

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 1023.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131295
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2013-12-30
Online:2014-05-10
Published:2014-04-18
Contact:
DING Yihong
E-mail:yhdd@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHU Weiwei, DING Yihong. Theoretical Studies on the Reaction Pathways of l-CnH(n=5,6)+
| l-C5H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | l-C5H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | ||
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | QTS1/2 | -43.9 | ||
| 1 | -118.4 | -85.0 | -77.8 | TS1/3 | -112.6 | -88.3 | -82.5 |
| Q1 | -49.4 | TS3/P2 | -466.6 | -484.6 | -473.3 | ||
| 2 | -196.3 | -159.0 | -151.5 | TS3/4 | -465.4 | -475.4 | -465.4 |
| Q2 | -183.3 | TS4/5 | -490.5 | -497.6 | -491.3 | ||
| 3 | -552.4 | -581.3 | -565.0 | P1(CO+HC4O) | -632.8 | -614.4 | -608.5 |
| 4 | -492.6 | -506.8 | -498.4 | P2(CO2+C4H) | -498.4 | -523.1 | -508.9 |
| 5 | -633.2 | -660.8 | -653.3 | P3(3O+HC5O) | -182.0 | -183.3 | -178.3 |
Table 1 Relative energies of reactant, intermediates, transition states and products for the l-C5H+O2 reaction at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level and CCSD(T)/CC-PVTZ//B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p)+ ZPVE level
| l-C5H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | l-C5H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | ||
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | QTS1/2 | -43.9 | ||
| 1 | -118.4 | -85.0 | -77.8 | TS1/3 | -112.6 | -88.3 | -82.5 |
| Q1 | -49.4 | TS3/P2 | -466.6 | -484.6 | -473.3 | ||
| 2 | -196.3 | -159.0 | -151.5 | TS3/4 | -465.4 | -475.4 | -465.4 |
| Q2 | -183.3 | TS4/5 | -490.5 | -497.6 | -491.3 | ||
| 3 | -552.4 | -581.3 | -565.0 | P1(CO+HC4O) | -632.8 | -614.4 | -608.5 |
| 4 | -492.6 | -506.8 | -498.4 | P2(CO2+C4H) | -498.4 | -523.1 | -508.9 |
| 5 | -633.2 | -660.8 | -653.3 | P3(3O+HC5O) | -182.0 | -183.3 | -178.3 |
| l-C6H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | l-C6H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | ||
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | TS2/3 | -190.8 | -225.2 | -218.0 |
| 1 | -179.1 | -209.3 | -193.3 | TS3/4 | -506.8 | -540.3 | -527.7 |
| 2 | -198.8 | -230.2 | -219.3 | TS3/P2 | -425.2 | -434.8 | -426.9 |
| 3 | -508.5 | -543.2 | -529.4 | TS4/P1 | -545.7 | -587.6 | -579.6 |
| 4 | -583.8 | -620.6 | -604.7 | P1(3O+HC6O) | -604.7 | -584.2 | -581.3 |
| TS1/2 | -114.3 | -126.8 | -117.6 | P2(CO2+C5H) | -467.9 | -490.1 | -488.0 |
| TS1/P3 | -126.8 | -124.7 | -117.2 | P3(CO+HC5O) | -181.6 | -185.1 | -178.7 |
Table 2 Relative energies of reactant, intermediates, transition states and products for the l-C6H+O2 reaction at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level and CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ//B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p)+ ZPVE level
| l-C6H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | l-C6H+O2 | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | B3LYP/6-311++ G(d,p) | CCSD(T)/ CC-PVTZ | CCSD(T)/CC- PVTZ+ZPVE | ||
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | TS2/3 | -190.8 | -225.2 | -218.0 |
| 1 | -179.1 | -209.3 | -193.3 | TS3/4 | -506.8 | -540.3 | -527.7 |
| 2 | -198.8 | -230.2 | -219.3 | TS3/P2 | -425.2 | -434.8 | -426.9 |
| 3 | -508.5 | -543.2 | -529.4 | TS4/P1 | -545.7 | -587.6 | -579.6 |
| 4 | -583.8 | -620.6 | -604.7 | P1(3O+HC6O) | -604.7 | -584.2 | -581.3 |
| TS1/2 | -114.3 | -126.8 | -117.6 | P2(CO2+C5H) | -467.9 | -490.1 | -488.0 |
| TS1/P3 | -126.8 | -124.7 | -117.2 | P3(CO+HC5O) | -181.6 | -185.1 | -178.7 |
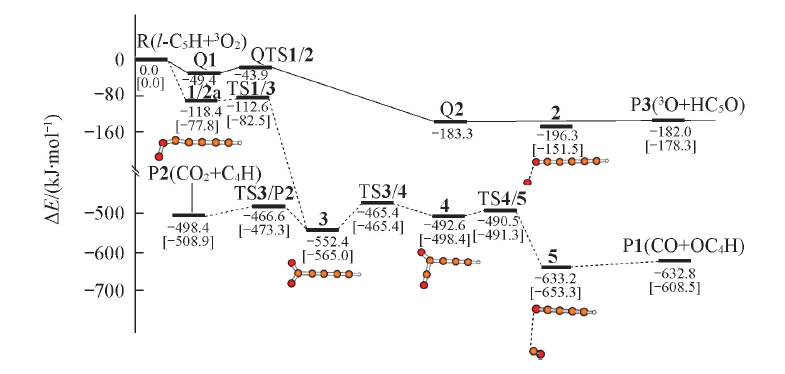
Fig.1 Potential energy surface of l-C5H+O2 reaction at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level and CCSD(T)/CC-PVTZ//B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p)+ZPVE level(square bracket)^Broken line(---) refer to the pathway in doublet state, real line(—) refer to quartet state.
