

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 1430.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200575
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Hanlin1,3, YIN Linlin1,2, CHEN Xifeng1, LI Guodong1,3( )
)
Received:2020-08-18
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-08
Contact:
LI Guodong
E-mail:liguodong@nanoctr.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Hanlin, YIN Linlin, CHEN Xifeng, LI Guodong. Recent Advances in Indium Oxide Based Nanocatalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1430.
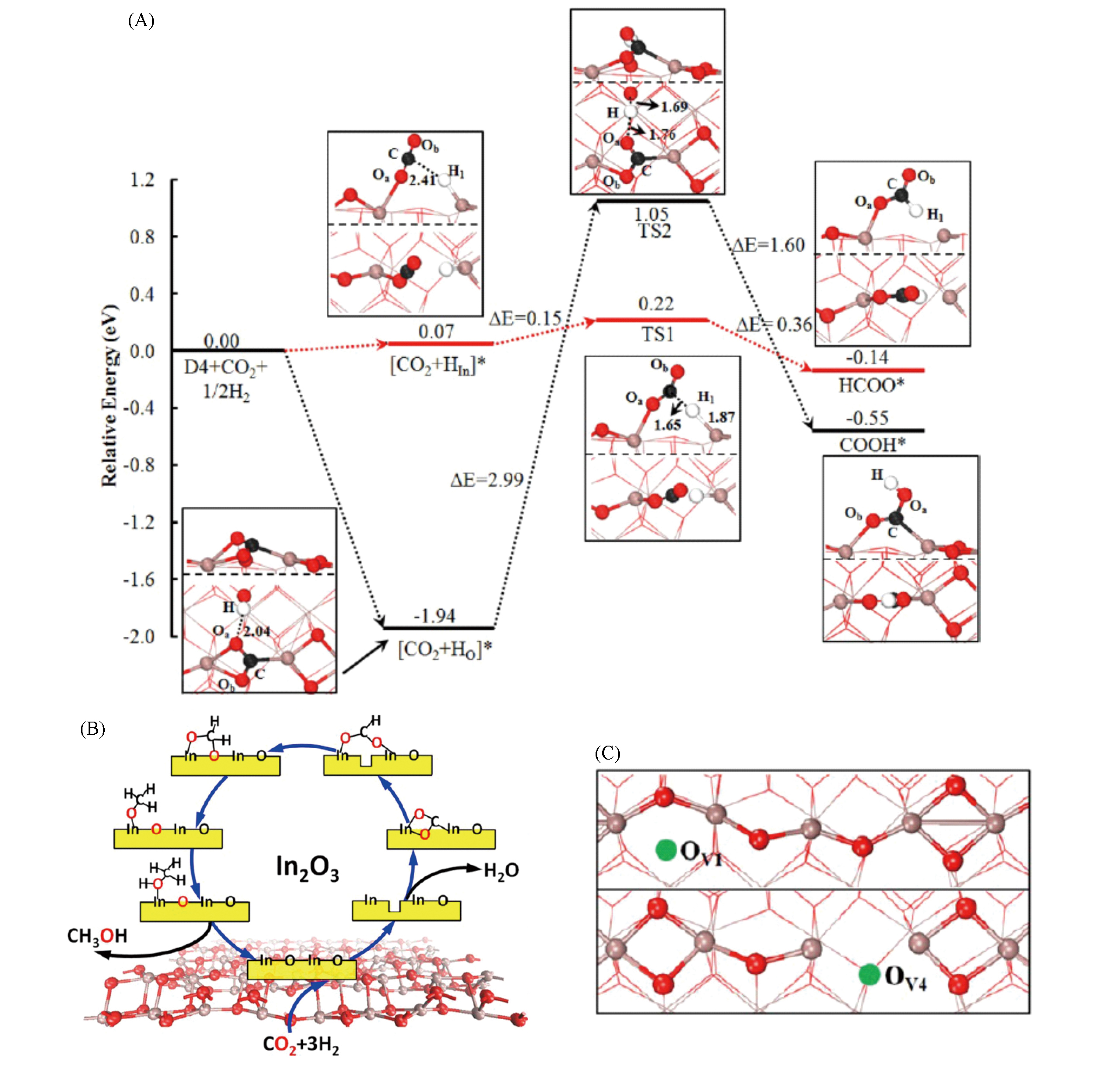
Fig.2 Potential energy profiles of CO2 hydrogenation on the defective (110) surface of In2O3(A),a possible reaction route for CO2 hydrogenation into methanol(B) and two different types of oxygen vacancies on defective (110) surface of In2O3(C)[29]Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
