

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (10): 2078.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140638
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Xueyi1, YU Huicheng1,*( ), WEI Yichun1, LEI Fuhou1, TAN Xuecai1,*, WU Haiying2
), WEI Yichun1, LEI Fuhou1, TAN Xuecai1,*, WU Haiying2
Received:2014-07-09
Online:2014-10-10
Published:2014-09-19
Contact:
YU Huicheng,TAN Xuecai
E-mail:doyhc@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Xueyi, YU Huicheng, WEI Yichun, LEI Fuhou, TAN Xuecai, WU Haiying. Preparation and Application of Novel Amobarbital Electrochemical Sensor Based on CuO Nanoparticles Modified Glassy Carbon†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10): 2078.
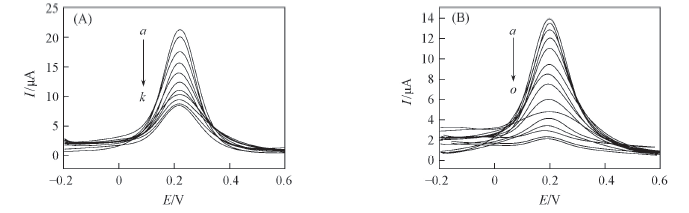
Fig.3 Effects of incubation time for the sensors CuO/MIP/GCE(A) and MIP/GCE(B) in 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]-0.1 mol/L PBS (A) t/min, a—k: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11; (B) t/min, a—o: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15.
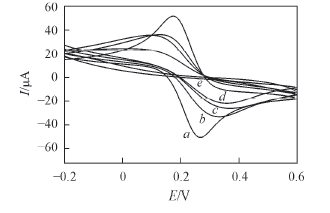
Fig.4 Cyclic voltammetries of different electrodes in 5.0×10-3 mol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]-0.1 mol/L PBS a. Bare GCE; b. MIP/CuO/GCE; c. MIP/GCE; d. MIP/CuO/GCE after interaction with 1.5×10-4mol/L AMB; e. NIP/CuO/GCE.
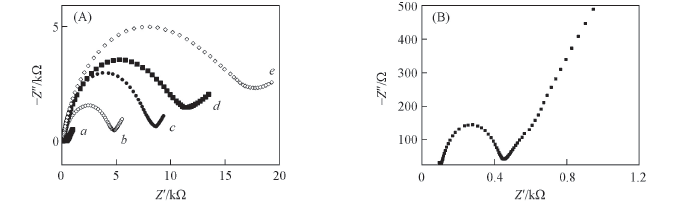
Fig.5 Electrochemical impedance spectra of different electrodes in 0.1 mol/L KCl-1.0×10-3 mol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/K4[Fe(CN)6](1∶1, molar ratio) (A) a. Bare GCE; b. MIP/CuO/GCE; c. MIP/GCE; d. MIP/CuO/GCE after interaction with 5.0×10-5 mol/L AMB; e. NIP/CuO/GCE.
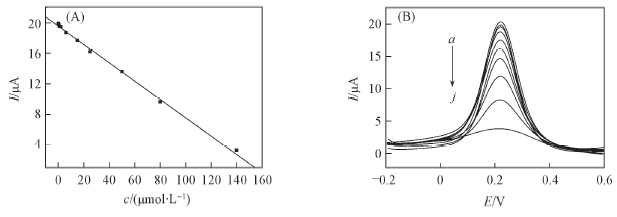
Fig.7 Calibrations curve of AMB(A) and the differential pulse voltammetry incubation in different concentrations of AMB(B) in 5.0×10-3 mol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]-0.1 mol/L PBS (B) c/(μmol·L-1), a—j: 1.0×10-7, 5.0×10-7, 8.0×10-7, 2.0×10-6, 6.0×10-6, 1.5×10-5, 2.5×10-5, 5.0×10-5, 8.0×10-5, 1.4×10-4.
