

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 955.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20141073
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Xiaoxia1, GAO Xiaoya2, ZHANG Xiaochao2, LI Rui2, WANG Yawen2, WANG Yunfang2, FAN Caimei2,*( )
)
Received:2014-12-05
Online:2015-05-10
Published:2015-04-17
Contact:
FAN Caimei
E-mail:fancm@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Xiaoxia, GAO Xiaoya, ZHANG Xiaochao, LI Rui, WANG Yawen, WANG Yunfang, FAN Caimei. Tunable Synthesis of Hierarchical BiOCl Microspheres for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Pharmaceutical Wastewater†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 955.
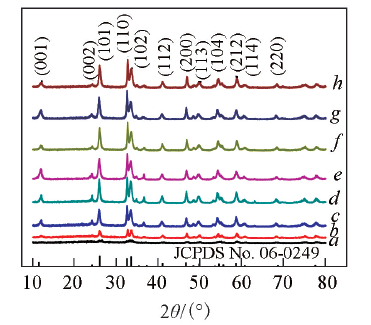
Fig.1 XRD patterns of as-prepared BiOCl photocatalysts with different Co(NH2)2/BiCl3 molar ratios(a—d) and hydrothermal time(e—h)n[CO(NH2)2]/n(BiCl3): a. 8∶1; b. 10∶1; c. 15∶1; d. 20∶1. Hydrothermal time/h: e. 4; f. 24; g. 48; h. 72.
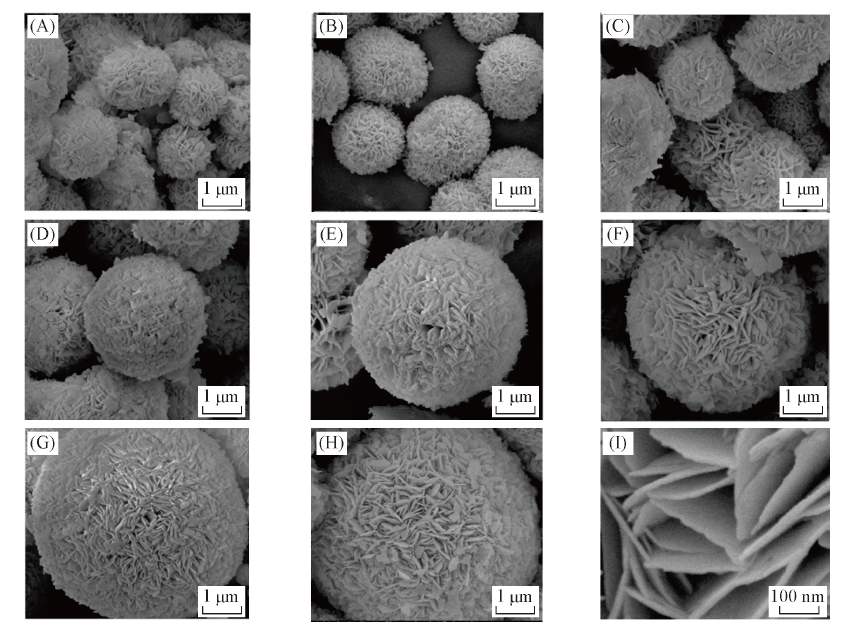
Fig.2 SEM images of as-prepared BiOCl photocatalysts with different Co(NH2)2/BiCl3 molar ratio(A—D) and hydrothermal time(E—I)n[CO(NH2)2]/n(BiCl3): (A) 8∶1; (B) 10∶1; (C) 15∶1; (D) 20∶1. Hydrothermal time/h: (E) 4; (F) 24; (G) 48; (H) 72. (I) is the HRSEM image of the sample of (G).
