

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 20250094.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250094
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
XUE Xiaokuang1,2, LI Jian1,2, LIANG Huanyi1,2, WANG Yiying3( ), GE Jiechao1,2(
), GE Jiechao1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-31
Online:2025-06-10
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
WANG Yiying, GE Jiechao
E-mail:therediceberg@163.com;jchge2010@mail.ipc.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XUE Xiaokuang, LI Jian, LIANG Huanyi, WANG Yiying, GE Jiechao. Red-emissive Mitochondria-targeting Iron-doped Carbon Dots for Tumor Therapy via Peroxidase-mimicking Activity-induced Ferroptosis[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20250094.
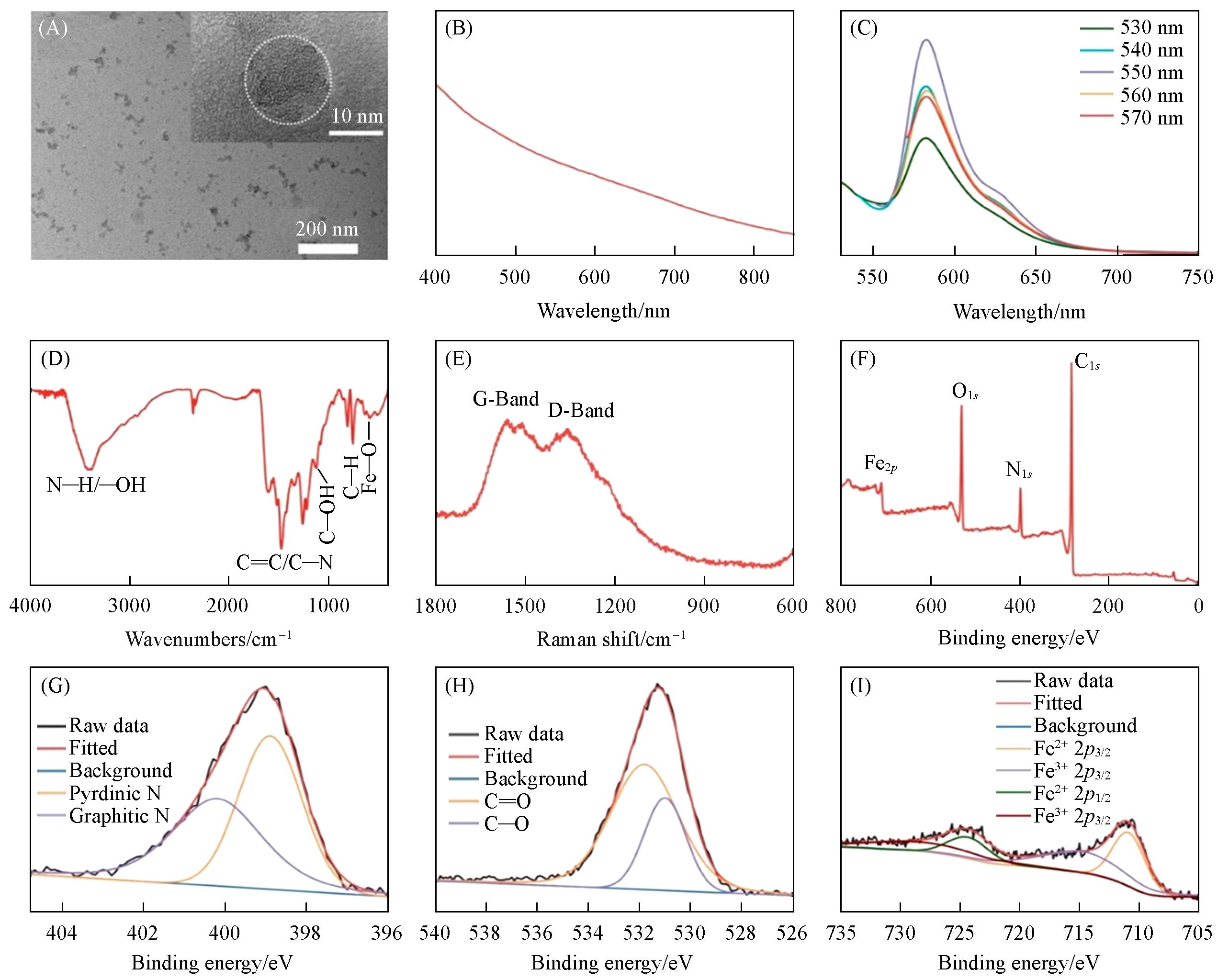
Fig.1 Characterization of Fe⁃CDs(A) TEM and HR-TEM images of Fe-CDs; (B) UV-Vis absorbance spectrum; (C) fluorescence emission spectra of Fe-CDs under excitation at different wavelengths; (D) FTIR spectrum; (E) raman spectrum; (F) XPS survey spectrum of Fe-CDs; high-resolution XPS spectra of N1s (G), O1s (H), and Fe2p (I).
