

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 1816.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140253
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yupeng, ZHANG Zhichao, LI Shengyao, SHI Wei, LEI Mingkai*( )
)
Received:2014-03-24
Online:2014-08-10
Published:2014-06-30
Contact:
LEI Mingkai
E-mail:surfeng@dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Yupeng, ZHANG Zhichao, LI Shengyao, SHI Wei, LEI Mingkai. Mechanism of Hydrophobic Over-recovery on Polyethylene Surface Modified by Oxygen Plasma†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1816.
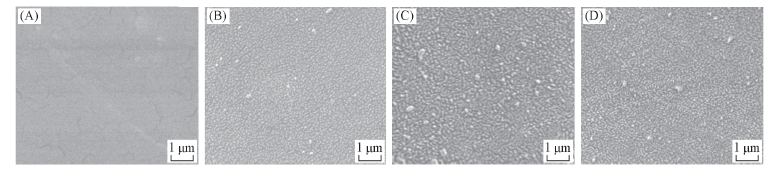
Fig.1 SEM images of original LDPE surface(A), as-modified surface under oxygen CCP of 200 W for an exposure time of 1 min(B), and post-aged surface at an aging temperature of 60 ℃(C) and 90 ℃(D) after an aging time of 24 h
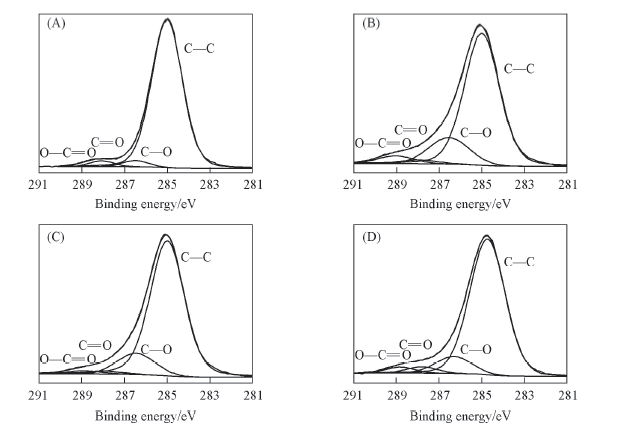
Fig.2 Deconvolution of XPS C1s spectra of original LDPE surface(A), as-modified surface under oxygen CCP of 200 W for 1 min(B), and the post-aged surface at 60 ℃(C) and 90 ℃(D) after 24 h
| Sample | Bonding contribution(%) | Elemental composition(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C—C(285.0 eV) | C—O(286.5 eV) | C | O—C | C | O | |
| Original | 93.1 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 0.7 | 95.6 | 4.4 |
| As-modified | 76.9 | 16.4 | 2.2 | 4.5 | 82.9 | 17.1 |
| Post-aged at 60 ℃ | 83.0 | 13.1 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 84.5 | 15.5 |
| Post-aged at 90 ℃ | 84.1 | 10.1 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 85.4 | 14.6 |
Table 1 Component percentage in the C1s spectra and atomic concentration of C and O measured by XPS for original LDPE surface, as-modified surface under oxygen CCP of 200 W for 1 min and the post-aged surface at 60 and 90 ℃ after 24 h
| Sample | Bonding contribution(%) | Elemental composition(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C—C(285.0 eV) | C—O(286.5 eV) | C | O—C | C | O | |
| Original | 93.1 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 0.7 | 95.6 | 4.4 |
| As-modified | 76.9 | 16.4 | 2.2 | 4.5 | 82.9 | 17.1 |
| Post-aged at 60 ℃ | 83.0 | 13.1 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 84.5 | 15.5 |
| Post-aged at 90 ℃ | 84.1 | 10.1 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 85.4 | 14.6 |
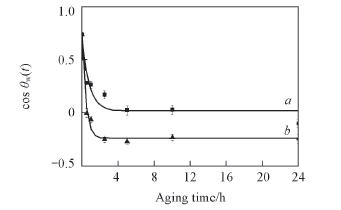
Fig.4 Fitting curve of the time-dependent contact angle θw(t) on the post-aged LDPE surface dependent on the aging time t at 60 ℃(a) and 90 ℃(b) during 24 h for the oxygen CCP modified sample under 200 W for 1 min
| Sample | f | fp(t=0 h) (%) | fnp(t=0) (%) | fp(t=24 h) (%) | fnp(t=24 h) (%) | fp(t=∞) (%) | fnp(t=∞) (%) | τ/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-aged at 60 ℃ | 26.7 | 34.0 | 60.7 | 39.3 | 26.7 | 73.3 | 26.7 | 73.3 | 0.81 |
| Post-aged at 90 ℃ | 13.5 | 48.2 | 61.7 | 38.3 | 13.5 | 86.5 | 13.5 | 86.5 | 0.41 |
Table 2 Surface restructuring parameters of the post-aged LDPE surface during aging estimated by using Eq.(1) from the experimental data in Fig.4
