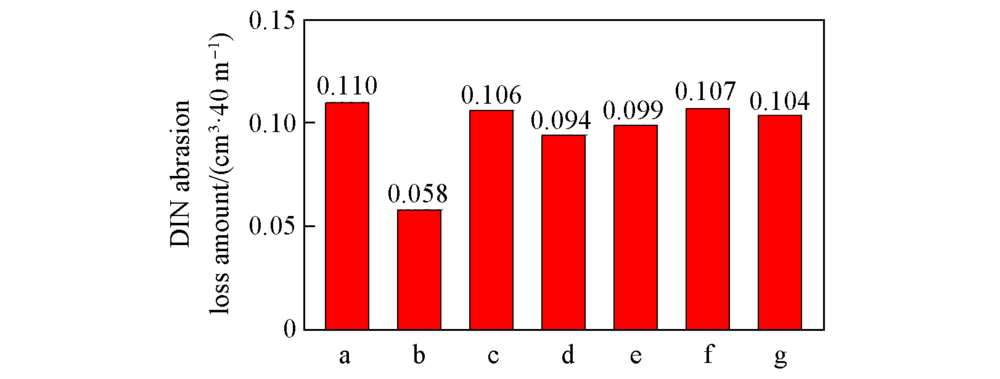
Fig.2 DIN abrasion loss amounts of NBR/TBIR and NBR/BR vulcanizates m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR): a. 100/0/0; b. 0/100/0; c. 95/5/0; d. 90/10/0; e. 85/15/0; f. 80/20/0; g. 80/0/20.
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat built-up/℃ | 62.2 | 59.7 | 59.2 | 58.3 | 58.2 | 59.0 |
| Dynamic compression set(%) | 9.8 | 8.9 | 7.6 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 7.9 |
| Compression set(%) | 10.7 | 10.4 | 10.9 | 12.0 | 12.3 | 10.6 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat built-up/℃ | 62.2 | 59.7 | 59.2 | 58.3 | 58.2 | 59.0 |
| Dynamic compression set(%) | 9.8 | 8.9 | 7.6 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 7.9 |
| Compression set(%) | 10.7 | 10.4 | 10.9 | 12.0 | 12.3 | 10.6 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δm100(%) | 1.7 | 3.1 | 4.6 | 7.5 | 12.1 | 16.4 |
| ΔV100(%) | 2.1 | 3.9 | 7.2 | 9.1 | 14.8 | 20.2 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δm100(%) | 1.7 | 3.1 | 4.6 | 7.5 | 12.1 | 16.4 |
| ΔV100(%) | 2.1 | 3.9 | 7.2 | 9.1 | 14.8 | 20.2 |
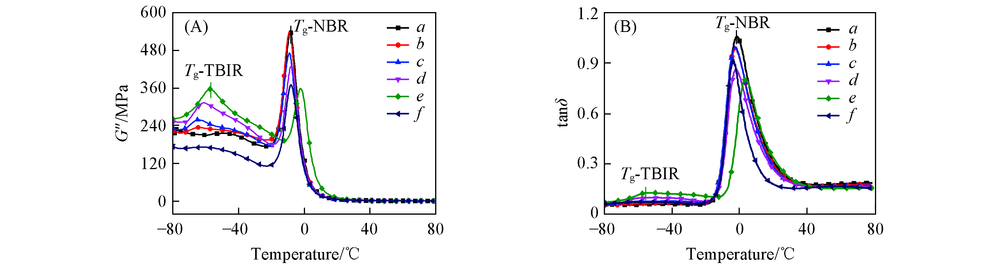
Fig.3 Loss modulus(G", A) and loss factor(tanδ, B) of NBR/TBIR and NBR/BR vulcanizates m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR): a. 100/0/0; b. 95/5/0; c. 90/10/0; d. 85/15/0; e. 80/20/0; f. 80/0/20.
