

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 839.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130796
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Huani1, YE Manyi2, YAO Guiyang2, LI Yajun2, ZHU Yongtao2, WANG Hengshan2,*( )
)
Received:2013-08-16
Online:2014-04-10
Published:2013-10-23
Contact:
WANG Hengshan
E-mail:whengshan@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Huani, YE Manyi, YAO Guiyang, LI Yajun, ZHU Yongtao, WANG Hengshan. Atropisomerism of Methyl Maleopimaric N-Arylimides and Their Kinetics Analysis†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 839.
| Compd. | 1H NMR(500 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(CDCl3, 125 MHz), δ | MS(APCI), (M+H+), m/z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 7.411—7.365(m, 2H, J=7.5 Hz, 2'-H, 6'-H), 7.335(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 4'-H), 7.116(d, 2H, J=8.0 Hz, 3'-H, 5'-H), 5.520(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.678(s, 3H, —CO2CH3), 3.163(s, 1H, 12-H), 2.970(dd, 1H, | 179.34, 177.71, 176.53, 147.53, 132.21, 129.19, 128.55, 126.61, 124.74, 54.41, 52.65, 52.13, 49.76, 47.36, 45.29, 41.28, 38.38, 37.97, 36.94, 36.34, 35.51, 33.00, 27.81, 22.01, 20.99, 20.28, 17.25, 16.95, 15.86 | 490 |
| 4b | 8.137(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 3'-H), 7.629(t, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 5'-H), 7.489(t, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 4'-H), 7.021(d, 1H, J=6.5 Hz, 6'-H), 5.547(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.664(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.162(s, 1H, 12-H), 3.034(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 21-H), 2.671(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 22-H ), 2.546(d, 1H, J=13.5 Hz, 7-Ha ), 2.302(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.690—1.827(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.410—1.593(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.240—1.324(m, 1H, 11-H), 1.176—1.237(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.164(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 1.031(d, 6H, J=6.5 Hz, 15-2CH3), 0.940—1.002(m, 1H, 1-Hb), 0.632(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.30, 177.93, 176.74, 168.42, 147.57, 134.04, 133.13, 132.34, 129.65, 129.26, 126.78, 124.92, 54.40, 53.12, 52.07, 49.70, 47.34, 45.76, 41.14, 38.40, 37.93, 36.88, 36.09, 35.39, 32.96, 27.80, 21.96, 20.96, 20.34, 17.23, 16.93, 15. 84 | 534 |
| 4c | 8.123(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 3'-H), 7.682(t, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 5'-H), 7.555(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 4'-H), 7.27(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 6'-H), 5.540(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.676(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.165(s, 1H, 12-H), 3.075(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 21-H), 2.715(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 22-H ), 2.518(d, 1H, J=14.0 Hz, 7-Ha ), 2.279(m, 1H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.672—1.821(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.400—1.584(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.243—1.324(m, 1H, 11-H), 1.176—1.235(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.161(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 0.942—1.056(m, 7H, 15-2CH3, 1-Hb), 0.619(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.24, 176.78, 175.67, 147.72, 145.48, 134.16, 130.29, 129.91, 126.42, 125.89, 124.95, 54.36, 53.10, 52.10, 49.67, 47.34, 45.74, 41.27, 38.39, 37.96, 36.88, 36.16, 35.37, 32.97, 27.76, 21.95, 20.98, 20.37, 17.24, 16.95, 15.85 | 535 |
