

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 20220722.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220722
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Jun1,2, DU Shiqian2( ), TAO Li1,2(
), TAO Li1,2( )
)
Received:2022-11-18
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-01-08
Contact:
DU Shiqian, TAO Li
E-mail:dushiqiian@hnu.edu.cn;taoli@hnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Jun, DU Shiqian, TAO Li. Recent Progress of Catalysts in the High Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220722.
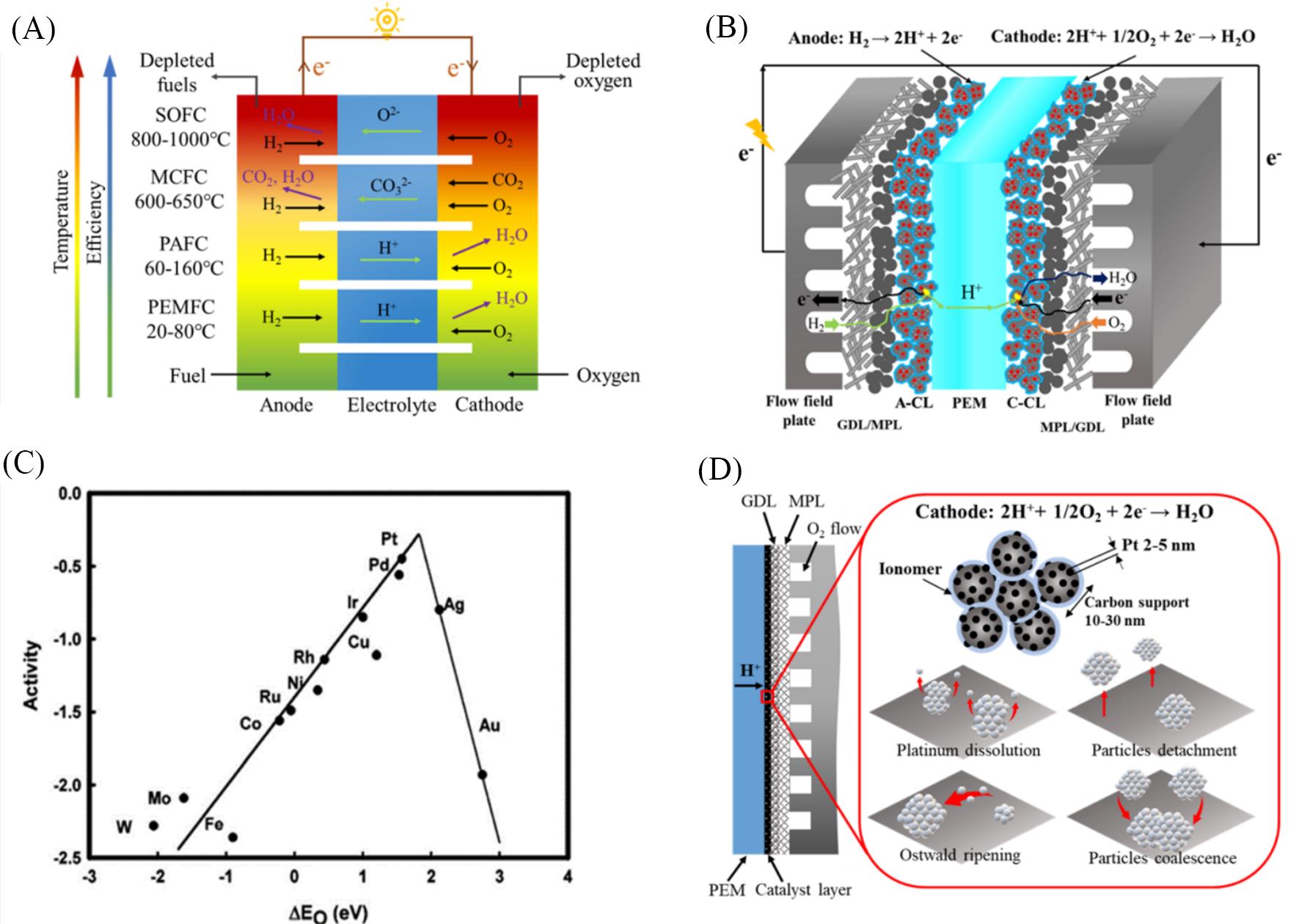
Fig.1 Structures of fuel cells and catalysts for ORR(A) Different types of fuel cells[11]; (B) a schematic of the basic structure and components for PEMFCs; (C) trends in ORR activity plotted as a function of the oxygen binding energy[20]; (D) illustration graph of Pt/C catalyst in the cathode catalyst layer and its degradation mechanism. (A) Copyright 2017, Oxford University Press; (C) Copyright 2004, America Chemistry Society.
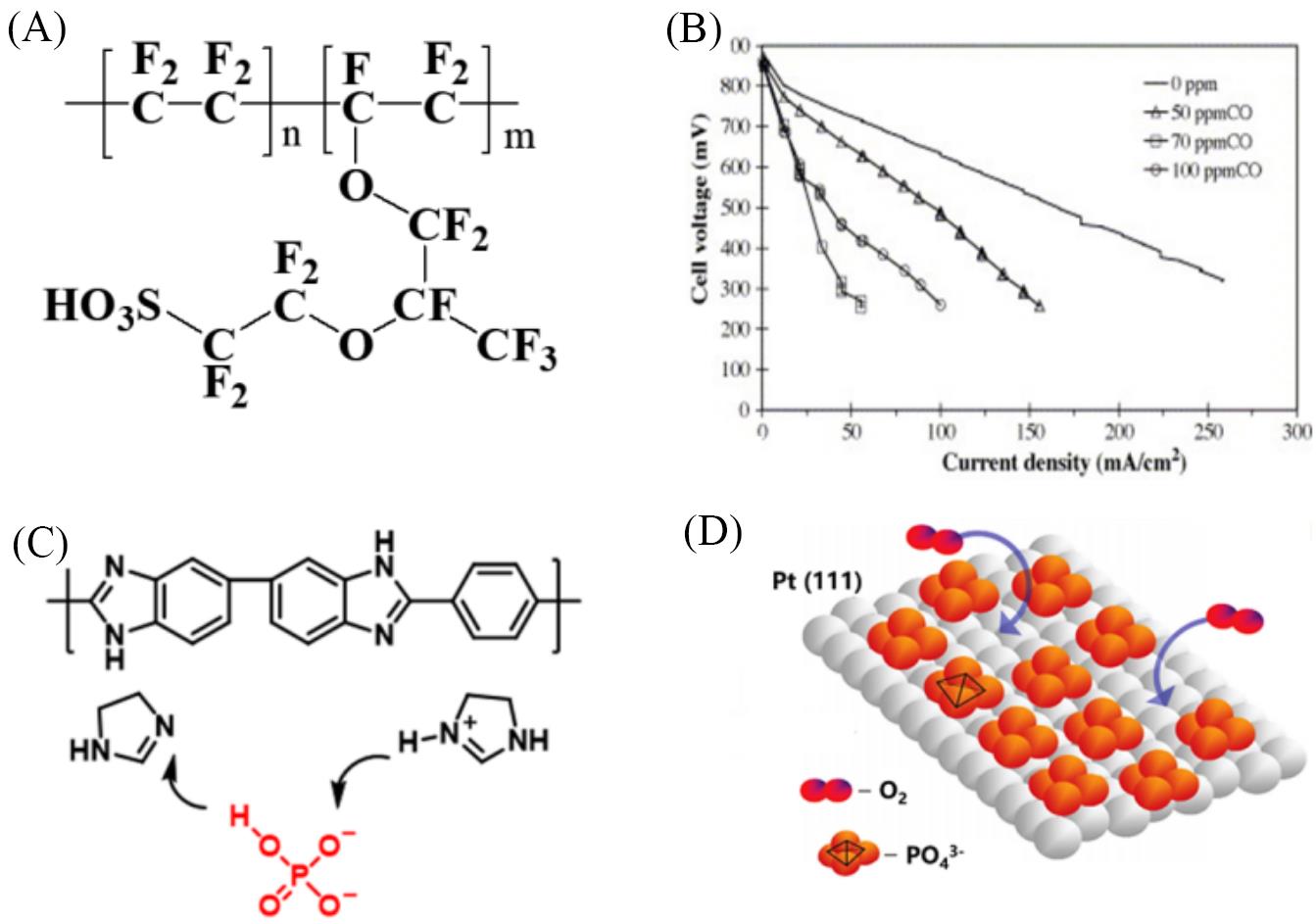
Fig.2 Structure of PEM and the negative effect of CO/phosphoric acid on Pt catalysts(A) Structure of the Nafion membrane; (B) the polarization curves after 6 h CO poisoning at different concentrations[37]; (C) the structure of PBI and mechanism of polymer transfer; (D) the absorption of phosphoric acid on the Pt surface. (B) Copyright 2005, Elsevier.