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dispersiona(%) | 99.89 | 99.87 | 99.63 | 99.85 | 99.92 | 99.75 |
| Mean aggregate sizea/μm | 10.12 | 9.79 | 9.97 | 8.77 | 7.68 | 8.32 |
| Dispersionb(%) | 99.84 | 99.78 | 99.72 | 99.74 | 99.87 | 99.47 |
| Mean aggregate sizeb/μm | 10.77 | 9.27 | 10.00 | 8.84 | 8.12 | 8.77 |
| m(NBR)/m(TBIR)/m(BR) | 100/0/0 | 95/5/0 | 90/10/0 | 85/15/0 | 80/20/0 | 80/0/20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dispersiona(%) | 99.89 | 99.87 | 99.63 | 99.85 | 99.92 | 99.75 |
| Mean aggregate sizea/μm | 10.12 | 9.79 | 9.97 | 8.77 | 7.68 | 8.32 |
| Dispersionb(%) | 99.84 | 99.78 | 99.72 | 99.74 | 99.87 | 99.47 |
| Mean aggregate sizeb/μm | 10.77 | 9.27 | 10.00 | 8.84 | 8.12 | 8.77 |
| [1] | Wu C. R., Wang Z. B., Chen Y. X ., Nucl. Elec. & Detect. Tech., 2013, 33( 3), 392— 394 |
| ( 吴朝润, 王召巴, 陈友兴 . 核电子学与探测技术, 2013, 33( 3), 392— 394) | |
| [2] | Zhou Y. F., Zhu W. M., Wang L ., Spec. Purp. Rub. Prod., 2014, 35( 3), 42— 46 |
| ( 周一帆, 朱卫明, 王岚 . 特种橡胶制品, 2014, 35( 3), 42— 46) | |
| [3] | Wang H. M., Lv X. R., Wang S. J ., Lubr. Eng., 2015, 40( 9), 30— 34 |
| ( 王慧明, 吕晓仁, 王世杰 . 润滑与密封, 2015, 40( 9), 30— 34) | |
| [4] | Li M., Wan C. R ., Spe. Purp. Rub. Prod., 2009, 30( 1), 46— 48 |
| ( 李蒙, 万昌瑞 . 特种橡胶制品, 2009, 30( 1), 46— 48) | |
| [5] | Zhang J., Li Q. J ., China Syn. Rub. Ind., 1991, ( 4), 287— 290 |
| ( 张军, 李乔钧 . 合成橡胶工业, 1991, ( 4), 287— 290) | |
| [6] | Syed I. H., Stratmann P., Hempel G., Kluppel M., Saalwachter K ., Macromolecules, 2016, 49( 23), 9004— 9016 |
| [7] | Shaltout N. A., Abouzeid M. M., Mohamed M. A., Mohamed A., Miligy E ., J. Macromol. Sci: Part A -Chem., 2008, 45( 3), 225— 231 |
| [8] | He A. H., Yao W., Jia Z. F., Huang B. C., Jiao S. K ., Acta. Polym. Sin., 2002, ( 1), 19— 24 |
| ( 贺爱华, 姚微, 贾志峰, 黄宝琛, 焦书科 . 高分子学报, 2002, ( 1), 19— 24) | |
| [9] | He A. H., Huang B. C., Jiao S. K., Hu Y. L ., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2003, 89( 7), 1800— 1807 |
| [10] | Zhang X. P., Cui H. H., Song L. Y ., Compos. Sci. Technol., 2018, 158, 156— 163 |
| [11] | Niu Q. T., Zou C., Liu X. Y., Wang R. G., He A. H ., Polymer, 2017, 109, 197— 204 |
| [12] | Wang H., Cui H. H., Ma Y. S., Zhang J. P., Song L. Y., He A. H ., Chinese Polym. Bull., 2016, ( 10), 61— 67 |
| ( 王浩, 崔虹虹, 马韵升, 张剑平, 宋丽媛, 贺爱华 . 高分子通报, 2016, ( 10), 61— 67) | |
| [13] | Zhang J. P., Song L. Y., Wang H., Wang R. G., He A. H ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39( 6), 1334— 1341 |
| ( 张剑平, 宋丽媛, 王浩, 王日国, 贺爱华 . 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39( 6), 1334— 1341) | |
| [14] | Ren H. C., Wu Y. F., Liu D. D., Nie H. R., He A. H ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39( 5), 1091— 1097 |
| ( 任惠成, 武营飞, 刘丹丹, 聂华荣, 贺爱华 . 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39( 5), 1091— 1097) | |
| [15] | Wang H., Zhang J. P., Ma Y. S., Wang R. G., He A. H ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38( 11), 2095— 2101 |
| ( 王浩, 张剑平, 马韵升, 王日国, 贺爱华 . 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38( 11), 2095— 2101) | |
| [16] | Wang H., Zou C., He A. H ., Acta Polym. Sin., 2015, ( 12), 1387— 1395 |
| ( 王浩, 邹陈, 贺爱华 . 高分子学报, 2015, ( 12), 1387— 1395) | |
| [17] | Zhang X. P., Cai L., Wang C. W., He A. H ., Compos. Sci. Technol., 2019, 184, 1— 9 |
| [18] | GB/T 25268-2010, Rubber-Measurement of Vulcanization Characteristics with Rotorless Curemeters, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 1996 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 25268-2010, 橡胶用无转子硫化仪测定硫化特性, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1996) | |
| [19] | ASTM Committee D11, ASTM D7723-11, Standard Test Method for Rubber Property-Macro-dispersion of Fill, American Societ for Testing and Materials, New York, 2011 |
| [20] | GB/T 528-2009, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic Deter Mination of Tensile Stress-strain Properties, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2009 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 528-2009, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶拉伸应力应变性能的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009) | |
| [21] | GB/T 529-2008, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic Deter Mination of Tear Strength, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2008 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 529-2008, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶撕裂强度的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [22] | GB/T 531.1-2008, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-Determination of Indentation Hardness—Part 1: Duromerer Method(Shore hardness), Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2008 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 531.1-2008, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶压入硬度试验方法第1部分: 邵氏硬度计法(邵尔硬度), 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [23] | GB/T 1681-2009, Rubber, Determination of Rebound Resilience of Vulcanizates, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2009 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 1681-2009 硫化橡胶回弹性的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009) | |
