

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 165.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200416
Special Issue: 分子筛功能材料 2021年,42卷,第1期
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-07-01
Online:2021-01-10
Published:2021-01-12
Contact:
HUANG Jun
E-mail:jun.huang@sydney.edu.au
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Shufang, HUANG Jun. Study by Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy on the Acidity and Shape-selectivity of Zeolites[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 165.
| MAS NMR | Resonance, δ | Assignment | Correlations with acid sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1H[ | 3.6—5.2 | SiOHAl, bridging hydroxyl group | BASs |
| 0.6—3.6 | Extraframework AlOH | LASs | |
| 1.2—2.2 | Nonacidic SiOH | ||
| 27Al[ | 50—65 | Four?coordinated framework Al | BASs |
| 30—40 | Five?coordinated extra?framework Al | LASs | |
| -10—15 | Six?coordinated extra?framework Al | LASs | |
| 29Si[ | -100—-115 | Si(0Al) | The strength of acidity |
| -95—-105 | Si(1Al) | ||
| -90—-100 | Si(2Al) | ||
| -85—-95 | Si(3Al) | ||
| -80—-90 | Si(4Al) | ||
| 17O[ | -20—20 | Si—O—Si | No direct correlation |
| 10—40 | Si—O—Al | ||
| 11B[ | 12 | B(OSi)3 | Weak BASs |
| 15 | B(OSi)2(OH) | ||
| 71Ga[ | 150—160 | Tetrahedral framework Ga | BASs |
| -7—12 | Octahedral extra?framework Ga | LASs | |
| 119Sn[ | -443 and -435 | 4?Coordinated closed Sn site | LASs |
| -420 | 6?Coordinated open Sn site |
Table 1 Assignments of MAS NMR chemical shift of framework atoms in zeolites