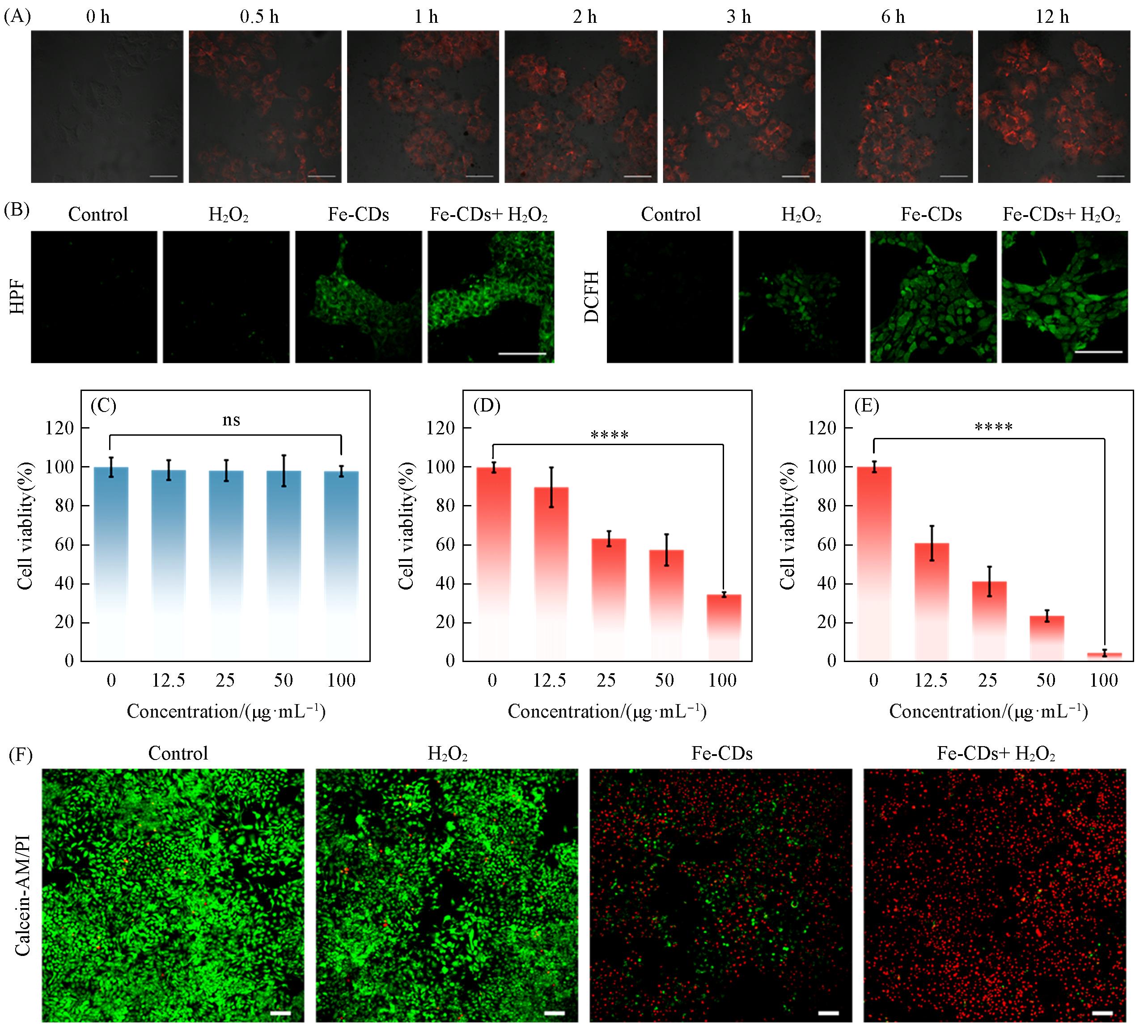
Fig.3 Cellular imaging and in vitro cytotoxicity(A) CLSM images of cells incubated with Fe-CDs for different durations(scale bar: 100 μm); (B) CLSM images of intracellular ROS generation under different treatments using HPF and DCFH as probes for •OH and total ROS, respectively(scale bar: 100 μm); (C) cell viability of HUVECs after 24 h incubation with Fe-CDs at different concentrations; (D) cell viability of 4T1 cells after 24 h incubation with Fe-CDs(culture medium adjusted to pH=6.5 using PIPES); (E) cell viability of 4T1 cells after 24 h incubation with Fe-CDs in a PIPES-buffered medium(pH=6.5) with 100 μmol/L H₂O₂; (F) CLSM images of live and dead 4T1 cells after different treatments(scale bar: 200 μm).