| Sample | f | fp(t=0 h) (%) | fnp(t=0) (%) | fp(t=24 h) (%) | fnp(t=24 h) (%) | fp(t=∞) (%) | fnp(t=∞) (%) | τ/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-aged at 60 ℃ | 26.7 | 34.0 | 60.7 | 39.3 | 26.7 | 73.3 | 26.7 | 73.3 | 0.81 |
| Post-aged at 90 ℃ | 13.5 | 48.2 | 61.7 | 38.3 | 13.5 | 86.5 | 13.5 | 86.5 | 0.41 |
| [1] | Desmet T., Morent R., de Geyter N., Leys C., Schacht E., Dubruel P., Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10(9), 2351—2378 |
| [2] | Lee S., Spencer N. D., Tribol. Int., 2005, 38(11/12), 922—930 |
| [3] | Nie H. R., Jiang Q. S., Han Z. C., He A. H., Chem. J. Chinese Univeristies, 2010, 31(7), 1451—1455 |
| (聂华荣, 江青松, 韩志超, 贺爱华. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(7), 1451—1455) | |
| [4] | Gupta B., Hilborn J., Hollenstein C. H., Plummer C. J. G., Houriet R., Xanthopoulos N., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2000, 78(5), 1083—1091 |
| [5] | Sanchis M. R., Blanes V., Blanes M., Garcia D., Balart R., Eur. Polym. J., 2006, 42(7), 1558—1568 |
| [6] | Siow K. S., Britcher L., Kumar S., Griesser H. J., Plasma Process Polym., 2006, 3(6/7), 392—418 |
| [7] | Tsougeni K., Vourdas N., Tserepi A., Gogolides E., Langmuir, 2009, 25(19), 11748—11759 |
| [8] | Slepiuk V., Plasma Process Polym., 2009, 9(2) 197—206 |
| [9] | Li Y. P., Shi W., Li S. Y., Lei M. K., Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 213, 139—144 |
| [10] | Chatelier R. C., Xie X., Gengenbach T. R., Griesser H. J., Langmuir, 1995, 11(7), 2576—2584 |
| [11] | Holmes-Farley S. R., Reamey R. H., Nuzzo R., McCarthya T. J., Whitesides G. M., Langmuir, 1987, 3(5), 799—815 |
| [12] | Rodriguez-Santiago V., Bujanda A. A., Stein B. E., Pappas D. D., Plasma Process Polym., 2011, 8(7), 631—639 |
| [13] | Zheng Z. W., Deng K. M., Ren L., Wang Y. J., Chem. J. Chinese Univeristies, 2012, 33(6), 1350—1354 |
| (郑志雯, 邓凯敏, 任力, 王迎军. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(6), 1350—1354) | |
| [14] | Wohlfart E., Fernández-Blázquez J. P., Knoche E., Bello A., Pérez E., Arzt E., del Campo A., Macromolecules, 2010, 43(23), 9908—9917 |
| [15] | Li Y. P., Li S. Y., Shi W., Lei M. K., Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 206, 4952—4958 |
| [16] | Vourdas N., Tserepi A., Gogolides E., Nanotechnology, 2007, 18(12), 125304-1—125304-7 |
| [17] | Lamb R. N., Furlong D. N., J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1, 1982, 78, 61—73 |
| [18] | Walczak M. M., Chung C., Stole S. M., Widrig C. A., Porter M. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113(7), 2370—2378 |
| [19] | Chatelier R. C., Xie X., Gengenbach T. R., Griesser H. J., Langmuir, 1995, 11(7), 2585—2591 |
| [1] | LIU Miao, LIU Ruibo, LIU Badi, QIAN Ying. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Lysosome-targeted Indole-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [2] | WANG Wei, ZOU Bingchen, HOU Jie, ZHOU Wanli, LUO Jianping, WANG Kangli, JIANG Kai. In⁃situ Analysis of Interfacial Reaction Process Inside Li-Ga Liquid Metal Battery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220261. |