| 4d | 7.446—7.512(m, 1H, 6'-H), 7.291—7.373(m, 2H, 3'-H, 5'-H), 6.925—7.134(m, 1H, 4'-H), 5.543(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.676(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.153—3.212(m, 1H, 12-H), 3.014—3.080(1H, 21-H), 2.601(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 22-H), 2.467—2.595(m, 1H, 7'-H), 2.289—2.270(m, 1H, 15-H), 1.663—1.824(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.411—1.560(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.244—1.330(m, 1H, 11-Hb), 1.182—1.442(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.162(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 0.930—1.058(m, 7H, 15-2CH3, 1-Hb), 0.625(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.28, 176.81, 175.74, 147.57, 132.41, 130.59, 130.50, 129.82, 127.76, 125.00, 124.83, 54.43, 52.87, 52.09, 49.73, 47.33, 45.50, 41.24, 38.38, 37.94, 36.90, 36.14, 35.40, 32.94, 27.79, 21.96, 20.96, 20.32, 17.23, 16.90, 15.83 | 524 |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(500 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(CDCl3, 125 MHz), δ | MS(APCI), (M+H+), m/z |
| 4e | 7.161—7.010(m, 1H, 6'-H), 6.734—6.915(m, 3H, 3'-H, 4-H, 5'-H), 5.530—5.579(m, 1H, 14-H), 3.678(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.450—3.530(m, 2H, —NH2), 3.188(d, 1H, J=15.0 Hz, 12-H), 3.016(dd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=11.0 Hz, 21-H), 2.635(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 22-H), 2.554—2.501(m, 1H, 7-Ha ), 2.284—2.178(m, 1H, 15-H), 1.690—1.826(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.407—1.553(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.262—1.322(m, 1H, 11-Hb), 1.182—1.248(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.165(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 0.994—1.049(m, 6H, 15-2CH3), 0.941—0.994(m, 1H, 1-Hb), 0.621(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.36, 177.68, 176.20, 147.52, 142.58, 130.22, 128.68, 128.50, 124.64, 119.00, 117.16, 54.78, 52.79, 52.14, 49.71, 47.33,45.96, 41.23, 38.33, 37.95, 36.91, 36.32, 35.36, 32.82, 27.64, 21.92, 20.93, 20.20, 17.22, 16.91, 15.86 | 504 |
| 4f-trans | 7.897(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 4'-H), 7.880(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 5-H), 7.422—7.530(m, 4H, 8'-H, 3'-H, 7'-H, 6'-H), 7.062(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 2'-H), 5.616(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.678(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.228—3.218(m, 1H, 12-H), 3.159(dd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=8.0 Hz, 21-H), 2.786(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 22-H), 2.607(dt, 1H, J1=3.2Hz, J2=14.0 Hz, 7-Heq), 2.345—2.200(m, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.721—1.833(m, 4H, 7-Hax, 5-H, 11-Hax, 3-Hax), 1.454—1.600(m, 5H, 3-Heq, 6-H, 9-H, 2-H), 1.440(dt, 1H, J=13 Hz, 1-Heq), 1.306(ddd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=5.4 Hz, J3=13.0 Hz, 11-Heq), 1.192—1.253(m, 1H, 6-Heq), 1.178(s, 3H, 4-CH3 ), 1.056(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.086(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.010(dt, 1H, J1=5.0 Hz, J2=13.0 Hz, 1-Hax), 0.657(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.24, 177.96, 176.63, 147.84, 134.50, 129.76, 129.59, 129.18, 128.60, 126.70, 126.49, 126.20, 125.46, 125.18, 122.92, 54.95, 53.02, 52.05, 49.72, 47.30, 46.30, 41.34, 38.33, 37.94, 36.90, 35.60, 35.36, 32.70, 27.67, 21.95, 20.46, 19.70, 17.22, 16.90, 15.90 | 540 |