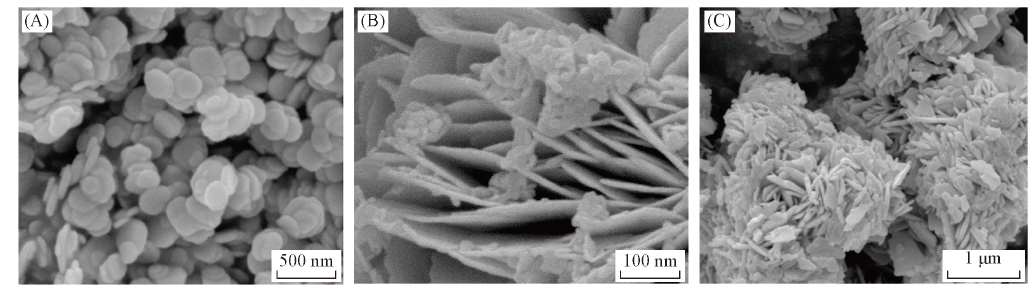
Fig.3 SEM images of BiOCl photocatalysts in mixed solvent(A) and with different hydrothermal time(B, C)n[CO(NH2)2]/n(BiCl3)=10∶1. (A) V(DEG)∶V(H2O)=1∶1; (B) hydrothermal time: 10 min; (C) hydrothermal time: 20 min.
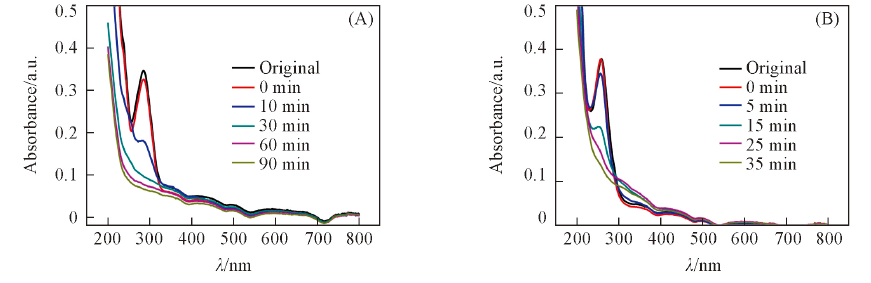
Fig.6 Photodegradation of CBZ(A) and SMZ(B) solution upon UV light irradiation in the presence of BiOCl prepared at n[CO(NH2)2]/n(BiCl3)=15∶1 (A) [CBZ]0=2.5 mg/L; (B) [SMZ]0=5 mg/L.
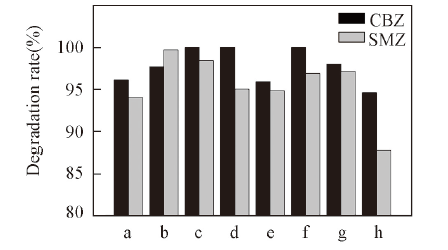
Fig.7 Photodegradation of CBZ and SMZ upon UV light irradiation in the presence of different BiOCl photocatalysts[CBZ]0=2.5 mg/L, [SMZ]0=5 mg/L, [BiOCl]=0.5 g/L. n[CO(NH2)2]/n(BiCl3): a. 8∶1; b. 10∶1; c. 15∶1; d. 20∶1. Hydrothermal time/h: e. 4; f. 24; g. 48; h. 72.
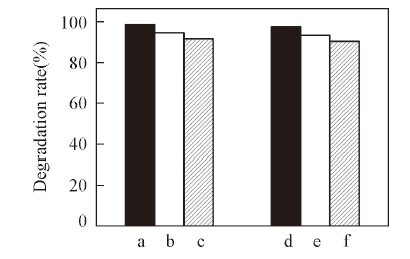
Fig.8 Effect of initial concentrations of CBZ and SMZ on their degradation rate under simulated solar light irradiation in the presence of BiOCl[CBZ]0/(mg·L-1): a. 2.5, b. 5, c. 10; [SMZ]0/(mg·L-1): d. 5, e. 10, f. 20; [BiOCl]=0.5 g/L.
