

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 1005.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180757
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Rui, YAO Zhilong*( ), SUN Peiyong, ZHANG Shenghong
), SUN Peiyong, ZHANG Shenghong
Received:2018-11-09
Online:2019-04-18
Published:2019-04-18
Contact:
YAO Zhilong
E-mail:yaozl@bipt.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Rui,YAO Zhilong,SUN Peiyong,ZHANG Shenghong. Effect of Structure and Properties of CuO-WO3-ZrO2 on Hydrogenation Catalytic of Benzaldehyde†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1005.
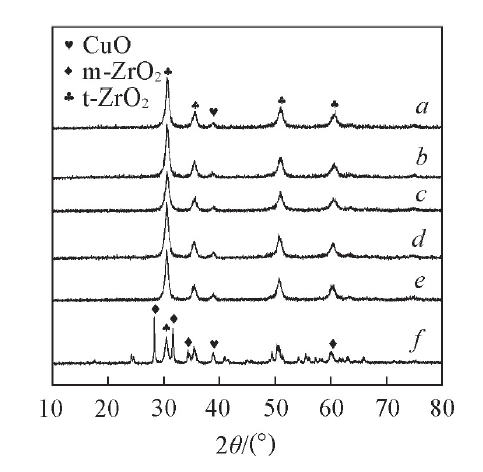
Fig.1 XRD patterns of catalysts with different WO3 contents a. 18CuO-12WO3-ZrO2; b. 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; c. 18CuO-8WO3-ZrO2; d. 18CuO-6WO3-ZrO2; e. 18CuO-4WO3-ZrO2; f. 18CuO-0WO3-ZrO2.
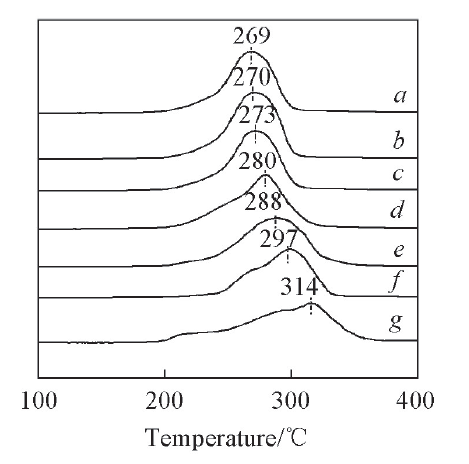
Fig.2 H2-TPR profiles of catalysts with different WO3 contentsa. 18CuO-14WO3-ZrO2; b. 18CuO-12WO3-ZrO2; c. 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; d. 18CuO-8WO3-ZrO2; e. 18CuO-6WO3-ZrO2; f. 18CuO-4WO3-ZrO2; g. 18CuO-0WO3-ZrO2.
| Catalyst | Mass fraction of WO3(%) | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm | Catalyst | Mass fraction of WO3(%) | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18CuO-0WO3-ZrO2 | 0.00 | 10.3 | 16.91 | 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 9.83 | 35.5 | 8.95 | ||||||
| 18CuO-4WO3-ZrO2 | 3.25 | 19.8 | 15.37 | 18CuO-12WO3-ZrO2 | 10.86 | 36.3 | 8.50 | ||||||
| 18CuO-6WO3-ZrO2 | 5.80 | 25.9 | 10.77 | 18CuO-14WO3-ZrO2 | 11.42 | 37.0 | 8.37 | ||||||
| 18CuO-8WO3-ZrO2 | 8.08 | 31.5 | 9.60 | ||||||||||
Table 1 Textural properties of catalysts with different WO3 contents
| Catalyst | Mass fraction of WO3(%) | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm | Catalyst | Mass fraction of WO3(%) | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18CuO-0WO3-ZrO2 | 0.00 | 10.3 | 16.91 | 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 9.83 | 35.5 | 8.95 | ||||||
| 18CuO-4WO3-ZrO2 | 3.25 | 19.8 | 15.37 | 18CuO-12WO3-ZrO2 | 10.86 | 36.3 | 8.50 | ||||||
| 18CuO-6WO3-ZrO2 | 5.80 | 25.9 | 10.77 | 18CuO-14WO3-ZrO2 | 11.42 | 37.0 | 8.37 | ||||||
| 18CuO-8WO3-ZrO2 | 8.08 | 31.5 | 9.60 | ||||||||||
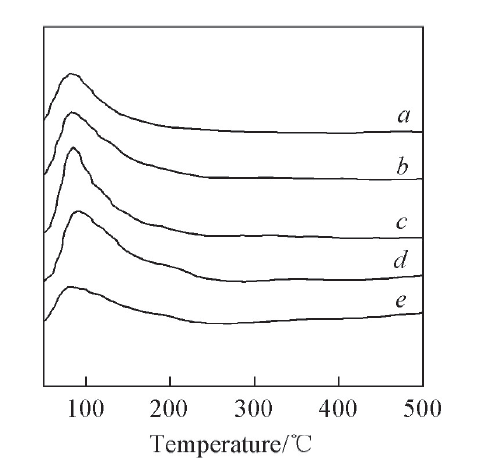
Fig.4 CO2-TPD profiles of catalysts with different WO3 contentsa. 18CuO-14WO3-ZrO2; b. 18CuO-12WO3-ZrO2; c. 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; d. 18CuO-8WO3-ZrO2; e. 18CuO-6WO3-ZrO2.