| 4f-cis | 7.890(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 4'-H), 7.885(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 5'-H), 7.422—7.530(m, 4H, 8-H, 3'-H, 7'-H, 6'-H), 7.232(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 2'-H ), 5.780(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.681(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.276—3.256(m, 1H, 12-H ), 3.128(dd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=8.0 Hz, 21-H), 2.731(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 22-H), 2.574(dt, 1H, J1=3.2Hz, J2=14.0 Hz, 7-Heq), 2.392(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.726—1.860(m, 4H, 7-Hax, 5-H, 11-Hax, 3-Hax), 1.472—1.615(m, 5H, 3-Heq, 6-Hax, 9-H, 2-H), 1.445(dt, 1H, J=13 Hz, 1-Heq), 1.308(ddd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=5.4 Hz, J3=13.0 Hz, 11-Heq), 1.190—1.250(m, 1H, 6-Heq), 1.189(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 1.062(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.111(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.010(dt, 1H, J1=5.0 Hz, J2=13.0 Hz, 1-Hax), 0.678(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.24, 177.96, 176.91, 147.52, 134.50, 129.86, 129.37, 129.18, 128.67, 127.04, 126.56, 126.06, 125.40, 124.78, 122.29, 54.45, 52.78, 52.05, 49.72, 47.30, 45.42, 41.36, 38.33, 37.94, 36.90, 36.21, 35.42, 32.93, 27.76, 21.95, 20.92, 20.27, 17.22, 16.90, 15.84 | 540 |
Table 1 NMR and MS data of compounds 4a—4f
| Compd. | 1H NMR(500 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(CDCl3, 125 MHz), δ | MS(APCI), (M+H+), m/z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 7.411—7.365(m, 2H, J=7.5 Hz, 2'-H, 6'-H), 7.335(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 4'-H), 7.116(d, 2H, J=8.0 Hz, 3'-H, 5'-H), 5.520(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.678(s, 3H, —CO2CH3), 3.163(s, 1H, 12-H), 2.970(dd, 1H, | 179.34, 177.71, 176.53, 147.53, 132.21, 129.19, 128.55, 126.61, 124.74, 54.41, 52.65, 52.13, 49.76, 47.36, 45.29, 41.28, 38.38, 37.97, 36.94, 36.34, 35.51, 33.00, 27.81, 22.01, 20.99, 20.28, 17.25, 16.95, 15.86 | 490 |
| 4b | 8.137(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 3'-H), 7.629(t, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 5'-H), 7.489(t, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 4'-H), 7.021(d, 1H, J=6.5 Hz, 6'-H), 5.547(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.664(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.162(s, 1H, 12-H), 3.034(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 21-H), 2.671(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 22-H ), 2.546(d, 1H, J=13.5 Hz, 7-Ha ), 2.302(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.690—1.827(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.410—1.593(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.240—1.324(m, 1H, 11-H), 1.176—1.237(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.164(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 1.031(d, 6H, J=6.5 Hz, 15-2CH3), 0.940—1.002(m, 1H, 1-Hb), 0.632(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.30, 177.93, 176.74, 168.42, 147.57, 134.04, 133.13, 132.34, 129.65, 129.26, 126.78, 124.92, 54.40, 53.12, 52.07, 49.70, 47.34, 45.76, 41.14, 38.40, 37.93, 36.88, 36.09, 35.39, 32.96, 27.80, 21.96, 20.96, 20.34, 17.23, 16.93, 15. 84 | 534 |