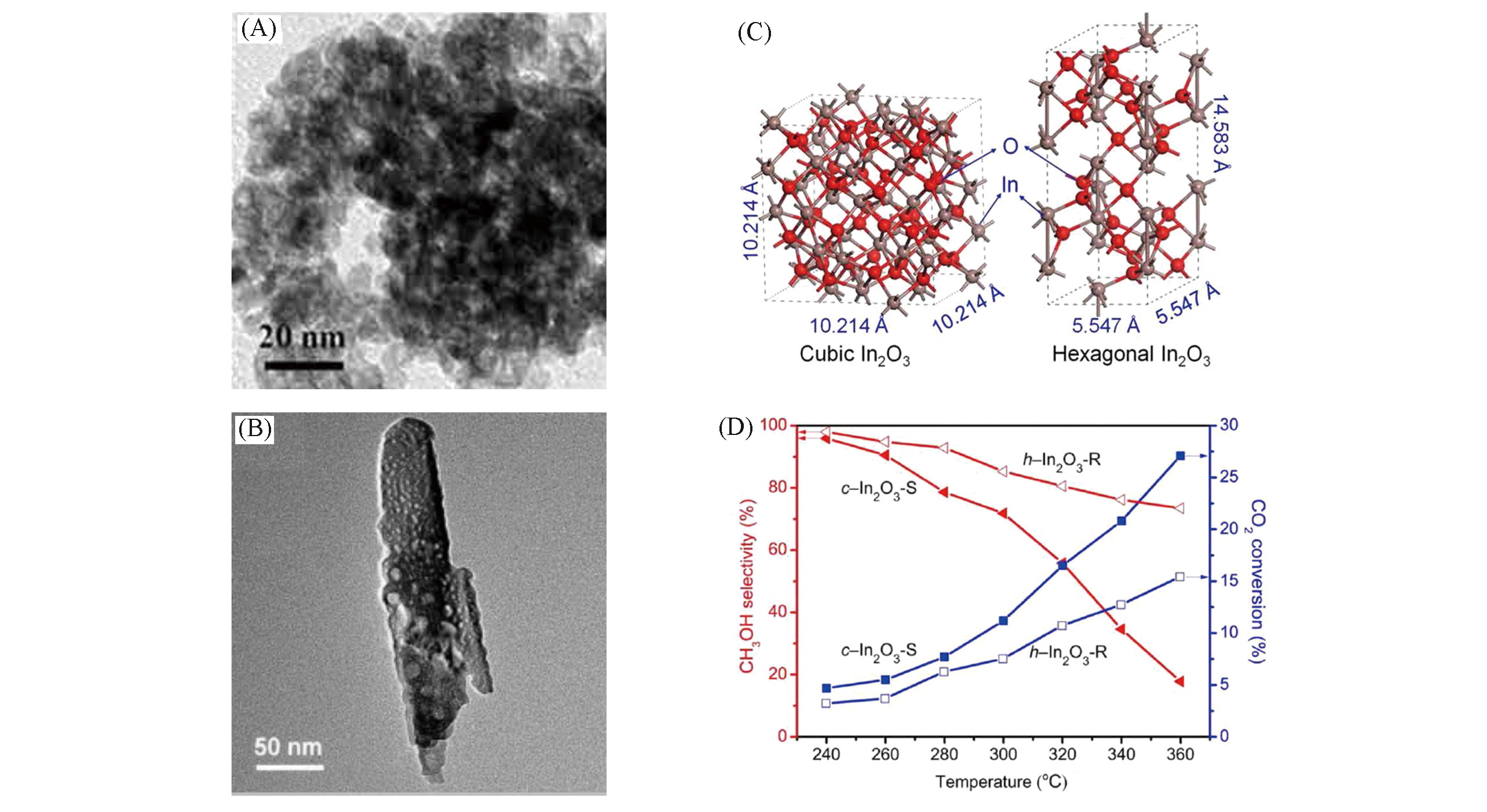
Fig.3 Characterizations and catalytic tests of c?In2O3 and h?In2O3[33](A) TEM image of c-In2O3 nanoparticles; (B) TEM image of h-In2O3 nanorods; (C) schematic models of c-In2O3 and h-In2O3 unit cells; (D) CO2 conversion and methanol selectivity over c-In2O3 and h-In2O3 at different temperatures. Reaction conditions: 5.0 MPa, GHSV=9000 mL?gcat-1?h-1, n(H2)∶n(CO2)∶n(N2)=73∶24∶3. Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
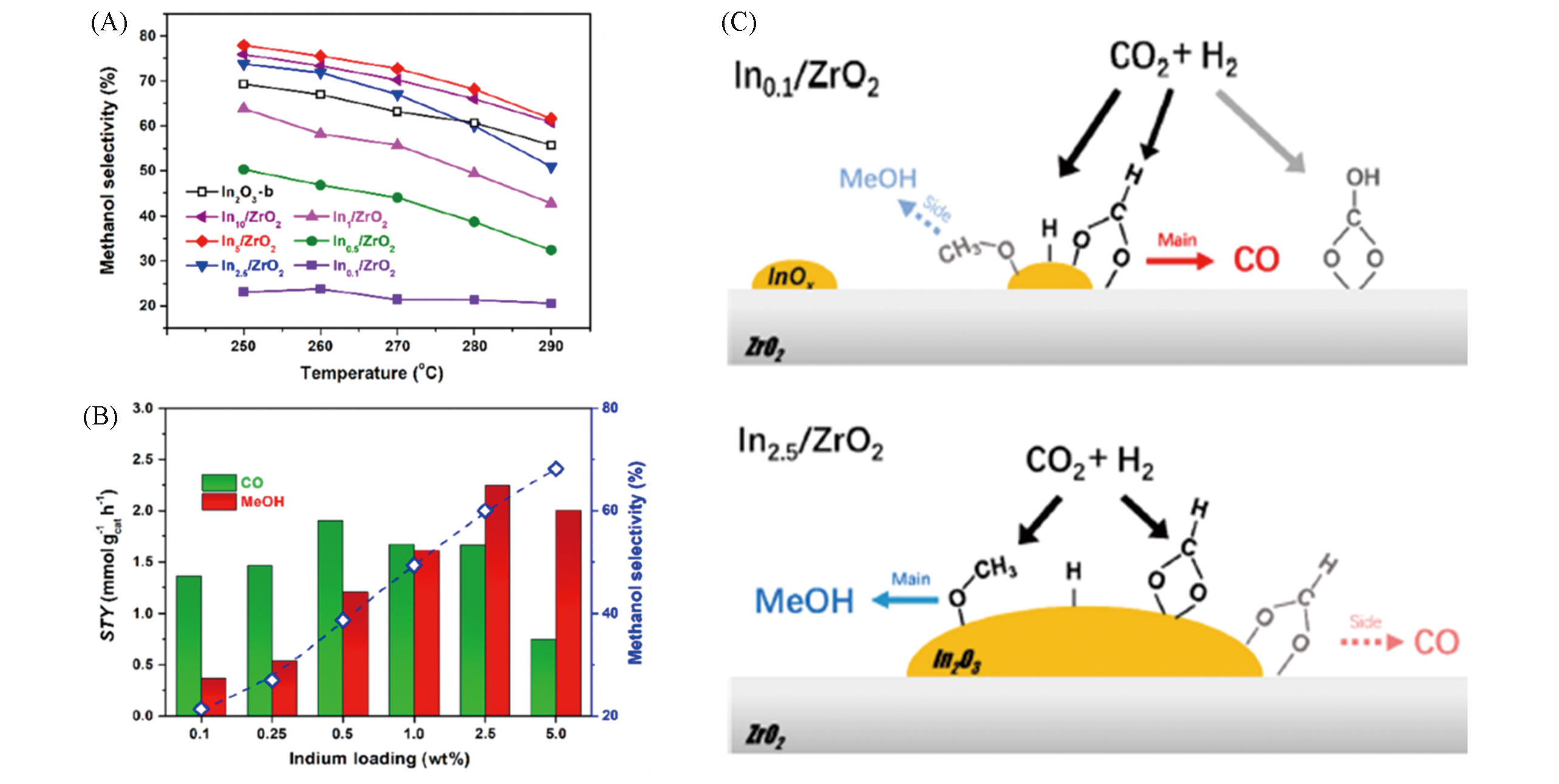
Fig.4 Catalytic tests and possible reaction pathways of CO2 hydrogenation over In2O3/ZrO2 with different indium mass?loading[41](A) Methanol selectivity over different Inx/ZrO2 at different temperatures; (B) STY