

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 763.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180744
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Yang1, LI Daixi1,*( ), LIU Baolin1, GUO Baisong2, WEI Dongqing3
), LIU Baolin1, GUO Baisong2, WEI Dongqing3
Received:2018-11-02
Online:2019-04-10
Published:2019-02-25
Contact:
LI Daixi
E-mail:dxli75@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GAO Yang, LI Daixi, LIU Baolin, GUO Baisong, WEI Dongqing. Inhibitory Mechanism of Glycerol on the Growth of Ice Crystals by Molecular Dynamics†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 763.
| System | NG | NW | NI | XG(%) | LX,LY,LZ/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 0 | 8040 | 432 | 0 | 4.38,2.65,22.90 |
| B1 | 10 | 8030 | 432 | 0.12 | 4.41,2.65,23.13 |
| B2 | 20 | 8020 | 432 | 0.25 | 4.42,2.62,23.18 |
| B3 | 30 | 8010 | 432 | 0.37 | 4.40,2.63,23.34 |
| B4 | 40 | 8000 | 432 | 0.50 | 4.39,2.64,23.44 |
| B5 | 50 | 7990 | 432 | 0.62 | 4.39,2.63,23.47 |
| B6 | 60 | 7980 | 432 | 0.75 | 4.39,2.62,23.56 |
Table 1 Detail component of ice, water and glycerol in each system*
| System | NG | NW | NI | XG(%) | LX,LY,LZ/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 0 | 8040 | 432 | 0 | 4.38,2.65,22.90 |
| B1 | 10 | 8030 | 432 | 0.12 | 4.41,2.65,23.13 |
| B2 | 20 | 8020 | 432 | 0.25 | 4.42,2.62,23.18 |
| B3 | 30 | 8010 | 432 | 0.37 | 4.40,2.63,23.34 |
| B4 | 40 | 8000 | 432 | 0.50 | 4.39,2.64,23.44 |
| B5 | 50 | 7990 | 432 | 0.62 | 4.39,2.63,23.47 |
| B6 | 60 | 7980 | 432 | 0.75 | 4.39,2.62,23.56 |
| hkl | Multiplicity | dhkl/nm | Total facet area/nm2 | Total facet area(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (110) | 4 | 0.389 | 32.3308 | 27.15 |
| (020) | 2 | 0.389 | 16.1668 | 13.58 |
| (111) | 4 | 0.344 | 15.7192 | 13.20 |
| (11 | 4 | 0.344 | 15.7192 | 13.20 |
| (002) | 1 | 0.366 | 11.7121 | 9.84 |
| (00 | 1 | 0.366 | 11.7121 | 9.84 |
| (021) | 2 | 0.344 | 7.8605 | 6.60 |
| (02 | 2 | 0.344 | 7.8605 | 6.60 |
Table 2 Crystal habit parameters of ice unit cell in vacuum
| hkl | Multiplicity | dhkl/nm | Total facet area/nm2 | Total facet area(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (110) | 4 | 0.389 | 32.3308 | 27.15 |
| (020) | 2 | 0.389 | 16.1668 | 13.58 |
| (111) | 4 | 0.344 | 15.7192 | 13.20 |
| (11 | 4 | 0.344 | 15.7192 | 13.20 |
| (002) | 1 | 0.366 | 11.7121 | 9.84 |
| (00 | 1 | 0.366 | 11.7121 | 9.84 |
| (021) | 2 | 0.344 | 7.8605 | 6.60 |
| (02 | 2 | 0.344 | 7.8605 | 6.60 |
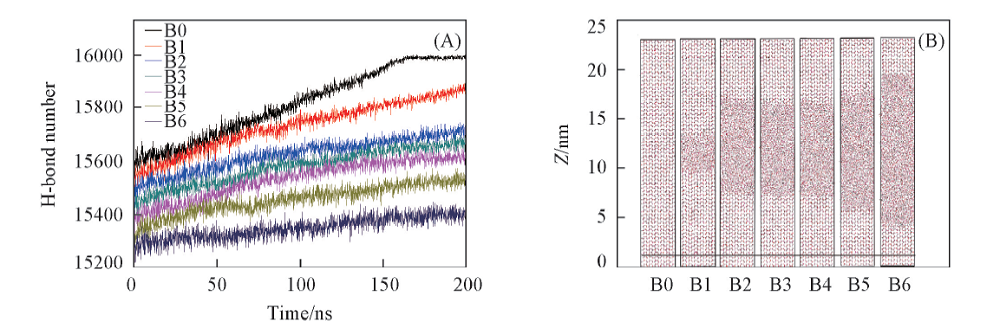
Fig.3 Growing status of the facet (020) in each system after 200 ns(A) The H-bond number between water molecules in each system; (B) snapshots of each system at 200 ns.