| 4c | 8.123(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 3'-H), 7.682(t, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 5'-H), 7.555(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 4'-H), 7.27(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 6'-H), 5.540(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.676(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.165(s, 1H, 12-H), 3.075(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 21-H), 2.715(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 22-H ), 2.518(d, 1H, J=14.0 Hz, 7-Ha ), 2.279(m, 1H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.672—1.821(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.400—1.584(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.243—1.324(m, 1H, 11-H), 1.176—1.235(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.161(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 0.942—1.056(m, 7H, 15-2CH3, 1-Hb), 0.619(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.24, 176.78, 175.67, 147.72, 145.48, 134.16, 130.29, 129.91, 126.42, 125.89, 124.95, 54.36, 53.10, 52.10, 49.67, 47.34, 45.74, 41.27, 38.39, 37.96, 36.88, 36.16, 35.37, 32.97, 27.76, 21.95, 20.98, 20.37, 17.24, 16.95, 15.85 | 535 |
| 4d | 7.446—7.512(m, 1H, 6'-H), 7.291—7.373(m, 2H, 3'-H, 5'-H), 6.925—7.134(m, 1H, 4'-H), 5.543(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.676(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.153—3.212(m, 1H, 12-H), 3.014—3.080(1H, 21-H), 2.601(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 22-H), 2.467—2.595(m, 1H, 7'-H), 2.289—2.270(m, 1H, 15-H), 1.663—1.824(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.411—1.560(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.244—1.330(m, 1H, 11-Hb), 1.182—1.442(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.162(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 0.930—1.058(m, 7H, 15-2CH3, 1-Hb), 0.625(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.28, 176.81, 175.74, 147.57, 132.41, 130.59, 130.50, 129.82, 127.76, 125.00, 124.83, 54.43, 52.87, 52.09, 49.73, 47.33, 45.50, 41.24, 38.38, 37.94, 36.90, 36.14, 35.40, 32.94, 27.79, 21.96, 20.96, 20.32, 17.23, 16.90, 15.83 | 524 |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(500 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(CDCl3, 125 MHz), δ | MS(APCI), (M+H+), m/z |
| 4e | 7.161—7.010(m, 1H, 6'-H), 6.734—6.915(m, 3H, 3'-H, 4-H, 5'-H), 5.530—5.579(m, 1H, 14-H), 3.678(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.450—3.530(m, 2H, —NH2), 3.188(d, 1H, J=15.0 Hz, 12-H), 3.016(dd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=11.0 Hz, 21-H), 2.635(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 22-H), 2.554—2.501(m, 1H, 7-Ha ), 2.284—2.178(m, 1H, 15-H), 1.690—1.826(m, 4H, 3-Ha, 5-H, 11-Ha, 7-Hb), 1.407—1.553(m, 6H, 1-Ha, 2-Ha, 2-Hb, 3-Hb, 6-Ha, 9-H), 1.262—1.322(m, 1H, 11-Hb), 1.182—1.248(m, 1H, 6-Hb), 1.165(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 0.994—1.049(m, 6H, 15-2CH3), 0.941—0.994(m, 1H, 1-Hb), 0.621(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.36, 177.68, 176.20, 147.52, 142.58, 130.22, 128.68, 128.50, 124.64, 119.00, 117.16, 54.78, 52.79, 52.14, 49.71, 47.33,45.96, 41.23, 38.33, 37.95, 36.91, 36.32, 35.36, 32.82, 27.64, 21.92, 20.93, 20.20, 17.22, 16.91, 15.86 | 504 |
| 4f-trans | 7.897(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 4'-H), 7.880(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 5-H), 7.422—7.530(m, 4H, 8'-H, 3'-H, 7'-H, 6'-H), 7.062(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 2'-H), 5.616(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.678(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.228—3.218(m, 1H, 12-H), 3.159(dd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=8.0 Hz, 21-H), 2.786(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 22-H), 2.607(dt, 1H, J1=3.2Hz, J2=14.0 Hz, 7-Heq), 2.345—2.200(m, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.721—1.833(m, 4H, 7-Hax, 5-H, 11-Hax, 3-Hax), 1.454—1.600(m, 5H, 3-Heq, 6-H, 9-H, 2-H), 1.440(dt, 1H, J=13 Hz, 1-Heq), 1.306(ddd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=5.4 Hz, J3=13.0 Hz, 11-Heq), 1.192—1.253(m, 1H, 6-Heq), 1.178(s, 3H, 4-CH3 ), 1.056(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.086(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.010(dt, 1H, J1=5.0 Hz, J2=13.0 Hz, 1-Hax), 0.657(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.24, 177.96, 176.63, 147.84, 134.50, 129.76, 129.59, 129.18, 128.60, 126.70, 126.49, 126.20, 125.46, 125.18, 122.92, 54.95, 53.02, 52.05, 49.72, 47.30, 46.30, 41.34, 38.33, 37.94, 36.90, 35.60, 35.36, 32.70, 27.67, 21.95, 20.46, 19.70, 17.22, 16.90, 15.90 | 540 |