| MAS NMR | Resonance, δ | Assignment | Correlations with acid sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1H[ | 3.6—5.2 | SiOHAl, bridging hydroxyl group | BASs |
| 0.6—3.6 | Extraframework AlOH | LASs | |
| 1.2—2.2 | Nonacidic SiOH | ||
| 27Al[ | 50—65 | Four?coordinated framework Al | BASs |
| 30—40 | Five?coordinated extra?framework Al | LASs | |
| -10—15 | Six?coordinated extra?framework Al | LASs | |
| 29Si[ | -100—-115 | Si(0Al) | The strength of acidity |
| -95—-105 | Si(1Al) | ||
| -90—-100 | Si(2Al) | ||
| -85—-95 | Si(3Al) | ||
| -80—-90 | Si(4Al) | ||
| 17O[ | -20—20 | Si—O—Si | No direct correlation |
| 10—40 | Si—O—Al | ||
| 11B[ | 12 | B(OSi)3 | Weak BASs |
| 15 | B(OSi)2(OH) | ||
| 71Ga[ | 150—160 | Tetrahedral framework Ga | BASs |
| -7—12 | Octahedral extra?framework Ga | LASs | |
| 119Sn[ | -443 and -435 | 4?Coordinated closed Sn site | LASs |
| -420 | 6?Coordinated open Sn site |
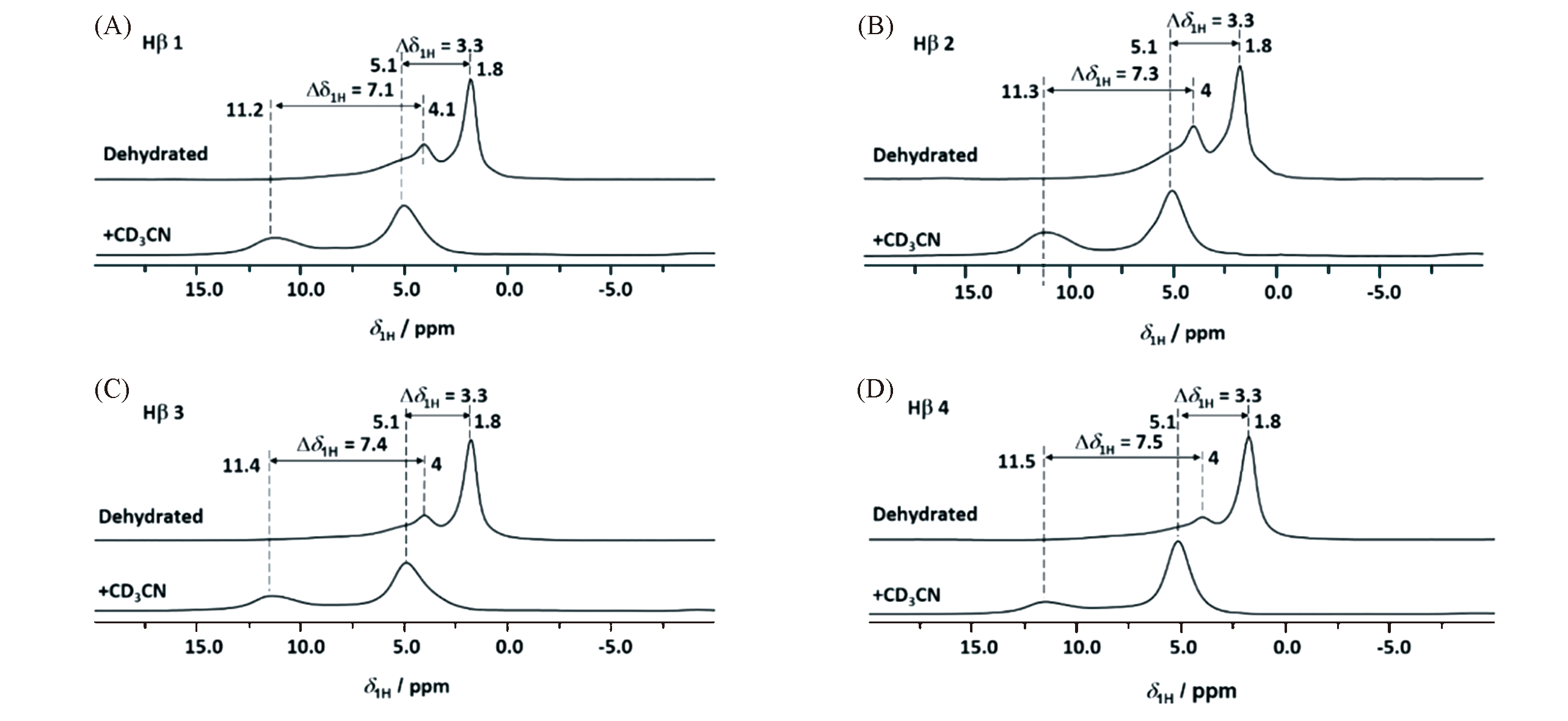
Fig.1 1H MAS NMR spectra of dehydrated Hβ with different Si/Al ratios of Hβ1 to Hβ4[38](A) Hβ1; (B) Hβ2; (C) Hβ3; (D) Hβ4. Recorded before(top) and after(bottom) adsorption of CD3CN at room temperature and purged with under a N2 flow of 50 mL for 10 min. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
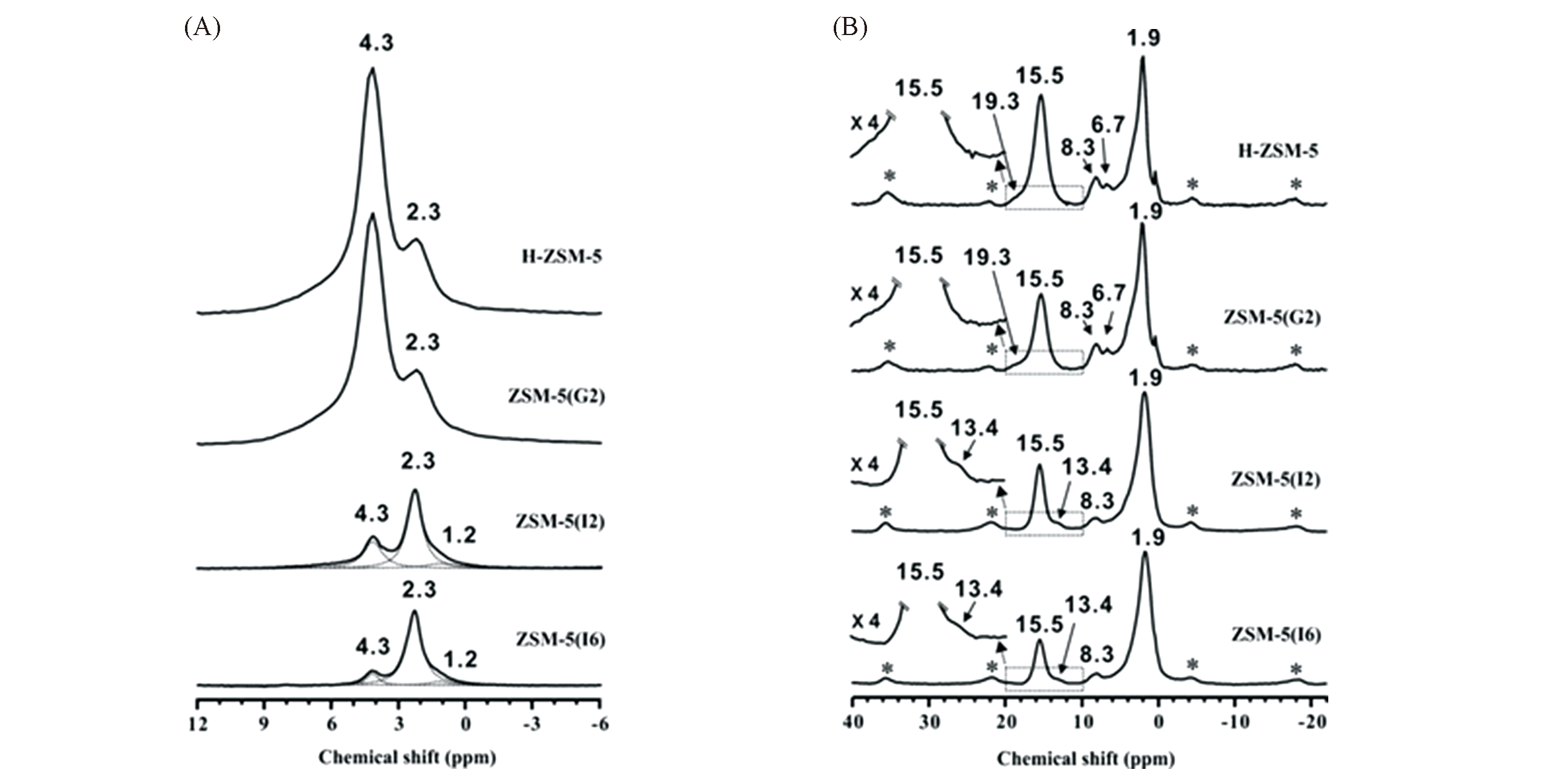
Fig.2 1H MAS NMR spectra recorded at 7.05?T of H‐ZSM‐5, ZSM‐5(G2), ZSM‐5(I2), and ZSM‐5(I6)(A) and pyridine?d5 adsorbed on these samples(B)[20]Copyright 2016, Wiley?VCH.
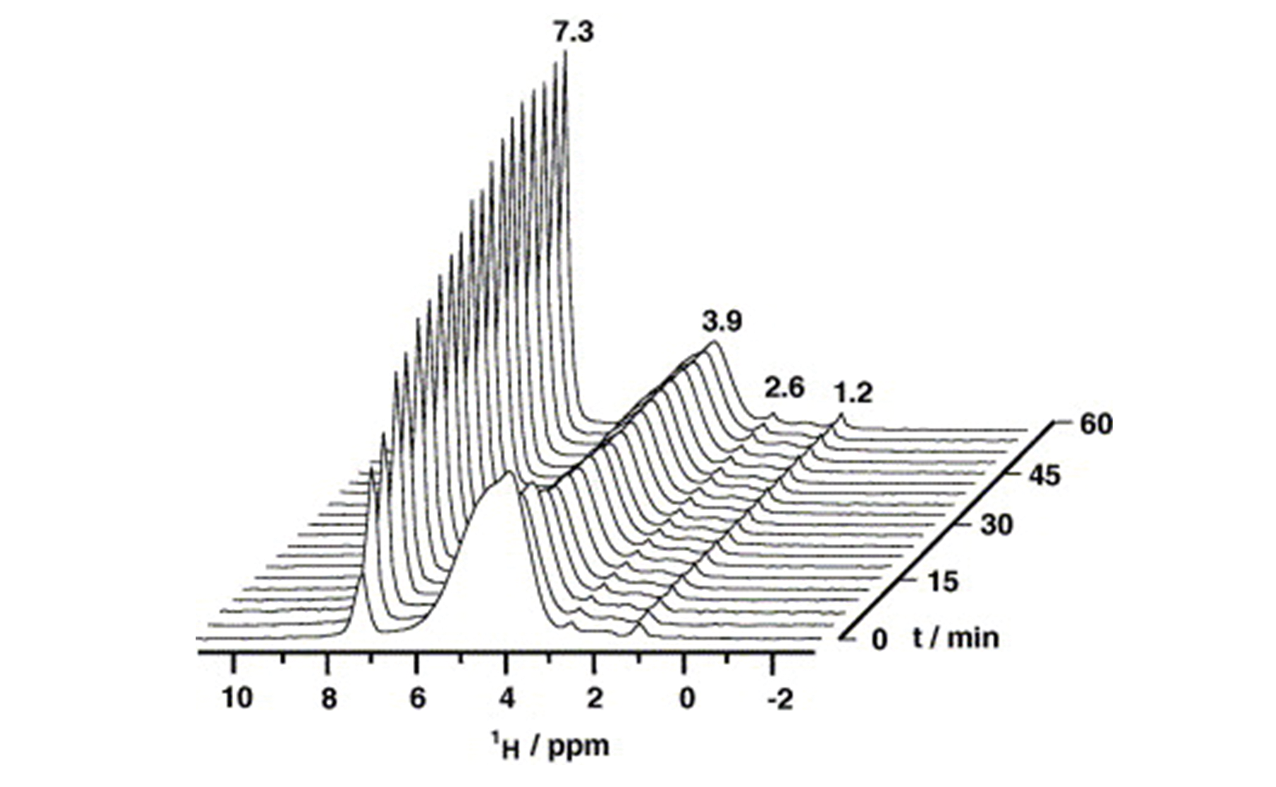
Fig.3 Stack plot of the 1H MAS NMR spectra recorded at the temperature of 358 K during H/D exchange of deuterated ethylbenzene loaded on dehydrated zeolite H?Y[49]Copyright 2006, Elsevier.