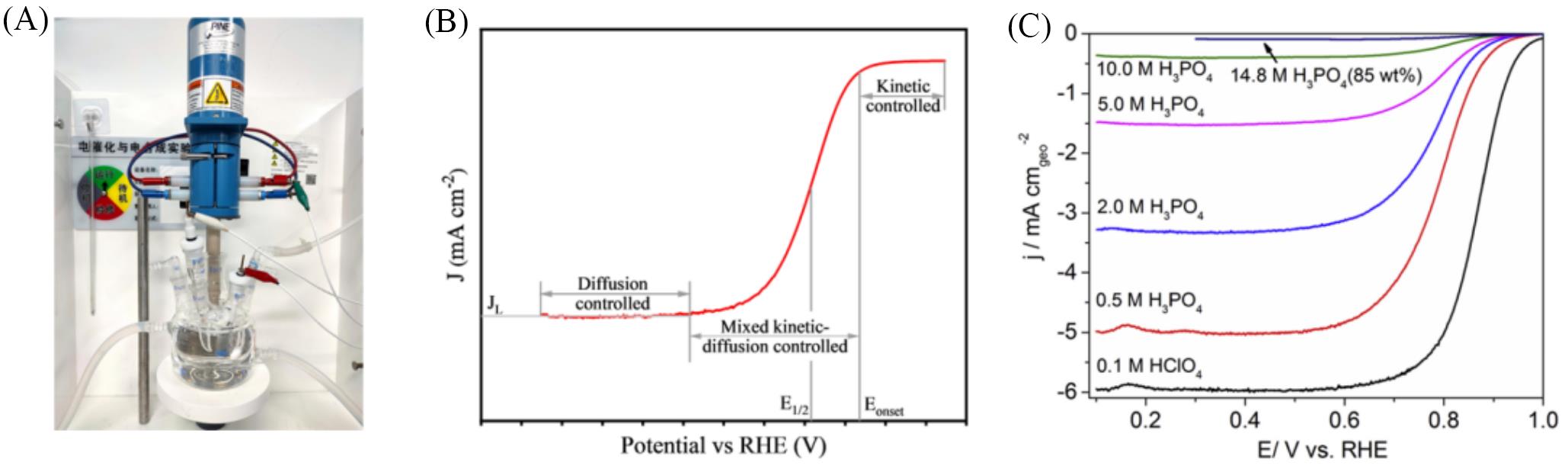
Fig.3 ORR test system and polarization curve(A) RDE test system; (B) typical ORR polarization curve; (C) ORR polarization curves of 20%(mass fraction) Pt/C by RDE testing at room temperature in 0.1 mol/L HClO4 and varying concentrations of PA[46].(C) Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
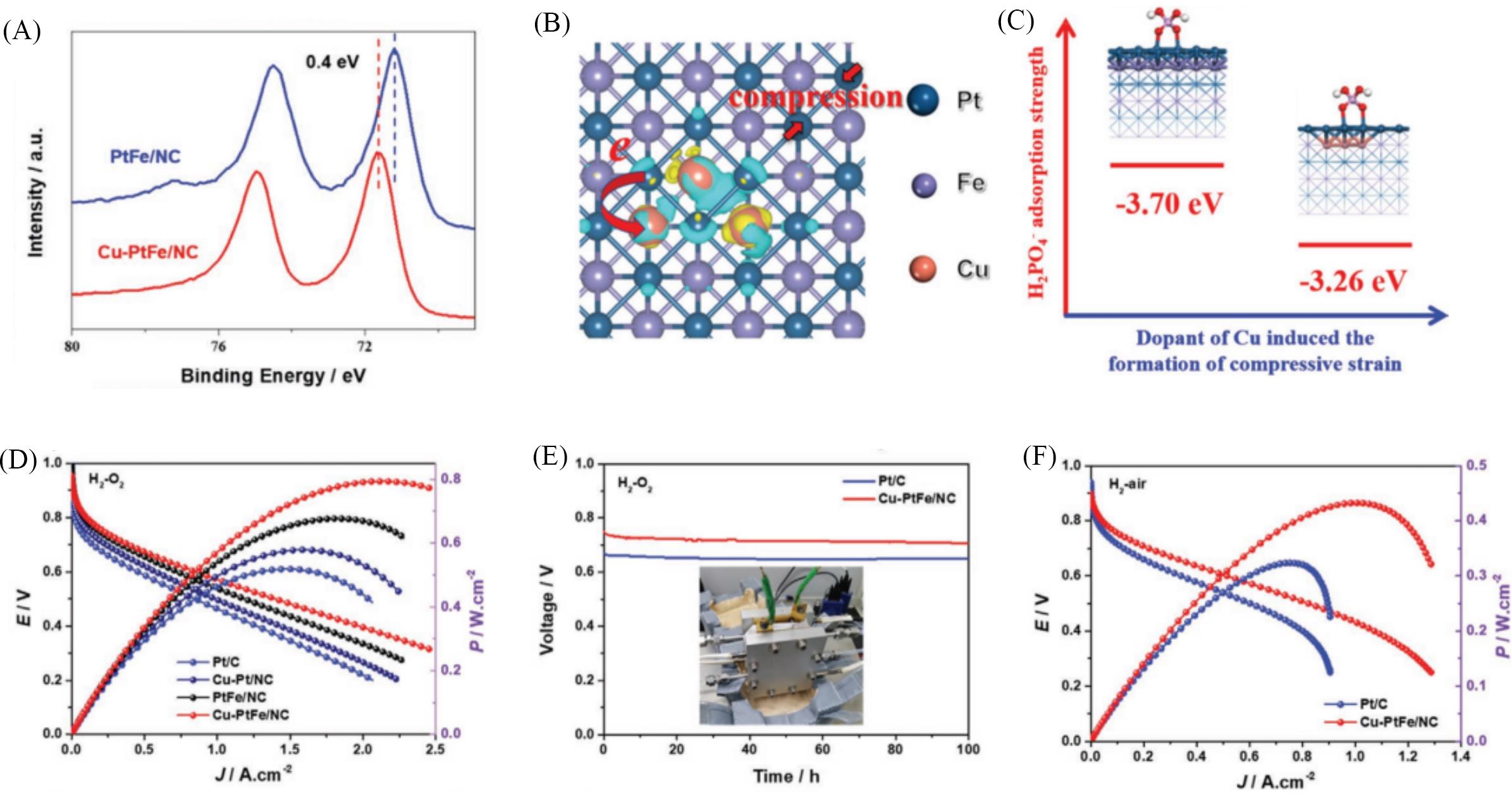
Fig.4 HT⁃PEMFCs performance and mechanism of Cu⁃PtFe/NC catalyst[64](A) High-resolution Pt4f spectra of PtFe/NC and Cu-PtFe/NC; (B) the charge density difference of the Cu-PtFe crystals; the yellow and green electron clouds correspond to an accumulation and depletion of electrons, respectively; (C) geometric structures and PA adsorption strength of H2PO4- adsorption on Cu-PtFe and PtFe; (D) H2-O2 HT-PEMFC polarization curves and corresponding power densities of Pt/C, Cu-Pt/NC, PtFe/NC, and Cu-PtFe/NC at 160 ℃; (E) durability test results of Pt/C and Cu-PtFe/NC under the current density of 0.2 A/cm2; (F) H2-air fuel cell of Pt/C and Cu-PtFe/NC.Copyright 2022, Wiley.