of CO and methanol, and methanol selectivity at 280 ℃ over Inx/ZrO2. Reaction conditions: 5.0 MPa, n(CO2)∶n(H2)∶n(N2)=4∶1∶1.67, GHSV= 24000 h-1; (C) schematic pathways for CO2 hydrogenation over In0.1/ZrO2 and In2.5/ZrO2. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
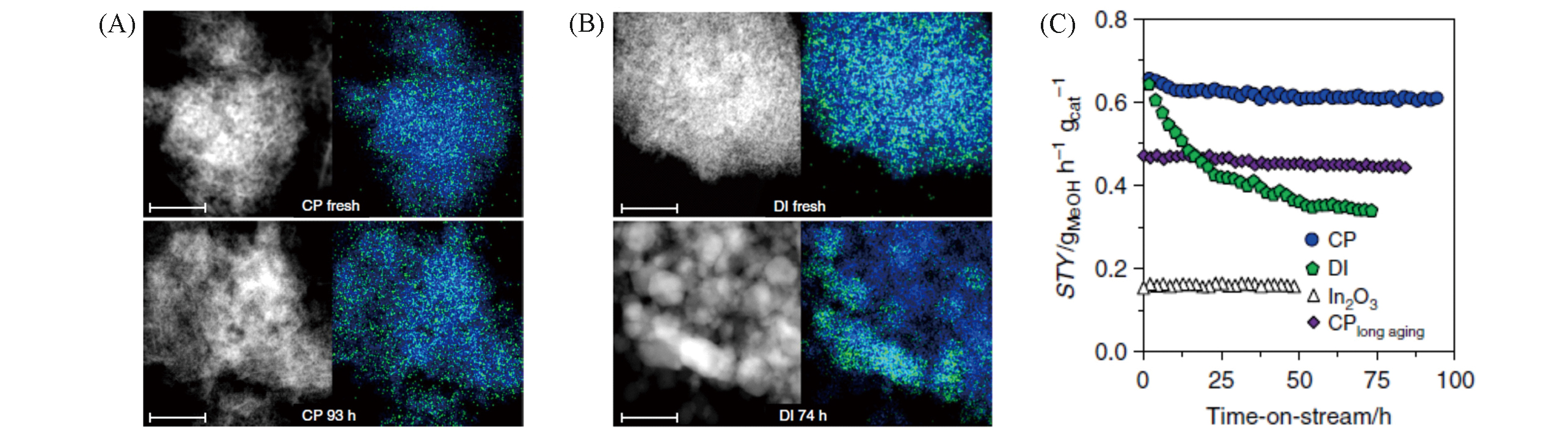
Fig.5 Characterizations and catalytic tests of 0.75wt% Pd/In2O3 catalysts[46](A, B) HAADF?STEM images and EDX maps of indium(blue) and palladium(green) for CP and DI catalysts produced by co?precipitation(A) and dry impregnation(B) methods before and after catalytic tests; (C) methanol STY for CP and DI catalysts, with pure In2O3 and 200 h aged CP catalyst as references. Reaction conditions: 553 K, 5 MPa, n(H2)∶n(CO2)=4∶1, and WHSV=24000 cm3?h-1?gcat-1.Copyright 2019, Nature Publishing Group.