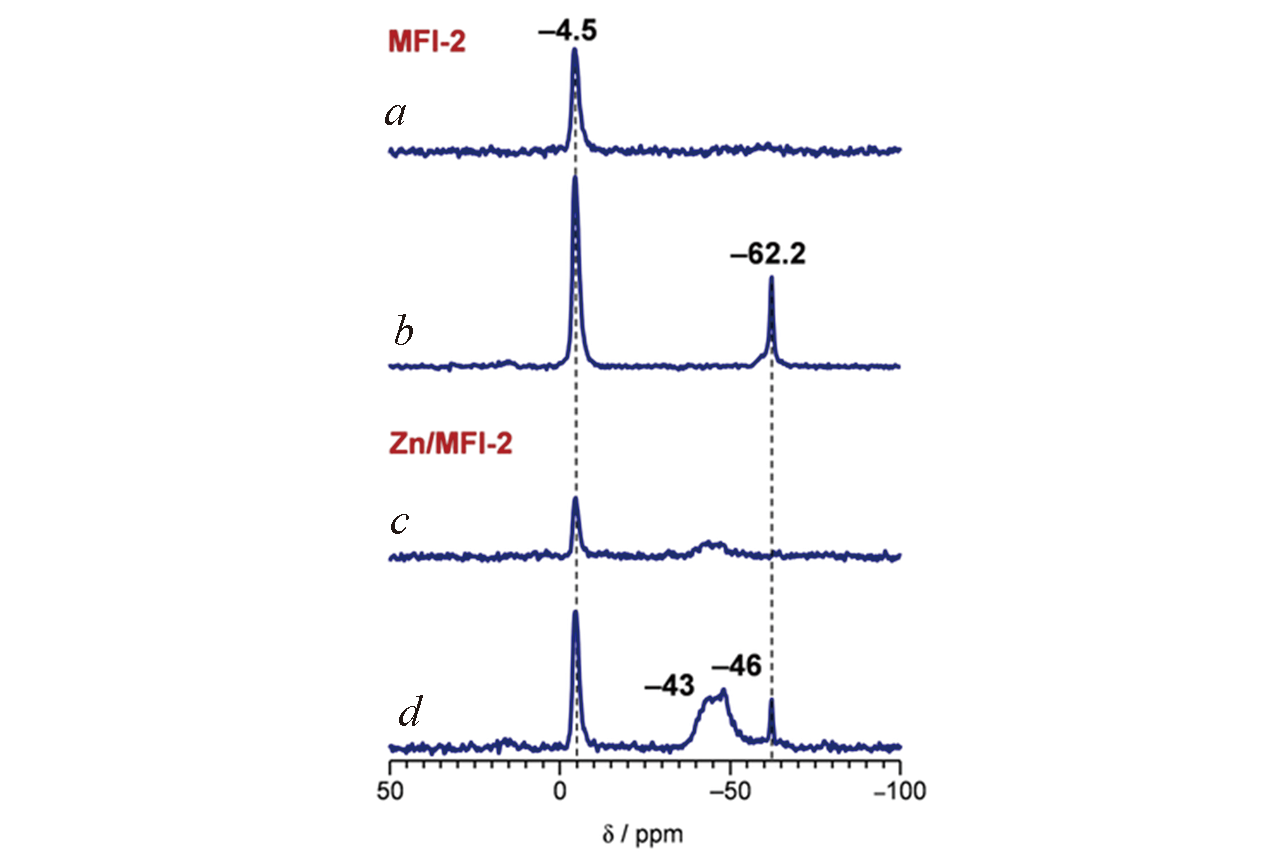
Fig.4 Proton‐decoupled 31P MAS NMR spectra of MFI‐2(a, b) and Zn/MFI‐2(c, d) zeolite samples[55]The ratio TMP/BAS: a. 0.4, b. 1.3, c. 0.5, d. 2.6. Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH.
