

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (7): 1269.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160116
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Min, KONG Huifang, GUO Zhihui*( )
)
Received:2016-02-28
Online:2016-07-10
Published:2016-06-15
Contact:
GUO Zhihui
E-mail:zhguo@snnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Min, KONG Huifang, GUO Zhihui. Detection of Copper Ion Based on the Interaction Between DNA Molecules and Copper Ions†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1269.
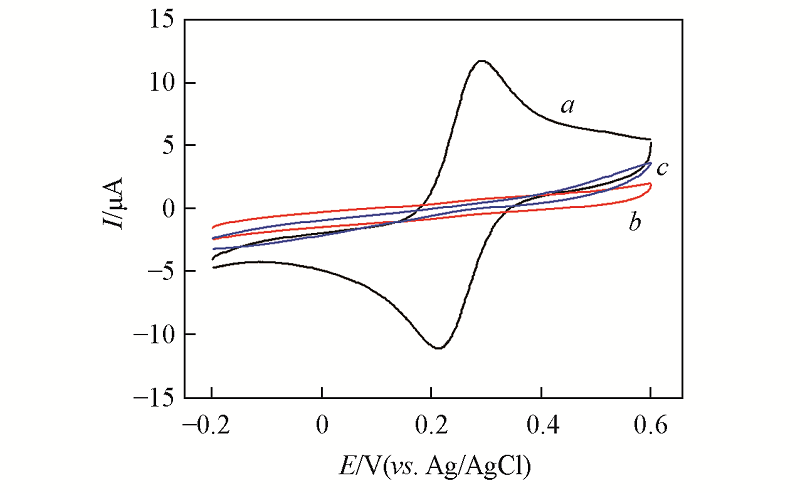
Fig.1 CV curves of 1 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/K4 [Fe(CN)6] at bare Au(a), Au-ssDNA(b) and Au-ssDNA-MCH(c) electrodesScan potential: -0.2—0.6 V; scan rate: 100 mV/s.
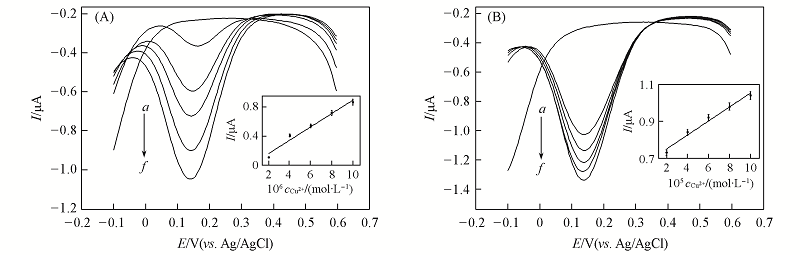
Fig.7 DPV response of the DNA modified electrode at different concentration of Cu2+ in 10 mmol/L PBS(pH=7.0) and 0.1 mol/L NaCl (A) cCu2+/(mol·L-1): a—f. 0, 2.0×10-6, 4.0×10-6, 6.0×10-6, 8.0×10-6, 1.0×10-5; (B) cCu2+/(mol·L-1): a—f. 0, 2.0×10-5 , 4.0×10-5, 6.0×10-5, 8.0×10-5, 1.0×10-4. Insets are the linear relationship between the peak current and the Cu2+ concentration.
