

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (10): 2174.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200272
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Rui1,2, HUANG Xinsong1, LIU Tian⁃Fu1( ), CAO Rong1(
), CAO Rong1( )
)
Received:2020-05-20
Online:2020-10-10
Published:2020-10-08
Contact:
LIU Tian?Fu,CAO Rong
E-mail:tfliu@fjirsm.ac.cn;rcao@fjirsm.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Rui, HUANG Xinsong, LIU Tian⁃Fu, CAO Rong. Metal-organic Frameworks for CO Oxidation[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(10): 2174.
| Entry | Catalyst | Active species | Feed gas and volume ratio | GHSVa/ (mL·h?1·g?1) | T50b/℃ | T100c/℃ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Cu(mipt)(H2O)](H2O)2 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | NDd | 200 | [ |
| 2 | [Cu5(OH)2(nip)4(H2O)6](H2O)4.25 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | 155 | 200 | [ |
| 3 | Cu3(OH)(C4H2N2O2)3 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/Ar, 1/6/93 | 30000 | ND | 230 | [ |
| 4 | CuBTC?443 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/98.5 | 30000 | ND | 240 | [ |
| 5 | CuBTC?503 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/98.5 | 30000 | ND | 200 | [ |
| 6 | CuBTC?523 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/98.5 | 30000 | ND | 170 | [ |
| 7 | CuBTC?553 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/78 | 30000 | ND | 290 | [ |
| 8 | FDM?3 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 200 | 220 | [ |
| 9 | FDM?4 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 180 | 210 | [ |
| 10 | FDM?5 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 215 | ND | [ |
| 11 | FDM?6 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/24/78 | 30000 | 195 | 220 | [ |
| 12 | FDM?7 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/24/78 | 30000 | 190 | 220 | [ |
| 13 | 2% Cu?MIL?101 | Cu NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 275 | 289 | [ |
| 14 | Cu?BTC(C?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | ND | [ |
| 15 | Cu?BTC(R?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | 240 | [ |
| 16 | Cu?BTC(O?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | 260 | [ |
| 17 | Cu?BTC(W?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | ND | [ |
| Entry | Catalyst | Active species | Feed gas and volume ratio | GHSVa/ (mL·h?1·g?1) | T50b/℃ | T100c/℃ | Ref. |
| 18 | Cu?BTC(S?350) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 190 | [ |
| 19 | Cu?BTC(S?400) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 190 | [ |
| 20 | Cu?BTC(S?500) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 155 | [ |
| 21 | Cu?BTC(S?600) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 185 | [ |
| 22 | Cu?BTC(S?700) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 170 | [ |
| 23 | Cu?BTC(CO?240) | Cu2O | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 110 | 145 | [ |
| 24 | Cu?BTC(Ar?240) | ND | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 237 | 255 | [ |
| 25 | Cu?BTC(O2?240) | CuO | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 144 | 170 | [ |
| 26 | Cu?BTC(H2?240) | ND | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 245 | 255 | [ |