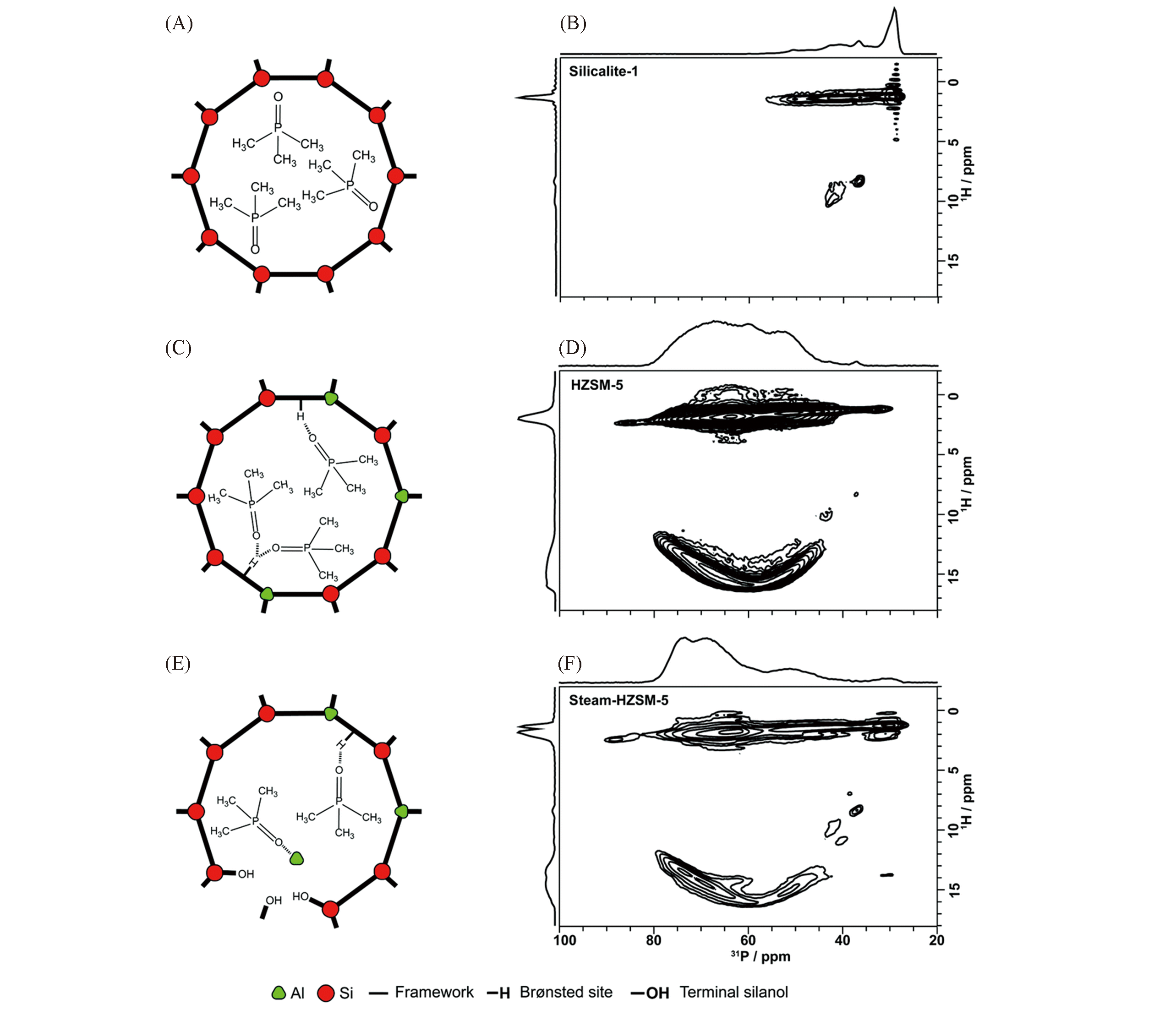
Fig.5 Schematic representation of TMPO?loaded HZSM?5[n(Si)/n(Al)=15] and silicalite?1(A, C, E), 1H?31P HETCOR NMR spectra of TMPO?lloaded silicalite?1, HZSM?5, and steam?HZM?5(B, D, F)[10](B, D, F) The F2 axes??(top) projections display the 31P CPMAS NMR spectra. Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry.
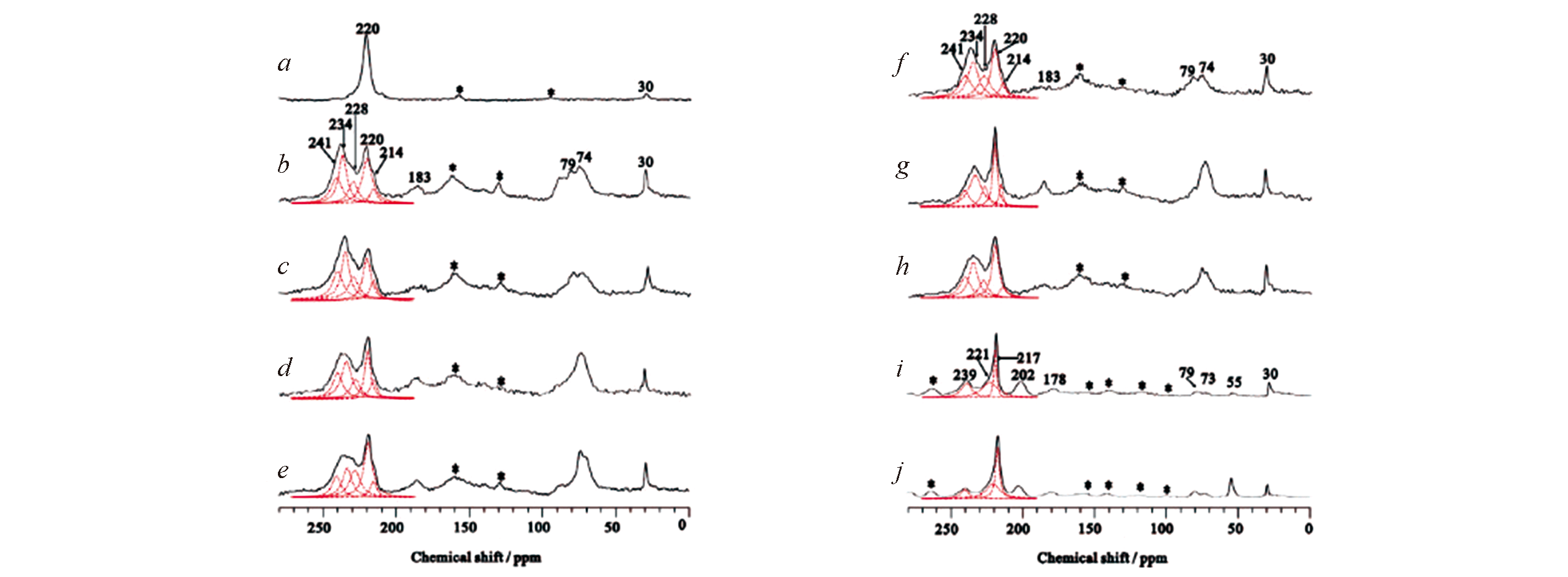
Fig.6 13C CP/MAS NMR spectra of 2?13C?acetone adsorbed on parent H?Y(a), CAL?400(b), CAL?500(c), CAL?600(d), CAL?700(e), STY?350(f), STY?450(g), STY?550(h), OXA?0.8(i), and OXA?1.4(j) zeolites[57]Asterisks denote spinning sidebands. Copyright 2008, American Chemical Society.
