

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1847.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190166
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2019-03-20
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-07-16
Contact:
JIN Baokang
E-mail:bkjinhf@aliyun.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
FAN Hui, JIN Baokang. Investigation on Electrochemical Capture of CO2 by Quinone Derivatives Based on in situ FTIR Spectroelectrochemistry †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1847.
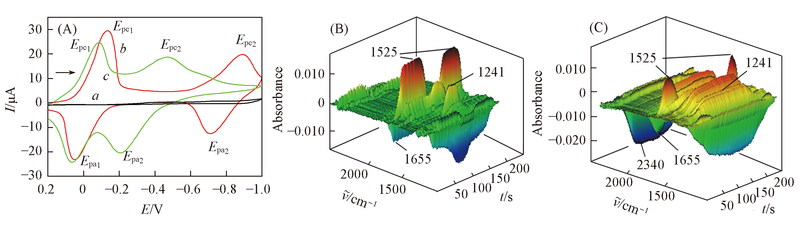
Fig.1 CV curves(A) in acetonitrile with saturated from CO2(a), DCBQ(b) and DCBQ+CO2(c) and the 3D spectra corresponding to curve b(B) and curve c(C) containing 10 mmol/L DCBQ, 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the supporting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
| System | Experimental peak position/cm-1 | Assignation | Calculated peak position/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DCBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1249, 1236 |
| 1525 | νC—C from DCBQ·- | 1521 | |
| 1655 | 1660 | ||
| DMOBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DMOBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1257, 1240 |
| 1627 | 1626, 1641 | ||
| 1697 | 1690 | ||
| CO2 | 2340 | 2346 |
| System | Experimental peak position/cm-1 | Assignation | Calculated peak position/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DCBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1249, 1236 |
| 1525 | νC—C from DCBQ·- | 1521 | |
| 1655 | 1660 | ||
| DMOBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DMOBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1257, 1240 |
| 1627 | 1626, 1641 | ||
| 1697 | 1690 | ||
| CO2 | 2340 | 2346 |
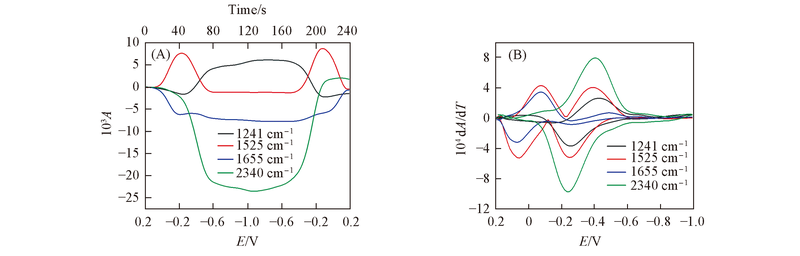
Fig.2 CVA(A) and DCVA(B) curves for DCBQ at 1241, 1525, 1655 and 2340 cm-1 To make the DCVA data readily comparable to CV, the DCVA of 1655 cm-1 and 2340 cm-1 was multiplied by -1, and 1525 cm-1 in the second reduction and first oxidation were multiplied by -1.
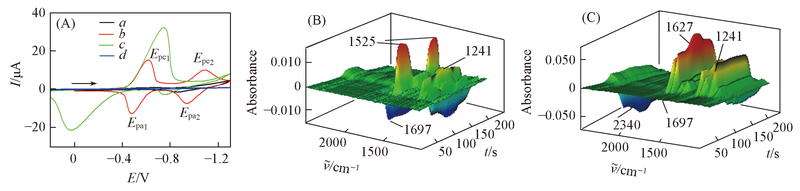
Fig.3 CV curves(A) in acetonitrile saturated from CO2(a), DMOBQ(b), DMOBQ + CO2(c) and the CV curve in acetonitrile without DMOBQ or CO2(d) and the 3D spectra corresponding to curve b(B) and curve c(C) containing 10 mmol/L DMOBQ, 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the suppor-ting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
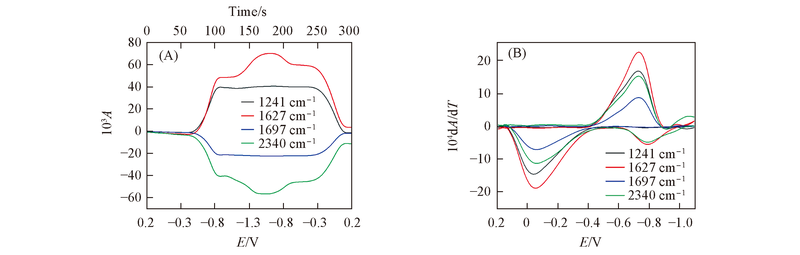
Fig.4 CVA(A) and DCVA(B) curves for DMOBQ at 1241, 1510 and 1697 cm-1 To make the DCVA data readily comparable to CV, the DCVA of 1697 cm-1 was multiplied by -1, and 1510 cm-1 in the second reduction and first oxidation were multiplied by -1.
