

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 2271.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170273
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Yanshan, WEI Bangzhi, HUANG Aimin, MA Lin*( )
)
Received:2017-04-28
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-11-20
Contact:
MA Lin
E-mail:malinzju@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WEI Yanshan, WEI Bangzhi, HUANG Aimin, MA Lin. Membrane Structure Alteration of DOPC Liposome Induced by Interaction with Gene Carrier Polyethyleneimine†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2271.
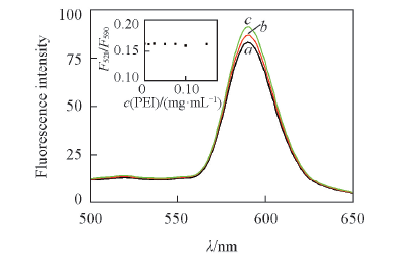
Fig.2 Fluorescence spectra of DOPC LUVs labeled with NBD-PE and Rh-PE in PBS(pH=7.4) containing 0(a), 0.05(b) and 0.1(c) mg/mL PEI25kInsert: relative intensity of fluorescence emission of NBD-PE and Rh-PE(F520/F590) in DOPC LUVs in PBS containing different concentrations of PEI25k. λex=463 nm, c(DOPC)=50 μmol/L.
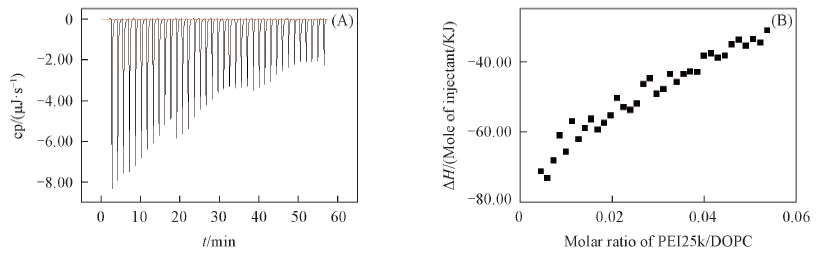
Fig.4 ITC profiles for titration of PEI25k into DOPC LUVs in PBS solution at 25 ℃ and pH=7.4(A) Exothermic heat release upon injection of PEI25k into DOPC LUVs dispersion; (B) integrated heat data associated with the interaction of PEI25k and DOPC LUVs. c(PEI25k)=5.0 mg/mL, c(DOPC)=750 μmol/L.
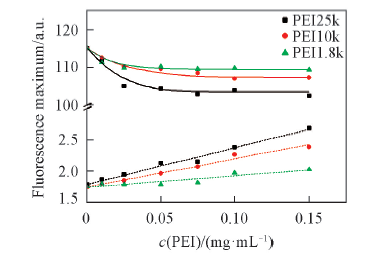
Fig.6 PEI concentration dependence of ANS fluorescence emission maximum in PBS(pH=7.4)in the absence(dash line) and presence(solid line) of DOPC LUVsλex=388 nm; c(ANS)=2.5 μmol/L; c(DOPC)=50 μmol/L.
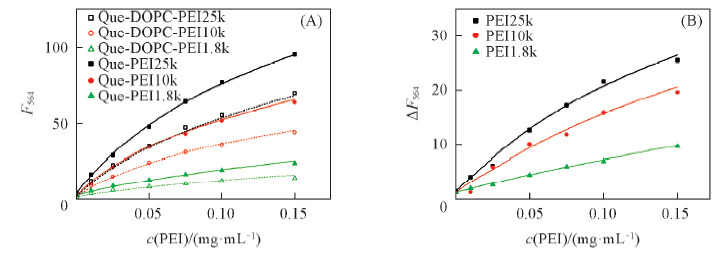
Fig.9 PEI concentration dependence of fluorescence intensity of quercetin at 564 nm(F564)(A) In the absence(solid line) and presence(dash line) of DOPC LUVs in PBS(pH=7.4); (B) difference in the fluorescence emission in the absence and presence of DOPC LUVs. λex=465 nm, c(DOPC)=50 μmol/L, c(Que)=5 μmol/L.