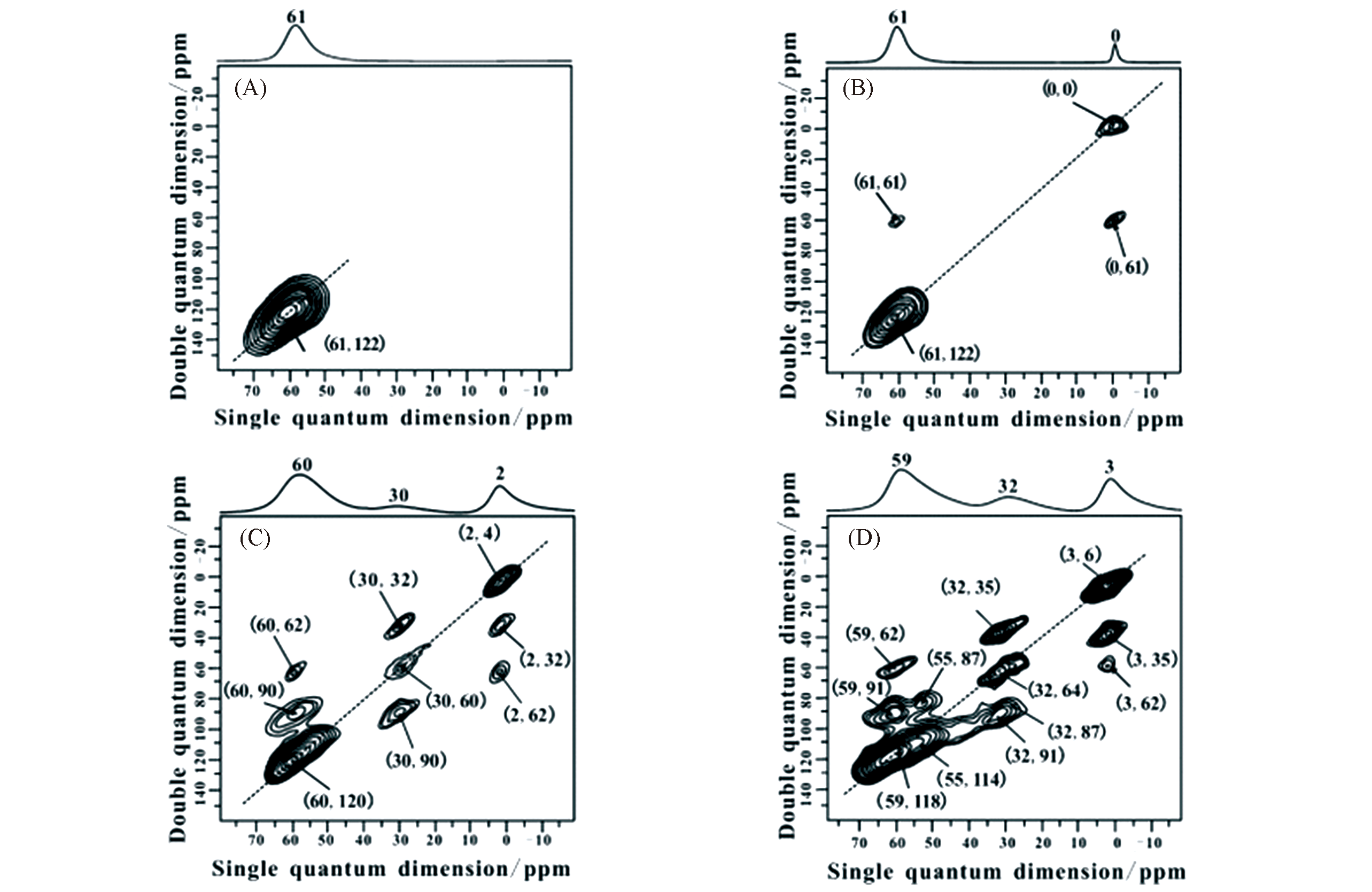
Fig.7 27Al MAS and DQ‐MAS NMR spectra of parent HY(A), HY‐500(B), HY‐600(C), and ?HY‐700(D) zeolites[64]One‐dimensional 27Al MAS spectra are plotted on top of the two‐dimensional 27Al DQ MAS spectra. All spectra were recorded on hydrated samples at 18.8?T with a 3.2?mm probe at a sample rotation rate of 21.5?kHz. About 45?h were required to record one 27Al DQ‐MAS NMR spectrum. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons.
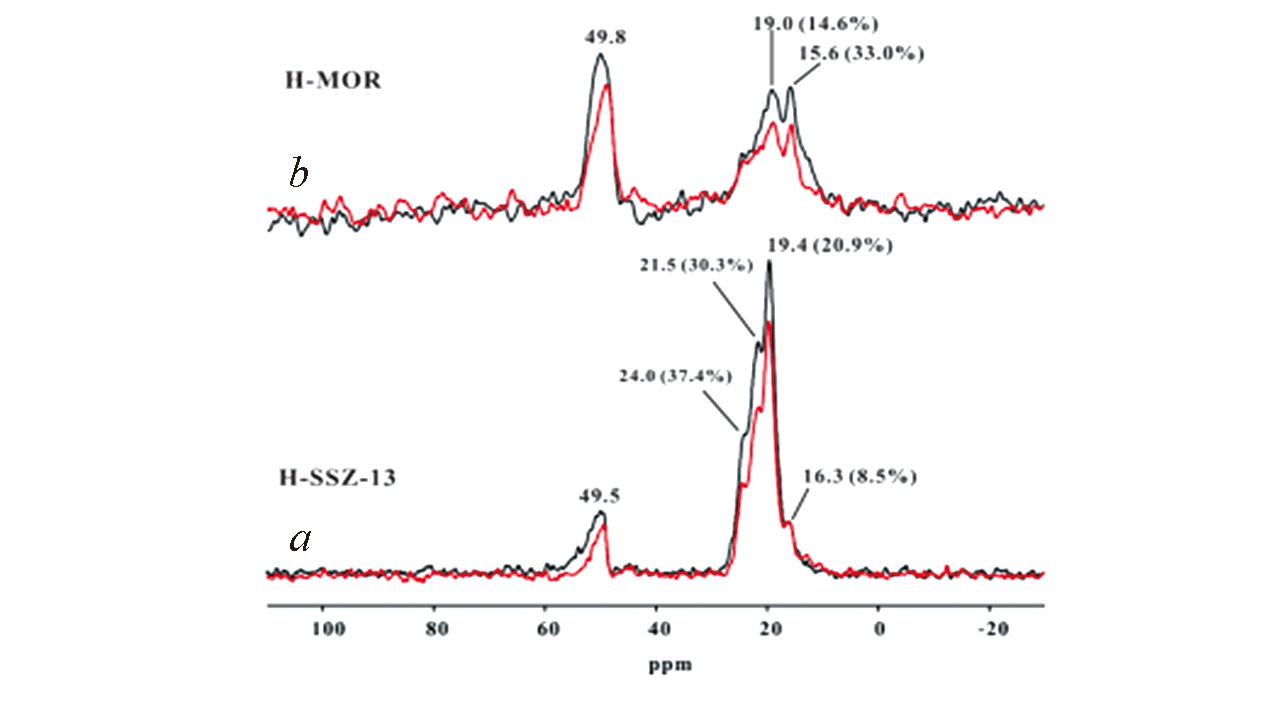
Fig.8 13C MAS NMR spectra of deactivated H?SSZ?13(a) and HMOR(b) at 400 °C for 250 and 100 min, respectively[67]The black and red lines represent the spectrum observed with(S) and without(S0) 13C?{27Al} S?RESPDOR dipolar dephasing, respectively. The ΔS/S0 is indicated in parentheses. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Muraoka K., Chaikittisilp W., Yanaba Y., Yoshikawa T., Okubo T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(14), 3742—3746 |
| 2 | Pan M., Zheng J., Liu Y., Ning W., Tian H., Li R., J. Catal., 2019, 369, 72—85 |
| 3 | Pugh S. M., Wright P. A., Law D. J., Thompson N., Ashbrook S. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(2), 900—906 |
| 4 | Jiao Y., Forster L., Xu S., Chen H., Han J., Liu X., Zhou Y., Liu J., Zhang J., Yu J., D'agostino C., Fan X., Angew. Chem., 2020, 132, 2—11 |
| 5 | Li C., Moliner M., Corma A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(47), 15330—15353 |
| 6 | Peng Q., Wang G., Wang Z., Jiang R., Wang D., Chen J., Huang J., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2018, 6(12), 16867—16875 |
| 7 | Xu J., Wang Q., Li S., Deng F., Solid⁃State NMR in Zeolite Catalysis, Springer, Singapore, 2019, 159—197 |
| 8 | Chen K., Horstmeier S., Nguyen V. T., Wang B., Crossley S. P., Pham T., Gan Z., Hung I., White J. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(16), 7514—7523 |
| 9 | Altvater N. R., Dorn R. W., Cendejas M. C., Mcdermott W. P., Thomas B., Rossini A. J., Hermans I., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(16), 6546—6550 |
| 10 | Bornes C., Sardo M., Lin Z., Amelse J., Fernandes A., Ribeiro M. F., Geraldes C., Rocha J., Mafra L., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(84), 12635—12638 |
| 11 | Xin S., Wang Q., Xu J., Chu Y., Wang P., Feng N., Qi G., Trébosc J., Lafon O., Fan W., Deng F., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(43), 10159—10169 |
| 12 | Jiang Y., Huang J., Dai W., Hunger M., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2011, 39(3/4), 116—141 |
| 13 | Zhong J., Han J., Wei Y., Tian P., Guo X., Song C., Liu Z., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7(21), 4905—4923 |
| 14 | Wang F., Chu X., Zhao P., Zhu F., Li Q., Wu F., Xiao G., Fuel, 2020, 262, 116538—116547 |
| 15 | Zeng S., Xu S., Gao S., Gao M., Zhang W., Wei Y., Liu Z., ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(2), 463—468 |
| 16 | Wang C., Zhang L., Huang X., Zhu Y., Li G. K., Gu Q., Chen J., Ma L., Li X., He Q., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1—8 |
| 17 | Degnan Jr T. F., J. Catal., 2003, 216(1/2), 32—46 |
| 18 | Wang Z., Li T., Jiang Y., Lafon O., Liu Z., Trébosc J., Baiker A., Amoureux J. P., Huang J., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 1—9 |
| 19 | Kim W. G., So J., Choi S. W., Liu Y., Dixit R. S., Sievers C., Sholl D. S., Nair S., Jones C. W., Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(17), 7213—7222 |
| 20 | Qi G., Wang Q., Xu J., Trébosc J., Lafon O., Wang C., Amoureux J. P., Deng F., Angew. Chem., 2016, 128(51), 16058—16062 |
| 21 | Kolyagin Y. G., Yakimov A. V., Tolborg S., Vennestrøm P. N., Ivanova I. I., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2018, 9(13), 3738—3743 |
| 22 | Gao P., Wang Q., Xu J., Qi G., Wang C., Zhou X., Zhao X., Feng N., Liu X., Deng F., ACS Catal., 2018, 8(1), 69—74 |
| 23 | Zhao R., Zhao Z., Li S., Zhang W., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8(10), 2323—2327 |
| 24 | Lin L., Qiu C., Zhuo Z., Zhang D., Zhao S., Wu H., Liu Y., He M., J. Catal., 2014, 309, 136—145 |
| 25 | Zhao S. F., Yao X. T., Yan B. H., Li L., Liu Y. M., He M. Y., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2017, 28(6), 1318—1323 |
| 26 | Lin L. F., Zhao S. F., Zhang D. W., Fan H., Liu Y. M., He M. Y., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(7), 4048—4059 |