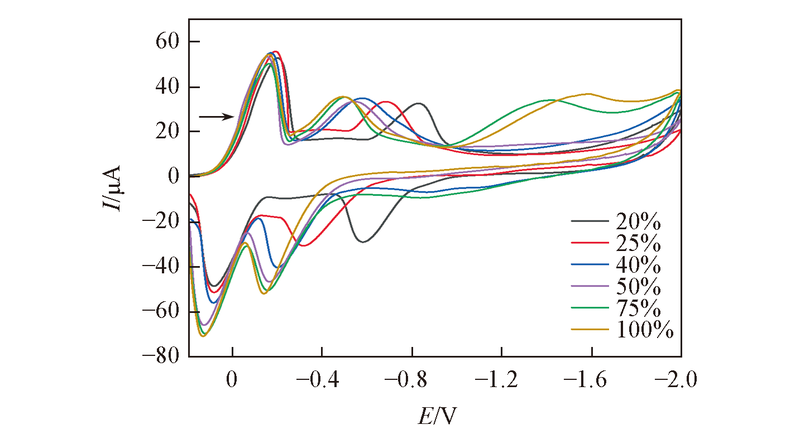
Fig.5 CV curves for DCBQ with varying percentage of saturated CO2 concentration in acetonitrile containing 20 mmol/L DCBQ and 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the supporting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
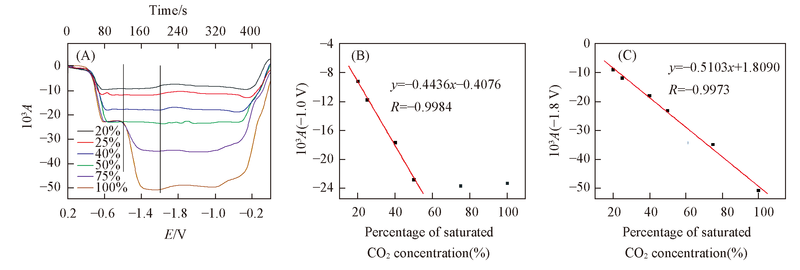
Fig.6 Corresponding CVA curve(A) for DCBQ at 2340 cm-1 and the linear fitting curve of absorbance value at 2340 cm-1 with percentage of saturated CO2 concentration at -1.00 V(B) and -1.80 V(C)
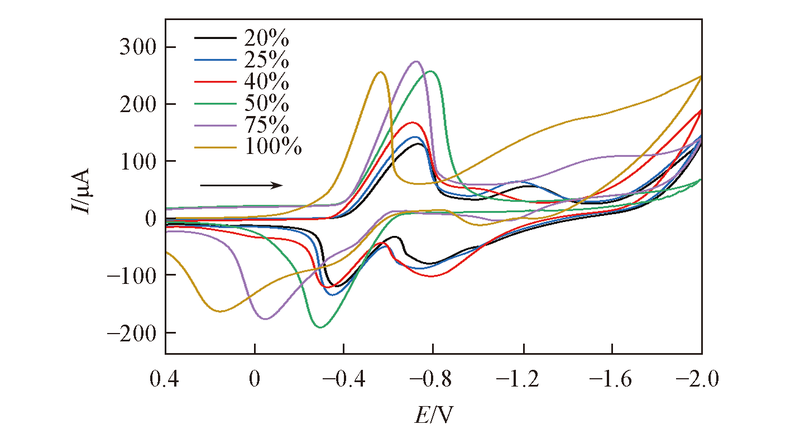
Fig.7 CV curve for DMOBQ with varying percentage of saturated CO2 concentration in acetonitrile containing 20 mmol/L DMOBQ and 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the supporting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
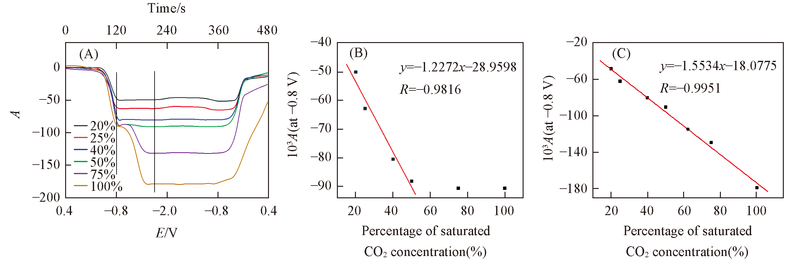
Fig.8 Corresponding CVA curve(A) for DMOBQ at 2340 cm-1 and the linear fitting curve of absorbance value at 2340 cm-1 with percentage of saturated CO2 concentration at -0.80 V(B) and-1.70 V(C)
| [1] | Ge Q. S., Liu Y., Wang F., Zheng J. Y., ,Acta Geographica Sinca, 2018,73( 1), 3— 12 |
| (葛全胜, 刘洋, 王芳, 郑景云.地理学报,2018,73(1), 3— 12) | |
| [2] | Nematollahi M. H., Carvalho P. J ., Current Opinion in Green and SustainableChemistry 2019, 18, 25— 30 |
| [3] | Liang X., Chen L. F., Zhang L., Su C. Y., ,Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018,63( 3), 248— 265 |
| (梁祥, 陈莲芬, 张利, 苏成勇, 科学通报.2018, 63(3), 248— 265) | |
| [4] | Lackner K. S., Brennan S., Matter J. M., Park A. H., Wright A., Zwaan B ., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109(33) 13156— 13162 |
| [5] | Haszeldine R. S ., Science 2009, 325( 5948), 1647— 1652 |
| [6] | Li P., Zhang J., Wang H., Hua J., Xu J., Sui X., Hu H., Yin H., ,. Catalysis Science & Technology 2014, 4( 4), 1070— 1077 |
| [7] | Li P., Wang H., Xu J., Jing H., Zhang J., Han H., Lu F ., Nanoscale 2013, 5( 23), 11748— 11754 |
| [8] | Rochelle G. T ., Science 2009, 325( 5948), 1652— 1654 |
| [9] | Wang M., Lawal A., Stephenson P., Sidders J., Ramshaw C ., Chemical Engineering Research & Design 2011, 89( 9), 1609— 1624 |
| [10] | Lu W., Ying Y., Shen W., Kong X., Ping L., Yu J., ,. Chemical Engineering Science 2013, 101( 14), 615— 619 |
| [11] | Du Y., Yuan Y., Rochelle G. T ., International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2017, 58, 1— 9 |
| [12] | Miedaner A., Curtis C. J., ,. Inorganic Chemistry 1994, 33( 24), 5482— 5490 |
