

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 530.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170343
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Fengmei, XU Guangwei, JIN Chengchang*( )
)
Received:2017-06-05
Online:2018-03-10
Published:2018-01-13
Contact:
JIN Chengchang
E-mail:jinchengchang@suda.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Fengmei, XU Guangwei, JIN Chengchang. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance for Supercapacitors of Bi-doped α-MnO2 Nanorods[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 530.
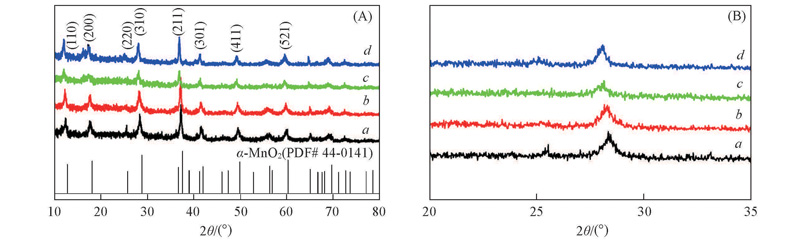
Fig.1 X-Ray diffraction patterns of samples(A) and magnified X-ray diffraction patterns of samples between the ranges of 2θ=25°—35°(B)a. MO; b. BMO-50; c. BMO-30; d. BMO-20.
| Sample | a/nm | c/nm | c/a | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO | 0.98723 | 0.28707 | 0.2908 | 0.27981 |
| BMO-50 | 0.98742 | 0.28689 | 0.2905 | 0.28021 |
| BMO-30 | 0.98780 | 0.28685 | 0.2904 | 0.28032 |
| BMO-20 | 0.98792 | 0.28669 | 0.2902 | 0.28065 |
Table 1 Lattice parameters and cell volumes of MO, BMO-50, BMO-30 and BMO-20
| Sample | a/nm | c/nm | c/a | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO | 0.98723 | 0.28707 | 0.2908 | 0.27981 |
| BMO-50 | 0.98742 | 0.28689 | 0.2905 | 0.28021 |
| BMO-30 | 0.98780 | 0.28685 | 0.2904 | 0.28032 |
| BMO-20 | 0.98792 | 0.28669 | 0.2902 | 0.28065 |
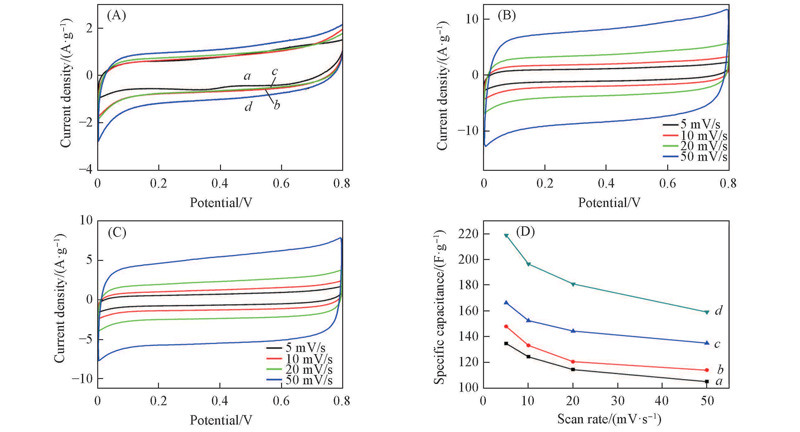
Fig.6 CV curves of α-MnO2 and Bi-doped α-MnO2 at scan rate of 5 mV/s(A), BMO-20(B) and MO(C) at different scan rates and specific capacitances of α-MnO2 and Bi-doped α-MnO2 at different scan rates(D)a. MO; b. BMO-50; c. BMO-30; d. BMO-20.
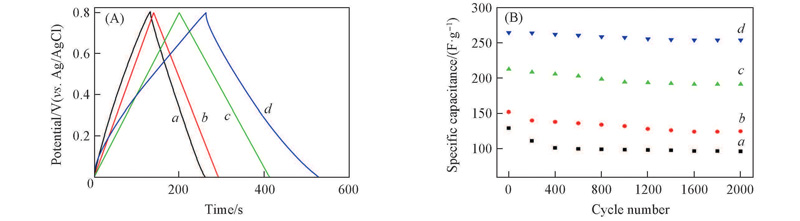
Fig.7 Galvanostatic charge/discharge curves of α-MnO2 and Bi-doped α-MnO2(A) and cycle performance of α-MnO2 and Bi-doped α-MnO2(current density: 1 A/g)(B)a. MO; b. BMO-50; c. BMO-30; d. BMO-20.
