

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 74.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200461
Special Issue: 分子筛功能材料 2021年,42卷,第1期
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZOU Run1, DONG Xiao1, JIAO Yilai2, Carmine D'AGOSTINO1, YAN Wenfu3, FAN Xiaolei1( )
)
Received:2020-07-16
Online:2021-01-10
Published:2021-01-12
Contact:
FAN Xiaolei
E-mail:xiaolei.fan@manchester.ac.uk
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZOU Run, DONG Xiao, JIAO Yilai, Carmine D'AGOSTINO, YAN Wenfu, FAN Xiaolei. Controllable Synthesis, Diffusion Study and Catalysis of Hierarchical Zeolites[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 74.
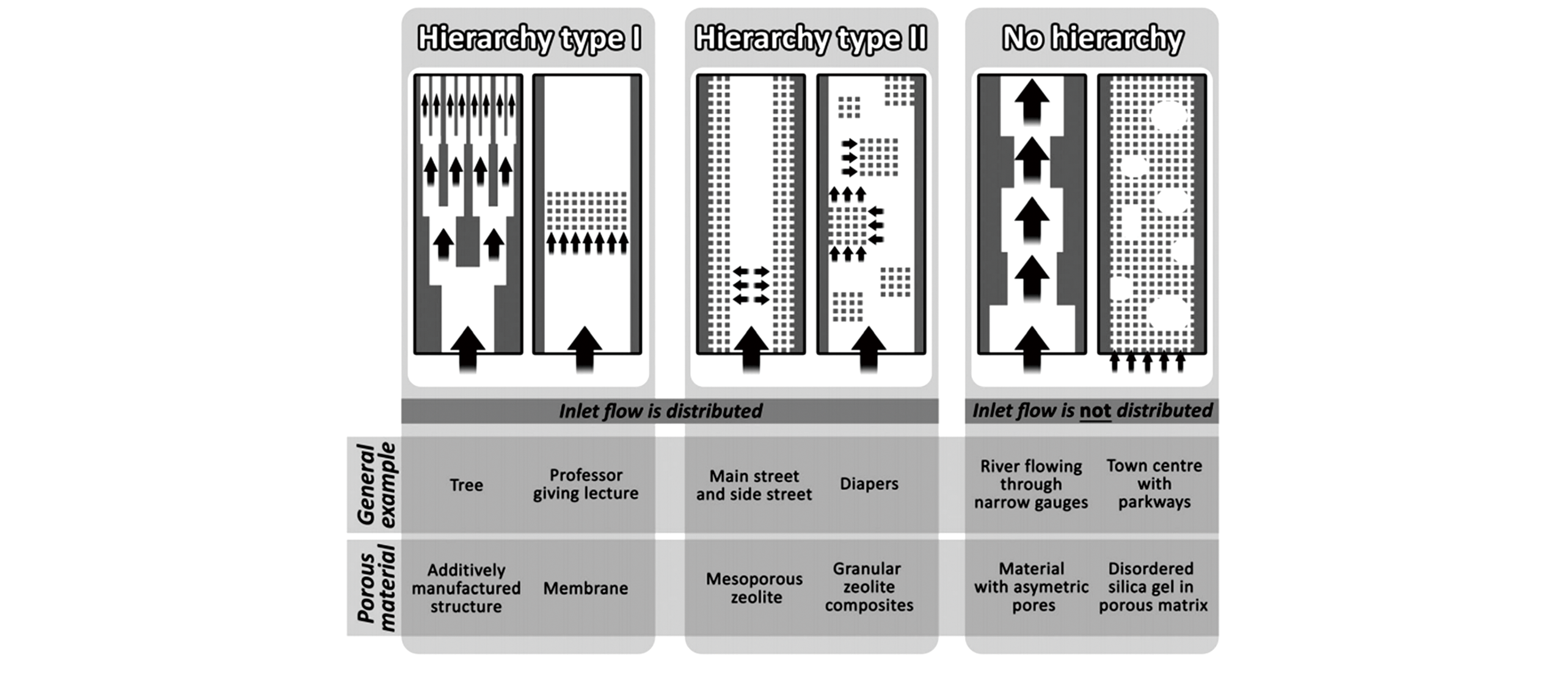
Fig.1 Schematics of the classification for different meso?/micro?pore systems in zeolitic materials[14]Copyright 2016, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