| [1] | Aguinaco, A. , Beltrá, n F. J. , Sagasti J. J., P. , Gimeno, O. , Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 235, 46- 51 |
| [2] | Hoque M., E. , Cloutier, F. , Arcieri, C. , McInnes, M. , Sultana, T. , Murray, C. , Vanrolleghem P., A. , Metcalfe C., D. , Sci. Total Environ., 2014, 487, 801- 812 |
| [3] | Lv, M. , Sun, Q. , Hu A., Y. , Hou L., Y. , Li J., W. , Cai, X. , Yu C., P. , J. Hazard. Mater., 2014, 280, 696- 705 |
| [4] | Mohapatra D., P. , Brar S., K. , Tyagi R., D. , Picard, P. , Surampalli R., Y. , Sci. Total Environ., 2014, 470, 58- 75 |
| [5] | Zhang Y., J. , Geiß, en S. U. , Gal C., M. , Chemosphere, 2008, 73, 1151- 1161 |
| [6] | Lekkerkerker-Teunissen, K. , Benotti M., J. , Snyder S., A. , Dijk H. C., V. , Sep. Purif. Technol., 2012, 96, 33- 43 |
| [7] | Donner, E. , Kosjek, T. , Qualmann, S. , Kusk K., O. , Heath, E. , Revitt D., M. , Ledin, A. , Andersen H., R. , Sci. Total Environ., 2013, 443, 870- 876 |
| [8] | Liu J., L. , Wong M., H. , Environ. Int., 2013, 59, 208- 224 |
| [9] | 刘建新, 王韵芳, 王雅文, 樊彩梅. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30, 729- 737 |
| Liu J., X. , Wang Y., F. , Wang Y., W. , Fan C., M. , Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30, 729- 737 | |
| [10] | 龙明策, 万磊, 曾曾, 刘伊依, 陈渊源. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28, 2917- 2923 |
| Long M., C. , Wan, L. , Zeng, C. , Liu Y., Y. , Chen Y., Y. , Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2012, 28, 2917- 2923 | |
| [11] | 戚克振, 王艳, 付嘉琦, Rengaraj Selvaraj, 王贵昌. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35( 12), 2523- 2528 |
| Qi K., Z. , Wang, Y. , Fu J., Q. , Rengaraj, S. , Wang G., C. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35( 12), 2523- 2528 | |
| [12] | Zhang X., C. , Liu X., X. , Fan C., M. , Wang Y., W. , Wang Y., F. , Liang Z., H. , Appl. Catal. B, 2013, 132, 332- 341 |
| [13] | 姬磊, 于瑞敏, 王浩人, 陈丽铎, 汪怀远. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36( 3), 551- 558 |
| Ji, L. , Yu R., M. , Wang H., R. , Chen L., D. , Wang H., Y. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36( 3), 551- 558 | |
| [14] | 王艳, 张小超, 赵丽军, 赵晓霞, 史宝萍, 樊彩梅. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35( 12), 2624- 2631 |
| Wang, Y. , Zhang X., C. , Zhao L., J. , Zhao X., X. , Shi B., P. , Fan C., M. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35( 12), 2624- 2631 | |
| [15] | Chen, F. , Liu H., Q. , Bagwasi, S. , Shen X., X. , Zhang J., L. , J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2010, 215, 76- 80 |
| [16] | Peng S., J. , Li L., L. , Zhu P., N. , Wu Y., Z. , Srinivasan, M. , Mhaisalkar S., G. , Ramakrishna, S. , Yan Q., Y. , Chem. Asian J., 2013, 8, 258- 268 |
| [17] | Tong, H. , Ouyang S., X. , Bi Y., P. , Umezawa, N. , Oshikiri, M. , Ye J., H. , Adv. Mater., 2012, 24, 229- 251 |
| [18] | 董占能, 赵兵, 郭玉忠. 昆明理工大学学报, 2000, 25, 58- 61 |
| Dong Z., N. , Zhao, B. , Guo Y., Z. , J. Kunming University Sci. Technol., 2000, 25, 58- 61 | |
| [19] | Xiong J., Y. , Cheng, G. , Qin, F. , Wang, R. , Sun H., Z. , Chen, R. , Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 220, 228- 236 |
| [20] | Hirano, M. , Morikawa, H. , Chem. Mater., 2003, 15, 2561- 2566 |
| [21] | 蒋琪英, 沈娟, 钟国清. 化学进展, 2006, 18, 1634- 1645 |
| Jiang Q., Y. , Shen, J. , Zhong G., Q. , Prog. Chem., 2006, 18, 1634- 1645 | |
| [22] | Duan, F. , Zheng, Y. , Liu, L. , Chen M., Q. , Xie, Y. , Mater. Lett., 2010, 64, 1566- 1569 |
| [23] | Ren K., X. , Zhang, K. , Liu, J. , Luo H., D. , Huang Y., B. , Yu X., B. , Cryst. Eng. Commmu., 2012, 14, 4384- 4390 |