| 24 | GB/T 9867-2008, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-determination of Abrasion Resistance Using a Rotating Cylindrical Drum Device, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2008 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 9867-2008, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶耐磨性能的测定(旋转辊筒式磨耗机法), 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [25] | GB/T 3512-2001, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-accelerated Ageing and Heat Resistance Tests-air-oven Method, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2001 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 3512-2001, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶热空气加速老化和耐热试验, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2001) | |
| [26] | GB/T 1690-2010, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-Determination of the Effect of Liquids, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2010 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 1690-2010, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶耐液体试验方法. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010) | |
| [27] | GB/T 7759.1-2015, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-Determination of Compression Set—Part 1: At Ambient or Elevated Temperatures, Standards Press of China, Beijing, 2015 |
| ( 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 7759.1-2015, 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶压缩永久变形的测定第1部分: 在常温及高温条件下, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015) | |
| [28] | Medalia A. I., Heckman F. A ., Carbon, 1969, 7( 5), 567— 582 |
| [29] | Song L. Y., Zhang J. P., Wang R. G., He A. H ., Chinese Polym. Bull., 2018, ( 4), 44— 52 |
| ( 宋丽媛, 张剑平, 王日国, 贺爱华 . 高分子通报, 2018, ( 4), 44— 52) | |
| [30] | Wang H., Zhang J. P., Wang R. G., He A. H ., China Rub. Ind., 2018, 65( 2), 167— 172 |
| ( 王浩, 张剑平, 王日国, 贺爱华 . 橡胶工业, 2018, 65( 2), 167— 172) | |
| [31] | Zhang Y. F., Shao H. F., Wang R. G., He A. H ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40( 8), 1733— 1739 |
| ( 张跃发, 邵华锋, 王日国, 贺爱华 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40( 8), 1733— 1739) |
| [1] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [2] | JIA Bingquan, YE Bin, ZHAO Wei, XU Fangfang, HUANG Fuqiang. Metallic 1T′ MoS2 Boosts Graphitic C3N4 for Efficient Visible-light Photocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 615. |
| [3] | NING Qiuyang, LI Wancheng. Preparation of Planar C2H5OH Fast Response Gas Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1745. |
| [4] | WANG Ruixue, YIN Dongmei, SONG Yongxin, SHAN Guiye. Preparation of CuS/Ag2S Nanocomposite and the Peroxidase-like Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1218. |
| [5] | SHENG Hui, XUE Bin, QIN Meng, WANG Wei, CAO Yi. Preparation and Applications of Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1194. |
| [6] | DAI Lijun, SUN Zhaoyan. Perspective on the Structure and Dynamics of Polymer Chains in Polymer Nanocomposites † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 924. |
| [7] | GUO Qinrui, SHAO Huafeng, HE Aihua. Thermal-oxidative Aging Performance of TBIR Modified NR/BR Vulcanizates in Aircraft Tire Sidewall † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 789. |
| [8] | OUYANG Mi, CHEN Lu, HU Xuming, LI Yuwen, DAI Dacheng, TU Yuanbo, BAI Ru, LÜ Xiaojing, ZHANG Cheng. Preparation and Electrochromic Properties of TiO2-PTPAT Nano Core/Shell Composite Films [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2796. |
| [9] | LI Chong,CHENG Zhongjun,AN Maozhong. Fabrication of Robust Underwater Superoleophobic Copper Mesh with Tunable Oil Adhesion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 125. |
| [10] | WANG Yihan,YIN Qiang,DU Kai,YIN Qinjian. Polypyrrole/Polyaniline Nanocomposite Nanotubes with Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 175. |
| [11] | MAO Long, LIU Yuejun, FAN Shuhong. Preparation and Properties of Polypyrrole Modified Layered Clay/poly(ε-caprolactone) Antibacterial Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1726. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yuefa, SHAO Huafeng, WANG Riguo, HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of Sidewall Compounds for Aircraft Tyre Modified by TBIR [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1733. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xinping, ZHANG Jianping, CAI Lei, ZONG Xin, HE Aihua. Structure and Properties of Damping Materials with Super Fatigue Resistance Based on Chloroprene Rubber† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1571. |
| [14] |
CHEN Yan,DONG Xuejiao,SHAN Guiye.
Preparation of Liposome@Ag/Au Nanocomposites and Their Interaction with H2 |
| [15] | ZHANG Kejie,LI Yu,XIA Yuan,HAN Shuo,CAO Jing,WANG Hanyang,LUO Wentao,ZHOU Zhiping. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of CdS/CuS Core-shell Nanocomposites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 489. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||