| Electrode | Linear range/(mol·L-1) | Detection limit/(mol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ssIDNA modified electrode DPV | 2.0×10-6—1.0×10-5, 2.0×10-5— 1.0×10-4 | 6.4×10-7 | This work |
| Bismuth film modified electrode ASV | 3.1×10-7—3.1×10-6 | 3.1×10-7 | [31] |
| Pd/PAC-modified GCE DPV | 5×10-7—5.0×10-6 | 6.6×10-8 | [32] |
| IP6 MWCNTs ITO DNPASV | 1.0×10-8—8.0×10-7 | 2.5×10-9 | [33] |
| DSP-AuNPs/PAMAM/MWCNT GCE DPV | 1.0×10-9—1.0×10-6 | 4.8×10-10 | [34] |
Table 1 Comparison of the electrochemical sensor in this work and other sensors
| Electrode | Linear range/(mol·L-1) | Detection limit/(mol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ssIDNA modified electrode DPV | 2.0×10-6—1.0×10-5, 2.0×10-5— 1.0×10-4 | 6.4×10-7 | This work |
| Bismuth film modified electrode ASV | 3.1×10-7—3.1×10-6 | 3.1×10-7 | [31] |
| Pd/PAC-modified GCE DPV | 5×10-7—5.0×10-6 | 6.6×10-8 | [32] |
| IP6 MWCNTs ITO DNPASV | 1.0×10-8—8.0×10-7 | 2.5×10-9 | [33] |
| DSP-AuNPs/PAMAM/MWCNT GCE DPV | 1.0×10-9—1.0×10-6 | 4.8×10-10 | [34] |
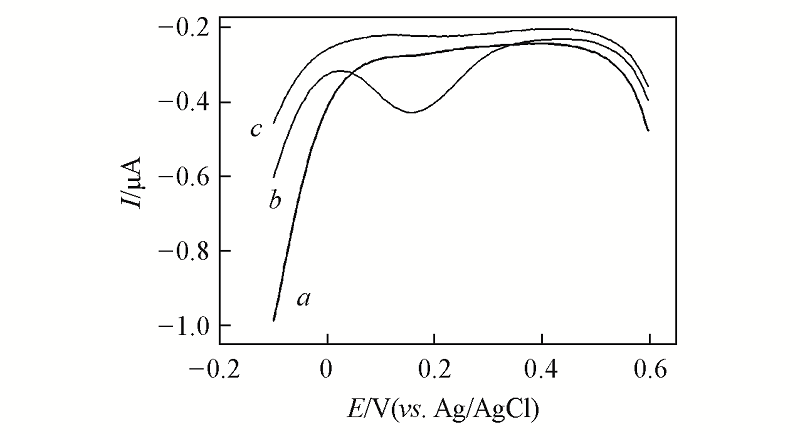
Fig.8 Differential pulse voltammograms of the DNA modified electrodes without Cu2 +(a)and with Cu2 +(b) and after being immersed into 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH=9.0) buffer solution containing excessive EDTA for 40 min(c)
| Sample | Cu2+ concentration/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | Sample | Cu2+ concentration/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Found | Added | Found | ||||
| Lake water 1 | 0 | 0 | Lake water 4 | 5 | 5.26 | 105.2 | |
| Lake water 2 | 5 | 4.71 | 94.2 | Lake water 5 | 5 | 5.55 | 111.1 |
| Lake water 3 | 5 | 4.76 | 95.2 | ||||
Table 2 Recovery analysis of Cu2+ in lake water samples
| Sample | Cu2+ concentration/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | Sample | Cu2+ concentration/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Found | Added | Found | ||||
| Lake water 1 | 0 | 0 | Lake water 4 | 5 | 5.26 | 105.2 | |
| Lake water 2 | 5 | 4.71 | 94.2 | Lake water 5 | 5 | 5.55 | 111.1 |
| Lake water 3 | 5 | 4.76 | 95.2 | ||||
| [1] | Gholivand M. B., Sohrabi A., Abbasi S., Electroanalysis,2007, 19(15), 1609—1615 |
| [2] | Reddy S. A., Reddy K. J., Narayan S. L., Reddy A. V., Food Chem., 2008, 109(3), 654—659 |
| [3] | Molinos-Senante M., Hernandez-Sancho F., Sala-Garrido R., Water Resour. Manage., 2013, 27(6), 1797—1808 |
| [4] | Aguilar F., Charrondiere U. R., Dusemund B., Galtier P., Gilbert J., Gott D. M., Grilli S., Guertler R., EFSA J., 2009, 1089, 1—15 |
| [5] | Pourreza N., Hoveizavi R., Anal. Chim. Acta,2005, 549(1), 124—128 |
| [6] | Atanassova D., Stefanova V., Russeva E., Talanta,1998, 47(5), 1237—1243 |
| [7] | Zhu Y. B., Inagaki K., Chiba K., J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2009, 24(9), 1179—1183 |
| [8] | Tang F.X., Detection of Heavy Metal in Water Based on Nanocomposite Material, Hunan University, Changsha, 2014(唐凤霞. 基于纳米复合材料检测水体中重金属含量. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2014) |
| [9] | Chen C., Research on Electrochemical Sensor for Heavy Metal Ions Detection, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 2013(陈晨. 用于重金属离子检测的电化学传感器研究, 上海: 华东理工大学, 2013) |