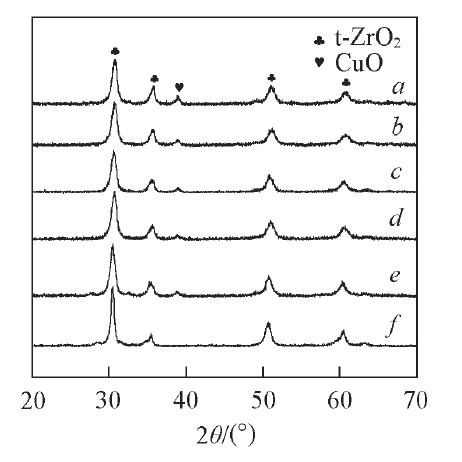
Fig.5 XRD patterns of catalysts with different CuO contents a. 24CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; b. 21CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; c. 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; d. 15CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; e. 12CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; f. 0CuO-10WO3-ZrO2.
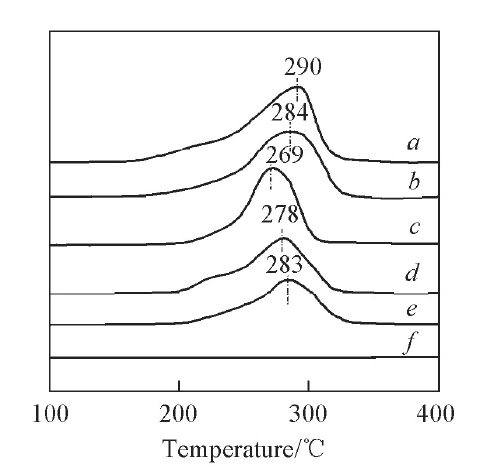
Fig.6 H2-TPR profiles of catalysts with different CuO contentsa. 24CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; b. 21CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; c. 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; d. 15CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; e. 12CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; f. 0CuO-10WO3-ZrO2.
| Catalyst | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm | Catalyst | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 36.4 | 9.02 | 21CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 33.0 | 9.96 |
| 15CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 36.4 | 9.68 | 24CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 32.2 | 9.39 |
| 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 35.5 | 8.95 |
Table 2 Textural properties of catalysts with different CuO contents
| Catalyst | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm | Catalyst | Surface area/(m2·g-1) | Average pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 36.4 | 9.02 | 21CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 33.0 | 9.96 |
| 15CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 36.4 | 9.68 | 24CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 32.2 | 9.39 |
| 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2 | 35.5 | 8.95 |
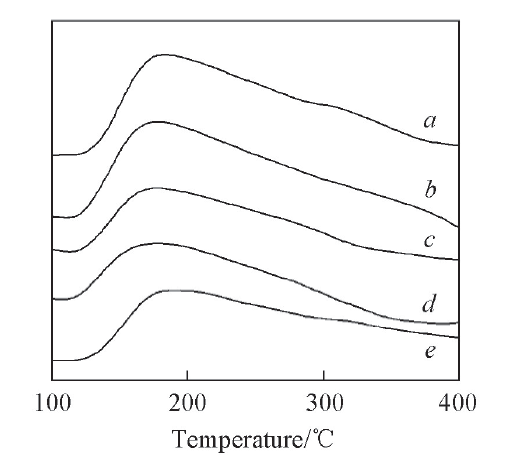
Fig.8 NH3-TPD profiles of catalysts with different CuO contentsa. 24CuO-10WO-ZrO23; b. 21CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; c. 18CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; d. 15CuO-10WO3-ZrO2; e. 12CuO-10WO3-ZrO2.