| Type | Template | Framework | Information of porestructure | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Hard template | Carbon nanoparticles | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; ca. 12. 5 or 34. 5 nm | [ |
| Carbon aerogel | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 9―25 nm | [ | |
| Carbon nanotube | MFI(ZSM?5), FAU(Y) | Intracrystalline; 20―30 nm | [ | |
| 3DOM carbon | MFI(silicalite?1) | Intracrystalline; ca. 6 nm | [ | |
| BEA(Beta) | Intracrystalline; 32 nm and 95 nm | [ | ||
| CaCO3 | MFI(silicalite?1) | Intracrystalline; 50―100 nm | [ | |
| Polystyrene bead | MFI(silicalite?1) | Core?shell; >200 nm | [ | |
| Polyurethane | MFI(TS?1) | Intracrystalline; ca. 4 nm | [ | |
| Wood cell | MFI(silicalite?1) | Intracrystalline; 2―20 μm | [ | |
Soft templates | Organosilane(APTMS, IBTES, PHAPTMS and ODTMS) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intercrystalline; 2―8 nm | [73―75] |
| Amino acid(e. g. lysine) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; ca. 40 nm | [ | |
| MFI(TS?1) | Intracrystalline and intercrystalline; 30―70 nm | [ | ||
| LTA | Intracrystalline; ca. 14 or 25 nm | [ | ||
| FAU(Y) | Intracrystalline; 19―24 nm | [ | ||
| Amphiphilic silane(TPHAC) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2. 1―7. 4 nm | [ | |
| Carbohydrate(glucose and starch) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2―25 nm | [ | |
| MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2―50 nm | [ | ||
| Dual?functional template(C22?6?6) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; ca. 15 nm | [ | |
| Silanised polymer(PEI) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2―5 nm | [ | |
| Cationic polymer(PDADMAC) | BEA(Beta) | Intracrystalline; 2―50 nm | [ |
Table 1 Preparation of hierarchical zeolites via the bottom-up templating methods
| Type | Template | Framework | Information of porestructure | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Hard template | Carbon nanoparticles | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; ca. 12. 5 or 34. 5 nm | [ |
| Carbon aerogel | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 9―25 nm | [ | |