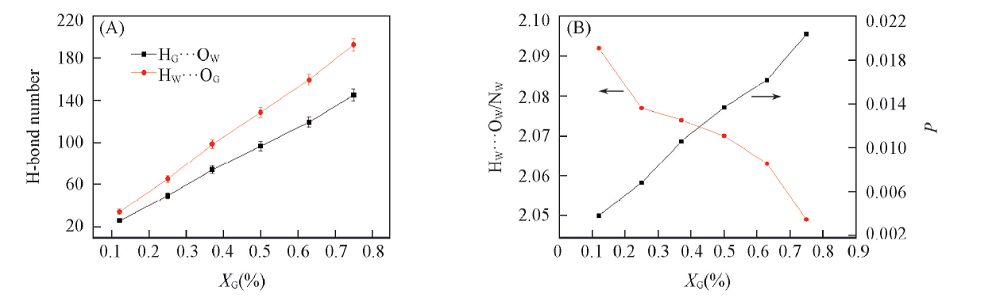
Fig.4 H-bond number between water molecules and glycerol molecules in each system(A) The number of H-bond between water and glycerol molecule vs. XG; (B) the water-water H-bond average number(HW…OW/NW) and the glycerol-water H-bond percentage P vs. XG.
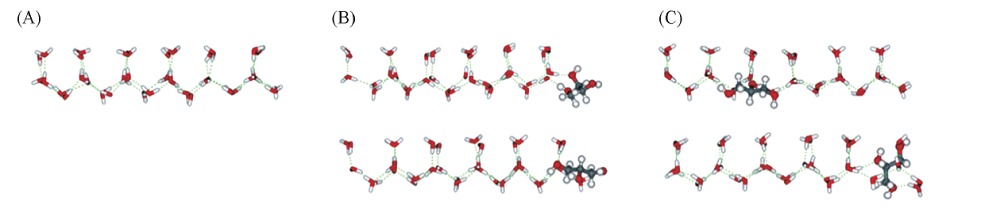
Fig.5 Competitive adsorption behavior of glycerol moleculeRed sticks represent O atoms, white sticks represent H atoms, and gray sticks represent C atoms. (A) A normal ice crystal layer; (B) an ice crystal layer which two water molecules are replaced by one glycerol molecules; (C) an ice crystal layer which three water molecules are replaced by one glycerol.
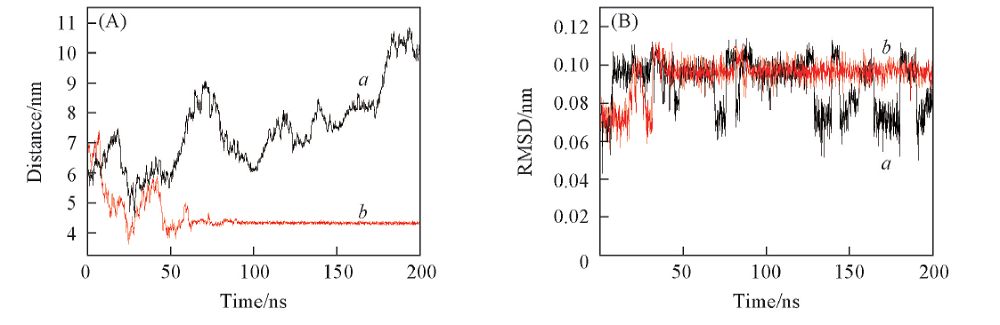
Fig.6 Dynamic adsorption process of glycerol molecule(A) The distance between initial crystal face and glycerols vs. time; (B) RMSD of Gly-free and Gly-bound vs. time. a. Gly-free; b. Gly-bound.
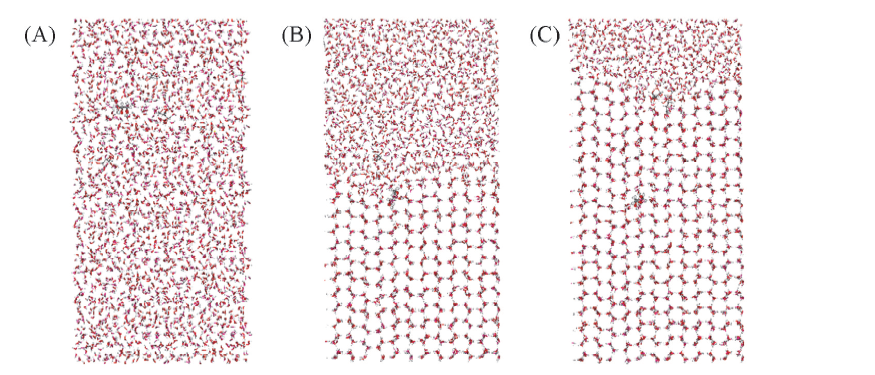
Fig.7 Snapshots of B1 system at 1 ns(A), 71 ns(B) and 141 ns(C)Red sticks represent O atoms, white sticks represent H atoms, and gray sticks represent C atoms.