| [10] | Chaiyo S., Chailapakul O., Sakai T., Teshima N., Siangproh W., Talanta,2013, 108, 1—6 |
| [11] | Zhai R. J., Liu Y. J., Zhao X., Qi Y., Yin N., Huang T., Chemical Research & Application,2015, 27(9), 1277—1282(翟荣佳, 刘娅静, 赵鑫, 戚裕, 尹妮, 黄甜. 化学研究与应用, 2015, 27(9), 1277—1282) |
| [12] | Kong W. W., Jiang Y. L., Han Q. R., Wang B. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(2), 287—292(孔伟伟, 江玉亮, 韩巧荣, 王炳祥. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(2), 287—292) |
| [13] | McLaughlin C. K., Hamblin G. D., Sleiman H. F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(12), 5647—5656 |
| [14] | Wang C. H., Li Y. H., Jia G. Q., Liu Y., Lu S. M., Li C., Chem. Commun., 2012, 48(50), 6232—6234 |
| [15] | Duprey J., Takezawa Y., Shionoya M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(4), 1250—1254 |
| [16] | Zhang L. Y., Guo C. X., Cui Z. M., Guo J., Dong Z. L., Li C. M., Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18(49), 15693—15698 |
| [17] | Zhang S., Yu T., Sun M., Yu H., Zhang Z., Wang S., Jiang H., Talanta,2014, 126, 185—190 |
| [18] | Izatt R. M., Christensen J. J., Rytting J. H., Chem. Rev., 1971, 71 (5), 439—481 |
| [19] | Patil S. D., Rhodes D. G., Nucleic Acids Res., 2000, 28(12), 2439—2445 |
| [20] | Berti L., Burley G. A., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3(2), 81—87 |
| [21] | Li W., Chen X. F., Fu Y., Zhang J. L., J. Phys. Chem.B,2014, 118(20), 5300—5309 |
| [22] | Berti L., Burley G. A., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3(2), 81—87 |
| [23] | Chen X.F., Enantioselective Recognition and Enantioseparation of Ofloxacin Enantiomers via DNA-Cu(Ⅱ) Self-assembly, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 2014(陈雄飞. DNA-Cu(Ⅱ)自组装体在氧氟沙星对映体手性识别和拆分中的研究, 天津: 天津大学, 2014) |
| [24] | Liu M. C., Zhao G. H., Tang Y. Y., Yu Z. M., Lei Y. Z., Li M. F., Zhang Y. N., Li D. M., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 4241—4246 |
| [25] | Babkina S. S., Ulakhovich N. A., Anal. Chem., 2005, 77, 5678—5685 |
| [26] | Andrushchenko V., van de Sande J. H., Wieser H., Biopolymers,2003, 72(5), 374—390 |
| [27] | Hackl E. V., Blagoi Y. P., J. Inorg. Biochem., 2004, 98(11), 1911—1920 |
| [28] | Kim S. H., Martin R. B., Inorg. Chim. Acta,1984, 91, 19—24 |
| [29] | Sigel H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 1993, 22, 255—267 |
| [30] | Lonnberg H., Vihanto P., Inorg. Chim. Acta,1981, 56, 157—161 |
| [31] | Yu P., The Research for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using Electrochemical Sensors, Central South University, Changsha, 2011(喻鹏. 用于检测重金属离子电化学传感器的研究, 长沙: 中南大学, 2011) |
| [32] | Veerakumar P., Veeramani V., Chen S. M., Madhu R., Liu S. B., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2015, 8(2), 1319—1326 |
| [33] | Cui L., Constructions of Electrochemical Sensors for Heavy Metal Ions and Their Application, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 2015(崔琳. 重金属离子电化学传感器的构建及其应用, 南京: 南京大学, 2015) |
| [34] | Liang Y. H., Liu Y., Guo X. Y., Ye P. P., Wen Y., Yang H. F., Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2014, 201, 107—113 |