| Carbon nanotube | MFI(ZSM?5), FAU(Y) | Intracrystalline; 20―30 nm | [ | |
| 3DOM carbon | MFI(silicalite?1) | Intracrystalline; ca. 6 nm | [ | |
| BEA(Beta) | Intracrystalline; 32 nm and 95 nm | [ | ||
| CaCO3 | MFI(silicalite?1) | Intracrystalline; 50―100 nm | [ | |
| Polystyrene bead | MFI(silicalite?1) | Core?shell; >200 nm | [ | |
| Polyurethane | MFI(TS?1) | Intracrystalline; ca. 4 nm | [ | |
| Wood cell | MFI(silicalite?1) | Intracrystalline; 2―20 μm | [ | |
Soft templates | Organosilane(APTMS, IBTES, PHAPTMS and ODTMS) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intercrystalline; 2―8 nm | [73―75] |
| Amino acid(e. g. lysine) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; ca. 40 nm | [ | |
| MFI(TS?1) | Intracrystalline and intercrystalline; 30―70 nm | [ | ||
| LTA | Intracrystalline; ca. 14 or 25 nm | [ | ||
| FAU(Y) | Intracrystalline; 19―24 nm | [ | ||
| Amphiphilic silane(TPHAC) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2. 1―7. 4 nm | [ | |