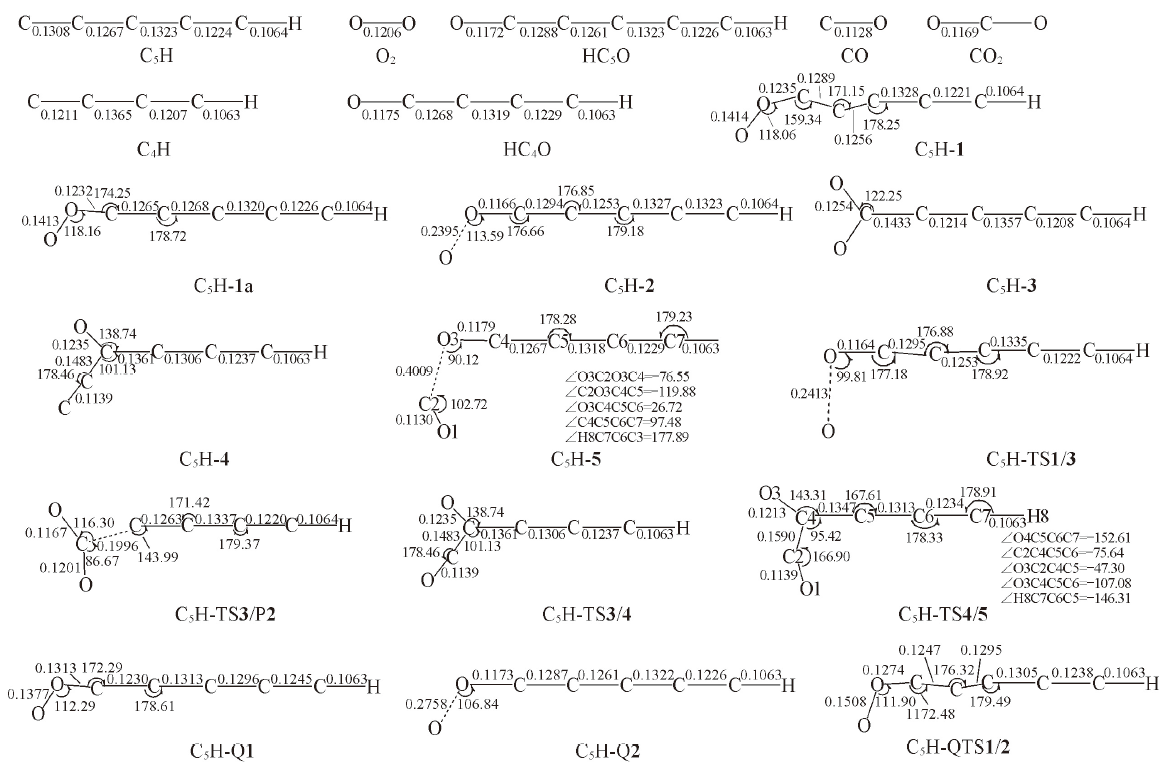
Fig.3 Optimized structures of the reactant, intermediates, transition states and products in the l-C5H+O2 reaction at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level[Bond lengths are in nm; bond angles are in degree]
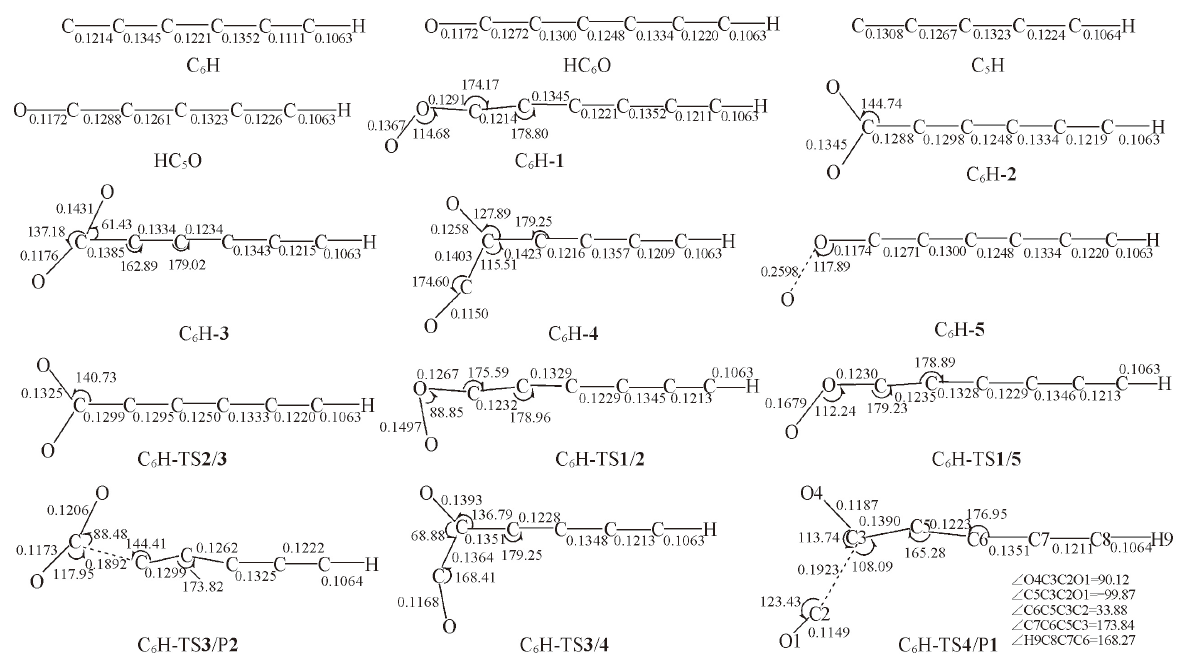
Fig.4 Optimized structures of the reactant, intermediates, transition states and products in the l-C6H+O2 reaction at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level[Bond lengths are in nm; bond angles are in degree]
| [1] | Blanksb S. J., McAnoy A. M., Dua S., Bowie J. H., Mon. Not. R., Astron. Soc., 2001, 328, 89—100 |
| [2] | Schmidt T. W., Boguslavskiy A. E., Pino T., Ding H., Maier J. P., Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2003, 228, 647—654 |
| [3] | Nagarajan R., Maier J. P., Int. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2010, 29, 521—554 |
| [4] | Bergeat A., Calvo T., Caralp F., Fillion J. H., Dorthe G., Loison J. C., Faraday Discuss, 2001, 119, 67—77 |
| [5] | Sumathi R., Peeters J., Nguyen M. T., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1998, 287, 109—118 |
| [6] | Su H., Yang J., Ding Y., Kong F., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2000, 326, 73—79 |
| [7] | Lee S., Leone S. R., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2000, 329, 443—449 |
| [8] | Vakhtin A. B., Heard D. E., Smith I. W. M., Leone S. R., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2001, 344, 317—324 |
| [9] | Elsamra R. M. I., Vranckx S., Carl S. A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2005, 109, 10287—10293 |
| [10] | Arrowsmith A. N., Chikan V., Leone S. R., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110, 7521—7526 |
| [11] | Larsson B., Astronomy Astrophys, 2007, 466(3), 999—1003 |
| [12] | Du Y. G., Shang J., Xu Z. L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2000, 16(3), 203—207 |
| [13] | Chi Y. J., Yu H. T., Fu H. G., Huang X. R., Li Z. S., Sun C. C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2002, 18(3), 341—344 |
| [14] | Wei Z. G., Huang X. R., Sun Y. B., Sun C. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(8), 1504—1506 |
| (魏志刚, 黄旭日, 孙延波, 孙家锺.高等学校化学学报, 2004,25(8), 1504—1506) | |