Fig.5 In vivo tumor therapeutic efficacy of Fe⁃CDs(A) Schematic illustration of the establishment of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice and the evaluation of Fe-CD therapy; (B—D) representative digital images of tumors and tumor growth curves for different treatment groups over 20 d; (E) average tumor volume of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice under various treatments; (F) changes in body mass over 20 d for different treatment groups; (G) H&E-stained tumor sections; (H) GPX4 immunofluorescence staining; (I) Ki67 immunohistochemical staining of tumors following different treatments; statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired t-test(*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001).
| 1 | Gao L., Zhuang J., Nie L., Zhang J., Zhang Y., Gu N., Wang T., Feng J., Yang D., Perrett S., Yan X., Nature Nanotechnology, 2007, 2(9), 577—583 |
| 2 | Gao L., Wei H., Dong S., Yan X., Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(10), 2305249 |
| 3 | Gao S., Lin H., Zhang H., Yao H., Chen Y., Shi J., Advanced Science, 2019, 6(3), 1801733 |
| 4 | Yang B., Shi J., Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(52), 21775—21785 |
| 5 | Wang M., Huang G., You Z., Jia R., Zhong Y., Bai F., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2023, 39(4), 612—623 |
| 6 | Wang W., Luo Q., Li J., Li L., Li Y., Huo X., Du X., Li Z., Wang N., Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(36), 2205461 |
| 7 | Liu B., Liu J., Nano Research, 2017, 10(4), 1125—1148 |
| 8 | Huang L., Chen J., Gan L., Wang J., Dong S., Science Advances, 2019, 5(5), eaav5490 |
| 9 | Cao M., Xing X., Shen X., Ouyang J., Na N., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2024, 40(2), 202—212 |
| 10 | Huo M., Wang L., Wang Y., Chen Y., Shi J., ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2), 2643—2653 |
| 11 | Fan K., Xi J., Fan L., Wang P., Zhu C., Tang Y., Xu X., Liang M., Jiang B., Yan X., Gao L., Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1), 1440 |
| 12 | Otasevic V., Vucetic M., Grigorov I., Martinovic V., Stancic A., Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 2021(1), 5537330 |
| 13 | Xie Y., Hou W., Song X., Yu Y., Huang J., Sun X., Kang R., Tang D., Cell Death & Differentiation, 2016, 23(3), 369—379 |
| 14 | Dixon S. J., Lemberg K. M., Lamprecht M. R., Skouta R., Zaitsev E. M., Gleason C. E., Patel D. N., Bauer A. J., Cantley A. M., Yang W. S., Morrison B., Stockwell B. R., Cell, 2012, 149(5), 1060—1072 |
| 15 | Wang H., Lin D., Yu Q., Li Z., Lenahan C., Dong Y., Wei Q., Shao A., Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2021, 9, 629150 |
| 16 | Chen X., Comish P. B., Tang D., Kang R., Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2021, 9, 637162 |
| 17 | Wu A., Han M., Ding H., Rao H., Lu Z., Sun M., Wang Y., Chen Y., Zhang Y., Wang X., Chen D., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 474, 145920 |
| 18 | Ragazzon G., Cadranel A., Ushakova E. V., Wang Y., Guldi D. M., Rogach A. L., Kotov N. A., Prato M., Chem, 2021, 7(3), 606—628 |
| 19 | Shi Y., Xu H., Yuan T., Meng T., Wu H., Chang J., Wang H., Song X., Li Y., Li X., Zhang Y., Xie W., Fan L., Aggregate, 2022, 3(3), e108 |
| 20 | Wang B., Lu S., Matter, 2022, 5(1), 110—149 |
| 21 | Hussain M. M., Khan W. U., Ahmed F., Wei Y., Xiong H., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 465, 143010 |
| 22 | Li J., Yang S., Deng Y., Chai P., Yang Y., He X., Xie X., Kang Z., Ding G., Zhou H., Fan X., Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(30), 1870206 |
| 23 | Xia C., Zhu S., Feng T., Yang M., Yang B., Advanced Science, 2019, 6(23), 1901316 |
| 24 | Nan F., Xue X., Li J., Liang K., Wang J., Yu W. W., Ge J., Wang P., Science China Materials, 2024, 67(11), 3742—3752 |
| 25 | Wang X., Lu Y., Hua K., Yang D., Yang Y., Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2021, 413(5), 1373—1382 |
| 26 | Yang M., Li H., Liu X., Huang L., Zhang B., Liu K., Xie W., Cui J., Li D., Lu L., Sun H., Yang B., Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2023, 21(1), 431 |
| 27 | Deng Z., Qian Y., Yu Y., Liu G., Hu J., Zhang G., Liu S., Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(33), 10452—10466 |
| 28 | Nan F., Jia Q., Xue X., Wang S., Liu W., Wang J., Ge J., Wang P., Biomaterials, 2022, 284, 121495 |