| [1] | Wang G. P., Zhang L., Zhang J. J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 797—828 |
| [2] | Huang M., Li L., Dong F., Zhang Y. X., Zhang L. L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 21380—21423 |
| [3] | Pan C., Gu H. T., Zong F. X., Gao J. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6), 953—958 |
| (潘超,谷海腾, 宗飞旭, 高婧怡. 高等学校化学学报2017,38, (6), 953—958) | |
| [4] | Qi F., Kanoh H., Kenta Q., J. Mater. Chem., 1999, 9(2), 319—333 |
| [5] | Salma A. A., Shaeel A. A., Wafa S. A., Maqsood A. M., J. Mol. Struct., 2017, 1137(5), 495—505 |
| [6] | Lv Q. Y., Sun H. Y., Li X. B., Xiao J. W., Liu L. M., Luo J., Wang S., Nano Energy, 2016, 21, 39—50 |
| [7] | Lina K., Santosh T., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 418, 22—29 |
| [8] | Aimal khan., Liao Z. W., Jawad Ali., Jerosha Ifthikar., Chen Z. Q., J. Hazard Mater., 2017, 329, 262—271 |
| [9] | Danae J. D., Timothy N. L., Julian A. V., Mark A. R., Michael T. B., Eric N. C., Steven J. L., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 17342—17350 |
| [10] | Yang Z. H., Wang X. Y., HuangY. Q., Curr. Appl. Phys., 2015, 15, 1556—1561 |
| [11] | Hu Z., Xiao X., Chen C., Li T., Huang L., Zhang C., Su J., Miao L., Jiang J., Zhang Y., Zhou J., Nano Energy, 2015, 11, 226—234 |
| [12] | Im D., Manthiram A., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(A), 68—73 |
| [13] | Dzieciuch M. A., Gupta N., Wroblowa H. S., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1988, 135, 2415—2419 |
| [14] | Qu D. Y., Conway B. E., Bai L., Zhou Y. H., Adams W. A., J. Appl. Electrochem., 1993, 23, 693—706 |
| [15] | Li X. L., Zhang L. S., Dong H. C., Xia T. C., Huang Z. C., Solid State Sci., 2015, 43, 46—52 |
| [16] | Ma J. J., Zhu S. J., Shan Q. Y., Liu S. F., Zhang Y. X., Dong F, Liu H. D., Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 168, 97—103 |
| [17] | Ji T.H., Yang F., Lv Y. Y., Zhou J. Y., Sun J. Y., Mater. Lett., 2009, 63, 2044—2046 |
| [18] | Wang H. Z., Shi X., Shi Y. L., Zhang W. G., Yao S. W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(4), 650—655 |
| [19] | Kanungo S. B., Parida K. M., Sant B. R., Electrochim. Acta, 1981, 26(8), 1147—1156 |
| [20] | Hu X. P., Pan D. W., Han H. T., Lin M. Y., Zhu Y, Wang C. C., Mater. Lett., 2017, 190, 83—85 |
| [21] | Handbook of Monochromatic XPS Spectra, The Elements and Native Oxides, Vincent Crist B., XPS International Inc., 1999 |
| [22] | Li H. Y., Liu J. F., Qian J. J., Li Q. Y., Yang J. J., Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(9), 1578—1589 |
| (李海燕, 刘金凤, 钱俊杰, 李秋叶, 杨建军催化学报, 2014,35(9), 1578—1589) | |
| [23] | Stypula B., Stoch J., Corros. Sci. ,1994, 36,2159-2167 |
| [24] | Tang C. L., Wei X., Jiang Y. M., Wu X. Y., Han L. N., Wang K. X., Chen J. S., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119, 8465—8471 |
| [1] | HOU Congcong, WANG Huiying, LI Tingting, ZHANG Zhiming, CHANG Chunrui, AN Libao. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH Composite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [2] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [3] | WEI Yuchen, WU Tingting, YANG Lei, JIN Biyu, LI Hongqiang, HE Xiaojun. Preparation and Supercapacitive Performance of Naphthalene-based Interconnected Porous Carbon Nanocapsules [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2852. |
| [4] | HUANG Dongxue, ZHANG Ying, ZENG Ting, ZHANG Yuanyuan, WAN Qijin, YANG Nianjun. Transition Metal Sulfides Hybridized with Reduced Graphene Oxide for High-Performance Supercapacitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 643. |
| [5] | SHA Huiwen, MA Weiting, ZHOU Xiaojuan, SONG Weixing. One-step Preparation and Applications of Laser Induced Three-dimensional Reticular Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 607. |
| [6] | CHEN Minghua, LI Hongwu, FAN He, LI Yu, LIU Weiduo, XIA Xinhui, CHEN Qingguo. Research Progress of Two-dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides in Supercapacitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 539. |
| [7] | ZHANG Weiguo, FAN Songhua, WANG Hongzhi, YAO Suwei. Synthesis of Self-assembled α-Fe2O3/Graphene Hydrogel for Supercapacitors with Promising Electrochemical Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1850. |
| [8] | GUAN Fanglan,LI Xin,ZHANG Qun,GONG Yan,LIN Ziyu,CHEN Yao,WANG Lejun. Fabrication and Capacitance Performance of Laser-machined RGO/MWCNT/CF In-plane Flexible Micro-supercapacitor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 300. |
| [9] | LI Botian,SHAO Wei,XIAO Da,ZHOU Xue,DONG Junwei,TANG Liming. Polypyrrole Nanowire Gels Based on Templating Fabrication and Their Energy Storage and Electrochemical Sensing Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 183. |
| [10] | LIU Ben,ZHANG Xingying,CHEN Shaoyun,HU Chenglong. Preparation and Electrochemical Energy Storage Performance of One Dimensional Orderly Polyaniline Nanowires Array† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 498. |
| [11] | LIU Hao,ZHAO Dingxuan,GONG Guodong,ZHANG Zhuxin,JIA Tuo,CHEN Hanzhe. Effect of Temperature on Morphology and Supercapacitor Performance of Carbon Nano-spheres† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 18. |
| [12] | LI Long,HU Hongli,DING Shujiang. Facile Synthesis of Scale-like CoMn2O4 Nanosheets on Reduced Graphene Oxide for Supercapacitors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2010. |
| [13] | NIE Guangdi, ZHU Yun, TIAN Di, WANG Ce. Research Progress in the Electrospun Nanofiber-based Supercapacitor Electrode Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1349. |
| [14] | ZHANG Baohai, LUO Min, YANG Shun, FU Rongrong, MA Jinfu. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Hierarchically Porous Carbon Microspheres Derived from Metal Phenolic Precursor† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 310. |
| [15] | FENG Dongyang,GUO Di,LIU Xiaoxia. Functionalization of Carbon Electrode and Subsequent Electrochemical Deposition of Nanostructured Manganese Oxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2280. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||