| 27 | CoMOF?74 | Co(II) | CO/Air, 1/99 | 18000 | 84 | ND | [ |
| 28 | 20% Co/MIL?53(Al) | Co NPs | CO/Air, 3/97 | 52000 | ND | 180 | [ |
| 29 | ZIF?67(Co3O4?Ther) | Co3O4 | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 30000 | 92 | ND | [ |
| 30 | ZIF?8(Co3O4?MOF) | Co3O4 | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 30000 | 58 | 80 | [ |
| 31 | ZIF?67(Co3O4) | Co3O4 | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 120 | [ |
| 32 | [Amine][Co(HCOO)3] (Co3O4?MA) | OV, OC and Co3+ sites | CO/O2 /He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 160 | 170 | [ |
| 33 | [Amine][Co(HCOO)3] (Co3O4?DMA) | OV, OC and Co3+ sites | CO/O2 /He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 157 | 170 | [ |
| 34 | Co3(BTC)2 | Co NPs | CO/Air, 1/99 | 48000 | ND | 160 | [ |
| 35 | Ce?BTC200 | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 280 | 375 | [ |
| 36 | Ce?BTC250 | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 240 | 340 | [ |
| 37 | Ce?BTC300 | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 330 | 425 | [ |
| 38 | Ce?BTC250 after catalytic reaction | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 260 | 340 | [ |
| 39 | Ce?UiO?66(0.01?CuCe) | Ce and O vacancies | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1/50/48 | 12000 | 89 | 128 | [ |
| 40 | Ce?UiO?66(0.04?CuCe) | Ce and O vacancies | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1/50/48 | 12000 | 78 | 112 | [ |
| 41 | Ce?UiO?66(0.08?CuCe) | Ce and O vacancies | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1/50/48 | 12000 | 84 | 122 | [ |
| 42 | 0.5% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 225 | 255 | [ |
| 43 | 1.0% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 200 | ND | [ |
| 44 | 2.0% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 185 | ND | [ |
| 45 | 5.0% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 175 | 210 | [ |
| 46 | 1.5% Au@UiO?66 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 15000 | 175 | ND | [ |
| 47 | 2.8% Au@UiO?66 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 15000 | 165 | ND | [ |
| 48 | 4.0% Au@UiO?66 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 15000 | 155 | ND | [ |
| 49 | Au/MIL?101(573) | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | ND | -120 | [ |
| 50 | 5.0% Pt@MIL?101 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | ND | 150 | [ |
| 51 | Pt/N?UiO?67 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 120000 | 100 | 120 | [ |
| 52 | Pt/UiO?67 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 120000 | 130 | 140 | [ |
| 53 | Pt/NH2?UiO?67 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 120000 | 145 | 150 | [ |
| 54 | 2.7% Pd/MIL?53(Al) | Pd NPs | CO/O2/Ar, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 100 | 115 | [ |
| 55 | 5% Pd/Ce?MOF | Pd NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 240000 | 77 | 92 | [ |
| 56 | 1% Pd/Cu3(BTC)2?P | PdO2 NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 24000 | ND | 220 | [ |
| 57 | 2.9% Pd@MIL?101 | Pd NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 97 | 147 | [ |
| 58 | 4.9% Pd@MIL?101 | Pd NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 92 | 407 | [ |