| 27 | Zhao S., Yang D., Zhang X., Yao X., Liu Y., He M., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(75), 11191—11194 |
| 28 | Zheng A., Liu S. B., Deng F., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(19), 12475—12531 |
| 29 | Wang Z., O'dell L. A., Zeng X., Liu C., Zhao S., Zhang W., Gaborieau M., Jiang Y., Huang J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(50), 18061—18068 |
| 30 | Zhang B., Douthwaite M., Liu Q., Zhang C., Wu Q., Shi R., Wu P., Liu K., Wang Z., Lin W., Green Chem., 2020, 22(5), 1630—1638 |
| 31 | Hu J. Z., Zhang X., Jaegers N. R., Wan C., Graham T. R., Hu M., Pearce C. I., Felmy A. R., Clark S. B., Rosso K. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(49), 27555—27562 |
| 32 | Hwang S. J., Chen C. Y., Zones S. I., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(48), 18535—18546 |
| 33 | Qi G., Wang Q., Xu J., Wu Q., Wang C., Zhao X., Meng X., Xiao F., Deng F., Commun. Chem., 2018, 1(1), 1—7 |
| 34 | Zhao S., Wang W. D., Wang L., Schwieger W., Wang W., Huang J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(2), 1185—1194 |
| 35 | Zhao S., Wang W. D., Wang L., Wang W., Huang J., J. Catal., 2020, 389, 166—175 |
| 36 | Sutrisno A., Lucier B. E., Zhang L., Ding L., Chu Y., Zheng A., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122(13), 7260—7277 |
| 37 | Dai W., Yang L., Wang C., Wang X., Wu G., Guan N., Obenaus U., Hunger M., Li L., ACS Catal., 2018, 8(2), 1352—1362 |
| 38 | Wang Z., Wang L., Zhou Z., Zhang Y., Li H., Stampfl C., Liang C., Huang J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(28), 15248—15255 |
| 39 | Kim K. D., Wang Z., Jiang Y., Hunger M., Huang J., Green Chem., 2019, 21(12), 3383—3393 |
| 40 | Huang J., Van Vegten N., Jiang Y., Hunger M., Baiker A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49(42), 7776—7781 |
| 41 | Zheng A., Zhang H., Chen L., Yue Y., Ye C., Deng F., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2007, 111(12), 3085—3089 |
| 42 | Zhao Z., Li X., Li S., Xu S., Bao X., Bilge Y., Andrei⁃Nicolae P., Ulrich M., Zhang W., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2019, 288, 109555 |
| 43 | Yu Z., Wang Q., Chen L., Deng F., Chin. J. Catal., 2012, 33(1), 129—139 |
| 44 | Zhang W., Ma D., Liu X., Liu X., Bao X., Chem. Commun., 1999, (12), 1091—1092 |
| 45 | Gabrienko A. A., Arzumanov S. S., Toktarev A. V., Freude D., Haase J. R., Stepanov A. G., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(28), 13877—13886 |
| 46 | Chen K., Abdolrahmani M., Horstmeier S., Pham T. N., Nguyen V. T., Zeets M., Wang B., Crossley S., White J. L., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(7), 6124—6136 |
| 47 | Kramer G., Van Santen R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117(6), 1766—1776 |
| 48 | Gabrienko A. A., Danilova I. G., Arzumanov S. S., Pirutko L. V., Freude D., Stepanov A. G., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122(44), 25386—25395 |
| 49 | Huang J., Jiang Y., Marthala V. R., Wang W., Sulikowski B., Hunger M., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2007, 99(1/2), 86—90 |
| 50 | Arzumanov S. S., Gabrienko A. A., Toktarev A. V., Freude D., Haase J., Stepanov A. G., J. Catal., 2019, 378, 341—352 |
| 51 | Stepanov A. G., Arzumanov S. S., Gabrienko A. A., Parmon V. N., Ivanova I. I., Freude D., Chemphyschem, 2008, 9(17), 2559—2563 |
| 52 | Xu J., Wang Q., Deng F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52(8), 2179—2189 |
| 53 | Gabrienko A. A., Arzumanov S. S., Toktarev A. V., Danilova I. G., Prosvirin I. P., Kriventsov V. V., Zaikovskii V. I., Freude D., Stepanov A. G., ACS Catal., 2017, 7(3), 1818—1830 |
| 54 | Peng Y. K., Ye L., Qu J., Zhang L., Fu Y., Teixeira I. F., Mcpherson I. J., He H., Tsang S. C. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(7), 2225—2234 |
| 55 | Gabrienko A. A., Danilova I. G., Arzumanov S. S., Freude D., Stepanov A. G., ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(2), 478—487 |
| 56 | Zheng A., Li S., Liu S. B., Deng F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49(4), 655—663 |
| 57 | Li S., Huang S. J., Shen W., Zhang H., Fang H., Zheng A., Liu S. B., Deng F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(37), 14486—14494 |