| [13] | Durand W. J., Petrson A. A., Studt F., Abild-Pedersen F., Nϕrskow J. K., ,. Surface Science 2011, 605( 15), 1354— 1359 |
| [14] | Gattrell M., Gupta N., Co A., ,. Energy Conversion & Management 2007, 48( 4), 1255— 1265 |
| [15] | Li Q., Fu J., Zhu W., Chen Z., Shen B., Wu L., Xi Z., Wang T., Lu G., Zhu J. J ., Journal of the American Chemical Society 2017, 139( 12), 4290— 4293 |
| [16] | Yang D., Zhu Q., Sun X., Chen C., Han B., ,. Green Chemistry 2018, 20( 16), 3705— 3710 |
| [17] | Cao J., Lu H. Y., Chen C. F ., Tetrahedron 2009, 65( 39), 8104— 8112 |
| [18] | Buffinton G. D., Ollinger K., Brunmark A., Cadenas E., ,. Biochemical Journal 1989, 257( 2), 561— 571 |
| [19] | Chambers J. Q., ,. The Quinonoid Compounds 1988, 1, 719— 757 |
| [20] | Daves G. D., ,. Journal of Chemical Education 1975, 52( 7), A359— A360 |
| [21] | Jacq J., ,. Electrochimica Acta 1967, 12( 9), 1345— 1361 |
| [22] | Pourbaix M., Staehle R W. ., Electrochemical Kinetics, Plenum Press,New York, 1973 |
| [23] | Macías-Ruvalcaba N., Cuevas G., González I., Aguilar-Martínez M., ,. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2002, 67( 11), 3673— 3681 |
| [24] | Izumi Y., Sawada H., Sakka N., Yamamoto N., Kume T., Katsuki H., Shimohama S., Akaike A., ,. Journal of Neuroscience Research 2005, 79( 6), 849— 860 |
| [25] | Meganathan R., ,. Vitamins & Hormones 2001, 61( 1), 173— 218 |
| [26] | Verma C., Olasunkanmi L. O., Ebenso E. E., Quraishi M. A., ,. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2018, 251, 100— 118 |
| [27] | Mizen M. B., Wrighton M. S ., Journal of the Electrochemical Society 1989, 136( 4), 941— 946 |
| [28] | Versteeg P., Rubin E S ., Energy Procedia, 2011, 4, 1957— 1964 |
| [29] | Stern M. C., Simeon F., Hammer T., Landes H., Herzog H. J., Hatton T. A., ,. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 860— 867 |
| [30] | Ganesh K., Satheshkumar A., Balraj C., Elango K. P ., Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular & Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2013, 107( 15), 156— 166 |
| [31] | Jin B., Liu P., Wang Y., Zhang Z., Tian Y., Yang J., Zhang S., Cheng F ., The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2007, 111( 7), 1517— 1522 |
| [32] | Kvarnström C., Neugebauer H., Kuzmany H., Sitter H., Sariciftci N. S., ,. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2001, 511( 1/2), 13— 19 |
| [33] | Gurkan B., Simeon F., Hatton T. A ., ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2015, 3( 7), 1394— 1405 |
