

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 2534.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190392
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ying MA1,Tian WANG2,Heng ZHANG1,*( )
)
Received:2019-07-15
Online:2019-12-04
Published:2019-12-04
Contact:
Heng ZHANG
E-mail:zhangheng@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
Ying MA,Tian WANG,Heng ZHANG. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Adsorption of Methylene Blue by Graphene Oxide †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2534.
| Site | Graphene oxide | Site | Methylene blue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e | σ/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e | ||
| C(graphene) | 0.355 | 0.293 | 0 | N(in N—CH3) | 0.325 | 0.711 | 0.216 |
| C(—COO-) | 0.375 | 0.439 | 0.700 | C(in N—CH3) | 0.380 | 0.209 | -0.323 |
| O(—COO-) | 0.296 | 0.879 | -0.900 | H(in N—CH3) | 0.250 | 0.125 | 0.137 |
| C(—C—O—) | 0.350 | 0.276 | 0.196 | S | 0.355 | 1.046 | -0.689 |
| O(-O-) | 0.290 | 0.586 | -0.393 | N(in middle) | 0.325 | 0.711 | -0.226 |
| O(—OH) | 0.307 | 0.711 | -0.592 | ||||
| H(—OH) | 0 | 0 | 0.329 | ||||
| Site | Graphene oxide | Site | Methylene blue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e | σ/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e | ||
| C(graphene) | 0.355 | 0.293 | 0 | N(in N—CH3) | 0.325 | 0.711 | 0.216 |
| C(—COO-) | 0.375 | 0.439 | 0.700 | C(in N—CH3) | 0.380 | 0.209 | -0.323 |
| O(—COO-) | 0.296 | 0.879 | -0.900 | H(in N—CH3) | 0.250 | 0.125 | 0.137 |
| C(—C—O—) | 0.350 | 0.276 | 0.196 | S | 0.355 | 1.046 | -0.689 |
| O(-O-) | 0.290 | 0.586 | -0.393 | N(in middle) | 0.325 | 0.711 | -0.226 |
| O(—OH) | 0.307 | 0.711 | -0.592 | ||||
| H(—OH) | 0 | 0 | 0.329 | ||||
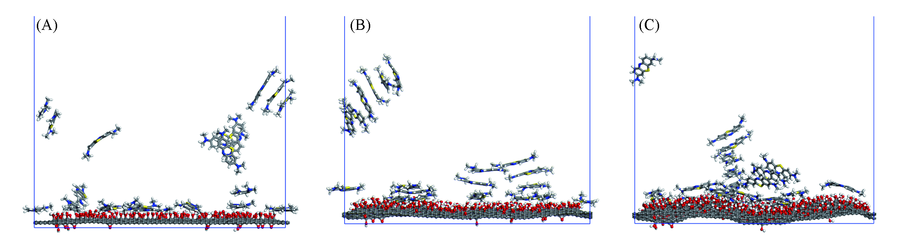
Fig.2 Adsorption of methylene blue on graphene oxide of GO10(A), GO20(B) and GO30(C) systems The water molecules in the system are removed for clarity.
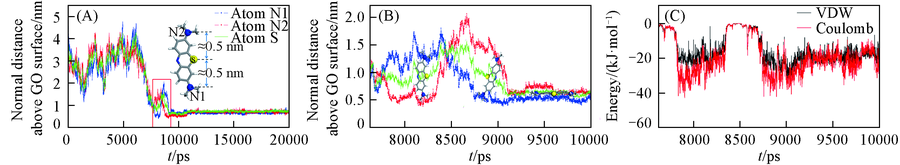
Fig.3 Trajectory displacement of methylene blue in the z direction changes with time evolution(A), local amplifications of trajectory displacement (A)(B) and the change of potential energy between amino groups of methylene blue and GO30 graphene oxide with time evolution(C)
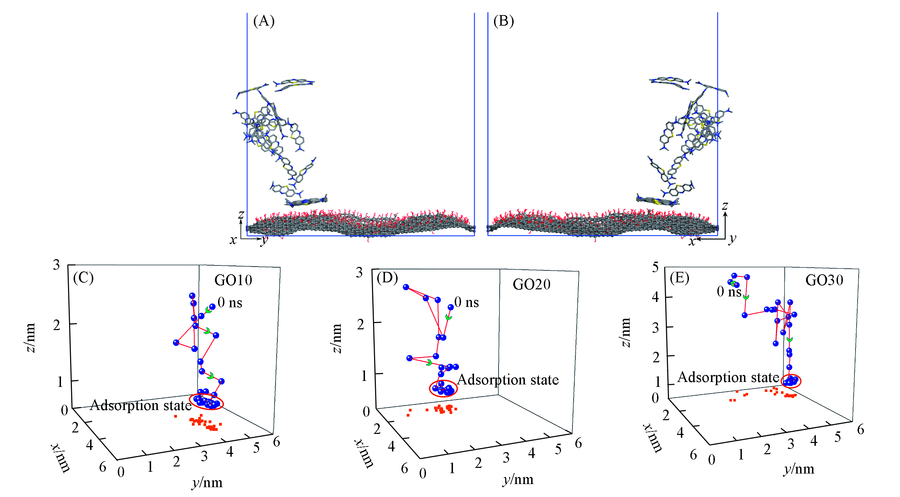
Fig.4 Side view of partial enlargements of the trajectory displacement of a methylene blue in the z direction(A), the opposite side view of a diagram(B), three-dimensional spatial coordinates of a methylene blue adsorption process change with time of GO10(C), GO20(D) and GO30(E) systems
| System | 105D/(cm2·s-1) | τr/ns |
|---|---|---|
| GO10 | 0.03±0.01 | 3.31 |
| GO20 | 0.007±0.005 | 4.94 |
| GO30 | 0.0057±0.004 | 6.16 |
| System | 105D/(cm2·s-1) | τr/ns |
|---|---|---|
| GO10 | 0.03±0.01 | 3.31 |
| GO20 | 0.007±0.005 | 4.94 |
| GO30 | 0.0057±0.004 | 6.16 |
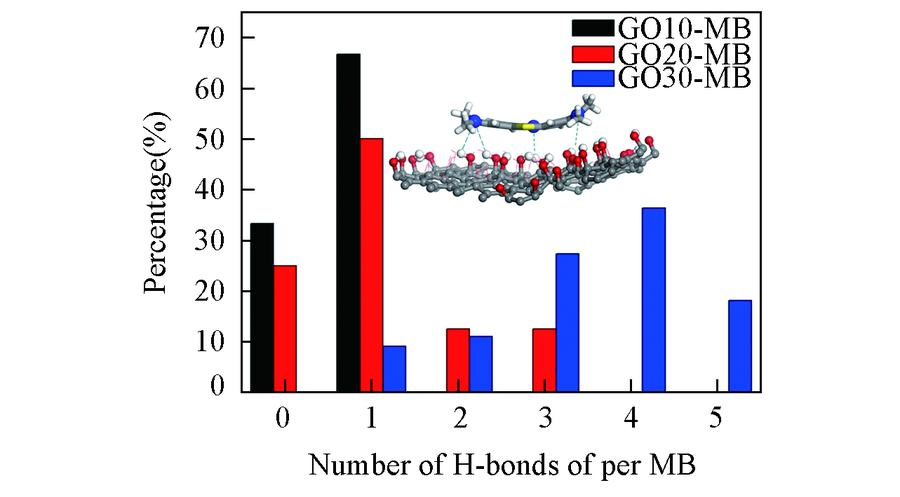
Fig.7 Hydrogen bond number distribution between methylene blue and graphene oxide in adsorption layer Inset: the microscopic structure of hydrogen bonds.
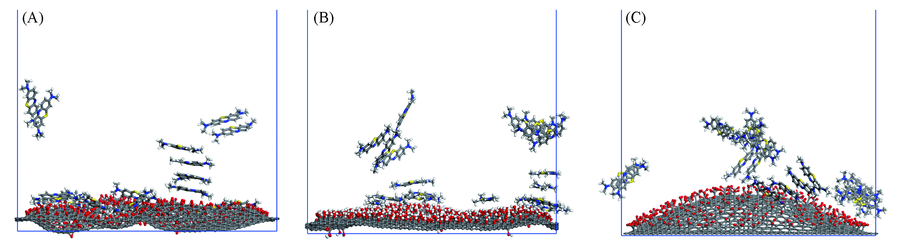
Fig.8 Adsorption of methylene blue on graphene oxide of GO20-O(A), GO20-OH(B) and GO20-COO system(C) The water molecules in the system are removed for clarity.