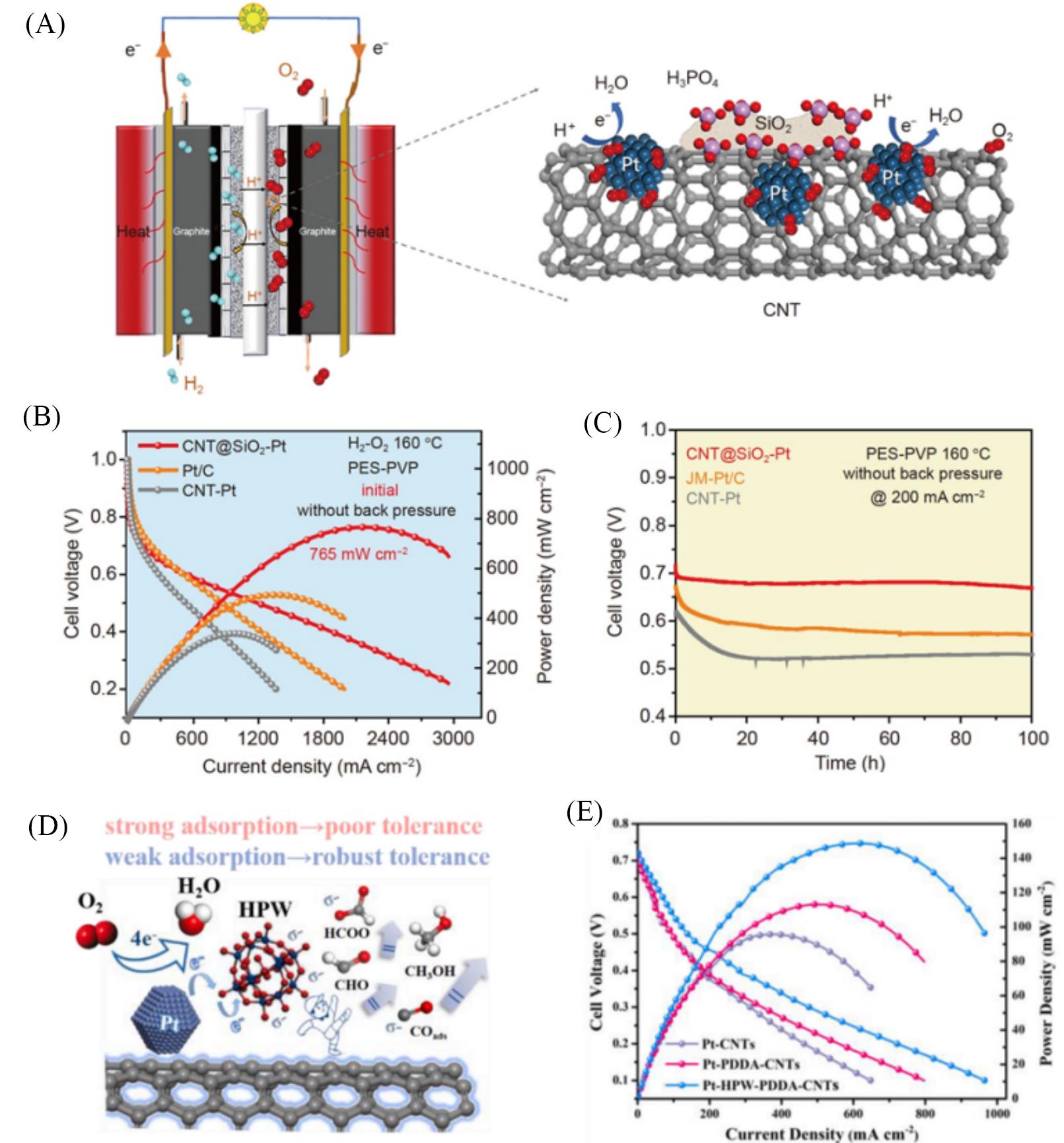
Fig.5 HT⁃PEMFCs performance of Pt⁃based catalysts with modified supports(A) Schematic representation for the HT-PEMFCs of the single cell and the CNT@SiO2-Pt in the catalytic layer of HT-PEMFCs; (B) the initial polarization and power density curves of Pt/C, CNT-Pt, CNT@SiO2-Pt at 160 ℃(H2/O2); (C) potential response of a 100 h HT-PEMFCs life test at a constant current density of 200 mA/cm2 at 160 ℃ in H2/O2[67]; (D) illustration graph for mechanism of methanol tolerance on Pt-HPW-PDDA-CNTs electrocatalyst; (E) polarization curves and powder densities for HT-DMFCs using as-designed catalysts cathodes at 240 ℃[68].(A—C) Copyright 2021, Springer; (D, E) Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
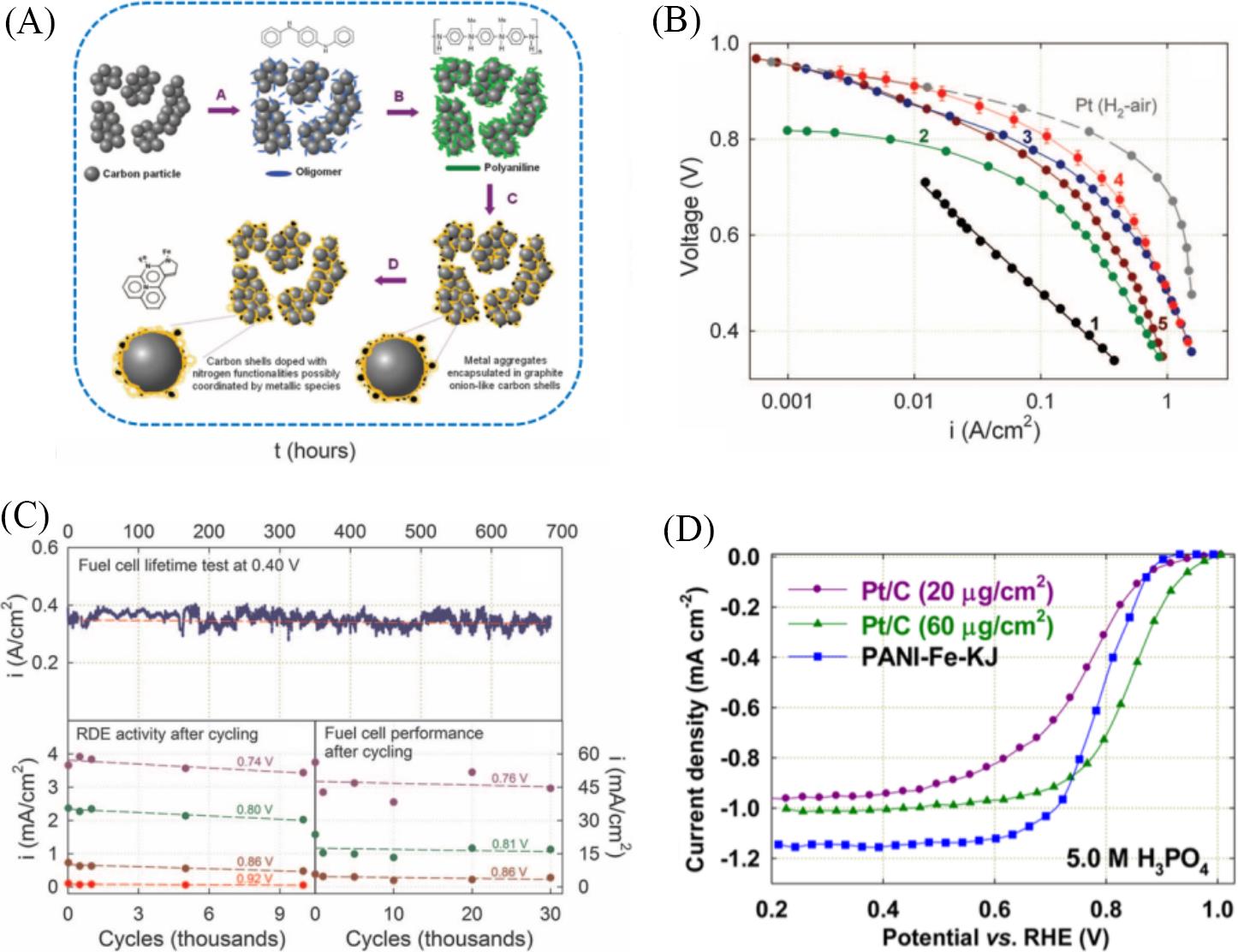
Fig.6 Performance of Fe⁃N⁃C catalysts as ORR catalysts(A) Schematic diagram of the synthesis of Fe-N-C catalysts; (B, C) fuel cell and performance durability test of the Fe-N-C catalysts[28]; (D) ORR activity comparison between