| [1] | Yin H., Kanasty R. L., Eltoukhy A. A., Vegas A. J., Dorkin J. R., Anderson D. G., Nat. Rev. Genet., 2014, 15, 541—555 |
| [2] | Giacca M., Zacchigna S., J. Control. Release, 2012, 161, 377—388 |
| [3] | Tiera M. J., Shi Q., Winnik F. M., Fernandes J. C., Curr. Gene Ther., 2011, 11, 288—306 |
| [4] | Neu M., Fischer D., Kissel T., J. Gene Med., 2005, 7, 992—1009 |
| [5] | Sawant R. R., Sriraman S. K., Navarro G., Biswas S., Dalvi R. A., Torchilin V. P., Biomaterials,2012, 33, 3942—3951 |
| [6] | Yamano S., Dai J., Hanatani S., Haku K., Yamanaka T., Ishioka M., Takayama T., Yuvienco C., Khapli S., Moursi A. M., Montclare J. K., Biomaterials,2014, 35, 1705—1715 |
| [7] | Chen L. N., Wang Y., Zhu Y., Sun Y. X., Wang Y. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(3), 720—725 |
| (陈丽娜, 王颖, 朱莹, 孙一新, 王幽香. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(3), 720—725) | |
| [8] | Liu Y. J., Zhang P., Du J. W., Wang Y. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5), 1003—1009 |
| (刘亚杰, 张鹏, 杜建委, 王幽香. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(5), 1003—1009) | |
| [9] | Yang S., Guo Z., Yang X., Xie J., Robert J. L., Jiang D., Teng L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(3), 401—405 |
| [10] | Zhong D., Jiao Y., Zhang Y., Zhang W., Li N., Zuo Q., Wang Q., Xue W., Liu Z., Biomaterials,2013, 34, 294—305 |
| [11] | Larsen A. K., Malinska D., Koszela-Piotrowska I., Parhamifar L., Hunter A. C., Moghimi S. M., Mitochondrion,2012, 12, 162—168 |
| [12] | Moghimi S. M., Symonds P., Murray J. C., Hunter A. C., Debska G., Szewczyk A., Mol. Ther., 2005, 11, 990—995 |
| [13] | Won Y. Y., Sharma R., Konieczny S. F., J. Control. Release, 2009, 139, 88—93 |
| [14] | Gabrielson N. P., Pack D. W., J. Control. Release, 2009, 136, 54—61 |
| [15] | Parhamifar L., Larsen A. K., Hunter A. C., Andresen T. L., Moghimi S. M., Soft Matter., 2010, 6, 4001—4009 |
| [16] | Yasuhara K., Tsukamoto M., Tsuji Y., Kikuchi J., Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects,2012, 415, 461—467 |
| [17] | Sabín J., Vázquez-Vázquez C., Prieto G., Bordi F., Sarmiento F., Langmuir,2012, 28, 10534—10542 |
| [18] | Haouz A., Mohsni S. E., Zentz C., Merola F., Alpert B., Eur. J. Biochem., 1999, 264, 250—257 |
| [19] | Stewart J. C. M., Anal. Biochem., 1980, 104, 10—14 |
| [20] | Torchilin V.P., Weissig V.; translated by Deng Y. H., Xu H., Liposomes: A Practical Approach, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2007, 89—92 |
| (Torchilin V.P., Weissig V.著; 邓意辉, 徐晖[译]. 脂质体, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007, 89—92) | |
| [21] | Struck D., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E., Biochem., 1981, 20, 4093—4099 |
| [22] | Morgan C. G., Thomas E. W., Yianni Y. P., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1983, 728, 356—362 |
| [23] | Ross P. D., Subramanian S., Biochem., 1981, 20, 3096—3102 |
| [24] | Pfau A., Schrepp W., Horn D., Langmuir,1999, 15, 3219—3225 |
| [25] | Rao Z., Taguchi T., Colloids Surf. B: Biointerf., 2012, 97, 248—253 |
| [26] | Lakowicz J.R., Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd Ed., Plenum Press, New York, 1999, 185—486 |
| [27] | Montesano G., Bartucci R., Belsito S., Marsh D., Sportelli L., J. Biophys., 2001, 80, 1372—1383 |
| [28] | Marsh D., J. Biophys., 2001, 81, 2154—2162 |
| [29] | Tribet C., Vial F., Soft Matter., 2008, 4, 68—81 |
| [30] | Tirosh O., Barenholz Y., Katzhendler J., Priev A., J. Biophys., 1998, 74, 1371—1379 |
| [31] | Kozlova N. O., Bruskovskaya I. B., Okuneva I. B., Melik-Nubarov N. S., Yaroslavov A. A., Kabanov V. A., Menger F. M., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2001, 1514, 139—151 |