| 4f-cis | 7.890(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 4'-H), 7.885(d, 1H, J=8.5 Hz, 5'-H), 7.422—7.530(m, 4H, 8-H, 3'-H, 7'-H, 6'-H), 7.232(d, 1H, J=7.5 Hz, 2'-H ), 5.780(s, 1H, 14-H), 3.681(s, 3H, —COOCH3), 3.276—3.256(m, 1H, 12-H ), 3.128(dd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=8.0 Hz, 21-H), 2.731(d, 1H, J=8.0 Hz, 22-H), 2.574(dt, 1H, J1=3.2Hz, J2=14.0 Hz, 7-Heq), 2.392(d, 1H, J=7.0 Hz, 15-H), 1.726—1.860(m, 4H, 7-Hax, 5-H, 11-Hax, 3-Hax), 1.472—1.615(m, 5H, 3-Heq, 6-Hax, 9-H, 2-H), 1.445(dt, 1H, J=13 Hz, 1-Heq), 1.308(ddd, 1H, J1=3.0 Hz, J2=5.4 Hz, J3=13.0 Hz, 11-Heq), 1.190—1.250(m, 1H, 6-Heq), 1.189(s, 3H, 4-CH3), 1.062(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.111(d, 3H, J=6.0 Hz, 15-CH3), 1.010(dt, 1H, J1=5.0 Hz, J2=13.0 Hz, 1-Hax), 0.678(s, 3H, 10-CH3) | 179.24, 177.96, 176.91, 147.52, 134.50, 129.86, 129.37, 129.18, 128.67, 127.04, 126.56, 126.06, 125.40, 124.78, 122.29, 54.45, 52.78, 52.05, 49.72, 47.30, 45.42, 41.36, 38.33, 37.94, 36.90, 36.21, 35.42, 32.93, 27.76, 21.95, 20.92, 20.27, 17.22, 16.90, 15.84 | 540 |
| Determination number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t/min | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 |
| [α | -7.5 | -12.7 | -17.9 | -22.2 | -26.6 | -29.8 | -33.7 | -36.5 | -39.3 | -41.7 | -43.9 | -45.6 | -47.2 | -47.6 | -47.6 |
| (c=0.084,CHCl3) |
Table 2 Specific rotation of compound 4f in CHCl3(293 K)
| Determination number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t/min | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 |
| [α | -7.5 | -12.7 | -17.9 | -22.2 | -26.6 | -29.8 | -33.7 | -36.5 | -39.3 | -41.7 | -43.9 | -45.6 | -47.2 | -47.6 | -47.6 |
| (c=0.084,CHCl3) |
| H atom | T/K | Linear equation | k1+ | H atom | T/K | Linear equation | k1+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14-H | 293 | y=1.931×10-4x +0.5666 | 1.931×10-4 | 22-H | 293 | y=1.833×10-4x +0.5652 | 1.833×10-4 |
| 303 | y=4.452×10-4x +0.4760 | 4.452×10-4 | 303 | y=4.830×10-4x +0.47757 | 4.830×10-4 | ||
| 313 | y=1.000×10-3x +0.4176 | 1.000×10-3 | 313 | y=1.050×10-3x +0.47797 | 1.050×10-3 | ||
| 323 | y=2.310×10-3x +0.5229 | 2.310×10-3 | 323 | y=1.740×10-3x +0.74405 | 1.740×10-3 | ||
| 333 | y=3.930×10-3x +0.6046 | 3.930×10-3 | 333 | y=3.260×10-3x +0.74935 | 3.260×10-3 |
Table 3 Relationship of -ln([A]-[A]eq) with t(s) of 14-H and 22-H in compound 4f
| H atom | T/K | Linear equation | k1+ | H atom | T/K | Linear equation | k1+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14-H | 293 | y=1.931×10-4x +0.5666 | 1.931×10-4 | 22-H | 293 | y=1.833×10-4x +0.5652 | 1.833×10-4 |
| 303 | y=4.452×10-4x +0.4760 | 4.452×10-4 | 303 | y=4.830×10-4x +0.47757 | 4.830×10-4 | ||
| 313 | y=1.000×10-3x +0.4176 | 1.000×10-3 | 313 | y=1.050×10-3x +0.47797 | 1.050×10-3 | ||
| 323 | y=2.310×10-3x +0.5229 | 2.310×10-3 | 323 | y=1.740×10-3x +0.74405 | 1.740×10-3 | ||
| 333 | y=3.930×10-3x +0.6046 | 3.930×10-3 | 333 | y=3.260×10-3x +0.74935 | 3.260×10-3 |
| T/K | Percentage of cis-isomer(%) | k1/s-1 | k2/s-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | 38.22 | 1.671 | 1.177×10-4 | 0.704×10-4 |
| 303 | 38.69 | 1.574 | 2.838×10-4 | 1.803×10-4 |