| w(WO3)(%) | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzyl alcohol | Benzyl benzoate | Diphenylmethane | ||
| 0 | 60.38 | 90.85 | 0.28 | Trace |
| 4 | 79.34 | 89.24 | 0.46 | 1.06 |
| 6 | 84.07 | 90.28 | 1.25 | 1.01 |
| 8 | 88.99 | 90.89 | 1.33 | 0.97 |
| 10 | 94.76 | 92.03 | 1.59 | 0.97 |
| 12 | 94.08 | 92.17 | 0.74 | 0.96 |
Table 3 Performance of catalysts with different WO3 contents*
| w(WO3)(%) | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzyl alcohol | Benzyl benzoate | Diphenylmethane | ||
| 0 | 60.38 | 90.85 | 0.28 | Trace |
| 4 | 79.34 | 89.24 | 0.46 | 1.06 |
| 6 | 84.07 | 90.28 | 1.25 | 1.01 |
| 8 | 88.99 | 90.89 | 1.33 | 0.97 |
| 10 | 94.76 | 92.03 | 1.59 | 0.97 |
| 12 | 94.08 | 92.17 | 0.74 | 0.96 |
| w(CuO)(%) | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzyl alcohol | Toluene | Diphenylmethane | Benzene | ||
| 0 | 15.56 | 42.38 | 1.45 | Trace | Trace |
| 12 | 47.61 | 92.70 | 1.96 | 0.98 | 0.22 |
| 15 | 81.80 | 90.96 | 2.68 | 0.98 | 0.23 |
| 18 | 94.76 | 92.03 | 4.34 | 0.97 | 0.20 |
| 21 | 74.42 | 90.52 | 2.58 | 0.89 | 0.22 |
| 24 | 66.93 | 96.36 | 2.05 | 0.87 | 0.21 |
Table 4 Performance of catalysts with different CuO contents*
| w(CuO)(%) | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzyl alcohol | Toluene | Diphenylmethane | Benzene | ||
| 0 | 15.56 | 42.38 | 1.45 | Trace | Trace |
| 12 | 47.61 | 92.70 | 1.96 | 0.98 | 0.22 |
| 15 | 81.80 | 90.96 | 2.68 | 0.98 | 0.23 |
| 18 | 94.76 | 92.03 | 4.34 | 0.97 | 0.20 |
| 21 | 74.42 | 90.52 | 2.58 | 0.89 | 0.22 |
| 24 | 66.93 | 96.36 | 2.05 | 0.87 | 0.21 |
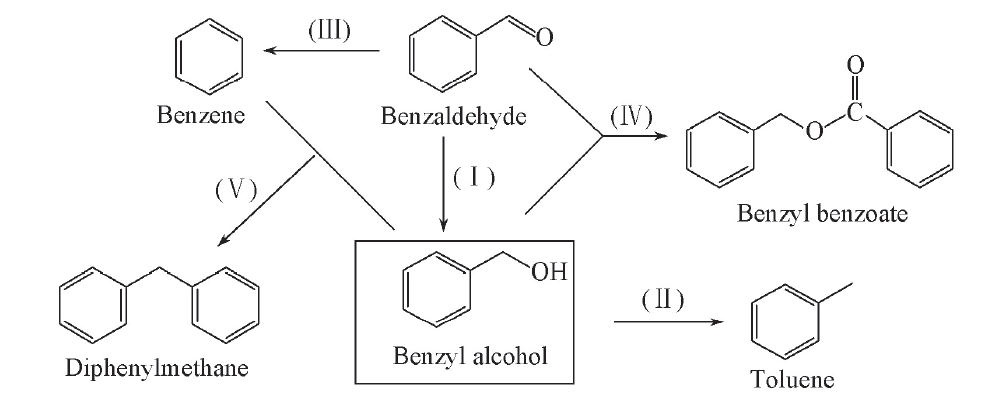
Scheme 2 Possible reaction pathways associated with the hydrogenation of benzaldehyde to the target benzyl alcohol and isolated byproducts(Ⅰ) Hydrogenation of benzaldehyde; (Ⅱ) hydrogenation of benzyl alcohol; (Ⅲ) decarburization of benzaldehyde; (Ⅳ) dehydrogenation and condensation of benzaldehyde and benzyl alcohol; (Ⅴ) alkylation of benzyl alcohol and benzene.
