

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 1311.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131185
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Xiaofeng1, XIE Xiaolu2, ZHANG Lei2, LI Chunhua2,*( ), LOU Jiaoying3, LIU Naibo1, DING Zhenshan1,*(
), LOU Jiaoying3, LIU Naibo1, DING Zhenshan1,*( )
)
Received:2013-12-05
Online:2014-06-10
Published:2014-04-29
Contact:
LI Chunhua,DING Zhenshan
E-mail:chunhuali@bjut.edu.cn;dzsfighting@sina.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHOU Xiaofeng, XIE Xiaolu, ZHANG Lei, LI Chunhua, LOU Jiaoying, LIU Naibo, DING Zhenshan. Idenpngication of Functional Residues in Maltose Transporter with the Elastic Network Model†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1311.
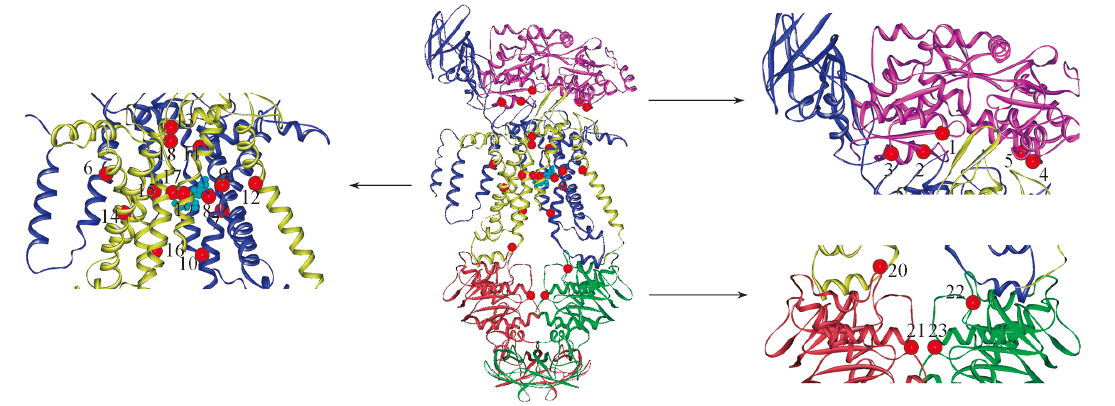
Fig.5 Key residues mapped onto the protein structureThe ball represents the location of the central residue of each residue cluster. The cluster number is the same as that in Fig.3.
| [1] | Jones P. M., George A. M., Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2004, 61(6), 682—699 |
| [2] | Rees D. C., Johnson E., Lewinson O., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2009, 10(3), 218—227 |
| [3] | Locher K. P., Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B., 2009, 364(1514), 239—245 |
| [4] | Oldham M. L., Khare D., Quiocho F. A., Davidson A. L., Chen J., Nature, 2007, 450(7169), 515—521 |
| [5] | Oldham M. L., Chen J., Science, 2011, 332(6034), 1202—1205 |
| [6] | Oldham M. L., Chen J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2011, 108(37), 15152—15156 |
| [7] | Hegedüs T., Gyimesi G., Gáspár M. E., Szalay K. Z., Gangal R., Csermely P., Curr. Pharm. Des., 2013, 19, 4155—4172 |
| [8] | Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L., Science, 1989, 245(4922), 1066—1073 |
| [9] | Mosser J., Douar A. M., Sarde C. O., Kioschis P., Feil R., Moser H., Poustka A. M., Mandel J. L., Aubourg P., Nature, 1993, 361(6414), 726—730 |
| [10] | Szakács G., Váradi A., Özvegy-Laczka C., Sarkadi B., Drug Discov. Today, 2008, 13(9/10), 379—393 |
| [11] | Dror R. O., Dirks R. M., Grossman J. P., Xu H., Shaw D. E., Annu. Rev. Biophys., 2012, 41, 429—452 |
| [12] | Isralewitz B., Gao M., Schulten K., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2001, 11(2), 224—230 |
| [13] | Ma J., Karplus M., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, 94(22), 11905—11910 |
| [14] | Sugita Y., Okamoto Y., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1999, 314, 141—151 |
| [15] | Zhang Z., Shi Y., Liu H., Biophys. J., 2003, 84(6), 3583—3593 |
| [16] | Haliloglu T., Bahar I., Erman B., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1997, 79, 3090—3093 |
| [17] | Bahar I., Rader A. J., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2005, 15(5), 586—592 |
| [18] | Li J. L., Geng C. Y., Bu Y. X., Chen X. H., Wang J., Huang X. R., Sun C. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(10), 2055—2058 |
| (李吉来, 耿彩云, 步宇翔, 陈效华, 王军, 黄旭日, 孙家锺.高等学校化学学报, 2009,30(10), 2055—2058) | |
| [19] | Atilgan C., Atilgan A. R., PLoS. Comput. Biol., 2009, 5(10), e1000544-1—e1000544-14 |
| [20] | Zheng W., Brooks B. R., Thirumalai D., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006, 103(20), 7664—7669 |
| [21] | Ming D., Cohn J. D., Wall M. E., BMC Struct. Biol., 2008, 8, 5 |
| [22] | Su J. G., Xu X. J., Li C. H., Chen W. Z., Wang C. X., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(17), 174101-1—174101-10 |
| [23] | Ehrle R., Pick C., Ulrich R., Hofmann E., Ehrmann M., J. Bacteriol., 1996, 178(8), 2255—2262 |
| [24] | Steinke A., Grau S., Davidson A., Hofmann E., Ehrmann M., J. Bacteriol., 2001, 183(1), 375—381 |