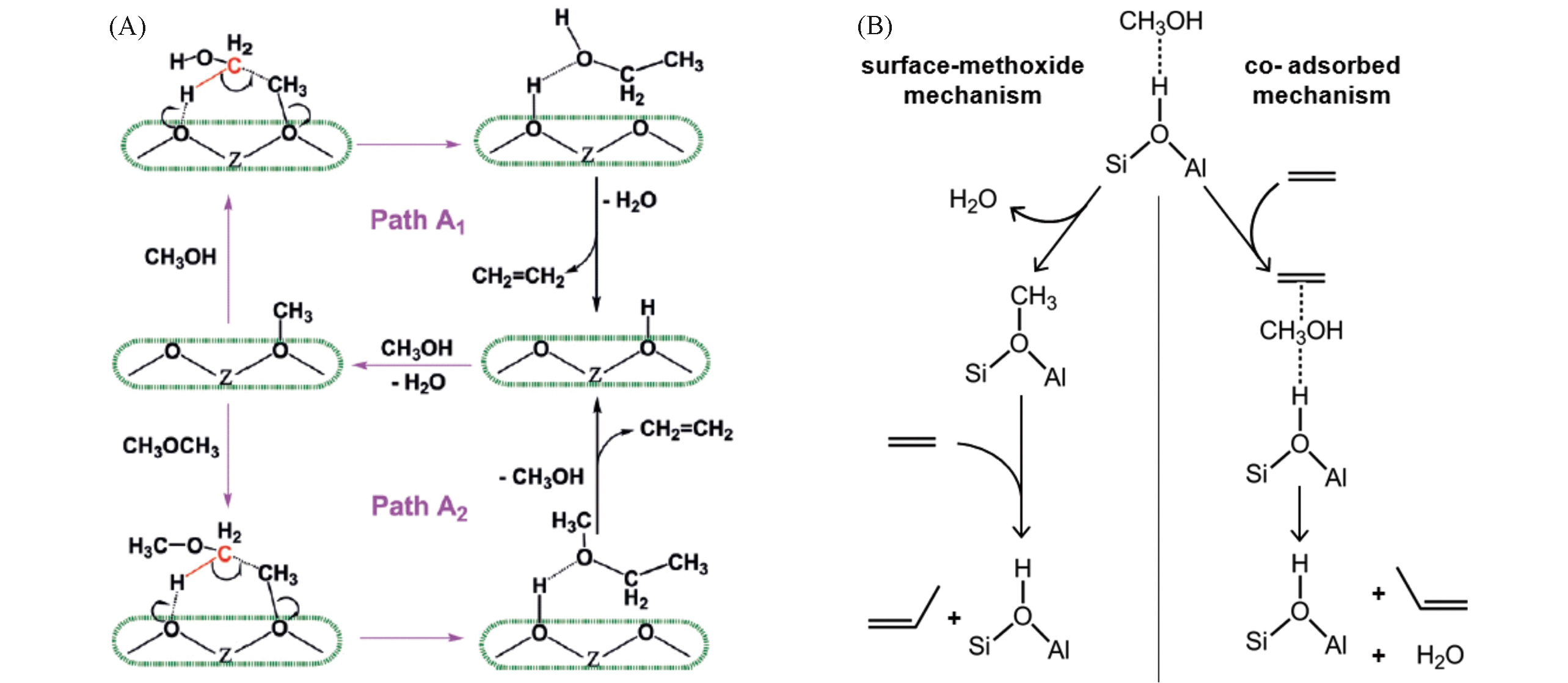
Fig.7 Probable mechanisms of the first C—C bond formation step over zeolites[58](A) and probable mechanisms of olefin methylation with methanol over zeolites[59](B)(A) Copyright 2017, Wiley; (B) Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
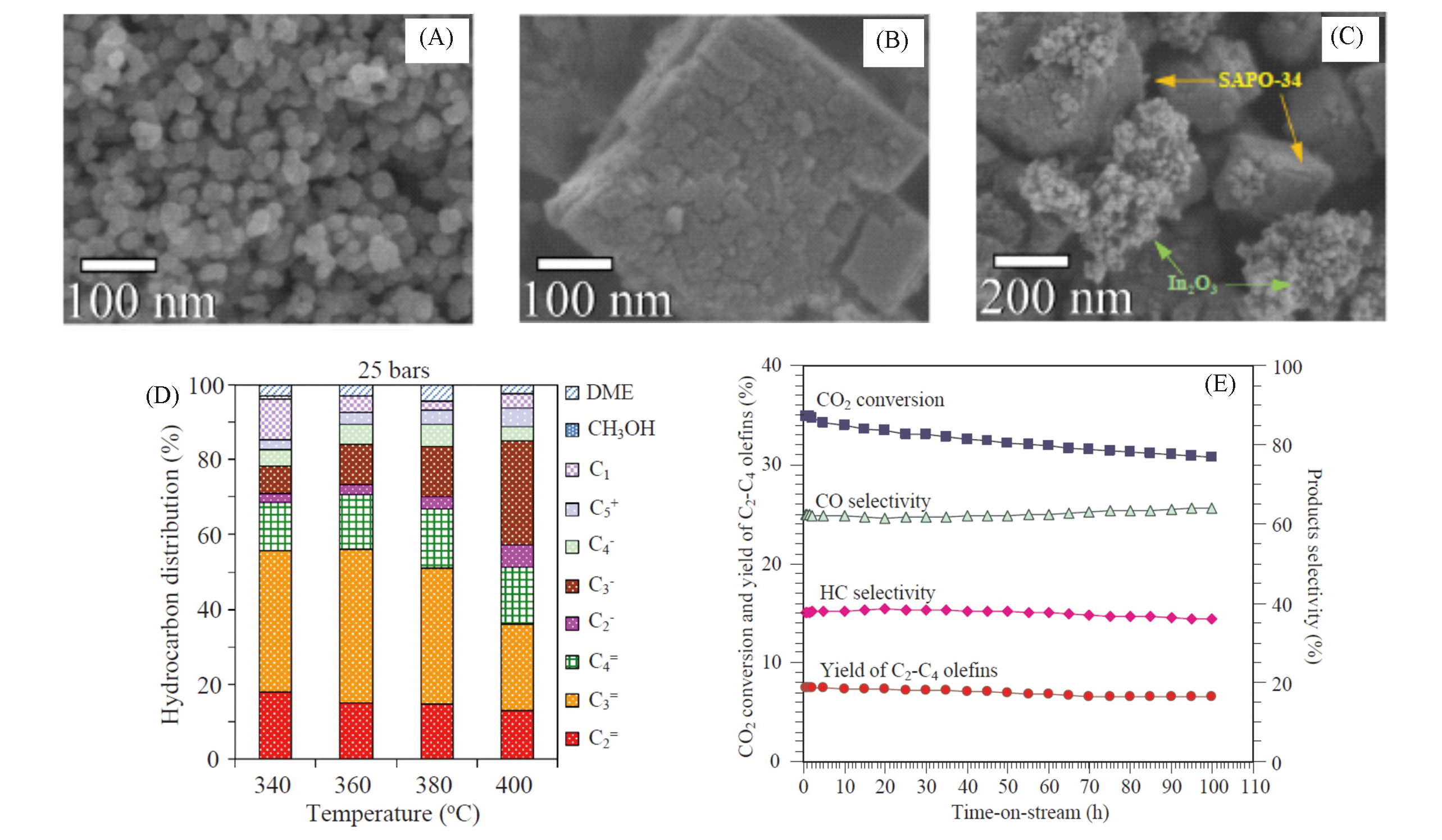
Fig.8 Characterizations and catalytic tests of In2O3/SAPO?34[63] TEM images of In2O3(A), SAPO?34(B) and hybrid In2O3/SAPO?34 catalyst(C); (D) product distribution of CO2 hydrogenation over In2O3/SAPO?34 at different temperatures under 2.5 MPa, n(H2)∶n(CO2)∶n(N2)=3∶1∶1; (E) stability test of In2O3/SAPO?34 at 380 ℃ under 25 bar.Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
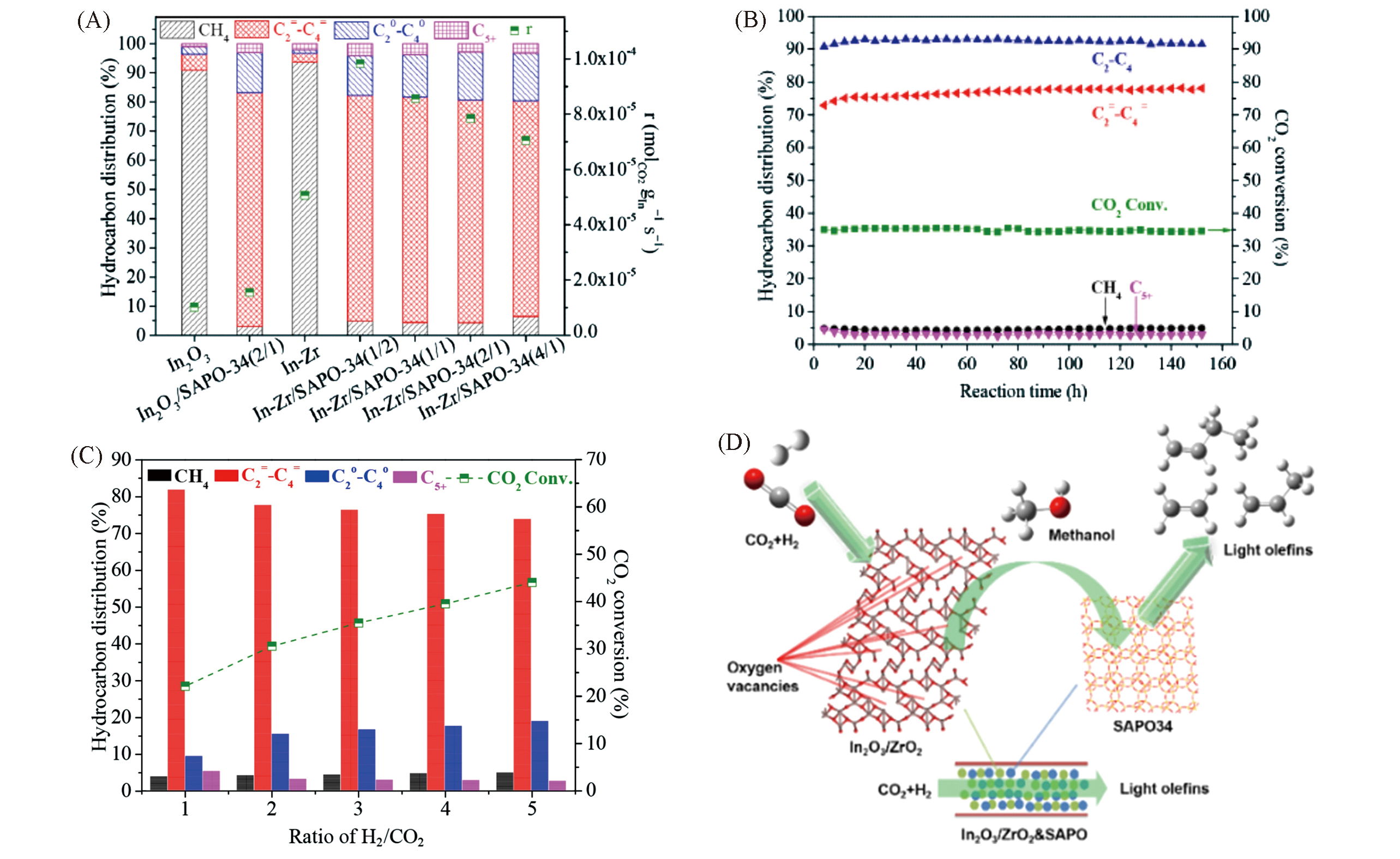
Fig.9 Catalytic tests for In?Zr?O/SAPO?34 catalysts and the reaction pathway[64, 67](A) Hydrocarbon distribution and reaction rate over In?Zr/SAPO?34 catalysts with different In/Zr ratios at 400 ℃, as well as over In2O3 and In?Zr oxide references; (B) stability test of In?Zr/SAPO?34 at 400 ℃; GHSV=9000 mL?gcat-1?h-1, n(H2)∶n(CO2)∶n(N2)=73∶24∶3; (C) catalytic tests for In?Zr/SAPO?34 at different H2/CO2 ratios[64]; (D) schematic reaction pathway of CO2 hydrogenation into light olefins over In?Zr/SAPO?34[67].(A)―(C) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (D) Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
| 1 | Wang L., Chen W., Zhang D., Du Y., Amal R., Qiao S., Wu J., Yin Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(21), 5310—5349 |
| 2 | Ding M., Flaig R. W., Jiang H. L., Yaghi O. M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(10), 2783—2828 |
| 3 | Hepburn C., Adlen E., Beddington J., Carter E. A., Fuss S., Mac Dowell N., Minx J. C., Smith P., Williams C. K., Nature, 2019, 575(7781), 87—97 |
| 4 | Grim R. G., Huang Z., Guarnieri M. T., Ferrell J. R., Tao L., Schaidle J. A., Energ. Environ. Sci.,2020, 13(2), 472—494 |
| 5 | Bao J., Yang G., Yoneyama Y., Tsubaki N., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(4), 3026—3053 |
| 6 | Podrojková N., Sans V., Oriňak A., Oriňaková R., ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(7), 1802—1825 |
| 7 | Tan L., Xu S. M., Wang Z., Xu Y., Wang X., Hao X., Bai S., Ning C., Wang Y., Zhang W., Jo Y. K., Hwang S. J., Cao X., Zheng X., Yan H., Zhao Y., Duan H., Song Y. F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(34), 11860—11867 |
| 8 | Xu W., Lu Z., Sun X., Jiang L., Duan X., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51(7), 1590—1598 |