| 58 | Yu Z., Li S., Wang Q., Zheng A., Jun X., Chen L., Deng F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(45), 22320—22327 |
| 59 | Wang Z., Jiang Y., Stampfl C., Baiker A., Hunger M., Huang J., ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(1), 287—293 |
| 60 | Wang Z., Wang L., Jiang Y., Hunger M., Huang J., ACS Catal., 2014, 4(4), 1144—1147 |
| 61 | Xu J., Wang Q., Li S., Deng F., Solid⁃State NMR in Zeolite Catalysis, Springer, Singapore, 2019, 199—254 |
| 62 | Zhang Y., Zhao R., Sanchez⁃Sanchez M., Haller G. L., Hu J., Bermejo⁃Deval R., Liu Y., Lercher J. A., J. Catal., 2019, 370, 424—433 |
| 63 | Li S., Zheng A., Su Y., Zhang H., Chen L., Yang J., Ye C., Deng F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(36), 11161—11171 |
| 64 | Yu Z., Zheng A., Wang Q., Chen L., Xu J., Amoureux J. P., Deng F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49(46), 8657—8661 |
| 65 | Baranowski C. J., Roger M., Bahmanpour A. M., Kröcher O., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(19), 4421—4431 |
| 66 | Weisz P. B., Pure Appl. Chem., 1980, 52(9), 2091—2103 |
| 67 | Wang C., Xu J., Wang Q., Zhou X., Qi G., Feng N., Liu X., Meng X., Xiao F., Deng F., ACS Catal., 2017, 7(9), 6094—6103 |
| 68 | Lv J., Hua Z., Zhou J., Liu Z., Guo H., Shi J., ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(10), 2278—2284 |
| 69 | Smit B., Maesen T. L., Nature, 2008, 451(7179), 671—678 |
| 70 | Corma A., J. Catal., 2003, 216(1/2), 298—312 |
| 71 | Sazama P., Pastvova J., Kaucky D., Moravkova J., Rathousky J., Jakubec I., Sadovska G., J. Catal., 2018, 364, 262—270 |
| 72 | Huang J., Jiang Y., Marthala V. R., Bressel A., Frey J., Hunger M., J. Catal., 2009, 263(2), 277—283 |
| 73 | Huang J., Jiang Y., Marthala V. R., Hunger M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(38), 12642—12644 |
| 74 | Shi Y., Xing E., Xie W., Zhang F., Mu X., Shu X., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2016, 418/419, 86—94 |
| 75 | Poursaeidesfahani A., De Lange M. F., Khodadadian F., Dubbeldam D., Rigutto M., Nair N., Vlugt T. J., J. Catal., 2017, 353, 54—62 |
| 76 | Anderson M. W., Klinowski J., Nature, 1989, 339(6221), 200—203 |
| 77 | Ivanova I. I., Kolyagin Y. G., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39(12), 5018—5050 |
| 78 | Zhang W., Xu S., Han X., Bao X., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(1), 192—210 |
| 79 | Zhao Z., Shi H., Wan C., Hu M. Y., Liu Y., Mei D., Camaioni D. M., Hu J. Z., Lercher J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(27), 9178—9185 |
| 80 | Radhakrishnan S., Goossens P. J., Magusin P. C., Sree S. P., Detavernier C., Breynaert E., Martineau C., Taulelle F., Martens J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(8), 2802—2808 |
| 81 | Zhou X., Wang C., Chu Y., Xu J., Wang Q., Qi G., Zhao X., Feng N., Deng F., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1—9 |
| 82 | Haw J., Song W., Marcus D., Nicholas J., Acc. Chem. Res, 2003, 36(5), 317—326 |
| 83 | Hereijgers B. P., Bleken F., Nilsen M. H., Svelle S., Lillerud K. P., Bjørgen M., Weckhuysen B. M., Olsbye U., J. Catal., 2009, 264(1), 77—87 |
| 84 | Gueudré L., Binder T., Chmelik C., Hibbe F., Ruthven D. M., Kärger J., Materials, 2012, 5(4), 721—740 |
| 85 | Blasco T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39(12), 4685—4702 |
| 86 | Dai W., Wang C., Dyballa M., Wu G., Guan N., Li L., Xie Z., Hunger M., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(1), 317—326 |
| 87 | Hu M., Wang C., Gao X., Chu Y., Qi G., Wang Q., Xu G., Xu J., Deng F., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(7), 4299—4305 |
| 88 | Wang C., Hu M., Chu Y., Zhou X., Wang Q., Qi G., Li S., Xu J., Deng F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(18), 7198—7202 |
| 89 | Xu S., Zheng A., Wei Y., Chen J., Li J., Chu Y., Zhang M., Wang Q., Zhou Y., Wang J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(44), 11564—11568 |
| 90 | Jiang Y., Huang J., Marthala V. R., Ooi Y. S., Weitkamp J., Hunger M., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2007, 105(1/2), 132—139 |
| 91 | Wang C., Chu Y., Zheng A., Xu J., Wang Q., Gao P., Qi G., Gong Y., Deng F., Chem. Eur. J., 2014, 20(39), 12432—12443 |
| 92 | Xiao D., Xu S., Brownbill N. J., Paul S., Chen L. H., Pawsey S., Aussenac F., Su B. L., Han X., Bao X., Chem. Sci., 2018, 9(43), 8184—8193 |