Fe-N-C, 20 μgPt/cm2 and 60 μgPt/cm2 Pt/C catalysts in O2-saturated 5.0 mol/L H3PO4 electrolyte by steady-state polarization curves; rotation rate: 900 r/min; room temperature[82].(A—C) Copyright 2011, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (D) Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society.
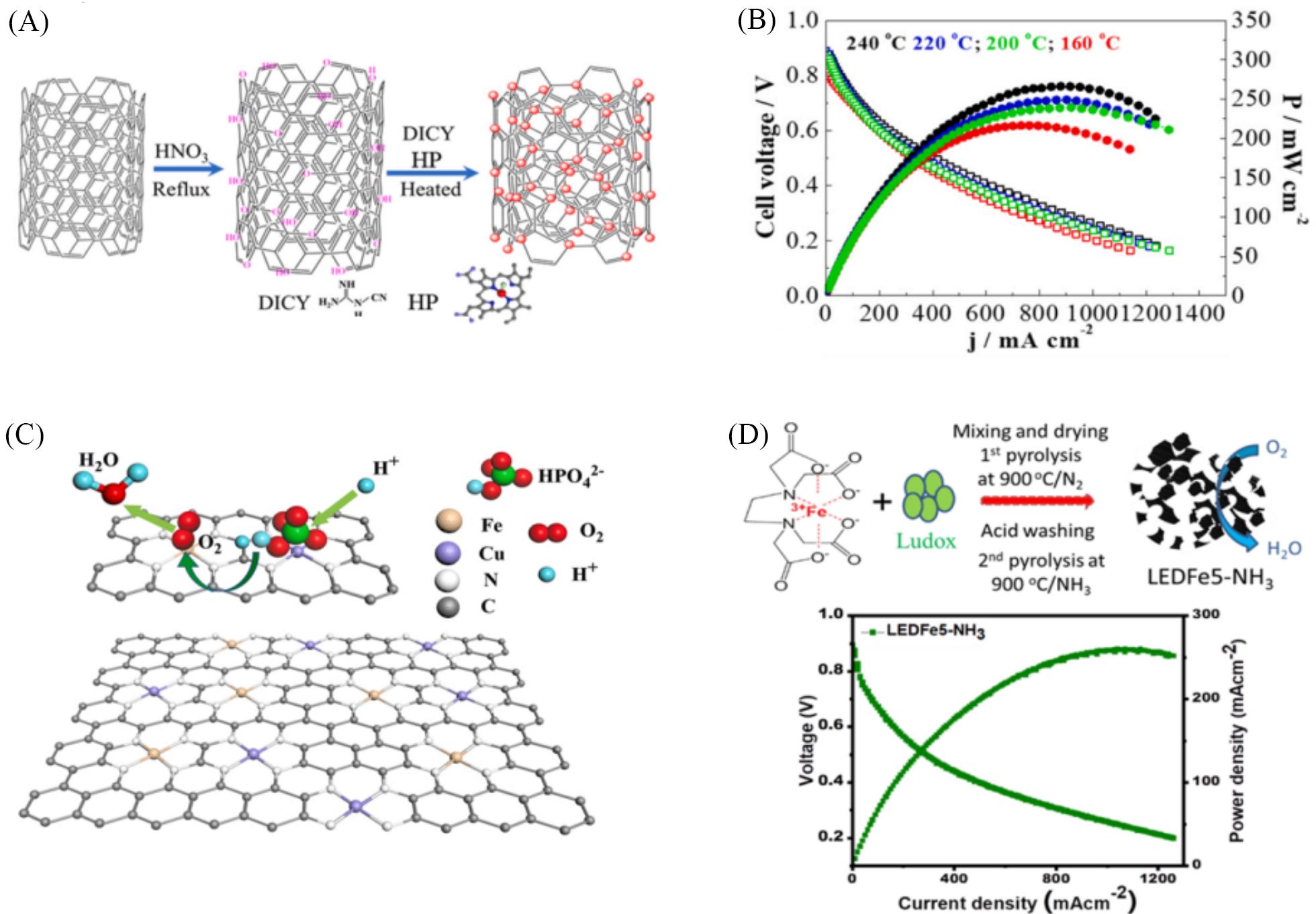
Fig.7 HT⁃PEMFCs performance of Fe⁃N⁃C catalysts(A) Scheme of the synthesis procedure of FeSA/HP; (B) I-V and power density curves of HT-PEMFCs with FeSA/HP cathode, measured at different temperatures[83]; (C) scheme of the phosphate promoted ORR, where PA adsorbed on Cu atoms provides local protons for ORR on the adjacent Fe atoms[84]; (D) schematic illustration of synthesis process for EDTA-Fe complex-based catalyst, and single-cell performance of HT-PEMFC with LEDFe5-NH3 in cathode measured at 1.5 bar(1 bar=1×105 Pa) O2 pressure and 150 ℃ cell temperature[87].(A, B) Copyright 2021, Elsevier; (C) Copyright 2021, Elsevier; (D) Copyright 2020, ACS.