| 59 | Ce?HKUST?1 | CuO?CeO2 | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 109800 | 124 | 170 | [ |
| 60 | 0.5% Pd + 2%Cu?MIL?10 | PdCu NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 175 | 180 | [ |
| 61 | 1% Pd + 2%Cu?MIL?101 | PdCu NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 146 | 152 | [ |
| 62 | ZIF?67(Pt@Co3O4) | Pt NPs and Co3O4 | CO/O2 /He, 1.5/30/60 | 109800 | ND | 110 | [ |
| 63 | ZIF?67(Co3O4) | Pt NPs and Co3O4 | CO/O2 /He, 1.5/30/60 | 109800 | ND | 145 | [ |
| 64 | Cu3(BTC)2(5%?CuO/CeO2?600) | CuO/CeO | CO/O2/H2/N2, 2/3.3/50/47.7 | 18000 | ND | 140 | [ |
| 65 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?Fe) | Olatt/Oads | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | 132 | 160 | [ |
| 66 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?Fe2O3) | ND | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | 180 | 215 | [ |
| 67 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?PB) | ND | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | >350 | >350 | [ |
| 68 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?Fe) | ND | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | 230 | 275 | [ |
| 69 | Ce?BTC(CeO2/CuO?400) | CeO2/CuO | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1.7/50/47.3 | 18000 | ND | 110 | [ |
Table 1 Summary of MOFs and MOF-based catalysts(classified by elements) for CO oxidation
| Entry | Catalyst | Active species | Feed gas and volume ratio | GHSVa/ (mL·h?1·g?1) | T50b/℃ | T100c/℃ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Cu(mipt)(H2O)](H2O)2 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | NDd | 200 | [ |
| 2 | [Cu5(OH)2(nip)4(H2O)6](H2O)4.25 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | 155 | 200 | [ |
| 3 | Cu3(OH)(C4H2N2O2)3 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/Ar, 1/6/93 | 30000 | ND | 230 | [ |
| 4 | CuBTC?443 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/98.5 | 30000 | ND | 240 | [ |
| 5 | CuBTC?503 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/98.5 | 30000 | ND | 200 | [ |
| 6 | CuBTC?523 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/98.5 | 30000 | ND | 170 | [ |
| 7 | CuBTC?553 | Cu(II) | CO/O2/N2, 1/0.5/78 | 30000 | ND | 290 | [ |
| 8 | FDM?3 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 200 | 220 | [ |
| 9 | FDM?4 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 180 | 210 | [ |
| 10 | FDM?5 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 215 | ND | [ |
| 11 | FDM?6 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/24/78 | 30000 | 195 | 220 | [ |
| 12 | FDM?7 | Cu(I) | CO/O2/N2, 1/24/78 | 30000 | 190 | 220 | [ |
| 13 | 2% Cu?MIL?101 | Cu NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 275 | 289 | [ |
| 14 | Cu?BTC(C?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | ND | [ |
| 15 | Cu?BTC(R?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | 240 | [ |
| 16 | Cu?BTC(O?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | 260 | [ |
| 17 | Cu?BTC(W?CuO/Cu2O) | CuO/Cu2O | CO/O2/He, 5/30/100 | 13500 | ND | ND | [ |
| Entry | Catalyst | Active species | Feed gas and volume ratio | GHSVa/ (mL·h?1·g?1) | T50b/℃ | T100c/℃ | Ref. |