| 9 | Burkart M. D., Hazari N., Tway C. L., Zeitler E. L., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(9), 7937—7956 |
| 10 | Liang J., Xie Y. Q., Wang X. S., Wang Q., Liu T. T., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(4), 342—345 |
| 11 | Saeidi S., Amin N. A. S., Rahimpour M. R., J. CO2 Util., 2014, 5, 66—81 |
| 12 | Kattel S., Liu P., Chen J. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(29), 9739—9754 |
| 13 | Alvarez A., Bansode A., Urakawa A., Bavykina A. V., Wezendonk T. A., Makkee M., Gascon J., Kapteijn F., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(14), 9804—9838 |
| 14 | Bowker M., ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(17), 4238—4246 |
| 15 | Roy S., Cherevotan A., Peter S. C., ACS Energ. Lett., 2018, 3(8), 1938—1966 |
| 16 | Ma Z., Porosoff M. D., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(3), 2639—2656 |
| 17 | Ye R. P., Ding J., Gong W., Argyle M. D., Zhong Q., Wang Y., Russell C. K., Xu Z., Russell A. G., Li Q., Fan M., Yao Y. G., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 5698 |
| 18 | Wang Y., Kattel S., Gao W., Li K., Liu P., Chen J. G., Wang H., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1166 |
| 19 | Liao F., Wu X. P., Zheng J., Li M. M. J., Kroner A., Zeng Z., Hong X., Yuan Y., Gong X. Q., Tsang S. C. E., Green Chem., 2017, 19(1), 270—280 |
| 20 | Chen Y., Li H., Zhao W., Zhang W., Li J., Li W., Zheng X., Yan W., Zhang W., Zhu J., Si R., Zeng J., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1885 |
| 21 | Wang L., He S., Wang L., Lei Y., Meng X., Xiao F. S., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(12), 11335—11340 |
| 22 | An B., Li Z., Song Y., Zhang J., Zeng L., Wang C., Lin W., Nat. Catal., 2019, 2(8), 709—717 |
| 23 | Han F. Q., Zhang Z., Niu N., Li J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2018, 34(4), 635—642 |
| 24 | Yao L., Shen X., Pan Y., Peng Z., J. Catal., 2019, 372, 74—85 |
| 25 | Jiang X., Nie X., Gong Y., Moran C. M., Wang J., Zhu J., Chang H., Guo X., Walton K. S., Song C., J. Catal., 2020, 383, 283—296 |
| 26 | Martin O., Martin A. J., Mondelli C., Mitchell S., Segawa T. F., Hauert R., Drouilly C., Curulla⁃Ferre D., Pérezv⁃Ramírez J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(21), 6261—6265 |
| 27 | Ye J., Liu C., Ge Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(14), 7817—7825 |