| [1] | LI Yulong, XIE Fating, GUAN Yan, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Guiqun, YAO Chao, YANG Tong, YANG Yunhui, HU Rong. A Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Ion Interaction with DNA for the Detection of Silver Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| [2] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| [3] | FU Kefei, LIAN Huiting, WEI Xiaofeng, SUN Xiangying, LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin-based Impedance Sensor for Recognition of L-Cysteine † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 706. |
| [4] | LI Botian,SHAO Wei,XIAO Da,ZHOU Xue,DONG Junwei,TANG Liming. Polypyrrole Nanowire Gels Based on Templating Fabrication and Their Energy Storage and Electrochemical Sensing Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 183. |
| [5] | CONG Fei, SUN Xiuhua, WANG Ke, GUI Taijiang, GAO Changlu. Characterization of Tertiary Amine-Cu Complex and Application in Copper Ion Slow-release Coatings† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1602. |
| [6] | LI Kaifeng,WU Dan,CHEN Yanwei. Effect of Copper Doping on the Growth and Optical Properties of Au Nanorods† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 855. |
| [7] | TONG Ti*, ZHAO Yangyang, FU Yilin, SHAN Guiye. Special Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering on Lung Cancer Tissues Based on Au/Cu Nanorods Substrate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1536. |
| [8] | YU Xijuan, HAN Lulu, HUN Xu. Cu2+ Modified Gold Nanoclusters for Fluorescence Turn-on Detection of Dopamine† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2169. |
| [9] | HU Yiping, SHAN Duoliang, LU Xiaoquan. Nonenzyme Sensor Based on Metal Organic Frameworks/Porphyrin/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Detection of Glucose† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1082. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yan, ZHENG Jing, WANG Juan, GUO Mandong. Preparation and Properties of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 860. |
| [11] | ZHUANG Qianfen, WANG Yong, NI Yongnian. Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Riboflavin Based on Nanocomposite Film of Polydeoxyadenylic Acid/Reduced Graphene Oxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1674. |
| [12] | HUANG Xueyi, YU Huicheng, WEI Yichun, LEI Fuhou, TAN Xuecai, WU Haiying. Preparation and Application of Novel Amobarbital Electrochemical Sensor Based on CuO Nanoparticles Modified Glassy Carbon† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10): 2078. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jin, WANG Chao-Ying, LI Xiao-Ping, NIU Yan-Hui. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for 2, 4-Dichlorophenol Based on Composite Film of o-Aminothiophenol and Au Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2296. |
| [14] | WEI Tai-Bao, LI Jun-Jian, LIN Qi, YAO Hong, GUO Ying, BAI Cui-Bing, XIE Yong-Qiang, ZHANG You-Ming. Highly Selective Colorimetric Recognition of Copper Ions Based on N-Aryl Coumarin Methyl Ketone Thiosemicarbazone Receptors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(11): 2452. |
| [15] | GU Jin-Ying, ZHU Ming-Li, SHI Xian-Fa. p-Tert-butylthiacalix[4]arene——a Potentially Useful Chelating Agent for Copper Poisoning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10): 2229. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||