| Carbohydrate(glucose and starch) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2―25 nm | [ | |
| MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2―50 nm | [ | ||
| Dual?functional template(C22?6?6) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; ca. 15 nm | [ | |
| Silanised polymer(PEI) | MFI(ZSM?5) | Intracrystalline; 2―5 nm | [ | |
| Cationic polymer(PDADMAC) | BEA(Beta) | Intracrystalline; 2―50 nm | [ |
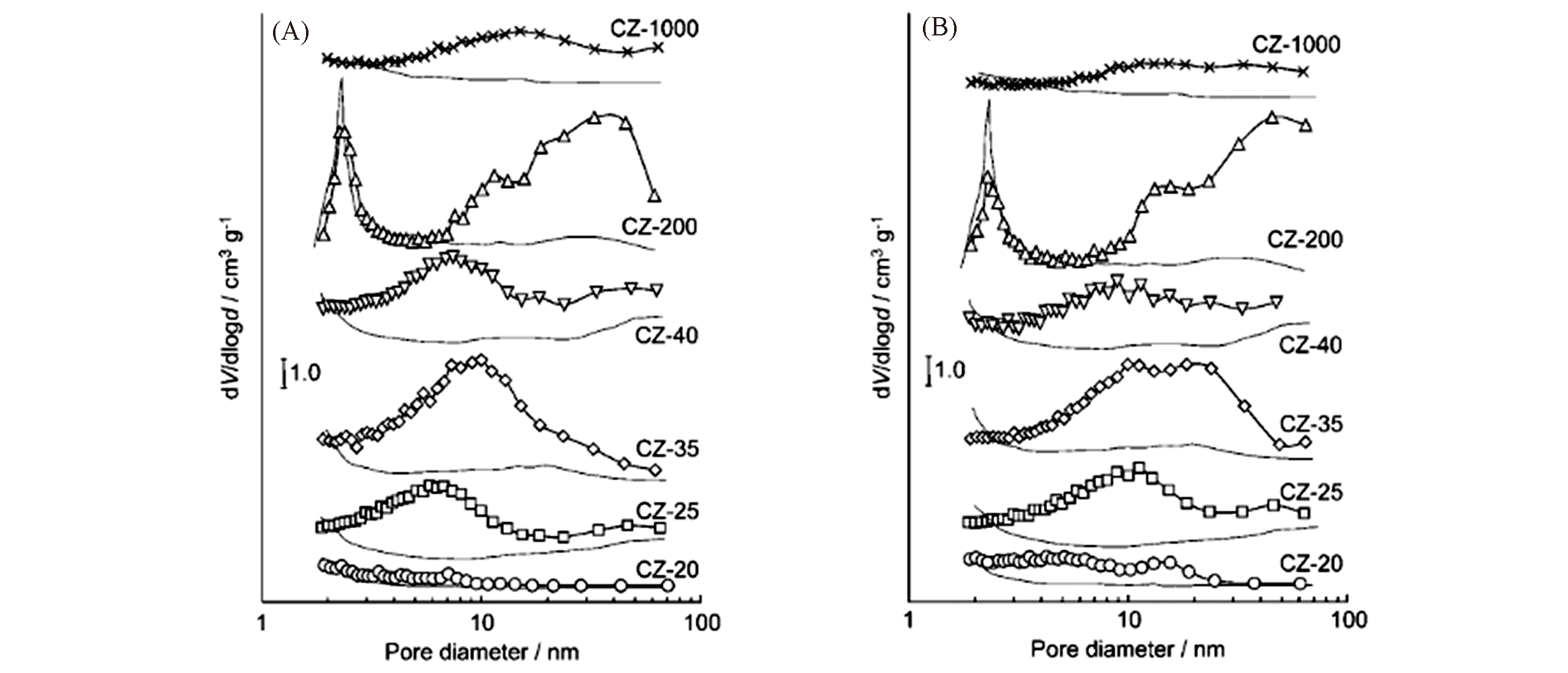
Fig.3 Pore size distribution(based on the Barrett?Joyner?Halenda, BJH, method) of the alkaline?treated commercial ZSM?5 zeolites[96]Alkaline treatment in 0.2 mol/L NaOH for 30 min at 65 ℃(A) and 85 ℃(B).Copyright 2005, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
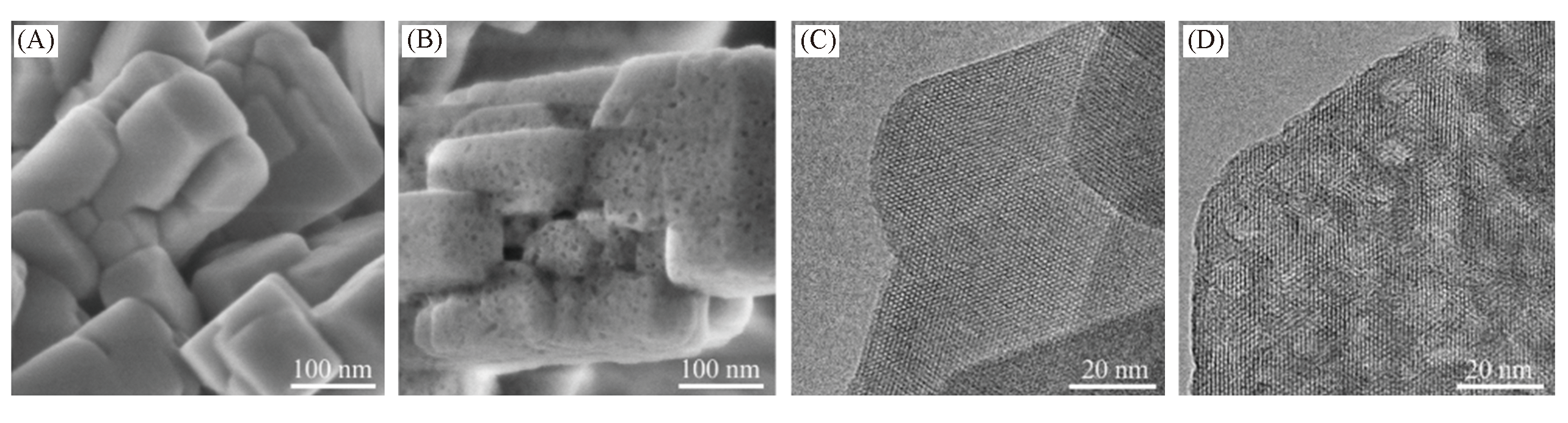
Fig.4 SEM(A, B) and TEM(C, D) images of pristine ZSM?5(A, C) and mesoporous ZSM?5(B, D) treated by sequential steaming and desilication(steaming at 400 °C for 3 h and desilication at 80 °C with 0.2 mol/L NaOH for 30 min)[51]Copyright 2017, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