| [1] |
Wang C., Shi Z. H., Peng L., He W. M., Li B. L., Li K. Z ., Surfaces & Interfaces, 2017,7, 116— 124
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.096 URL pmid: 31830629 |
| [2] |
Krika F., Benlahbib O. E. F ., Desalination & Water Treatment, 2015,53(13), 3711— 3723
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b04823 URL pmid: 31829572 |
| [3] |
Isloor A. M., Shenvi S. S., Ismail A. F., Shilton S. J., Al-Ahmad A ., Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015,54(18), 4965— 4975
doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.112710 URL pmid: 31829531 |
| [4] |
Mouzdahir Y. E., Elmchaouri A., Mahboub R., Gil A., Korili S. A ., J. Chem. Engin. Data, 2007,52(5), 1621— 1625
doi: 10.1021/je700008g URL |
| [5] |
Cheah W., Hosseini S., Khan M. A., Chuah T. G., Choong T. S. Y ., Chem. Engin. J., 2013,215/216(3), 747— 754
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.004 URL |
| [6] |
And C. D., Israelachvili J ., Macromolecules, 2000,33(13), 4910— 4920
doi: 10.1021/ma9919918 URL |
| [7] |
Sheng J., Xie Y., Yan Z ., Applied Clay Science, 2009,46(4), 422— 424
doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.10.006 URL |
| [8] |
Senthilkumaar S., Varadarajan P. R., Porkodi K., Subbhuraam C. V ., J. Colloid & Interface Science, 2005,284(1), 78— 82
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.122 URL pmid: 31830737 |
| [9] |
Wang S., Zhu Z. H ., J. Hazardous Mater., 2006,136(3), 946— 952
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.038 URL pmid: 16504394 |
| [10] |
Da C., Hongbin F., Jinghong L ., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(11), 6027— 6053
doi: 10.1021/cr300115g URL pmid: 22889102 |
| [11] |
Ramesha G. K., Kumara A. V., Muralidhara H. B., Sampath S ., J. Colloid & Interface Science, 2011,361(1), 270— 277
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.122 URL pmid: 31830737 |
| [12] |
Sun Y., Wang Q., Chen C., Tan X., Wang X ., Environmental Science & Technology, 2012,46(11), 6020— 6027
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1875-y URL pmid: 31830756 |
| [13] |
Bradder P., Ling S. K., Wang S., Liu S ., J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2011,56(1), 138— 141
doi: 10.1021/je101049g URL |
| [14] |
Zhang W., Zhou C., Zhou W., Lei A., Zhang Q., Wan Q., Zou B ., Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2011,87(1), 86— 90
doi: 10.1007/s00128-011-0304-1 URL pmid: 21567134 |
| [15] |
Pei Z., Li L., Sun L., Zhang S., Shan X. Q., Shuang Y., Bei W ., Carbon, 2013,51(1), 156— 163
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.08.024 URL |
| [16] |
Han Y., Xue T., Zhen Y., Li K., Hu Y., Li A., Cheng R ., J. Hazardous Mater., 2014,268(268), 191— 198
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.015 URL pmid: 24491443 |
| [17] | Liu S. S., Zheng H., Wang H., Yuan S. L., Hou S. F ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017,38(1), 63— 71 |
| ( 刘沙沙, 张恒, 王华, 苑世领, 侯士峰 . 高等学校化学学报, 2017,38(1), 63— 71) | |
| [18] |
Jorgensen W. L., Maxwell D. S., Tirado-Rives J ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996,118(45), 11225— 11236
doi: 10.1021/ja9621760 URL |
| [19] |
Van Der Spoel D., Lindahl E., Hess B., Groenhof G., Mark A. E., Berendsen H. J ., J. Comput. Chem., 2005,26(16), 1701— 1718