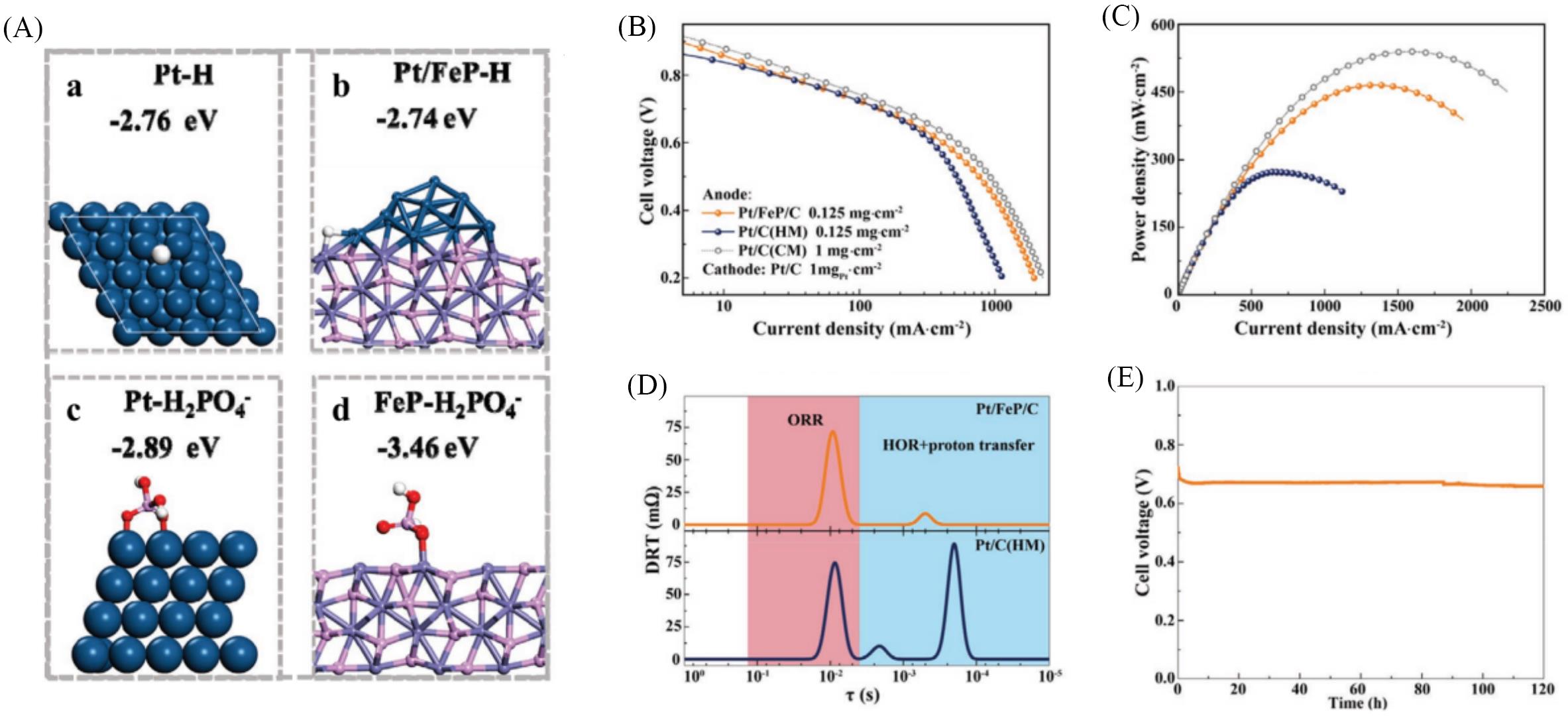
Fig.8 HT⁃PEMFCs performance using Pt/FeP/C as anode catalyst[95](A) The absorption energy of H species on Pt (111)(a) and Pt/FeP(b) models and the absorption energy of H2PO4- species on Pt(111)(c) and FeP (d) models; (B, C) fuel cell performance, I-V plots(B) and power density curves(C) of the HT-PEMFCs; (D) DRT analysis of the HT-PEMFCs with Pt/FeP/C and Pt/C(HM) anode; (E) stability test of Pt/FeP/C in HT-PEMFCs.Copyright 2022, Wiley.