| [1] | Acker J., Cryobiology, 2018, 80, 156—195 |
| [2] | Acker J. P., Cryobiology, 2016, 73(3), 410—411 |
| [3] | Yuan X. H., Chem.Life, 2009, 29(4), 490—494 |
| (袁晓华. 生命的化学, 2009, 29(4), 490—494) | |
| [4] | Gonda T., Sei T., Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater.,2005, 51(1), 70—80 |
| [5] | Yang B., Liu B. L., J.Refriger.,2014, 35(3), 39—44 |
| (杨波, 刘宝林. 制冷学报,2014, 35(3), 39—44) | |
| [6] | Gao C., Zhou G. Y., Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.,2004, 20(2), 123—128 |
| (高才, 周国燕. 物理化学学报, 2004, 20(2), 123—128) | |
| [7] | Yang S., Zhu Y., Qian H., Lü Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2017, 33(2), 261—267 |
| [8] | Li D. X., Liu B. L., Liu Y. S., Chen C. L., Cryobiology,2008, 56(2), 114—119 |
| [9] | Chen C., Li W. Z., Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.,2009, 25(3), 507—512 |
| (陈聪, 李维仲. 物理化学学报, 2009, 25(3), 507—512) | |
| [10] | Sanz E., Vega C., Abascal J. L., MacDowell L. G., Phys. Rev.Lett.,2004, 92(25), 255701 |
| [11] | Leadbetter A. J., Ward R. C., Clark J. W., Tucker P. A., Matsuo T., Suga H., J. Chem.Phys.,1985, 82(1), 424—428 |
| [12] | Wang Y., Xiao J., Suzek T. O., Zhang J., Wang J., Bryant S. H., Nucleic Acids Research,2009, 37, W623—W633 |
| [13] | Zhuang C. Q., Yue H., Zhang H. J., Plastics,2010, 39(4), 81—84 |
| [14] | Spoel D. V. D., Lindahl E., Hess B., Groenhof G., Mark A. E., Berendsen H. J. C., J. Comput.Chem.,2005, 26(16), 1701—1718 |
| [15] | Nikitin A. M., Milchevskiy Y. V., Lyubartsev A. P., J. Mol.Model.,2014, 20(3), 2143 |
| [16] | Han W., Florian D., Christian H., J. Chem.Phy.,2010, 133(3), 03411701 |
| [17] | Graña Drummond L. M., Svaiter B. F., J. Comput. & Appl. Math.,2005, 175(2), 395—414 |
| [18] | Pal T., Kar T., Mol.Phys.,2004, 102(7), 681—685 |
| [19] | Giovanni B., Tatyana Z. T., Michele P., J. Chem.Phys.,2009, 130(7), 074101 |
| [20] | Prywer J.,J. Cryst.Growth, 2004, 270(3/4), 699—710 |
| [21] | Rozmanov D., Kusalik P. G., PhysChemChemPhys.,2011, 13(34), 15501 |
| [22] | Guàrdia E., Martí J., Padró J. A., Saiz L., Komolkin A. V., J. Mol.Liq.,2002, 96, 3—17 |
| [23] | Zhang N., Li W., Chen C., Zuo J., Weng L., Bull. Korean Chem.Soc.,2013, 34(9), 2711—2719 |
| [24] | Zhang N., Li W., Chen C., Zuo J., Weng L., Mol.Phys.,2013, 111(7), 939—949 |
| [25] | Adam Z., Nucleic Acids Res., 2003, 31(13), 3370—3374 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [3] | CHEN Hanxiang, BIAN Shaoju, HU Bin, LI Wu. Molecular Simulation of the Osmotic Pressures for LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O Solution System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [4] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [5] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [7] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [8] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [9] | LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling, LIU Chengbu. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pulsed Electric Field O/W Emulsion Demulsification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| [10] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [11] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [12] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [13] | HE Jinlu, LONG Run, FANG Weihai. A-site Cation Effects on Hot Carrier Relaxation in Perovskites by Nonadiabatic Molecular Dynamics Simulations † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 439. |
| [14] | ZHU Yuquan, ZHAO Xiaojie, ZHONG Yuan, CHEN Ziru, YAN Hong, DUAN Xue. Theoretical Study on the Construction and Characteristics of the Host-guest Intercalated Structure of Layered Double Hydroxides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2287. |
| [15] | QU Siying, XU Qin. Different Roles of Some Key Residues in the S4 Pocket of Coagulation Factor Xa for Rivaroxaban Binding † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||