| 18 | Cu?BTC(S?350) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 190 | [ |
| 19 | Cu?BTC(S?400) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 190 | [ |
| 20 | Cu?BTC(S?500) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 155 | [ |
| 21 | Cu?BTC(S?600) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 185 | [ |
| 22 | Cu?BTC(S?700) | Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO interface | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 170 | [ |
| 23 | Cu?BTC(CO?240) | Cu2O | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 110 | 145 | [ |
| 24 | Cu?BTC(Ar?240) | ND | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 237 | 255 | [ |
| 25 | Cu?BTC(O2?240) | CuO | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 144 | 170 | [ |
| 26 | Cu?BTC(H2?240) | ND | CO/O2/N2, 1/20/79 | 24000 | 245 | 255 | [ |
| 27 | CoMOF?74 | Co(II) | CO/Air, 1/99 | 18000 | 84 | ND | [ |
| 28 | 20% Co/MIL?53(Al) | Co NPs | CO/Air, 3/97 | 52000 | ND | 180 | [ |
| 29 | ZIF?67(Co3O4?Ther) | Co3O4 | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 30000 | 92 | ND | [ |
| 30 | ZIF?8(Co3O4?MOF) | Co3O4 | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 30000 | 58 | 80 | [ |
| 31 | ZIF?67(Co3O4) | Co3O4 | CO/Air, 1/99 | 36000 | ND | 120 | [ |
| 32 | [Amine][Co(HCOO)3] (Co3O4?MA) | OV, OC and Co3+ sites | CO/O2 /He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 160 | 170 | [ |
| 33 | [Amine][Co(HCOO)3] (Co3O4?DMA) | OV, OC and Co3+ sites | CO/O2 /He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 157 | 170 | [ |
| 34 | Co3(BTC)2 | Co NPs | CO/Air, 1/99 | 48000 | ND | 160 | [ |
| 35 | Ce?BTC200 | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 280 | 375 | [ |
| 36 | Ce?BTC250 | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 240 | 340 | [ |
| 37 | Ce?BTC300 | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 330 | 425 | [ |
| 38 | Ce?BTC250 after catalytic reaction | Ce3+ and O vacancies | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 260 | 340 | [ |
| 39 | Ce?UiO?66(0.01?CuCe) | Ce and O vacancies | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1/50/48 | 12000 | 89 | 128 | [ |
| 40 | Ce?UiO?66(0.04?CuCe) | Ce and O vacancies | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1/50/48 | 12000 | 78 | 112 | [ |
| 41 | Ce?UiO?66(0.08?CuCe) | Ce and O vacancies | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1/50/48 | 12000 | 84 | 122 | [ |
| 42 | 0.5% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 225 | 255 | [ |
| 43 | 1.0% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 200 | ND | [ |
| 44 | 2.0% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 185 | ND | [ |
| 45 | 5.0% Au@ZIF?8 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 60000 | 175 | 210 | [ |
| 46 | 1.5% Au@UiO?66 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 15000 | 175 | ND | [ |
| 47 | 2.8% Au@UiO?66 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 15000 | 165 | ND | [ |
| 48 | 4.0% Au@UiO?66 | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 15000 | 155 | ND | [ |
| 49 | Au/MIL?101(573) | Au NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | ND | -120 | [ |