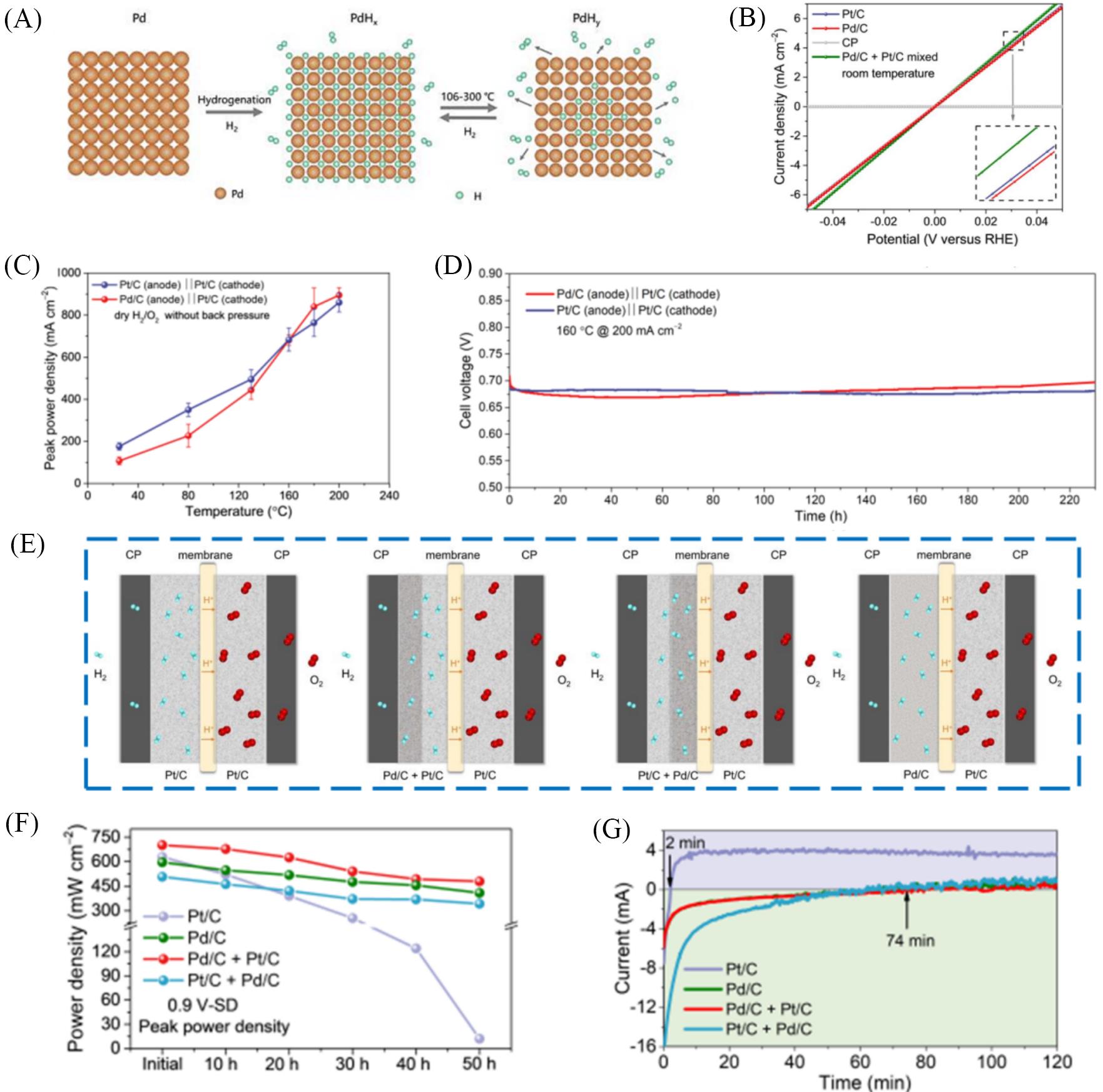
Fig.9 The application of Pd in HT⁃PEMFCs[96](A) Schematic diagram of intercalation and release of hydrogen in the Pd lattice interstitial sites with temperature changes; (B) GDE test for Pt/C, Pd/C, Pt/C+Pd/C mixed (the same total amount of precious metals: 1 mgPGM/cm2 ), and carbon paper (CP) in 0.1 mol/L HClO4 at 25 °C; (C) the plots of PPD change with increasing temperature of Pt/C and Pd/C individually for HT-PEMFCs; (D) voltage response of 230 h lifetime test for HT-PEMFCs at a constant current density of 200 mA/cm2; (E) schematic diagram of different anode catalytic layer structure designs; (F) The peak power density after the anode fuel starvation at 0.9 V; (G) the current change curve of HT-PEMFCs in the first 120 min after the shut down(SD) process of H2. Copyright 2023, Wiley.
| 1 | Huang M. T., Zhai P. M., Adv. Climate Change Res., 2021, 12, 281—286 |
| 2 | Midilli A., Dincer I., Ay M., Energy Policy, 2006, 34, 3623—3633 |
| 3 | Midilli A., Dincer I., Rosen M. A., Int. J. Green Energy, 2007, 4, 65—87 |
| 4 | Ramadan M., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46, 30547—30558 |
| 5 | Holladay J. D., Hu J., King D. L., Wang Y., Catal. Today, 2009, 139, 244—260 |
| 6 | Debe M. K., Nature, 2012, 486, 43—51 |
| 7 | Jiao Y., Zheng Y., Jaroniec M., Qiao S. Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 2060—2086 |
| 8 | Staffell I., Scamman D., Abad A. V., Balcombe P., Dodds P. E., Ekins P., Shah N., Ward K. R., Energy Environ. Sci., 2019, 12, 463—491 |
| 9 | Grove W. R., Philos. Mag., 1838, 13, 430—431 |
| 10 | Grove W. R., Philos. Mag., 1842, 21, 417—420 |
| 11 | Wang S., Jiang S. P., Natl. Sci. Rev., 2017, 4, 163—166 |
| 12 | Borup R., Meyers J., Pivovar B., Kim Y. S., Mukundan R., Garland N., Myers D., Wilson M., Garzon F., Wood D., Zelenay P., More K., Stroh K., Zawodzinski T., Boncella J., McGrath J. E., Inaba M., Miyatake K., Hori M., Ota K., Ogumi Z., Miyata S., Nishikata A., Siroma Z., Uchimoto Y., Yasuda K., Kimijima K., Iwashita N., Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 3904—3951 |
| 13 | Gasteiger H. A., Kocha S. S., Sompalli B., Wagner F. T., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2005, 56, 9—35 |
| 14 | Lefevre M., Proietti E., Jaouen F., Dodelet J. P., Science, 2009, 324, 71—74 |
| 15 | Li Q. F., He R. H., Jensen J. O., Bjerrum N. J., Chem. Mater., 2003, 15, 4896—4915 |
| 16 | Wang Y., Chen K. S., Mishler J., Cho S. C., Adroher X. C., Appl. Energ., 2011, 88, 981—1007 |
| 17 | Freyschlag C. G., Madix R. J., Mater. Today, 2011, 14, 134—142 |
| 18 | Jin R., Nanotechnol. Rev., 2012, 1, 31—56 |
| 19 | Quinson J., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 303, 102643 |
| 20 | Nørskov J. K., Rossmeisl J., Logadottir A., Lindqvist L., Kitchin J. R., Bligaard T., Jonsson H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 17886—17892 |
| 21 | Stamenkovic V., Mun B. S., Mayrhofer K. J. J., Ross P. N., Markovic N. M., Rossmeisl J., Greeley J., Nørskov J. K., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 2897—2901 |
| 22 | Bu L., Zhang N., Guo S., Zhang X., Li J., Yao J., Wu T., Lu G., Ma J. Y., Su D., Huang X., Science, 2016, 354, 1410—1414 |
| 23 | Wang X., Choi S. I., Roling L. T., Luo M., Ma C., Zhang L., Chi M., Liu J., Xie Z., Herron J. A., Mavrikakis M., Xia Y., Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 7594 |
| 24 | Xia W., Mahmood A., Liang Z., Zou R., Guo S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 2650—2676 |
| 25 | Greeley J., Stephens I. E. L., Bondarenko A. S., Johansson T. P., Hansen H. A., Jaramillo T. F., Rossmeisl J., Chorkendorff I., Norskov J. K., Nat. Chem., 2009, 1, 552—556 |
| 26 | Stamenkovic V. R., Mun B. S., Arenz M., Mayrhofer K. J. J., Lucas C. A., Wang G., Ross P. N., Markovic N. M., Nat. Mater., 2007, 6, 241—247 |
| 27 | Chen Y., Ji S., Chen C., Peng Q., Wang D., Li Y., Joule, 2018, 2, 1242—1264 |
| 28 | Wu G., More K. L., Johnston C. M., Zelenay P., Science, 2011, 332, 443—447 |
| 29 | Cheng X., Yang J., Yan W., Han Y., Qu X., Yin S., Chen C., Ji R., Li Y., Li G., Li G., Jiang Y., Sun S., Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 5958—5967 |
| 30 | Han Y., Yin S., Chen Y., Chen C., Yan W., Cheng X., Li Y., Zhang T., Yang J., Jiang Y., Sun S., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2022, 914, 116322 |
| 31 | Wang F., Zhou Y., Lin S., Yang L., Hu Z., Xie D., Nano Energy, 2020, 78, 105128 |
| 32 | Yin S. H., Yang J., Han Y., Li G., Wan L. Y., Chen Y. H., Chen C., Qu X. M., Jiang Y. X., Sun S. G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 21976—21979 |
| 33 | Zhang P. Y., Yang X. H., Jiang Q. R., Cui P. X., Zhou Z. Y., Sun S. H., Wang Y. C., Sun S. G., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 30724—30734 |
| 34 | Mauritz K. A., Moore R. B., Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 4535—4585 |
| 35 | Ehteshami S. M. M., Chan S. H., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 93, 334—345 |
| 36 | Hassan A., Paganin V. A., Ticianelli E. A., J. Power Sources, 2016, 325, 375—382 |
| 37 | Jiménez S., Soler J., Valenzuela R. X., Daza L., J. Power Sources, 2005, 151, 69—73 |
| 38 | Lee S. J., Mukerjee S., Ticianelli E. A., McBreen J., Electrochim. Acta, 1999, 44, 3283—3293 |
| 39 | Aili D., Henkensmeier D., Martin S., Singh B., Hu Y., Jensen J. O., Cleemann L. N., Li Q., Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2020, 3, 793—845 |
| 40 | Antonio Asensio J., Sanchez E. M., Gomez⁃Romero P., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 3210—3239 |