| Sample | 105c/(mol·L-1) | 105 Added/(mol·L-1) | 105 Total found* /(mol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00 | 1.0 | 0.96 | 96.00 | 1.86 |
| 2 | 0.00 | 1.5 | 1.41 | 94.00 | 1.57 |
| 3 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 2.07 | 103.50 | 1.96 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 2.50 | 2.47 | 98.80 | 2.17 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 3.14 | 104.67 | 2.45 |
Table 1 Determination results of recovery using the sensor
| Sample | 105c/(mol·L-1) | 105 Added/(mol·L-1) | 105 Total found* /(mol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00 | 1.0 | 0.96 | 96.00 | 1.86 |
| 2 | 0.00 | 1.5 | 1.41 | 94.00 | 1.57 |
| 3 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 2.07 | 103.50 | 1.96 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 2.50 | 2.47 | 98.80 | 2.17 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 3.14 | 104.67 | 2.45 |
| [1] | Jahan B. R., Mehdi B., Reza O., Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2012, 95, 121—128 |
| [2] | Thomas A. T., TrAC Trends Analytical Chem., 2001, 20(8), 419—434 |
| [3] | Mira P., Maria D. H., Damià B., J. Chromatogr. A,2005, 1067, 1—14 |
| [4] | Kaori H., Shizuyo H., Hisami M., Jun H., J. Chromatogr. A,2009, 1226(25), 4957—4962 |
| [5] | Qin Y. P., Huang X. Y., Yu H. C., Tan X. C., Tang X. M., Huang X. H., Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm., 2014, 31(5), 528—534 |
| (覃燕平, 黄学艺, 余会成, 谭学才, 唐响妹, 黄雪花. 中国现代应用药学杂志. 2014, 31(5), 528—534) | |
| [6] | Duan S. J., He X. W., Chen L. X., Zhang Y. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(3), 464—469 |
| (段淑静, 何锡文, 陈朗星, 张玉奎. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(3), 464—469) | |
| [7] | Fan C. H., Yang Y. Q., Zhao W., Xiao Y., Luo J., Liu X. Y., Acta Chimica Sinica,2013, 71, 934—940 |
| (范存华, 杨逸群, 赵伟, 肖宇, 罗静, 刘晓亚. 化学学报, 2013, 71, 934—940) | |
| [8] | Xing X. R., Liu S., Yu J. H., Lian W. J., Huang J. D., Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2012, 31, 277—283 |
| [9] | Cosimino M., Elisabetta M., Rosaria A. P., Alessandro P., Iva C., Sergey A. P., Anal Bioanal Chem., 2012, 402, 1827—1846 |
| [10] | Wang Q., Liu W., Yang X. H., Wang K. M., Liu P., He L. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(8), 1845—1850 |
| (王青, 刘卫, 羊小海, 王柯敏, 刘沛, 何磊良. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(8), 1845—1850) | |
| [11] | Liu Z. G., Zhang A., Guo Y. J., Dong C., Biosensors and Bioelectronics., 2014, 58, 242—248 |
| [12] | Bhim B. P., Deepak K., Rashmi M., Mahavir P. T., Electrochimica Acta., 2011, 56, 7202—7211 |
| [13] | Yuan B. Q., Xu C. Y., Liu L., Zhang Q. Q., Ji S. Q., Pi L. P., Zhang D. J., Huo Q. S., Electrochimica Acta,2013, 104, 78—83 |
| [14] | Huang X. Y., Yu H. C., Tan X. C., Lei F. H., Huang X. H., Chin. J. Ananl. Lab., 2014, 33(5), 550—554 |
| (黄学艺, 余会成, 谭学才, 雷福厚, 黄雪花. 分析试验室, 2014, 33(5), 550—554) | |
| [15] | Ali P., Vinod K. G., Afsaneh L. S., Fatemeh K., Mehdi Y., Mojtaba G., Electrochimica Acta,2014, 123, 456—462 |
| [16] | Mao Y., Bao Y., Han D. X., Li F. H., Niu L., Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2012, 38, 55—60 |
| [17] | Yang Y. K., Fang G. Z., Liu G. Y., Pan M. F., Wang X. M., Kong L. J., He X. L., Wang S., Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2013, 37, 475—481 |
| [18] | Tong Y. J., Li H. D., Guan H. M., Zhao J. M., Saadat M., Saima A., Liang F., Xu G. B., Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2013, 37, 553—558 |
| [19] | Mehdi B., Melika N., Electrochimica Acta,2013, 108, 22—31 |
| [20] | Fang B., Zhang C. H., Zhang W., Wang G. F., Electrochimica Acta,2009, 55, 178—182 |