| 50 | 5.0% Pt@MIL?101 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 20000 | ND | 150 | [ |
| 51 | Pt/N?UiO?67 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 120000 | 100 | 120 | [ |
| 52 | Pt/UiO?67 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 120000 | 130 | 140 | [ |
| 53 | Pt/NH2?UiO?67 | Pt NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 120000 | 145 | 150 | [ |
| 54 | 2.7% Pd/MIL?53(Al) | Pd NPs | CO/O2/Ar, 1/21/78 | 30000 | 100 | 115 | [ |
| 55 | 5% Pd/Ce?MOF | Pd NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 240000 | 77 | 92 | [ |
| 56 | 1% Pd/Cu3(BTC)2?P | PdO2 NPs | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 24000 | ND | 220 | [ |
| 57 | 2.9% Pd@MIL?101 | Pd NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 97 | 147 | [ |
| 58 | 4.9% Pd@MIL?101 | Pd NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 92 | 407 | [ |
| 59 | Ce?HKUST?1 | CuO?CeO2 | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 109800 | 124 | 170 | [ |
| 60 | 0.5% Pd + 2%Cu?MIL?10 | PdCu NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 175 | 180 | [ |
| 61 | 1% Pd + 2%Cu?MIL?101 | PdCu NPs | CO/O2/He, 4/20/76 | 120000 | 146 | 152 | [ |
| 62 | ZIF?67(Pt@Co3O4) | Pt NPs and Co3O4 | CO/O2 /He, 1.5/30/60 | 109800 | ND | 110 | [ |
| 63 | ZIF?67(Co3O4) | Pt NPs and Co3O4 | CO/O2 /He, 1.5/30/60 | 109800 | ND | 145 | [ |
| 64 | Cu3(BTC)2(5%?CuO/CeO2?600) | CuO/CeO | CO/O2/H2/N2, 2/3.3/50/47.7 | 18000 | ND | 140 | [ |
| 65 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?Fe) | Olatt/Oads | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | 132 | 160 | [ |
| 66 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?Fe2O3) | ND | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | 180 | 215 | [ |
| 67 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?PB) | ND | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | >350 | >350 | [ |
| 68 | MIL?100(Fe)(Ag?Fe) | ND | CO/O2/He, 1/20/79 | 18000 | 230 | 275 | [ |
| 69 | Ce?BTC(CeO2/CuO?400) | CeO2/CuO | CO/O2/H2/N2, 1/1.7/50/47.3 | 18000 | ND | 110 | [ |
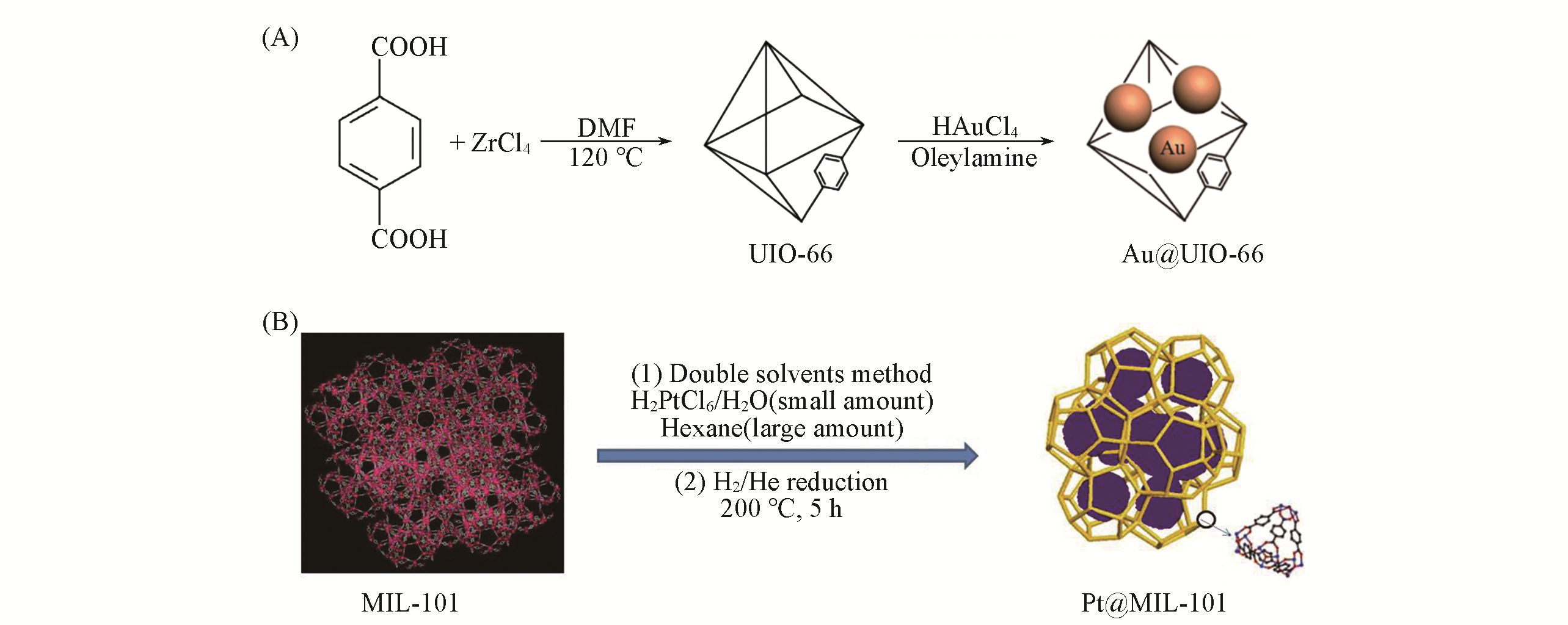
Fig.2 MNPs@MOF for CO oxidation(A) Schematic representation of synthesis of Au@UIO-66 using a one-step chemical wetting method[39]. Copyright 2013, Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Schematic representation of synthesis of Pt nanoparticles inside the MIL-101 matrix using double solvents method[41]. Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
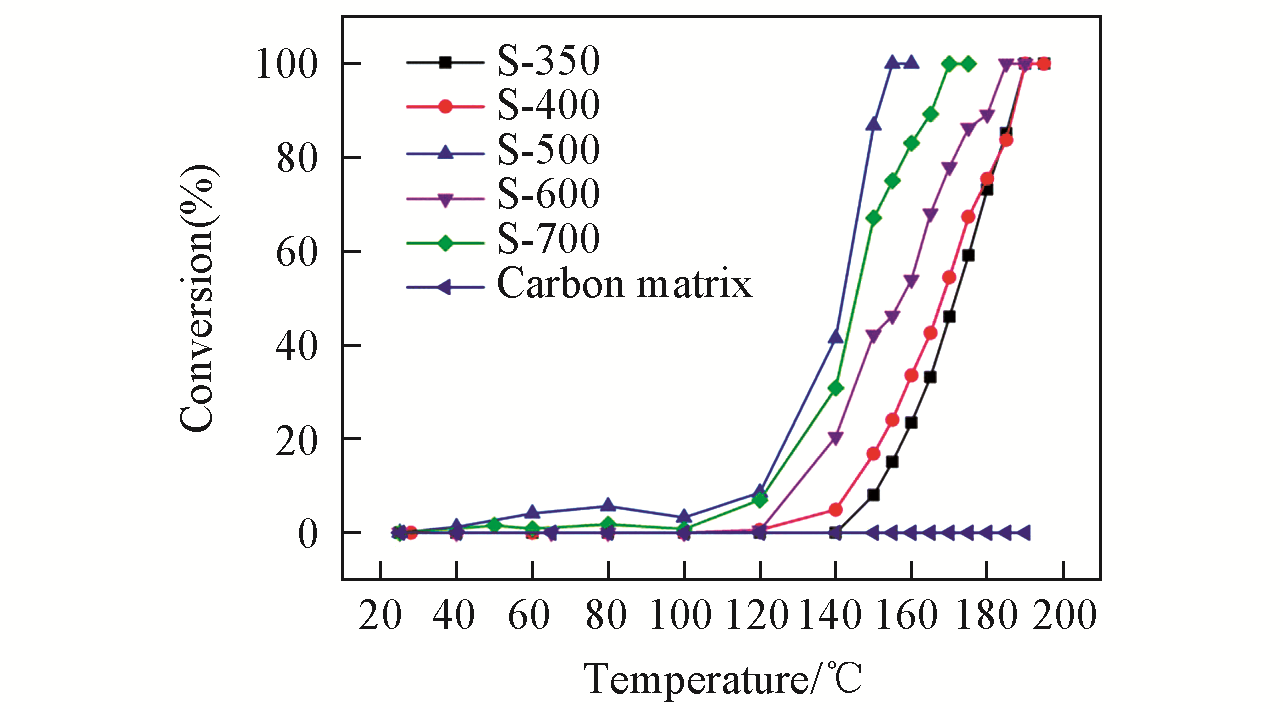
Fig.3 Metal(oxide)/carbon nanocomposites derived from MOFs[28]Temperature-programmed profiles of the 1%(volume fraction) CO oxidation for the prepared samples annealed at different temperatures. Copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry.
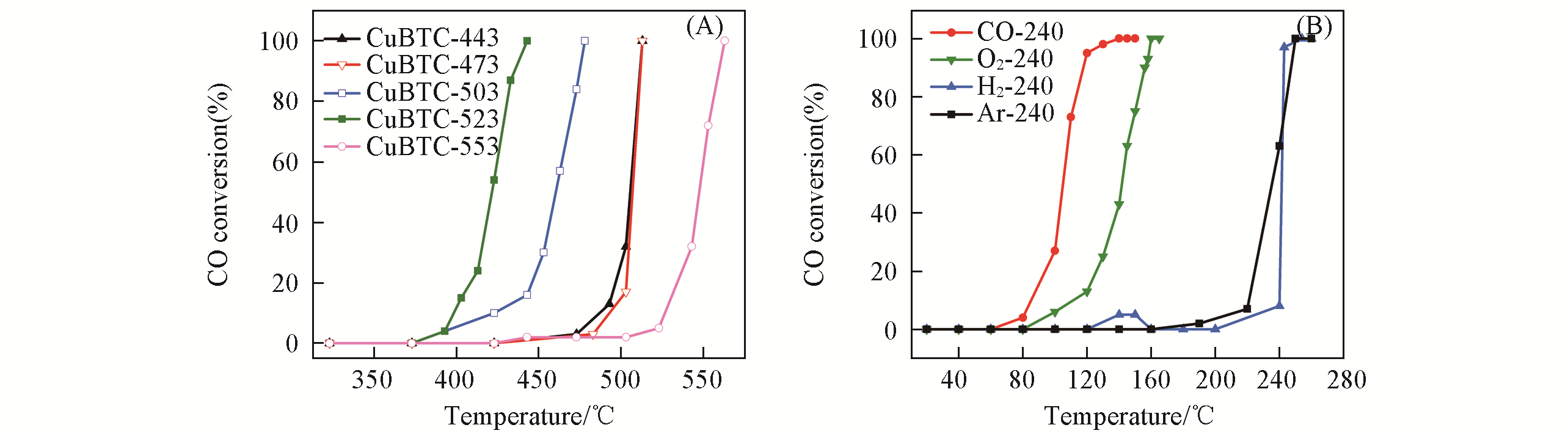
Fig.4 Effects of activation temperature and atmosphere on CO oxidation(A) CO conversion over the CuBTC catalysts activated at 443, 473, 503, 523, and 553 K, respectively. Reaction conditions: 1% CO, 0.5% O2, N2 as balance, GHSV=30000 h?1. Redrawn based on the information and description from Ref.[24]. (B) CO conversion over G-240(G for Ar, H2, O2, and CO reaction gas). Redrawn based on the information and description from Ref.[29].