doi: 10.1002/jcc.20291 URL pmid: 16211538 |
| [20] |
Guo K., Zheng H., Sun J. C., Yuan S. L., Liu C. B ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015,36(11), 2171— 2178
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150546 URL |
|
( 郭凯, 张恒, 孙继超, 苑世领, 刘成卜 . 高等学校化学学报, 2015,36(11), 2171— 2178)
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150546 URL |
|
| [21] | Accelrys Software Inc., Materials Studio, Release 4.4, Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego, 2008 |
| [22] |
Madadrang C. J., Kim H. Y., Gao G., Wang N., Zhu J., Feng H., Gorring M ., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2012,4(3), 1186— 1193
doi: 10.1021/am201645g URL pmid: 22304446 |
| [23] |
Essmann U., Perera L., Berkowiz ML., Darden T., Lee H., Pedersen L. G ., J. Chem. Phys., 1995,103(19), 8577— 8593
doi: 10.1063/1.470117 URL |
| [24] |
Berendsen H. J. C., Postma J. P. M., van Gunsteren W. F., DiNola A., Haak J. R ., J. Chem. Phys., 1984,81(8), 3684— 3690
doi: 10.1063/1.448118 URL |
| [25] |
Hess B., Bekker H., Berendsen H. J. C., Fraaije J. G. E. M ., J. Comput. Chem., 1997,18(12), 1463— 1472
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-987X URL |
| [26] |
Qing S., Yi H., White A. D., Shaoyi J ., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010,114(49), 16625— 16631
doi: 10.1021/jp107272n URL pmid: 21086974 |
| [27] |
Yi H., Jason H., Shengfu C., Bernards M. T., Yung C., Shaoyi J ., Langmuir the ACS J. Surfaces & Colloids, 2008,24(18), 10358— 10364
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.10.034 URL pmid: 21056425 |
| [28] |
Yi H., Yung C., Hower J. C., Jie Z., Shengfu C., Shaoyi J ., Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys., 2008,10(36), 5539— 5544
doi: 10.1039/b807129b URL pmid: 18956088 |
| [29] |
Hower J. C., Yi H., Bernards M. T., Shaoyi J ., J. Chem. Phys., 2006,125(21), 214704
doi: 10.1063/1.2397681 URL pmid: 17166037 |
| [1] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [2] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [3] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [4] | CHEN Hanxiang, BIAN Shaoju, HU Bin, LI Wu. Molecular Simulation of the Osmotic Pressures for LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O Solution System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [5] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [7] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [8] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [9] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [10] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [11] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [12] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [13] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [14] | ZHU Deshuai, ZHAO Jianying, YANG Zhenghui, GUO Haiquan, GAO Lianxun. Graphene Oxide/Polyimide Composites with High Energy Storage Density Based on Multilayer Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2694. |
| [15] | LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling, LIU Chengbu. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pulsed Electric Field O/W Emulsion Demulsification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||