| [15] | Kong Z. G., Ren A. M., Feng J. K., Gan L. F., Sun C. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(10), 1932—1936 |
| (孔治国, 任爱民, 封继康, 甘霖锋, 孙家锺.高等学校化学学报, 2006,27(10), 1932—1936) | |
| [16] | Zhu W. W., Jin L., Cui Z. H., Zhang S. W., Ding Y. H., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2013, 113, 2506—2513 |
| [17] | Zhu W. W., Zhang S. W., Ding Y. H., J. Theor. Comput. Chem., 2013, 12, 1340002 |
| [18] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Vreven T.,Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N.,Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y.,Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., AlLaham M. A., Peng C. Y., Nanayakkara A.,Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 03, Wallingford CT, Gaussian Inc., 2004 |
| [19] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam N. J., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas Ö., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Wallingford CT, Gaussian Inc., 2009 |
| [20] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94(14), 5523—5527 |
| [1] | YANG Lijun, YU Yang, ZHANG Lei. Construction of Dual-functional 2D/3D Hydrid Co2P-CeO x Heterostructure Integrated Electrode for Electrocatalytic Urea Oxidation Assisted Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220082. |
| [2] | GONG Yanxi, WANG Jianbing, CHAI Buyu, HAN Yuanchun, MA Yunfei, JIA Chaomin. Preparation of Potassium Doped g-C3N4 Thin Film Photoanode and Its Application in Photoelectrocatalytic Oxidation of Diclofenac Sodium in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220005. |
| [3] | WANG Mingzhi, ZHENG Yanping, WENG Weizheng. Catalytic Methane Combustion over CeO2 Supported PdO and Ce1‒x Pd x O2‒δ Species [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210816. |
| [4] | ZHAO Wanjun, LI Xiao, Dang Hui, WANG Yongzhao, ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation of Supported Pd-Cu Catalyst and Its Preferential Oxidation of CO Under Hydrogen-rich Atmosphere [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210754. |
| [5] | CHEN Wangsong, LUO Lan, LIU Yuguang, ZHOU Hua, KONG Xianggui, LI Zhenhua, DUAN Haohong. Recent Progress in Photoelectrochemical H2 Production Coupled with Biomass-derived Alcohol/aldehyde Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210683. |