| [25] | Grote M., Polyhach Y., Jeschke G., Steinhoff H. J., Schneider E., Bordignon E., J. Biol. Chem., 2009, 284(26), 17521—17526 |
| [26] | Michael L., Oldham Jue C., Science, 2011, 332, 1202—1205 |
| [27] | Hor L. I., Shuman H. A., J. Mol. Biol., 1993, 233(4), 659—670 |
| [28] | Shilton B. H., Biochimica. et Biophysica. Acta, 2008, 1778, 1772—1780 |
| [29] | Daus M. L., Grote M., Müller P., Doebber M., Herrmann A., Steinhoff H. J., Dassa E., Schneider E., J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282(31), 22387—22396 |
| [30] | Hunke S., Mourez M., Jéhanno M., Dassa E., Schneider E., J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275(20), 15526—15534 |
| [31] | Loo T. W., Bartlett M. C., Clarke D. M., J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(44), 41303—41306 |
| [32] | UrbatschI. L., Gimi K., Wilke-Mounts S., Senior A. E., Biochemistry, 2000, 39(39), 11921—11927 |
| [33] | Dalmas O., Orelle C., Foucher A. E., Geourjon C., Crouzy S., Pietro A. D., Jault J. M., J. Biol. Chem., 2005, 280(44), 36857—36864 |
| [34] | Grote M., Bordignon E., Polyhach Y., Jeschke G., Steinhoff H. J., Schneider E., Biophys. J., 2008, 95(6), 2924—2938 |
| [35] | Oldham M. L., Khare D., Quiocho F. A., Davidson A. L., Chen J., Nature, 2007, 450, 515—521 |
| [36] | Hunke S., Landmesser H., Schneider E., J. Bacteriol., 2000, 182(5), 1432—1436 |
| [1] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [2] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [3] | WANG Sijia, HOU Lu, LI Chenglong, LI Wencui, LU Anhui. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of Hollow Nano-carbons [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220637. |
| [4] | WU Qingying, ZHU Zhenyu, WU Jianming, XU Xin. A Dataset Representativeness Metric and A Slicing Sampling Strategy for the Kennard-Stone Algorithm [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220397. |
| [5] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [7] | SHEN Qi, CHEN Haiyao, GAO Denghui, ZHAO Xi, NA Risong, LIU Jia, HUANG Xuri. A Study on the Interaction Mechanism of the Natural Product Falcarindiol with Human GABAA Receptor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 0. |
| [8] | CHEN Shaochen, CHENG Min, WANG Shihui, WU Jinkui, LUO Lei, XUE Xiaoyu, JI Xu, ZHANG Changchun, ZHOU Li. Transfer Learning Modeling for Predicting the Methane and Hydrogen Delivery Capacity of Metal-Organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220459. |
| [9] | PENG Xinzhe, GE Jiaoyang, WANG Fangli, YU Guojing, ZHOU Dong, RAN Xueqin, YANG Lei, XIE Linghai. A Theoretical Study on Tension and Reorganization Energy of Benzothiophene Grid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220313. |
| [10] | GUO Cheng, ZHANG Wei, TANG Yun. Ordered Mesoporous Materials: History, Progress and Perspective [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220167. |
| [11] | TANG Qiaowei, CAI Xiaoqing, LI Jiang, ZHU Ying, WANG Lihua, TIAN Yang, FAN Chunhai, HU Jun. Synchrotron-based X-ray Microscopy for Brain Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220379. |
| [12] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [13] | DAI Wei, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Theoretical Investigations on the Electronic Structures and Reactivity of Heptafluoro-iso-butyronitrile Anion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220044. |
| [14] | SHI Naike, ZHANG Ya, SANSON Andrea, WANG Lei, CHEN Jun. Uniaxial Negative Thermal Expansion and Mechanism in Zn(NCN) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [15] | REN Nana, XUE Jie, WANG Zhifan, YAO Xiaoxia, WANG Fan. Effects of Thermodynamic Data on Combustion Characters of 1,3-Butadiene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||