| 41 | Zhang J., Xie Z., Zhang J., Tang Y., Song C., Navessin T., Shi Z., Song D., Wang H., Wilkinson D. P., Liu Z. S., Holdcroft S., J. Power Sources, 2006, 160, 872—891 |
| 42 | Shao Y., Yin G., Wang Z., Gao Y., J. Power Sources, 2007, 167, 235—242 |
| 43 | Nie Y., Li L., Wei Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 2168—2201 |
| 44 | Haider R., Wen Y., Ma Z. F., Wilkinson D. P., Zhang L., Yuan X., Song S., Zhang J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 1138—1187 |
| 45 | Araya S. S., Zhou F., Liso V., Sahlin S. L., Vang J. R., Thomas S., Gao X., Jeppesen C., Kær S. K., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41, 21310—21344 |
| 46 | Hu Y., Jiang Y., Jensen J. O., Cleemann L. N., Li Q., J. Power Sources, 2018, 375, 77—81 |
| 47 | Stephens I. E. L., Bondarenko A. S., Gronbjerg U., Rossmeisl J., Chorkendorff I., Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 6744—6762 |
| 48 | Escudero E. M., Malacrida P., Hansen M. H., Vej⁃Hansen U. G., Velazquez P. A., Tripkovic V., Schiotz J., Rossmeisl J., Stephens I. E. L., Chorkendorff I., Science, 2016, 352, 73—76 |
| 49 | Li W., Zhao L., Jiang X., Chen Z., Zhang Y., Wang S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2207727 |
| 50 | Paulus U. A., Wokaun A., Scherer G. G., Schmidt T. J., Stamenkovic V., Markovic N. M., Ross P. N., Electrochim. Acta, 2002, 47, 3787—3798 |
| 51 | Paulus U. A., Wokaun A., Scherer G. G., Schmidt T. J., Stamenkovic V., Radmilovic V., Markovic N. M., Ross P. N., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 4181—4191 |
| 52 | Stamenkovic V., Schmidt T. J., Ross P. N., Markovic N. M., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 11970—11979 |
| 53 | Stonehart P., Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94, 913—921 |
| 54 | Lim B., Jiang M., Camargo P. H. C., Cho E. C., Tao J., Lu X., Zhu Y., Xia Y., Science, 2009, 324, 1302—1305 |
| 55 | Wang D., Yu Y., Xin H. L., Hovden R., Ercius P., Mundy J. A., Chen H., Richard J. H., Muller D. A., DiSalvo F. J., Abruna H. D., Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 5230—5238 |
| 56 | Wang D., Xin H. L., Hovden R., Wang H., Yu Y., Muller D. A., DiSalvo F. J., Abruna H. D., Nat. Mater., 2013, 12, 81—87 |
| 57 | Du X. X., He Y., Wang X. X., Wang J. N., Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9, 2623—2632 |
| 58 | Qin Y., Luo M., Sun Y., Li C., Huang B., Yang Y., Li Y., Wang L., Guo S., ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 5581—5590 |
| 59 | Liu M., Zhao Z., Duan X., Huang Y., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1802234 |
| 60 | Choi S. I., Xie S., Shao M., Odell J. H., Lu N., Peng H. C., Protsailo L., Guerrero S., Park J., Xia X., Wang J., Kim M. J., Xia Y., Nano Lett., 2013, 13, 3420—3425 |
| 61 | Wu J., Gross A., Yang H., Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 798—802 |
| 62 | Li M., Zhao Z., Cheng T., Fortunelli A., Chen C. Y., Yu R., Zhang Q., Gu L., Merinov B. V., Lin Z., Zhu E., Yu T., Jia Q., Guo J., Zhang L., Goddard W. A., III, Huang Y., Duan X., Science, 2016, 354, 1414—1419 |
| 63 | Wang C., Daimon H., Onodera T., Koda T., Sun S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 3588—3591 |
| 64 | Li W., Wang D., Liu T., Tao L., Zhang Y., Huang Y. C., Du S., Dong C. L., Kong Z., Li Y. F., Lu S., Wang S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2109244 |
| 65 | Lim S. Y., Martin S., Gao G., Dou Y., Simonsen S. B., Jensen J. O., Li Q., Norrman K., Jing S., Zhang W., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 31, 2006771 |
| 66 | Long P., Du S., Liu Q., Tao L., Peng C., Wang T., Gu K., Xie C., Zhang Y., Chen R., Lu S., Cheng Y., Feng W., Wang S., Sci. China Mater., 2022, 65, 904—912 |
| 67 | Huang G., Li Y., Du S., Wu Y., Chen R., Zhang J., Cheng Y., Lu S., Tao L., Wang S., Sci. China Chem., 2021, 64, 2203—2211 |
| 68 | Wu Y., Wang J., Huang G., Du S., Lin J., Zhou B., Lu Y., Wang D., Li M., Tao L., Wang S., J. Power Sources, 2022, 541, 231643 |
| 69 | Parrondo J., Mijangos F., Rambabu B., J. Power Sources, 2010, 195, 3977—3983 |
| 70 | Xiao L., Zhuang L., Liu Y., Lu J., Abruna H. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 602—608 |
| 71 | Antolini E., Energy Environ. Sci., 2009, 2, 915—931 |
| 72 | Luo M., Zhao Z., Zhang Y., Sun Y., Xing Y., Lv F., Yang Y., Zhang X., Hwang S., Qin Y., Ma J. Y., Lin F., Su D., Lu G., Guo S., Nature, 2019, 574, 81—85 |
| 73 | Shao M. H., Sasaki K., Adzic R. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 3526—3527 |
| 74 | Shao M. H., Huang T., Liu P., Zhang J., Sasaki K., Vukmirovic M. B., Adzic R. R., Langmuir, 2006, 22, 10409—10415 |
| 75 | You D. J., Pak C., Jin S. A., Lee K. H., Kwon K., Choi K. H., Heo P. W., Jang H., Kim J. Y., Kim J. M., J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2016, 16, 4357—4361 |
| 76 | Wu G., Santandreu A., Kellogg W., Gupta S., Ogoke O., Zhang H., Wang H. L., Dai L., Nano Energy, 2016, 29, 83—110 |
| 77 | Li J. C., Zhong H., Xu M., Li T., Wang L., Shi Q., Peng S., Lyu Z., Liu D., Du D., Beckman S. P., Pan X., Lin Y., Shao M., Sci. China Mater., 2020, 63, 965—971 |
| 78 | Wen X., Qi H., Cheng Y., Zhang Q., Hou C., Guan J., Chin. J. Chem., 2020, 38, 941—946 |
| 79 | Wang R., Zhang P., Wang Y., Wang Y., Zaghib K., Zhou Z., Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int., 2020, 30, 855—860 |
| 80 | Wang H. F., Chen L., Pang H., Kaskel S., Xu Q., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 1414—1448 |
| 81 | Chen Y., Gao R., Ji S., Li H., Tang K., Jiang P., Hu H., Zhang Z., Hao H., Qu Q., Liang X., Chen W., Dong J., Wang D., Li Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 3212—3221 |