| 93 | Wang C., Wang Q., Xu J., Qi G., Gao P., Wang W., Zou Y., Feng N., Liu X., Deng F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(7), 2507—2511 |
| 94 | Li S., Pourpoint F., Trebosc J., Zhou L., Lafon O., Shen M., Zheng A., Wang Q., Amoureux J. P., Deng F., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5(17), 3068—3072 |
| 95 | Wu J., Wang S., Li H., Zhang Y., Shi R., Zhao Y., Nanomaterials, 2019, 9(9), 1192 |
| 96 | Zhang H., Hu Z., Huang L., Zhang H., Song K., Wang L., Shi Z., Ma J., Zhuang Y., Shen W., Zhang Y., Xu H., Tang Y., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(4), 2548—2558 |
| 97 | Shang Y., Wang W., Zhai Y., Song Y., Zhao X., Ma T., Wei J., Gong Y., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2019, 276, 173—182 |
| 98 | Yang X., Wang F., Wei R., Li S., Wu Y., Shen P., Wang H., Gao L., Xiao G., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2018, 257, 154—161 |
| [1] | LI Zhiguang, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Role of Catalyst Acidity in Glucose Conversion over Sn-Al-β Zeolite as Studied by Solid-state NMR [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220138. |
| [2] | DAI Wei, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Theoretical Investigations on the Electronic Structures and Reactivity of Heptafluoro-iso-butyronitrile Anion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220044. |
| [3] | LI Jiafu, ZHANG Kai, WANG Ning, SUN Qiming. Research Progress of Zeolite-encaged Single-atom Metal Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220032. |
| [4] | TIAN Runsai, LU Qian, ZHANG Hongbin, ZHANG Bo, FENG Yuanyuan, WEI Jinxiang, FENG Jijun. Design and Construction of N-Doping Carbon in⁃situ Coated Cu2O/Co3O4@C Heterostructured Composite Material for Highly Efficient Lithium-ion Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2592. |
| [5] | HAN Yixiu, WU Dianguo, LI Hongpu, YIN Hongyao, MEI Yongjun, FENG Yujun, ZHONG Zuqin. Interactions Between Hydrophobic Associating Poly(sodium acrylate) and a Zwitterionic Surfactant in Non-aqueous Media and Low Temperature Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2056. |
| [6] | WU Shuaini, ZHU Pengfei, SHI Huaiqi, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation of CoCrx/SAPO-34 Catalyst and Its Catalytic Combustion Performance for 1,2-Dichloroethane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3731. |
| [7] | QI Guodong, YE Xiaodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Progress in NMR Studies of Carbohydrates Conversion on Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 148. |
| [8] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [9] | JIAO Meichen, JIANG Jingang, XU Hao, WU Peng. Structural Stabilization, Modification and Catalytic Applications of Germanosilicates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 29. |
| [10] | WANG Binyu, LI Li, LI Jing, JIN Keyan, ZHANG Shaoqing, ZHANG Jianan, YAN Wenfu. Recent Progresses on the Synthesis of Zeolites from the Industrial Solid Wastes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 40. |
| [11] | CHEN Siqi, LI Li, LI Yi, YU Jihong. Applications of Materials Genome Engineering in Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 179. |
| [12] | ZHANG Guoqiang, SUN Yuchen, SHI Yabo, ZHENG Huayan, LI Zhong, SHANGGUAN Ju, LIU Shoujun, SHI Pengzheng. Surface Properties of Ce1-xMnxO2 Catalyst on the Catalytic Activities for Direct Synthesis of DMC from CO2 and Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2061. |
| [13] | ZHAO Xingling, QI Guodong, WANG Qiang, CHU Yueying, GAO Wei, LI Shenhui, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Structure, Nature and Activity of Ga Species for Propane Aromatization in Ga/ZSM-5 Revealed by Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2681. |
| [14] | ZHANG Ling,DUAN Hongchang,TAN Zhengguo,WU Qinming,MENG Xiangju,XIAO Fengshou. Recent Advances in the Preparation of 8MR Zeolites for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx(NH3-SCR) in Diesel Engines † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 19. |
| [15] | YI Jiang, QIN Xingmei, CHEN Feiwu. Theoretical Studies on Cationic Chalcogen and Pnicogen Bonds in Binary and Ternary Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1439. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