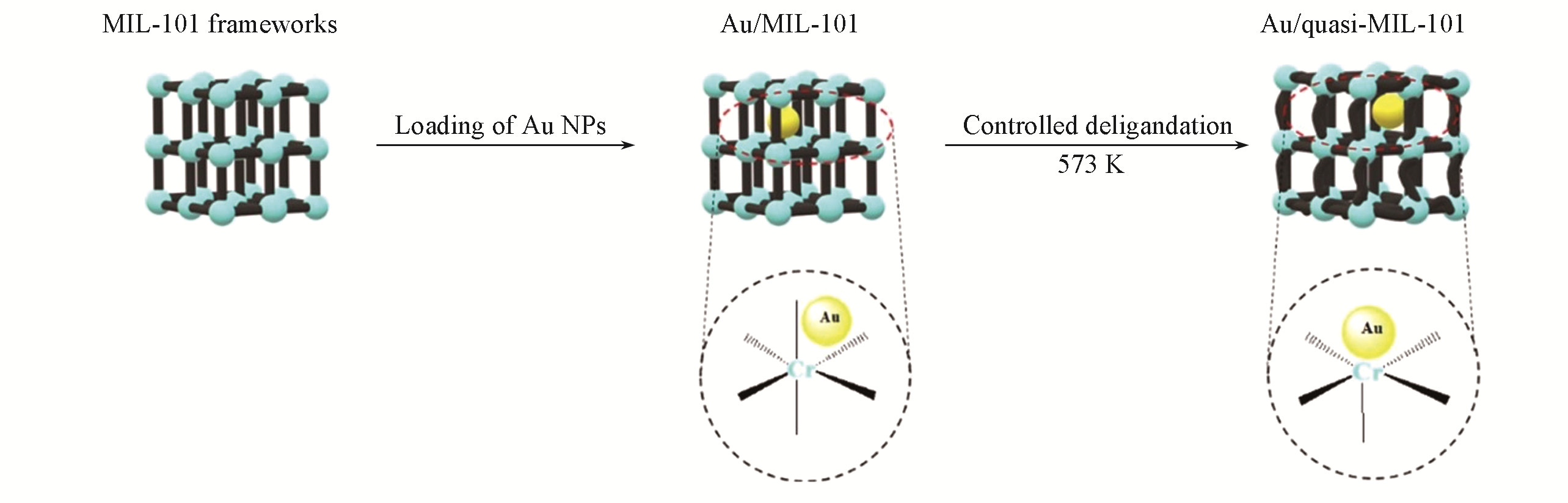
Fig.5 Impacts of calcination temperature on the formed crystal structureSchematic illustration showing the synthesis of Au/quasi-MIL-101 through controlled deligandation of Au/MIL-101. Redrawn based on the information and description from Ref.[40].
| 1 | Goldsmith J. R., Cohen S. I., J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc., 1969, 19(9), 704—713 |
| 2 | Dey S., Dhal G. C., Mohan D., Prasad R., Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal., 2017, 12(3), 1—15 |
| 3 | Lim S. S., Vos T., Flaxman A. D., Danaei, G., Shibuya K., Adair⁃Rohani H., Amann M., Lancet, 2012, 380(9859), 2224—2260 |
| 4 | Stevens G., Mascarenhas M., Mathers C., Bull. W. H. O., 2009, 87(9), 646 |
| 5 | Zhang X. B., Ma K. Y., Zhang L. H., Chin. J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 24(1), 97—102 |
| 6 | Chhatwal G. R., Mehra M. C., Nagahiro T., Environmental Air Pollution and Its Control, Anmol Publications, New Delhi, 1975 |
| 7 | Jiao L., Wang Y., Jiang H. L., Xu Q., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(37), 1703663 |
| 8 | Liu T. T., Liang J., Xu R., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(28), 4063—4066 |
| 9 | Liu T. T., Xu R., Yi J. D., Liang J., Wang X. S., Shi P. C., Huang Y. B., Cao R., ChemCatChem, 2018,10(9), 2036—2040 |
| 10 | Liang J., Xie Y. Q., Wu Q., Wang X. Y., Liu T. T., Li H. F., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Inorg. Chem., 2018, 57(5), 2584—2593 |
| 11 | Liang J., Xie Y. Q., Wang X. S., Wang Q., Liu T. T., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(4), 342—345 |
| 12 | Liang J., Chen R. P., Wang X. Y., Liu T. T., Wang X. S., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Chem. Sci., 2017, 8(2), 1570—1575 |
| 13 | Liu T. T., Liang J., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(90), 13288—13291 |
| 14 | Xu W. L., Thapa K. B., Ju Q., Fang Z. L., Huang W., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2018, 373, 199—232 |
| 15 | Eddaoudi M., Sava D. F., Eubank J. F., Adil K., Guillerm V., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(1), 228—249 |
| 16 | Cohen S. M., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(2), 970—1000 |
| 17 | O’Keeffe M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(5), 1215—1217 |
| 18 | Chang Z., Yang D. H., Xu J., Hu T. L., Bu X. H., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(36), 5432—5441 |
| 19 | Jiao L., Seow J.Y. R., Skinner W. S., Wang Z. U., Jiang H. L., Mater. Today, 2019, 27, 43—68 |
| 20 | Cui W. G., Zhang G. Y., Hu T. L., Bu X. H., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 387, 79—120 |
| 21 | Zou R. Q., Sakurai H., Han S., Zhong R. Q., Xu Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(27), 8402—8403 |
| 22 | Zhao Y., Padmanabhan M., Gong Q. H., Tsumori N., Xu Q., Li J., Chem. Commun.(Camb), 2011, 47(22), 6377—6379 |
| 23 | Su S. Q., Zhang Y. B., Zhu M., Song X. Z., Wang S., Zhao S. N., Song S. Y., Yang X. G., Zhang H. J., Chem. Commun.(Camb), 2012, 48(90), 11118—11120 |
| 24 | Qiu W., Wang Y., Li C. Q., Zhan Z. C., Zi X. H., Zhang G. Z., Wang R., He H., Chin. J. Catal., 2012, 33(6), 986—992 |
| 25 | Tu B. B., Pang Q. Q., Xu H. S., Li X. M., Wang Y. L., Ma Z., Weng L. H., Li Q. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(23), 7998—8007 |
| 26 | El⁃Shall M. S., Abdelsayed V., Khder A. E. R. S., Hassan H. M. A., El-Kaderi H. M., Reich T. E., J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19(41), 7625—7631 |