| 82 | Li Q., Wu G., Cullen D. A., More K. L., Mack N. H., Chung H. T., Zelenay P., ACS Catal., 2014, 4, 3193—3200 |
| 83 | Cheng Y., Zhang J., Wu X., Tang C., Yang S. Z., Su P., Thomsen L., Zhao F., Lu S., Liu J., Jiang S. P., Nano Energy, 2021, 80, 105534 |
| 84 | Cheng Y., Wang M., Lu S., Tang C., Wu X., Veder J. P., Johannessen B., Thomsen L., Zhang J., Yang S. Z., Wang S., Jiang S. P., Appl. Catal. B: Environ, 2021, 284, 119717 |
| 85 | Eren E. O., Ozkan N., Devrim Y., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45, 33957—33967 |
| 86 | Gokhale R., Asset T., Qian G., Serov A., Artyushkova K., Benicewicz B. C., Atanassov P., Electrochem. Commun., 2018, 93, 91—94 |
| 87 | Razmjooei F., Yu J. H., Lee H. Y., Lee B. J., Singh K. P., Kang T. H., Kim H. J., Yu J. S., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 11164—11176 |
| 88 | Mittermeier T., Madkikar P., Wang X., Gasteiger H. A., Piana M., Materials, 2017, 10, 661 |
| 89 | Zhang W., Shironita S., Umeda M., Catal. Lett., 2014, 144, 112—116 |
| 90 | Das R. K., Wang Y., Vasilyeva S. V., Donoghue E., Pucher I., Kamenov G., Cheng H. P., Rinzler A. G., ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 8447—8456 |
| 91 | Park H. Y., Park I. S., Choi B., Lee K. S., Jeon T. Y., Sung Y. E., Yoo S. J., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 2125—2130 |
| 92 | Elezovic N. R., Babic B. M., Vracar L. M., Radmilovic V. R., Krstajic N. V., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 5192—5197 |
| 93 | Sheng W., Bivens A. P., Myint M., Zhuang Z., Forest R. V., Fang Q., Chen J. G., Yan Y., Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7, 1719—1724 |
| 94 | Davydova E. S., Mukerjee S., Jaouen F., Dekel D. R., ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 6665—6690 |
| 95 | Du S., Li Y., Wu X., Huang G., Wu Y., Zhang J., Zhang J., Lu S., Cheng Y., Tao L., Wang S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2106758 |
| 96 | Huang G., Li Y., Tao L., Huang Z., Kong Z., Xie C., Du S., Wang T., Wu Y., Liu Q., Zhang D., Lin J., Li M., Wang J., Zhang J., Lu S., Cheng Y., Wang S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202215177 |
| 97 | Li Q., Hjuler H. A., Bjerrum N. J., J. Appl. Electrochem., 2001, 31, 773—779 |
| 98 | Oettel C., Rihko⁃Struckmann L., Sundmacher K., J. Fuel Cell Sci. Tech., 2012, 9, 031009 |
| [1] | LI Xuan, QI Shuai, ZHOU Weiliang, LI Xiaojie, JING Lingyan, FENG Chao, JIANG Xingxing, YANG Hengpan, HU Qi, HE Chuanxin. Advances in Nanofiber-based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 316. |
| [2] | BAO Chunzhu, XIANG Zhonghua. Pyrolysis-free Strategy of Covalent Organic Polymers-based Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalytic Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220715. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, QU Gan, XUE Dongping, YAN Wenfu, ZHANG Jianan. Recent Process of Carbon-based Catalysts for the Production of H2O2 by Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction: Strategies, Calculation and Practical Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220775. |
| [4] | LI Ruisong, MIAO Zhengpei, LI Jing, TIAN Xinlong. Research Progress on Hollow Precious Metal-based Nanostructures for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 190. |
| [5] | LI Ziruo, ZHANG Hongjuan, ZHU Guoxun, XIA Wei, TANG Jing. Iron Phthalocyanine Coated Nitrogen-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres for Efficient Catalysis of Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220677. |
| [6] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [7] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [8] | GU Yu, XI Baojuan, LI Jiangxiao, XIONG Shenglin. Structure Regulation of Single-atom Catalysts in Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220036. |
| [9] | HU Huimin, CUI Jing, LIU Dandan, SONG Jiaxin, ZHANG Ning, FAN Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Zhen, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean. Influence of Different Transition Metal Decoration on the Propane Dehydrogenation Performance over Pt/M-DMSN Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210815. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, XUE Dongping, DU Yu, JIANG Su, WEI Yifan, YAN Wenfu, XIA Huicong, ZHANG Jianan. MOF-derived Carbon-based Electrocatalysts Confinement Catalyst on O2 Reduction and CO2 Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [11] | HE Yujing, LI Jiale, WANG Dongyang, WANG Fuling, XIAO Zuoxu, CHEN Yanli. Zinc-based Activated Fe/Co/N Doped Biomass Carbon Electrocatalysts with High Oxygen Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [12] | MA Jun, ZHONG Yang, ZHANG Shanshan, HUANG Yijun, ZHANG Lipeng, LI Yaping, SUN Xiaoming, XIA Zhenhai. Design and Theoretical Calculation of Heteroatoms Doped Graphdiyne Towards Efficiently Catalyzing Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 624. |
| [13] | WANG Yuemin, MENG Qinglei, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Enhancement of Performance of Fe-N-C Catalysts by Copper and Sulfur Doping for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1843. |
| [14] | YIN Wenjing, LIU Xiao, QIAN Huidong, ZOU Zhiqing. Preparation and Oxygen Reduction Performance of Fe, N co-Doped arbon Nanoplate with High Density of Active Sites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1480. |
| [15] | XU Zhaoquan, MA Junhong, SHI Minhui, FENG Chao, XIE Yahong, MI Hongyu. Preparation and Application of a Novel Natural Product-based Fe and N Codoped Carbon Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1532. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||