| [24] | Zhang, X. , Ai Z., H. , Jia F., L. , Zhang L., Z. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 747- 753 |
| [25] | Toyoda, M. , Nanbu, Y. , Nakazawa, Y. , Hirano, M. , Inagaki, M. , Appl. Catal. B, 2004, 49, 227- 232 |
| [26] | 王龙. 几种纳米材料的制备及其安全性评价, 成都: 四川大学, 2007) |
| Wang, L. , Preparation and Bio-safe Assessing of Several Nanomaterials Including Nano-ZnO, Nano-Mn3O4 and Ce-doped Nano-TiO2, Sichuan Uversity, Chengdu, 2007( | |
| [27] | 刘晓霞, 樊彩梅, 王韵芳, 王雅文, 张小超, 梁镇海. 中国科学: 化学, 2012, 42, 1145- 1151 |
| Liu X., X. , Fan C., M. , Wang Y., F. , Wang Y., W. , Zhang X., C. , Liang Z., H. , Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2012, 42, 1145- 1151 | |
| [28] | Deng, J. , Shao Y., S. , Gao N., Y. , Deng, Y. , Zhou S., Q. , Hu X., H. , Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 228, 765- 771 |
| [29] | Wang A., M. , Li Y., Y. , Estrada A., L. , Appl. Catal. B, 2011, 102, 378- 386 |
| [1] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [2] | LIN Zhi, PENG Zhiming, HE Weiqing, SHEN Shaohua. Single-atom and Cluster Photocatalysis: Competition and Cooperation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| [3] | TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325. |
| [4] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [6] | QIU Liqi, YAO Xiangyang, HE Liangnian. Visible-light-driven Selective Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Catalyzed by Earth-abundant Metalloporphyrin Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220064. |
| [7] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [8] | TAO Yu, OU Honghui, LEI Yongpeng, XIONG Yu. Research Progress of Single-atom Catalysts in Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220143. |
| [9] | FENG Li, SHAO Lanxing, LI Sijun, QUAN Wenxuan, ZHUANG Jinliang. Synthesis of Ultrathin Sm-MOF Nanosheets and Their Visible-light Induced Photodegradation of Mustard Simulant [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210867. |
| [10] | MENG Xiangyu, ZHAN Qi, WU Yanan, MA Xiaoshuang, JIANG Jingyi, SUN Yueming, DAI Yunqian. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogenation Performance of Au/RGO/Na2Ti3O7 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210655. |
| [11] | GUO Biao, ZHAO Chencan, LIU Xinxin, YU Zhou, ZHOU Lijing, YUAN Hongming, ZHAO Zhen. Effects of Surface Hydrothermal Carbon Layer on the Photocatalytic Activity of Magnetic NiFe2O4 Octahedron [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220472. |
| [12] | LI Chenchen, NA Yong. g-C3N4/CdS/Ni Composite as a Bifunctional Photocatalyst for H2 Generation and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2896. |
| [13] | LI Yishan, GUO Liang, PENG Sifan, ZHANG Qingmao, ZHANG Yuhao, XU Shiqi. Cobalt Substitutions in Lanthanum Manganate Photocatalyst: First-principles and Visible-light Photocatalytic Ability Investigation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1881. |
| [14] | WANG Peng, YANG Min, TANG Sengpei, CHEN Feitai, LI Youji. Preparation of Cellular C3N4/CoSe2/GA Composite Photocatalyst and Its CO2 Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1924. |
| [15] | YANG Sixian, ZHONG Wenyu, LI Chaoxian, SU Qiuyao, XU Bingjia, HE Guping, SUN Fengqiang. Photochemical Fabrication and Performance of Polyaniline Nanowire/SnO2 Composite Photocatalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1942. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||