| 27 | Zhang S. Y., Liu H., Sun C. C., Liu P. F., Li L. C.,Yang Z. H., Feng X., Huo F. W., Lu X. H., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(10), 5294—5298 |
| 28 | Zhang R. R., Hu L., Bao S. X., Li R., Gao L., Li R., Chen Q. W., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(21), 8412—8420 |
| 29 | Zhang X. L., Zhan Z. B., Li Z., Di L. B., Catal., 2017, 7(12), 106 |
| 30 | Kim T., Kim D. H., Kim S., Kim Y. D., Bae Y. S., Lee C. Y., Polyhedron, 2015, 90, 18—22 |
| 31 | Tan H. Y., Wu J. P., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30(4), 715—722 |
| 32 | Wang W. X., Li Y. W., Zhang R. J., He D. H., Liu H. L., Liao S. J., Catal. Commun., 2011, 12(10), 875—879 |
| 33 | Zheng F. C., Yin Z. C., Xu S. H., Zhang Y. G., Mater. Lett., 2016, 182, 214—217 |
| 34 | Zhang C., Zhang L., Xu G. C., Ma X., Li Y. H., Zhang C. H., Jia D. Z., New J. Chem., 2017, 41(4), 1631—1636 |
| 35 | Tan H., Liu C., Yan Y., Wu J., J. Wuhan Univ. Technol., Mater. Sci. Ed., 2015, 30(1), 71—75 |
| 36 | Zhang X. D., Hou F. L., Li H. X., Yang Y., Wang Y. X., Liu N., Yang Y. Q., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2018, 259, 211—219 |
| 37 | Zhu C. L., Ding T., Gao W. X., Ma K., Tian Y., Li X. G., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(27), 17457—17465 |
| 38 | Jiang H. L., Liu B., Akita T., Haruta M., Sakurai H., Xu Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(32), 11302—11303 |
| 39 | Wu R. B., Qian X. K., Zhou K., Liu H., Yadian B., Wei J., Zhu H. W., Huang Y. Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(45), 14294—14299 |
| 40 | Tsumori N., Chen L. Y., Wang Q. J., Zhu Q. L., Kitta M., Xu Q., Chem., 2018, 4(4), 845—856 |
| 41 | Aijaz A., Karkamkar A., Choi Y. J., Tsumori N., Ronnebro E., Autrey T., Shioyama H., Xu Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(34), 13926—13929 |
| 42 | Zhuang G. L., Bai J. Q., Zhou X. Gao Y. F., Huang H. L., Cui H. Q., Zhong X., Zhong C. L., Wang J. G., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2017, 2017(1), 172—178 |
| 43 | Liang Q., Zhao Z., Liu J., Wei Y. C., Jiang G. Y., Duan A. J., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30(1), 129—134 |
| 44 | Lin A., Ibrahim A. A., Arab P., El⁃Kaderi H. M., El⁃Shall M. S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(21), 17961—17968 |
| 45 | Ye J. Y., Liu C. J., Chem. Commun.(Camb), 2011, 47(7), 2167—2169 |
| 46 | Zamaro J. M., Perez N.C., Miro E. E., Casado C., Seoane B., Tellez C., Coronas J., Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 195, 180—187 |
| 47 | Ji W. L., Xu Z. L., Liu P.F., Zhang S. Y., Zhou W. Q., Li H. F., Zhang T., Li L. J., Lu X. H., Wu J. S., Zhang W. N., Huo F. W., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(18), 15394—15398 |
| 48 | Zhang F., Chen C., Xiao W. M., Zhang N., Catal. Commun., 2012, 26, 25—29 |
| 49 | Zhang X., Yang Y., Lv X., Wang Y., Cui L., Catal., 2017, 7(12), 382—394 |
| 50 | Chen C., Wang R., Shen P., Zhao D., Zhang N., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(14), 4830—4839 |
| 51 | Huang T. J., Tsai D. H., Catal. Lett., 2003, 87, 173—178 |
| 52 | Wu C. D., Zhao M., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(14), 1605446 |
| 53 | Xiang S. C., Zhou W., Zhang Z. J., Green M. A., Liu Y., Chen B. L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 122(27), 4719—4722 |
| 54 | Park K. S., Ni Z., Cote A. P., Choi J. Y., Huang R. D., Uribe⁃Romo F. J., Chae H. K., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2006, 103(27), 10186—10191 |
