

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 1782.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131257
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MENG Qingqiang, SUN Wanting, LUAN Yunbo, JING Liqiang*( )
)
Received:2013-12-20
Online:2014-08-10
Published:2019-08-01
Contact:
JING Liqiang
E-mail:jinglq@hlju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MENG Qingqiang, SUN Wanting, LUAN Yunbo, JING Liqiang. Effects of Phosphate Modification on the Thermal Stability and Photocatalytic Activity of Nanosized Fe2
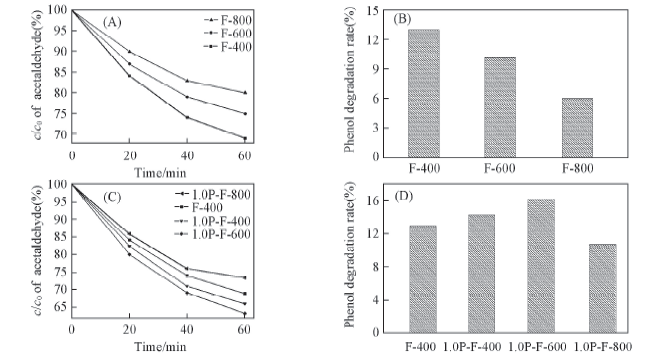
Fig.6 Photocatalytic degradation rates of different Fe2O3 samples(A,B) and different P-Fe2O3 samples(C, D) on acetaldehyde(A, C) and phenol(B, D) (B) After reaction for 2 h; (D) after reaction for 1.5 h.
| [1] | Yu C. C., Dong X. P., Guo L. M., Li J. T., Qin F., Zhang L. X., Shi J. L., Yan D. S., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 3378—3382 |
| [2] | Cao S. W., Zhu Y. J., J. Phys., Chem. C, 2008, 112, 6253—6257 |
| [3] | Pailhé N., Wattiaux A., Gaudon M., Demourgues A., J. Solid State Chem., 2008, 181, 2697—2704 |
| [4] | Hu X. L., Yu J. C., Gong J. M., Li Q., Li G. S., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 2324—2329 |
| [5] | Li L., Koshizaki N., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 2972—2978 |
| [6] | Zhou W., Lin L. J., Wang W. J., Zhang L. L., Wu Q., Li J. H., Guo L., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 7126—7133 |
| [7] | Si S. F., Yang S. L., Yan X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(11), 2035—2039 |
| (司书峰, 杨松林, 延玺. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(11), 2035—2039) | |
| [8] | Li X. Y., Wang J. Y., Wang X. Y., Su D., Han X. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(4), 662—666 |
| (李秀莹, 王靖宇, 王晓宇, 苏丹, 韩喜江. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(4), 662—666) | |
| [9] | Zhang Z. H., Hossain M. F., Miyazaki T., Takahashi T., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 4741—4746 |
| [10] | Hu Y. S., Kleiman-Shwarsctein A., Forman A. J., Stucky G. S., McFarland E. W., Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 3803—3805 |
| [11] | Wei Y. H., Han S. B., Walker D. A., Warren S. C., Grzybowski B. A., Chem. Sci., 2012, 3, 1090—1094 |
| [12] | Niu M. T., Huang F., Cui L. F., Huang P., Yu Y. L., Wang Y. S., ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 681—688 |
| [13] | Wu W., Zhang S. F., Ren F., Xiao X. H., Zhou J., Jiang C. Z., Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 4676—4684 |
| [14] | Wei X., Xie T. F., Peng L. L., Fu W., Chen J. S., Gao Q., Hong G. Y., Wang D. J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 8637—8642 |
| [15] | Peng L. L., Xie T. F., Lu Y. C., Fan H. M., Wang D. J., J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 8033—8041 |
| [16] | Cesar I., Kay A., Martinez J. A. G., Gratzel M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 4582—4583 |
| [17] | Saremi-Yarahmadi S., Wijayantha K. G. U., Tahir A. A., Vickie M. K., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 4768—4778 |
| [18] | Zhang J., Li M. J., Feng Z. C., Chen J., Li C., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 927—935 |
| [19] | Yu H. F., J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2007, 68, 600—607 |
| [20] | Yu J. C., Zhang L. Z., Zheng Z., Zhao J. C., Chem. Mater., 2003, 15, 2280—2286 |
| [21] | Qin X., Jing L. Q., Xue L. P., Luan Y. B., Fu H. G., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2008, 24, 1108—1112 |
| (秦旭, 井立强, 薛连鹏, 栾云博, 付宏刚. 无机化学学报, 2008, 24, 1108—1112) | |
| [22] | Li K. Y., Wang D. J., Wu F. Q., J. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2000, 64, 269—273 |
| [23] | Qian X. M., Qin D. Q., Song Q., Bai Y. B., Li T. J., Tang X. Y., Wang E. K., Dong S. J., Thin Solid Films, 2001, 385, 152—161 |
| [24] | Sun W. T., Meng Q. Q., Jing L. Q., Liu D. N., Cao Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 1358—1365 |
| [25] | Jing L. Q., Sun X. J., Shang J., Cai W. M., Z. L., Du Y. G., Fu H. G., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2003, 79, 133—151 |
| [26] | Kronik L., Shapira Y., Surf. Sci. Rep., 1999, 37, 1—206 |
| (Ed.: S, Z, M) |
| [1] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [2] | LIN Zhi, PENG Zhiming, HE Weiqing, SHEN Shaohua. Single-atom and Cluster Photocatalysis: Competition and Cooperation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| [3] | TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325. |
| [4] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [5] | QIU Liqi, YAO Xiangyang, HE Liangnian. Visible-light-driven Selective Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Catalyzed by Earth-abundant Metalloporphyrin Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220064. |
| [6] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [7] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [8] | TAO Yu, OU Honghui, LEI Yongpeng, XIONG Yu. Research Progress of Single-atom Catalysts in Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220143. |
| [9] | FENG Li, SHAO Lanxing, LI Sijun, QUAN Wenxuan, ZHUANG Jinliang. Synthesis of Ultrathin Sm-MOF Nanosheets and Their Visible-light Induced Photodegradation of Mustard Simulant [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210867. |
| [10] | MENG Xiangyu, ZHAN Qi, WU Yanan, MA Xiaoshuang, JIANG Jingyi, SUN Yueming, DAI Yunqian. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogenation Performance of Au/RGO/Na2Ti3O7 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210655. |
| [11] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [12] | GUO Biao, ZHAO Chencan, LIU Xinxin, YU Zhou, ZHOU Lijing, YUAN Hongming, ZHAO Zhen. Effects of Surface Hydrothermal Carbon Layer on the Photocatalytic Activity of Magnetic NiFe2O4 Octahedron [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220472. |
| [13] | LI Chenchen, NA Yong. g-C3N4/CdS/Ni Composite as a Bifunctional Photocatalyst for H2 Generation and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2896. |
| [14] | LI Yishan, GUO Liang, PENG Sifan, ZHANG Qingmao, ZHANG Yuhao, XU Shiqi. Cobalt Substitutions in Lanthanum Manganate Photocatalyst: First-principles and Visible-light Photocatalytic Ability Investigation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1881. |
| [15] | WANG Peng, YANG Min, TANG Sengpei, CHEN Feitai, LI Youji. Preparation of Cellular C3N4/CoSe2/GA Composite Photocatalyst and Its CO2 Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1924. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||