| [6] | DONG Yanhong, LU Xinhuan, YANG Lu, SUN Fanqi, DUAN Jingui, GUO Haotian, ZHANG Qinjun, ZHOU Dan, XIA Qinghua. Preparation of Bifunctional Metal-organic Framework Materials and Application in Catalytic Olefins Epoxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [7] | SUN Jinshi, CHEN Peng, JING Liping, SUN Fuxing, LIU Jia. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Aromatic Frameworks for Immobilization of Thiourea Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220171. |
| [8] | WEI Lina, PENG Li, ZHU Feng, GU Pengfei, GU Xuehong. Preparation of Au-CeZr/FAU Catalytic Membranes for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-rich Stream [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220175. |
| [9] | GAO Zhongnan, GUO Lihong, ZHAO Dongyue, LI Xingang. Effect of A Site-deficiency on the Structure and Catalytic Oxidation Activity of the La-Sr-Co-O Perovskite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2869. |
| [10] | LI Chenchen, NA Yong. g-C3N4/CdS/Ni Composite as a Bifunctional Photocatalyst for H2 Generation and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2896. |
| [11] | LUO Qiangqiang, JIN Shaoqing, SUN Hongmin, YANG Weimin. Post-synthesis of Ti-MWW Zeolite via Titanium Incorporation in Liquid Acid Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2742. |
| [12] | XU Xiaolong, FANG Lining, LIU Changyu, LIU Minchao, JIA Jianbo. Preparation of Z-type g-C3N4/Pt/TiO2 Nanotube Array Composite Electrode and Its Performance of Photoelectric Oxidation of Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2926. |
| [13] | GUO Yang, LIN Kai, XIE Kaiqiang, LIU Sheng. Novel Approach to Isatins via Pd-Cu Catalyzed Oxidative Transformation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2798. |
| [14] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xu, QUE Jiaqian, HOU Yuexin, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, LEI Kunhao, YU Shen, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Hierarchical Mesoporous-microporous TS-1 Single Crystal Catalysts for Epoxidation of Allyl Chloride [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2529. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