| 55 | Cavka J. H., Jakobsen S., Olsbye U., Guillou N., Lamberti C., Bordiga S., Lillerud K. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(42), 13850—13851 |
| 56 | Schaate A., Roy P., Godt A., Lippke J., Waltz F., Wiebcke M., Behrens P., Chem. Eur. J., 2011, 17(24), 6643—6651 |
| 57 | Lu G., Cui C. L., Zhang W. N., Liu Y. Y., Huo F. W., Chem. Asian J., 2013, 8(1), 69—72 |
| 58 | Ferey G., Mellot-Draznieks C., Serre C., Millange F., Dutour J., Surble S., Margiolaki I., Science, 2005, 309(5743), 2040—2042 |
| 59 | Noei H., Amirjalayer S., Müller M., Zhang X. N., Schmid R., Muhler M., Fischer R. A., Wang Y. M., ChemCatChem, 2012, 4(6), 755—759 |
| [1] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [2] | LU Cong, LI Zhenhua, LIU Jinlu, HUA Jia, LI Guanghua, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescence Detection Properties of a New Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220037. |
| [3] | TIAN Xueqin, MO Zheng, DING Xin, WU Pengyan, WANG Yu, WANG Jian. A Squaramide-containing Luminescent Metal-organic Framework as a High Selective Sensor for Histidine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210589. |
| [4] | XING Peiqi, LU Tong, LI Guanghua, WANG Liyan. Controllable Syntheses of Two Cd(II) Metal-organic Frameworks Possessing Related Structures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220218. |
| [5] | MO Zongwen, ZHANG Xuewen, ZHOU Haolong, ZHOU Dongdong, ZHANG Jiepeng. Guest-responses of A Porous Coordination Polymer Based on Synergistic Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210576. |
| [6] | LIU Xueguang, YANG Xiaoshan, MA Jingjing, LIU Weisheng. Separating Methyl Blue Selectively from the Mixture of Dyes by Europium Metal-organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210715. |
| [7] | SHI Xiaofan, ZHU Jian, BAI Tianyu, FU Zixuan, ZHANG Jijie, BU Xianhe. Research Status and Progress of MOFs with Application in Photoelectrochemical Water-splitting [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210613. |
| [8] | WU Ji, ZHANG Hao, LUO Yuhui, GENG Wuyue, LAN Yaqian. A Microporous Cationic Ga(III)-MOF with Fluorescence Properties for Selective sensing Fe3+ Ion and Nitroaromatic Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210617. |
| [9] | LI Wen, QIAO Junyi, LIU Xinyao, LIU Yunling. Zirconium-based Metal-Organic Framework with Naphthalene for Fluorescent Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210654. |
| [10] | WANG Jie, HUO Haiyan, WANG Yang, ZHANG Zhong, LIU Shuxia. General Strategy for In situ Synthesis of NENU-n Series Polyoxometalate-based MOFs on Copper Foil [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210557. |
| [11] | HAN Zongsu, YU Xiaoyong, MIN Hui, SHI Wei, CHENG Peng. A Rare Earth Metal-Organic Framework with H6TTAB Ligand [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210342. |
| [12] | LI Shurong, WANG Lin, CHEN Yuzhen, JIANG Hailong. Research Progress of Metal⁃organic Frameworks on Liquid Phase Catalytic Chemical Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [14] | GAO Zhongnan, GUO Lihong, ZHAO Dongyue, LI Xingang. Effect of A Site-deficiency on the Structure and Catalytic Oxidation Activity of the La-Sr-Co-O Perovskite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2869. |
| [15] | ZHANG Renli, WANG Yao, YU Zhiquan, SUN Zhichao, WANG Anjie, LIU Yingya. Molybdenum Peroxide Anchored on Fluoronated UiO-66 as Catalyst in the Oxidation of Sulfur Containing Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1914. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||