| 29 | Lu S., Sui L., Liu J., Zhu S., Chen A., Jin M., Yang B., Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(15), 1603443 |
| 30 | Li J., Wang J., Liang K., Xue X., Chen T., Gao Z., Ren H., Gao L., Ge J., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 500, 157033 |
| 31 | Yang Y., Xu J., Zhou R., Qin Z., Liao C., Shi S., Chen Y., Guo Y., Zhang S., Carbon, 2024, 219, 118831 |
| 32 | Xie M., Li F., Li Y., Qian K., Liang Y., Lei B., Liu Y., Cui J., Xiao Y., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 506, 159956 |
| 33 | Jiang B., Duan D., Gao L., Zhou M., Fan K., Tang Y., Xi J., Bi Y., Tong Z., Gao G. F., Xie N., Tang A., Nie G., Liang M., Yan X., Nature Protocols, 2018, 13(7), 1506—1520 |
| 34 | Huo M., Wang L., Chen Y., Shi J., Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1), 357 |
| [1] | LIU Yupeng, YANG Junxiang, HAO Yiming, QU Songnan. Recent Advances in Carbon Dots with Near-infrared Absorption/Emission [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240070. |
| [2] | LIU Yize, LI Pengfei, SUN Zaicheng. Correlation Between the Photoluminescene Mechanism and Structure of Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20250103. |
| [3] | YANG Chunyuan, CHEN Hao, ZHANG Pan, LI Fucheng, YUAN Weixiong, GUO Jiazhuang, WANG Caifeng, CHEN Su. Synthesis, Fluorescence Mechanism and Patterning of Green-emissive Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20250093. |
| [4] | LI Dan, HU Honghui, HOU Hongshuai, ZHANG Sheng, LIU Lijie, JING Mingjun, WU Tianjing. Sodium Storage Performance of Mixed-phase Sodium Titanate Tuned by Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240356. |
| [5] | LI Fengshi, JIANG Kai, TONG Xinyuan, WU Yongjian, LIN Hengwei. Regulating Trap Density and Energy Levels Through Boron Doping to Achieve Duration-tunable Afterglow from Carbon Dots for Dynamic Information Encryption [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240545. |
| [6] | WANG Changying, ZHANG Dawei, CHEN Guanji, ZHANG Zhenwei, XIAO Weihong, WANG Bin, CHEN Qidan, YANG Bai. Preparation of Carbon Dots Fluorescent Marker and Its Application in Highly Selective NO2‒ Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240519. |
| [7] | LIU Jinkun, RAN Zhun, LIU Qingqing, LIU Yingliang, ZHUANG Jianle, HU Chaofan. Preparation of Carbon Dot-based Multicolor Room-temperature Phosphorescent Materials via Precursor Structure Regulation Strategies [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240412. |
| [8] | PANG E, TANG Yuanyu, ZHAO Shaojing, CHENG Qiang, WANG Chen, CHEN Jianmin, LAN Minhuan. Hypoxia Activated Chemotherapy Drug AQ4N and Carbon Dots Self-assembly for Chemotherapy Combined with Sonodynamic Therapy of Tumors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240489. |
| [9] | NI Jiawen, HUANG Zunhui, SONG Tianbing, MA Qianli, HE Tianle, ZHANG Xirong, XIONG Huanming. Ordered Lithium Deposition on Lithium Metal Anode Controlled by Boron-doped Carbon Dots from Solid-state Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240185. |
| [10] | LI Yan, CAI Hao, BI Hong. Antioxidative Carbon Dots Improving Acute Liver Injury Induced by Acetaminophen [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240130. |
| [11] | CHEN Qidan, CHEN Guanji, YOU Shanmei, ZANG Xinyao, YANG Bai. Preparation of Broad-spectrum UV Protection Carbon Dots for the Application of Sunscreen Absorber [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240313. |
| [12] | PAN Zhuohan, AI Lin, LU Siyu. Research Progress on the Mechanism, Synthesis and Application of Solid-state Luminescent Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20250081. |
| [13] | GUO Dan, HUANG Genghong, BAI Huijie, WANG Yaling, CAO Guangqun, LIU Bin, HU Shengliang. Preparation and Applications of CO2-Derived Red-emissive Carbon Dots with a High Quantum Yield [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20250091. |
| [14] | LIU Yingqi, WANG Yemei, JIANG Kai, ZHENG Fenfen, ZHU Junjie. Colorimetric and Fluorescence Determination of Glucose Based on Cell-derived Fluorescent Carbon Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240386. |
| [15] | HAO Yongliang, LI Jian, WANG Zehua, GE Jiechao. Active Shrinkage Hydrogel Based on Red Emissive Carbon Dots Photosensitizers for Bacterial Infected Wound Healing [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(6): 20240409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||