| [34] | Becke A. D ., The Journal of Chemical Physics 1993, 98( 7), 5648— 5652 |
| [35] | Hahn S., Lee H., Cho M ., The Journal of Chemical Physics 2004, 121( 4), 1849— 1865 |
| [36] | Fabian J., Hartmann H ., Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry 2004, 17( 5), 359— 369 |
| [37] | And S. W. R., Yoo K. P., Lee J. S., Nam S. C., And J. E. S., Min B. M ., Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 1997, 42( 6), 1161— 1164 |
| [38] | Costentin C., Robert M., Saveant J. M., ,. Chemical Society Reviews 2013, 42( 6), 2423— 2436 |
| [1] | YANG Jingyi, SHI Siqi, PENG Huaitao, YANG Qihao, CHEN Liang. Integration of Atomically Dispersed Ga Sites with C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Photo-driven CO2 Cycloaddition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220349. |
| [2] | WANG Xintian, LI Pan, CAO Yue, HONG Wenhao, GENG Zhongxuan, AN Zhiyang, WANG Haoyu, WANG Hua, SUN Bin, ZHU Wenlei, ZHOU Yang. Techno-economic Analysis and Industrial Application Prospects of Single-atom Materials in CO2 Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [3] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [4] | JIANG Shenghan, CAO Changlin, XIAO Liren, YANG Tang, QIAN Qingrong, CHEN Qinghua. Preparation of Composite Semiconductor Micro-sheets with UV Shielding Performance and Its Application in Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [5] | GE Yicong, NIE Wanli, SUN Guofeng, CHEN Jiaxuan, TIAN Chong. Silver-catalyzed [5+1] Cyclization of 2-Vinylanilines with Benzisoxazoles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220142. |
| [6] | YAO Yiting, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Yu, LI Xiaoyun, SU Baolian, CHEN Lihua. Preparation of Hierarchical Microporous-mesoporous Fe2O3/ZSM-5 Hollow Molecular Sieve Catalytic Materials and Their Catalytic Properties for Benzylation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220090. |
| [7] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [8] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [9] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [11] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [12] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [13] | WANG Zhengwen, GAO Fengxiang, CAO Han, LIU Shunjie, WANG Xianhong, WANG Fosong. Synthesis and Property of CO2 Copolymer⁃based UV-curable Polymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220236. |
| [14] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