| 28 | Tsoukalou A., Abdala P. M., Stoian D., Huang X., Willinger M. G., Fedorov A., Muller C. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(34), 13497—13505 |
| 29 | Ye J., Liu C., Mei D., Ge Q., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(6), 1296—1306 |
| 30 | Sun K., Fan Z., Ye J., Yan J., Ge Q., Li Y., He W., Yang W., Liu C. J., J. CO2 Util., 2015, 12, 1—6 |
| 31 | Frei M. S., Capdevila⁃Cortada M., García⁃Muelas R., Mondelli C., López N., Stewart J. A., Curulla⁃Ferré D.,Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Catal., 2018, 361, 313—321 |
| 32 | Yang B., Li L., Jia Z., Liu X., Zhang C., Guo L., Chinese Chem. Lett., 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.05.031 |
| 33 | Dang S., Qin B., Yang Y., Wang H., Cai J., Han Y., Li S., Gao P., Sun Y., Sci. Adv.,2020,6(25),eaaz2060 |
| 34 | Chen P., Tao L., Zhu J., Zhao G., Liu Y.,Lu Y., Energy Technol., 2019, 7(3), 1800747—1800756 |
| 35 | Pan Y. X., You Y., Xin S., Li Y., Fu G., Cui Z., Men Y. L., Cao F. F., Yu S. H., Goodenough J. B., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2017, 139(11), 4123—4129 |
| 36 | Ghuman K. K., Hoch L. B., Wood T. E., Mims C., Singh C. V., Ozin G. A., ACS Catal.,2016, 6(9), 5764—5770 |
| 37 | Ghuman K. K., Hoch L. B., Szymanski P., Loh J. Y., Kherani N. P., El⁃Sayed M. A., Ozin G. A., Singh C. V., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2016, 138(4), 1206—1214 |
| 38 | Yan T., Li N., Wang L., Liu Q., Jelle A., Wang L., Xu Y., Liang Y., Dai Y., Huang B., You J., Ozin G. A., Energ. Environ. Sci.,2020, 13, 3054—3063 |
| 39 | Ben S. G., Yuan F. L., Zhu Y. J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(6), 1005—1009 |
| 40 | Frei M. S., Mondelli C., Cesarini A., Krumeich F., Hauert R., Stewart J. A., Curulla⁃Ferré D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., ACS Catal., 2019, 10(2), 1133—1145 |
| 41 | Chen T. Y., Cao C., Chen T. B., Ding X., Huang H., Shen L., Cao X., Zhu M., Xu J., Gao J., Han Y. F., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(9), 8785—8797 |
| 42 | Chou C. Y., Lobo R. F., Appl. Catal. A, 2019, 583, 117144 |
| 43 | Wang H., Jia J., Wang L., Butler K., Song R., Casillas G., He L., Kherani N. P., Perovic D. D., Jing L., Walsh A., Dittmeyer R., Ozin G. A., Adv. Sci.,2019, 6(22), 1902170 |
| 44 | Ye G., Gong Y., Lin J., Li B., He Y., Pantelides S. T., Zhou W., Vajtai R., Ajayan P. M., Nano Lett., 2016, 16(2), 1097—1103 |
| 45 | Rui N., Wang Z., Sun K., Ye J., Ge Q., Liu C. J., Appl. Catal. B, 2017, 218, 488—497 |