| [21] | Huang L., Jiao S. F., Li M. G., Electrochimica Acta,2014, 121, 233—239 |
| [1] | LI Yulong, XIE Fating, GUAN Yan, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Guiqun, YAO Chao, YANG Tong, YANG Yunhui, HU Rong. A Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Ion Interaction with DNA for the Detection of Silver Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| [2] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| [3] | FU Kefei, LIAN Huiting, WEI Xiaofeng, SUN Xiangying, LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin-based Impedance Sensor for Recognition of L-Cysteine † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 706. |
| [4] | LI Botian,SHAO Wei,XIAO Da,ZHOU Xue,DONG Junwei,TANG Liming. Polypyrrole Nanowire Gels Based on Templating Fabrication and Their Energy Storage and Electrochemical Sensing Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 183. |
| [5] | LI Min, KONG Huifang, GUO Zhihui. Detection of Copper Ion Based on the Interaction Between DNA Molecules and Copper Ions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1269. |
| [6] | HU Yiping, SHAN Duoliang, LU Xiaoquan. Nonenzyme Sensor Based on Metal Organic Frameworks/Porphyrin/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Detection of Glucose† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1082. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yan, ZHENG Jing, WANG Juan, GUO Mandong. Preparation and Properties of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 860. |
| [8] | ZHUANG Qianfen, WANG Yong, NI Yongnian. Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Riboflavin Based on Nanocomposite Film of Polydeoxyadenylic Acid/Reduced Graphene Oxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1674. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jin, WANG Chao-Ying, LI Xiao-Ping, NIU Yan-Hui. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for 2, 4-Dichlorophenol Based on Composite Film of o-Aminothiophenol and Au Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2296. |
| [10] | WANG Lin, TAN Xue-Cai, ZHAO Dan-Dan, LIU Li, LEI Fu-Hou, HUANG Zai-Yin, GONG Qi. Electrochemical Sensor for Caffeine Detection Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Maleic Rosin Acrylic Acid Glycol Ester as Cross-linker [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(08): 1708. |
| [11] | LI Lin-Ru, FU Hong-Gang, LU Tian-Hong. Electrocatalytic Performance of Graphene Supported Ir Catalyst for Ammonia Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(01): 102. |
| [12] | HU Yu-Fang, ZHANG Zhao-Hui*, ZHANG Hua-Bin, YU Xiao-Xiao, YAO Shou-Zhuo. Research on Self-assembly MWNTs-clindamycin Molecularly Imprinted Sol-gel Electrochemical Sensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(9): 1703. |
| [13] | LU Hai-Xia, WU Zai-Sheng, JIN Xiao-Yong, SHEN Guo-Li*, YU Ru-Qin. Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Seminetwork-type Au Nanoparticles Labled Horseradish Peroxidase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(2): 263. |
| [14] | CHEN Rong-Sheng1, HU Liang-Sheng1, ZHANG Xu-Ming1, FU Ji-Jiang1, HUO Kai-Fu1,3*, CHU Paul-K.3, CHENG Jie-Ke2. Fabrication of TiO2 @C Core-shell Nanofiber Arrays Electrode and Its Appdication in Electrochemical Sensing [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(12): 2542. |
| [15] | WANG Gui-Xiang, PAN Qian-Xiu, WANG Huai-Sheng . Preparation of a Novel DNA Electrochemical Sensor and Its Application to Detection of DNA Oxidative Damage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(10): 1812. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||