| 313 | 39.67 | 1.521 | 6.183×10-4 | 4. 067×10-4 |
| 323 | 40.31 | 1.481 | 1.209×10-3 | 8.163×10-4 |
| 333 | 38.74 | 1.584 | 2.20×10-3 | 1.391×10-3 |
Table 4 Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters for transformation of two isomers at different temperatures(CDCl3)
| T/K | Percentage of cis-isomer(%) | k1/s-1 | k2/s-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | 38.22 | 1.671 | 1.177×10-4 | 0.704×10-4 |
| 303 | 38.69 | 1.574 | 2.838×10-4 | 1.803×10-4 |
| 313 | 39.67 | 1.521 | 6.183×10-4 | 4. 067×10-4 |
| 323 | 40.31 | 1.481 | 1.209×10-3 | 8.163×10-4 |
| 333 | 38.74 | 1.584 | 2.20×10-3 | 1.391×10-3 |
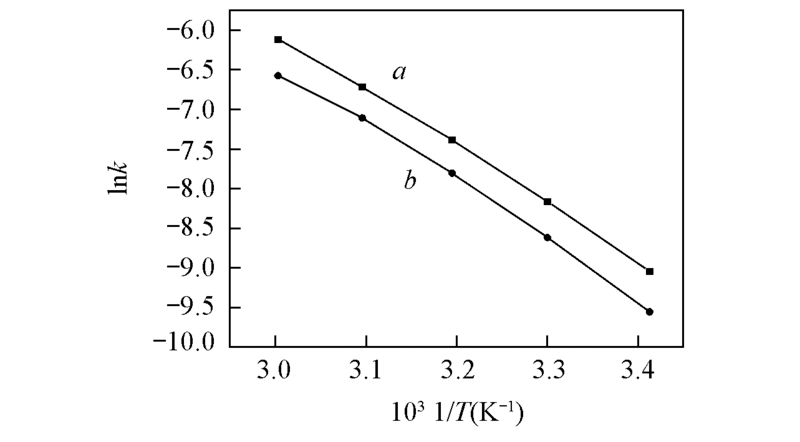
Fig.4 Linear rehression equations between temperature(T) and the observed rate constant(k) during the kinetic transformation of two atropisomera. lnk1 vs. 1/T; b. lnk2 vs. 1/T.
| [1] | Clayden J., Moran W. J., Edwards P. J., LaPlante S. R., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 6398—6401 |
| [2] | Laplante S. R., Edwards P. J., Fader L. D., Jakalian A., Hucke O., Chem. Med. Chem., 2011, 6, 505—513 |
| [3] | Bringmann G., Mortimer A. J. P., Keller P. A., Gresser M. J., Garner J., Breuning M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 5384—5427 |
| [4] | Shirakawa S., Liu K., Maruoka K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(2), 916—919 |
| [5] | Gustafson J. L., Lim D., Barrett K. T., Miller S. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(2), 5125—5129 |
| [6] | Lunazzi L., Mancinelli M., Mazzanti A., J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76(5), 1487—1490 |
| [7] | Sakamoto M., Utsumi N., Ando M., Saeki M., Mino T., Fujita T., Katoh A., Nishio T., Kashima C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 4360—4363 |
| [8] | Aikawa H., Takahira Y., Yamaguchi M., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(5), 1479—1481 |
| [9] | Wang H. S., He C. H., Pan Y. M., Yao G. Y., Wu Q., Deng H. G., J. Incl. Phenom. Macro., 2012, 73(1—4), 177—183 |
| [10] | Clayden J., Moran W. J., Laplante S. R., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(35), 6398—6401 |
| [11] | Jiang X. X., Zhang Y. F., Chan A. S. C., Wang R., Org. Lett., 2008, 11(1), 153—156 |
| [12] | Jiang X. X., Zhang Y. F., Liu X., Zhang G., Lai L. H., Wu L. P., Zhang J. N., Wang R., J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74(18), 5562—5567 |
| [13] | Jiang X. X., Zhang Y. F., Wu L. P., Zhang G., Liu X., Zhang H. L., Fu D., Wang R., Adv. Synth. Catal., 2009, 351(13), 2096—2100 |
| [14] | Jiang X. X., Zhang G., Fu D., Cao Y. M., Shen F. F., Wang R., Org. Lett., 2010, 12(7), 1544—1549 |
| [15] | Ye F. G., Wang H. S., Huang B. J., Zhao S. L., Electrophoresis,2010, 31(9), 1488—1492 |
| [16] | Wang H. S., Zhao S. L., He M., Zhao Z. C., Pan Y. M., Liang Q., J. Sep. Sci., 2007, 30, 2748—2753 |
| [17] | Zhao S. L., Wang H. S., Pan Y. M., He M., Zhao Z. C., J. Chromatogr. A,2007, 1145(1/2), 246—249 |
| [18] | Zhao S. L., Wang H. S., Zhang R. C., Tang L. D., Liu Y. M., Electrophoresis,2006, 27(17), 3428—3433 |
| [19] | Wang H. S., Zhang R. C., Zhao S. L., Tang L. D., Pan Y. M., Anal. Chim. Acta,2006, 560(1/2), 64—68 |
| [20] | Wang L., Tan X. C., Zhao D. D., Liu L., Lei F. H., Huang Z. Y., Gong Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(8), 1708—1713 |
| (王琳, 谭学才, 赵丹丹, 刘力, 雷福厚, 黄在银, 龚琦. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(8), 1708—1713) | |
| [21] | Qin R. X., Huang P. X., Liu X. M., Ma L., Wu Y. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2009, 30(5), 954—958 |
| (秦荣秀, 黄品鲜, 刘雄民, 马丽, 吴晏玲. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(5), 954—958) | |
| [22] | Pan Y. M., Yang L., Wang H. S., Zhang R. C., Zhang Y., Acta Cryst. Section E,2006, 62, o5701—o5703 |