| 46 | Frei M. S., Mondelli C., Garcia⁃Muelas R., Kley K. S., Puertolas B., Lopez N., Safonova O. V., Stewart J. A., Curulla⁃Ferre D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 3377 |
| 47 | Sun K., Rui N., Zhang Z., Sun Z., Ge Q., Liu C. J., Green Chem., 2020, 22(15), 5059—5066 |
| 48 | Wang J., Sun K., Jia X., Liu C. J., Catal. Today, 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.05.020 |
| 49 | Jia X., Sun K., Wang J., Shen C., Liu C. J., J. Energ. Chem., 2020, 50, 409—415 |
| 50 | Shi Z., Tan Q., Tian C., Pan Y., Sun X., Zhang J., Wu D., J. Catal., 2019, 379, 78—89 |
| 51 | Bavykina A., Yarulina I., Al Abdulghani A. J., Gevers L., Hedhili M. N., Miao X., Galilea A. R., Pustovarenko A., Dikhtiarenko A., Cadiau A., Aguilar⁃Tapia A., Hazemann J. L., Kozlov S. M., Oud⁃Chikh S., Cavallo L., Gascon J., ACS Catal.,2019, 9(8), 6910—6918 |
| 52 | Shi Z., Tan Q., Wu D., AIChE J., 2018, 65(3), 1047—1058 |
| 53 | Pustovarenko A., Dikhtiarenko A., Bavykina A., Gevers L., Ramírez A., Russkikh A., Telalovic S., Aguilar A., Hazemann J. L., Ould⁃Chikh S., Gascon J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(9), 5064—5076 |
| 54 | Kubelková L., Nováková J., Nedomová K., J. Catal., 1990, 124(2), 441—450 |
| 55 | Narula C. K., Li Z., Casbeer E. M., Geiger R. A., Moses⁃Debusk M., Keller M., Buchanan M. V., Davison B. H., Sci. Rep.,2015, 5, 16039 |
| 56 | Chen Y., Gong K., Jiao F., Pan X., Hou G., Si R., Bao X., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2020, 59(16), 6529—6534 |
| 57 | Yarulina I., Chowdhury A. D., Meirer F., Weckhuysen B. M., Gascon J., Nat. Catal.,2018, 1(6), 398—411 |
| 58 | Wu X., Xu S., Zhang W., Huang J., Li J., Yu B., Wei Y., Liu Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2017, 56(31), 9039—9043 |
| 59 | Ilias S., Bhan A., ACS Catal.,2012, 3(1), 18—31 |
| 60 | Dessau R. M., LaPierre R. B., J. Catal., 1982, 78(1), 136—141 |
| 61 | Gao P., Li S., Bu X., Dang S., Liu Z., Wang H., Zhong L., Qiu M., Yang C., Cai J., Wei W., Sun Y., Nat. Chem., 2017, 9(10), 1019—1024 |
| 62 | Remi J. C. S., Lauerer A., Chmelik C., Vandendael I., Terryn H., Baron G. V., Denayer J. F. M., Kärger J., Nat. Mater., 2016, 15(4), 401—406 |
| 63 | Numpilai T., Wattanakit C., Chareonpanich M., Limtrakul J., Witoon T., Energ. Convers. Manage., 2019, 180, 511—523 |
| 64 | Gao P., Dang S., Li S., Bu X., Liu Z., Qiu M., Yang C., Wang H., Zhong L., Han Y., Liu Q., Wei W., Sun Y., ACS Catal., 2017, 8(1), 571—578 |