| [3] | MENG Fanwei, GAO Qi, YE Qing, LI Chenxi. Potassium Poisoning Mechanism of Cu-SAPO-18 Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Ammonia [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2832. |
| [4] | ZHU Zhaotian, LI Shengkai, SONG Minghui, CAI Xinqi, SONG Zhiling, CHEN Long, CHEN Zhuo. Recent Progress of Versatile Metal Graphitic Nanocapsules in Biomedical Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2701. |
| [5] | LI Anran, ZHAO Bing, KAN Wei, SONG Tianshu, KONG Xiangdong, BU Fanqiang, SUN Li, YIN Guangming, WANG Liyan. ON-OFF-ON Double Colorimetric and Fluorescent Probes Based on Phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole Derivatives and Their Living Cells Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2403. |
| [6] | HUANG Chibao, KANG Shuai, PAN Qi, LYU Guoling. Carbazole-derived Dicyanostilbene Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Lipid Raft [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2443. |
| [7] | CHEN Hongda, ZHANG Hua, WANG Zhenxin. Development of Small Animals in vivo Fluorescence-photothermal Dual Mode Imaging System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 725. |
| [8] | CHEN Weiju, CHEN Shiya, XUE Caoye, LIU Bo, ZHENG Jing. Fluorescent Probe for Hypoxia-triggered Imaging and Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3433. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yaqing, LI Linyao, HAO Mengqi, LUO Qin, DENG Siyu, YANG Yun, LIANG Xuewei, FANG Weiwei, SONG Erqun. Research Progress of Bacterial Infection Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3265. |
| [10] | LIU Hong, JIANG Jinghong, DUAN Zhijuan, XU Shijun, HUANG Fujian, XIA Fan. Recent Advance in Light-controlled CRISPR Technology [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3321. |
| [11] | KE Mengting, YUAN Jiangpei, ZHANG Heng, FANG Yu. Coordination Porous Polymers for Targeting Subcellular Organelles: Bio-imaging, Diagnosis and Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3295. |
| [12] | WANG Mengmeng, LUAN Tianjiao, YANG Mingyan, LYU Jiajia, GAO Jie, LI Hongyu, WEI Gang, YUAN Zeli. Rhodamine Fluorescent Probe for Tumor Targeted Hypoxia-imaging as Intra-operative Navigators [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3071. |
| [13] | GONG Shaohua, ZHANG Xia, LI Na, TANG Bo. Recent Progress of Fluorescent Nanoprobes for Organelle pH Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1933. |
| [14] | BAI Cuiting, YUE Renye, LUO Liegao, MA Nan. Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNA Content by Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer Cells Using Dual-color Fluorescence Nanosensor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1252. |
| [15] | LIANG Yuxin, ZHAO Rong, LIANG Xinyue, FANG Xiaohong. Single-molecule Imaging and Analysis of Signal Transduction Proteins on Cell Membranes † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1127. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||