| [23] | Okamoto I., Terashima M., Masu H., Nabeta M., Ono K., Morita N., Katagiri K., Azumaya I., Tamura O., Tetrahedron,2011, 67, 8536—8543 |
| [1] | REN Nana, XUE Jie, WANG Zhifan, YAO Xiaoxia, WANG Fan. Effects of Thermodynamic Data on Combustion Characters of 1,3-Butadiene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [2] | LI Zhiguang, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Role of Catalyst Acidity in Glucose Conversion over Sn-Al-β Zeolite as Studied by Solid-state NMR [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220138. |
| [3] | SUN Cuihong, LYU Liqiang, LIU Ying, WANG Yan, YANG Jing, ZHANG Shaowen. Mechanism and Kinetics on the Reaction of Isopropyl Nitrate with Cl, OH and NO3 Radicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [4] | WANG Meiyin, HUANG Daofeng, CHEN Xin, ZHOU Junfu, REN Yuanhang, YE Lin, YUE Bin, HE Heyong. Liquid Phase Assembly of Mesoporous CsxH3-xPW12O40 and Characterization of Their Acidity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2734. |
| [5] | MA Zihui, WANG Mengyan, CAO Hongyu, TANG Qian, WANG Lihao, ZHENG Xuefang. Transient Absorption and Decay Kinetic Properties of Photo-excited Metal Coordinated Tetraphenylporphyrin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 767. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhilan, WANG Ning, TANG Dandan, SHU Jie, LI Xiaohong. Experimental Set-up and Application Research of Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Multiple-CP Technique [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 784. |
| [7] | SHUAI Die, ZHAO Meijuan, CHEN Bingnian, WANG Li. Inhibitory Effect of Four Kinds of Keegin-type Phosphomolybdate on Tyrosinase and Melanin Formation and Its Antioxidant Activities [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3579. |
| [8] | ZHAO Shufang, HUANG Jun. Study by Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy on the Acidity and Shape-selectivity of Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 165. |
| [9] | ZOU Run, DONG Xiao, JIAO Yilai, Carmine D'AGOSTINO, YAN Wenfu, FAN Xiaolei. Controllable Synthesis, Diffusion Study and Catalysis of Hierarchical Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 74. |
| [10] | ZHANG Aiqin, WANG Man, SHEN Gangyi, JIN Jun. Interactions Between Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Using SPR and Molecular Docking [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2054. |
| [11] | ZHU Ling,WANG Yuchen,ZHAO Jiangyuan,WEN Mengliang,LI Minggang,HAN Xiulin. Transformation of Ginsenoside Rb3 and C-Mx by Recombinant β-Xylosidase † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1010. |
| [12] | YE Xiaodong, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Glucose Oxidation on Au-supported SBA-15 Molecular Sieve † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 960. |
| [13] | XIAO Yuqing,LI Shenhui,TANG Jing,XU Jun,DENG Feng. Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy Studies on Structure, Dynamics and Host-guest Interaction in Metal-organic Framework Materials † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 204. |
| [14] | ZHAO Xingling, QI Guodong, WANG Qiang, CHU Yueying, GAO Wei, LI Shenhui, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Structure, Nature and Activity of Ga Species for Propane Aromatization in Ga/ZSM-5 Revealed by Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2681. |
| [15] | WANG Biwen, DU Tian, TANG Weijun. Synthesis and Application of Chiral Ru Pincer Catalysts on the Hydrogenation of α-Hydroxy Esters by Dynamic Kinetic Resolution† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(10): 2256. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||