| [32] | Evans K. O., Laszlo J. A., Compton D. L., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2014, 1838, 445—455 |
| [33] | Tammela P., Laitinen L., Galkin A., Wennberg T., Heczko R., Vuorela H., Slotte J. P., Vuorela P., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2004, 425(2), 193—199 |
| [34] | Wolfbeis O. S., Begum M., Geiger H., Z. Naturforsch., 1984, 39 b , 231—237 |
| [35] | Falkovskaia E., Sengupta P. K., Kasha M., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1998, 297, 109—114 |
| [36] | Sengupta P. K., Kasha M., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1979, 68(2/3), 382—385 |
| [1] | REN Shijie, QIAO Sicong, LIU Chongjing, ZHANG Wenhua, SONG Li. Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Research Progress on Platinum Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220466. |
| [2] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [3] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [4] | HU Huimin, CUI Jing, LIU Dandan, SONG Jiaxin, ZHANG Ning, FAN Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Zhen, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean. Influence of Different Transition Metal Decoration on the Propane Dehydrogenation Performance over Pt/M-DMSN Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210815. |
| [5] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [6] | JIANG Shan, SHEN Qianqian, LI Qi, JIA Husheng, XUE Jinbo. Pd-loaded Defective TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220206. |
| [7] | XU Wenzhe, ZHANG Hao. Supramolecular Interactions-mediated Nanodrug Nucleation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220264. |
| [8] | PAN Xiaojun, BAO Rongrong, PAN Caofeng. Research Progress of Flexible Tactile Sensors Applied to Wearable Electronics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2359. |
| [9] | WEN Wei, HUANG Dading, BAO Jingxiao, ZHANG John Z. H.. Residue Specific Binding Mechanisms of PD-1 to Its Monoclonal Antibodies by Computational Alanine Scanning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2161. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jun, LIU Yixuan, DU Xiaohui, YANG Hui. Highly Adhesive and Stretchable Polymers for the Interface of Cyber-human Interaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1093. |
| [11] | MA Zhuoyuan, WANG Dayang. Status and Prospect of Surface Wettability of Molecular Self-assembled Monolayers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1031. |
| [12] | WANG Yupeng, ZHAO Yang, LI Mohan, SHI Suqing, GONG Yongkuan. Fabrication of Antifouling-antibacterial Dual Functional Polymer Coating via Dopamine-based Multiple Interactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 811. |
| [13] | LI Mengshuo, ZHANG Jing, LIU Dan, ZHU Yaxian, ZHANG Yong. Interactions of Pyrene with Human Serum Albumin and Bovine Serum Albumin: Microenvironmental Polarity Differences at Binding Sites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 731. |
| [14] | CHEN Binggang, LIU Sanrong, YU Xifei, JIANG Zijiang. Preparation and Properties Characterization of Polysiloxane Skin Tissue Adhesive [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3746. |
| [15] | LI Xiaolei, SUN Yunjiao, TANG Ying, WANG Changsheng. Rapid and Accurate Calculation of the Three⁃body Interaction Strength in the Hydrogen⁃bonded Complexes of Alcohols or Deoxyribose with Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3664. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||