| [1] | Messiha F. S., Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C, 1991, 99(3), 445—449 |
| [2] | Ingamells W., Narasimham K. V., Color. Technol.,2010, 93(8), 306—312 |
| [3] | Distaso J., J. Clean Prod., 1998, 5(1), 170 |
| [4] | Zhang Z., Yuan A., Wang H., Ling Z., Hong X., Zheng C., Korean J. Chem. Eng.,2014, 31(4), 719—723 |
| [5] | Dong D.F.,Photosensitive Mater., 1990, (4), 45—46 |
| (董代富. 感光材料, 1990, (4), 45—46) | |
| [6] | Nair B., Int. J. Toxicol., 2001, 20(Suppl. 3), 23—50 |
| [7] | Xu H.L., Hydrogenation of Methyl Benzoate to Benzaldehyde and Benzyl Alcohol Over MnO/γ-Al2O3 and Cu/SiO2 Catalysts, Fudan University, Shanghai, 2006 |
| (徐华龙. MnO/γ-Al2O3和Cu/SiO2催化剂在苯甲酸甲酯加氢合成苯甲醛和苯甲醇反应过程中的研究, 上海: 复旦大学, 2006) | |
| [8] | Okamoto M., Hirao T., Yamaai T., J. Catal.,2010, 276(2), 423—428 |
| [9] | Merabti R., Bachari K., Halliche D., Rassoul Z., Saadi A., React. Kinet. Mech. Cat.,2010, 101(1), 195—208 |
| [10] | Kong X. J., Chen L. G., Appl. Catal. A-Gen.,2014, 476, 34—38 |
| [11] | Saadi A., Merabti R., Rassoul Z., Bettahar M. M., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem.,2006, 253(1), 79—85 |
| [12] | Jenck J., Germain J. E., Cheminform,1980, 65(1), 141—149 |
| [13] | Bhanushali J. T., Kainthla I., Keri R. S., Nagaraja B. M., Chemistry Select,2016, 1(13), 3839—3853 |
| [14] | Lanasri K., Saadi A., Bachari K., Halliche D., Cherifi O., Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal.,2008, 174(8), 1279—1282 |
| [15] | Saadi A., Rassoul Z., Bettahar M. M., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem.,2000, 164(1/2), 205—216 |
| [16] | Saadi A., Bettahar M. M., Rassoul Z., Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal.,2000, 130, 2261—2266 |
| [17] | Zhang H., Fu X., Niu S., Mater. Chem. Phys.,2005, 91(2/3), 361—364 |
| [18] | Lü C.X., The Study of Crystallization Process of ZrO2, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, 2010 |
| (吕彩霞. 氧化锆晶化过程的研究, 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2010) | |
| [19] | Marrero-Jerez J., Chinarro E., Moreno B., Peña-Martínez. J., Núñez. P., Ceram. Int.,2015, 41(9), 10904—10909 |
| [20] | Hanson J. C., Si R., Xu W., Senanayake S. D., Mudiyanselage K., Stacchiola D., Rodriguez J. A., Zhao H., Beyer K. A., Jennings G., Catal. Today,2014, 229(9), 64—71 |
| [21] | Perret N., Cárdenas-Lizana F., Keane M. A., Catal. Commun.,2011, 16(1), 159—164 |
| [22] | Huirache-Acuña R., Pawelec B., Rivera-Muñoz E., Nava R., Espino J., Fierro J. L. G., Appl. Catal. B: Environ.,2009, 92(1), 168—184 |
| [1] | HUANG Xiaoshun, MA Haiying, LIU Shujuan, WANG Bin, WANG Hongli, QIAN Bo, CUI Xinjiang, SHI Feng. Recent Advances on Indirect Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220222. |
| [2] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [3] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [5] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [6] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [7] | HU Huimin, CUI Jing, LIU Dandan, SONG Jiaxin, ZHANG Ning, FAN Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Zhen, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean. Influence of Different Transition Metal Decoration on the Propane Dehydrogenation Performance over Pt/M-DMSN Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210815. |
| [8] | MENG Xiangyu, ZHAN Qi, WU Yanan, MA Xiaoshuang, JIANG Jingyi, SUN Yueming, DAI Yunqian. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogenation Performance of Au/RGO/Na2Ti3O7 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210655. |
| [9] | LI Xueyu, WANG Zhao, CHEN Ya, LI Keke, LI Jianquan, JIN Shunjing, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Enhanced Catalytic Performance of Supported Nano-gold by the Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance for Selective Hydrogenation of Butadiene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220174. |
| [10] | FAN Ye, HAN Huihui, FANG Yun, FENG Ruiqin, XIA Yongmei. Facile Synthesis of Hollow Nickel Submicrospheres with Hierarchical Nano-structure and Its Catalytic Hydrogenation of Phenol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1801. |
| [11] | YAN Pengquan, WANG Jingrong, SHEN Yaxing, ZUO Zhijun, GAO Zhihua, HUANG Wei. Effect of CuAl2O4 Spinel Structure on CO Hydrogenation in Slurry Reactor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1846. |
| [12] | LIU Hanlin, YIN Linlin, CHEN Xifeng, LI Guodong. Recent Advances in Indium Oxide Based Nanocatalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1430. |
| [13] | XIAO Zhaozhong, MA Zhi, PIAO Lingyu. Co-catalytic Effect of Ni2P on Photocatalytic Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over Different Semiconductors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3692. |
| [14] | CHEN Xiangyun, ZHU Benqiang, YUAN Bing, YU Fengli, XIE Congxia, YU Shitao. Hydrogenation of α-Pinene Catalyzed by Ru Nanoparticles Stabilized by Magnetic Alkali Lignin Amine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1826. |
| [15] | CAI Zhongshun, ZHU Zihui, PAN Jing, SUN Yanyan, XI Lingling, HOU Zhaoyin. Application of Co-Al Catalysts in Hydrogenation of Glycidol to 1,3-Propanediol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1818. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||