| 65 | Dang S., Gao P., Liu Z., Chen X., Yang C., Wang H., Zhong L., Li S., Sun Y., J. Catal., 2018, 364, 382—393 |
| 66 | Gao J., Jia C., Liu B., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7(23), 5602—5607 |
| 67 | Tan L., Zhang P., Cui Y., Suzuki Y., Li H., Guo L., Yang G., Tsubaki N., Fuel Sci. Technol., 2019, 196, 106174 |
| 68 | Wang J., Zhang A., Jiang X., Song C., Guo X., J. CO2 Util., 2018, 27, 81—88 |
| 69 | Dang S., Li S., Yang C., Chen X., Li X., Zhong L., Gao P., Sun Y., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(15), 3582—3591 |
| 70 | Shen Q., Cao C., Huang R., Zhu L., Zhou X., Zhang Q., Gu L., Song W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(3), 1216—1219 |
| [1] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [3] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [4] | ZHANG Weizhong,WEN Yueli,SONG Rongpeng,WANG Bin,ZHANG Qian,HUANG Wei. Effect of Surface Cu0 Content of the Catalysts on CO2 Hydrogenation to C2+ Alcohols † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1297. |
| [5] | LI Zhenhua, SHI Run, ZHAO Jiaqi, ZHANG Tierui. Research Progress of Photo-driven C1 Conversion to Value-added Chemicals † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 604. |
| [6] | LI Zhixiong, NA Wei, WANG Hua, GAO Wengui. Direct Syntheses of Cu-Zn-Zr/SBA-15 Mesoporous Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(12): 2616. |
| [7] | CAO Yong, CHEN Li-Fang, DAI Wei-Lin, FAN Kang-Nian, WU Dong, SUN Yu-Han . Preparation of High Performance Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 Catalyst for Methanol Synthesis from CO2 Hydrogenation by Coprecipitation-reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(7): 1296. |
| [8] | LI Ji-Tao, Au-Chak-Tong, CHEN Ming-Dan, ZHANG Wei-De . The Role of CO in the Synthesis of Methanol from the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1998, 19(6): 926. |
| [9] | SHEN Bai-Rong, HAN Ji-Hong, SUN Qi, FAN Kang-Nian, GU Chang-Xin, DENG Jing-Fa. EXAFS Studies on Cu/ZnO/MxOy Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(12): 2038. |
| [10] | YANG Xiu-Juan, CHOU Ju, LU Tian-Hong. Direct Electron Transfer Reaction of Horse Heart Hemoglobin at the Indium Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1996, 17(12): 1932. |
| [11] | LIN Zhong-Hua, LUO Jin, CHEN Hai-Yi, TIAN Zhao-Wu. Anodic Oxide Film In2O3 (Ⅰ)——Preparation and Electronic Properties of the Film [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1993, 14(7): 978. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||