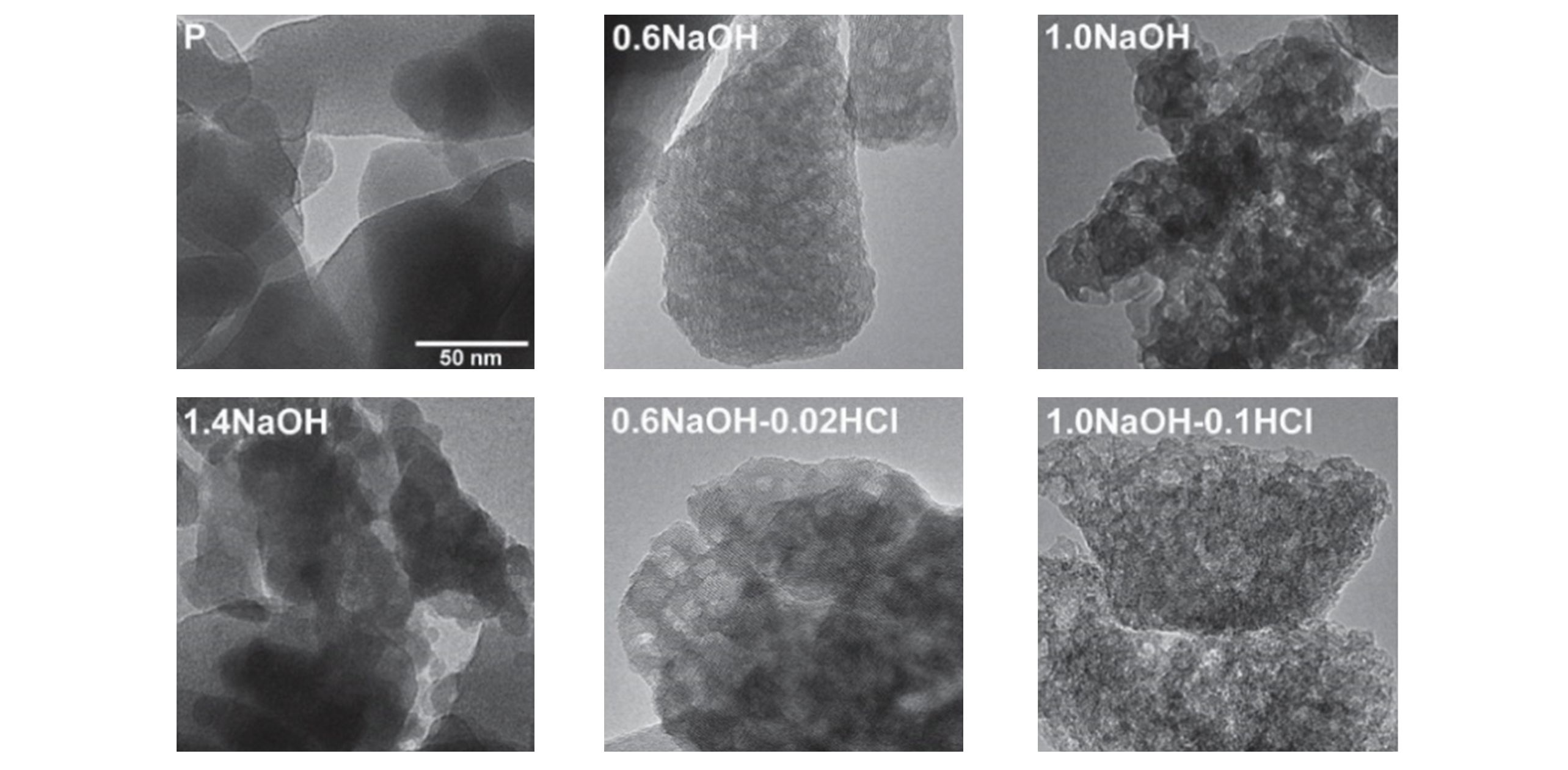
Fig.5 TEM images of parent ZSM?5(SAR=37) and mesoporous ZSM?5 obtained by sequential desilication and dealumination treatments with different acid and base concentration[58]Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society.
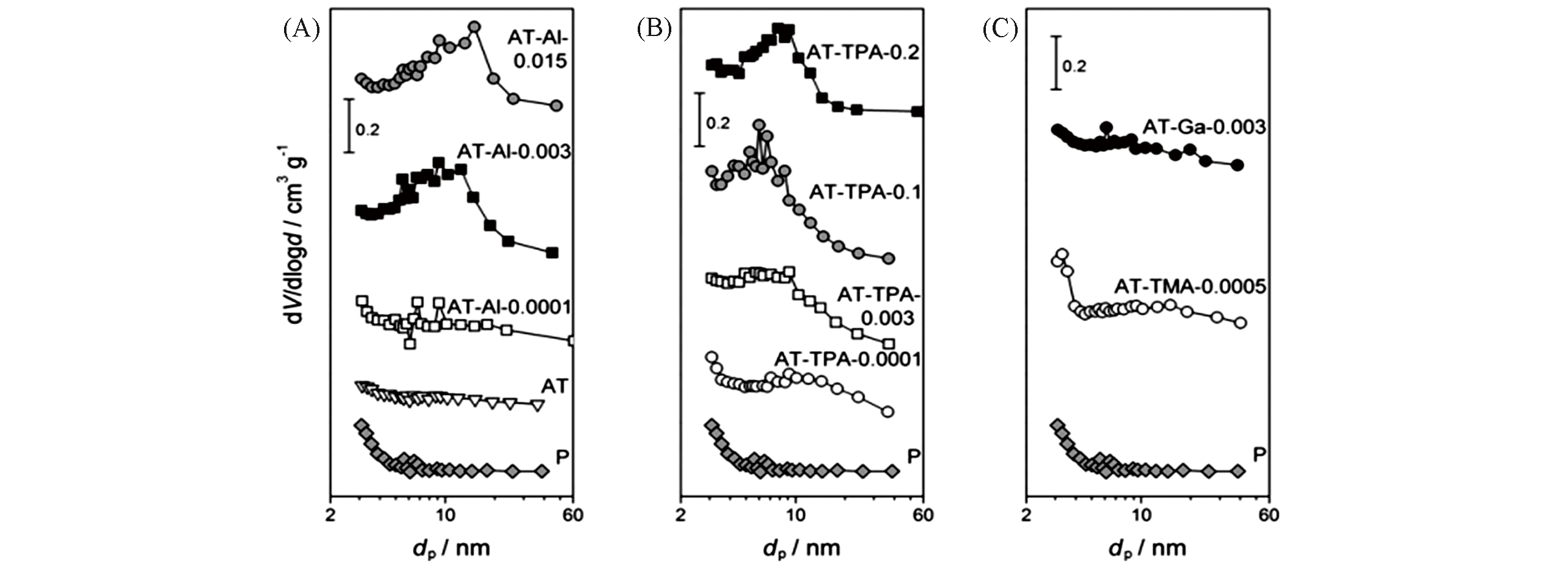
Fig.6 BJH pore size distributions of the parent and alkaline?treated silicalite?1 zeolites derived from the N2 isotherms[57]Pore?directing agent: (A) Al(OH)4+ ; (B) TPA+; (C) Ga(OH)4+ or TMA+.Copyright 2011, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
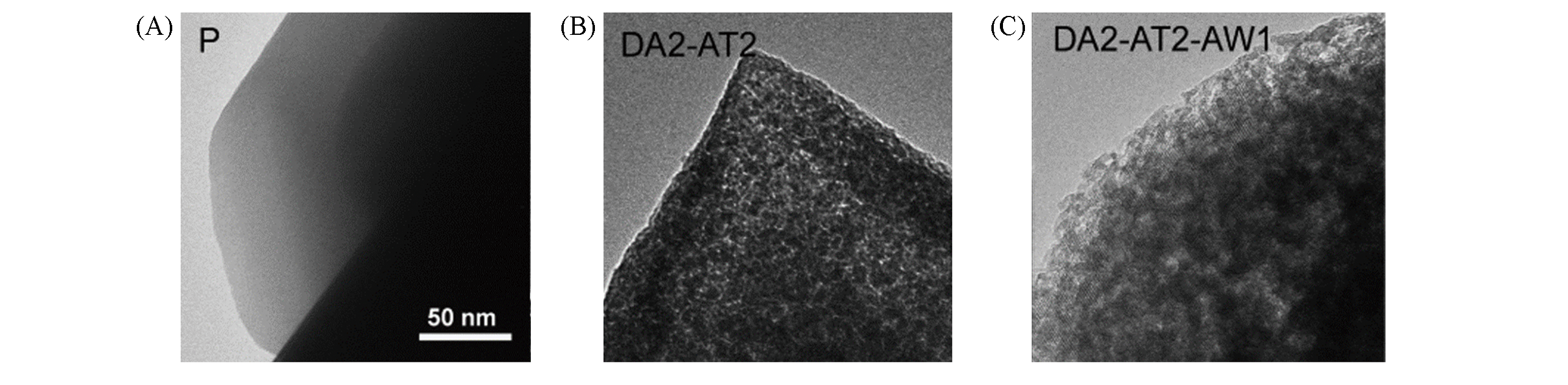
Fig.7 Sequential dealumination and desilication of NH4?Y zeolite[37](A) Parent Y; (B) DA2?AT2: dealuminated(0.11 mol/L EDTA) and desilicated Y(0.2mol/L NaOH); (C) DA2?AT2?AW1: dealuminated, desilicated and acid?washed Y.Copyright 2011, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
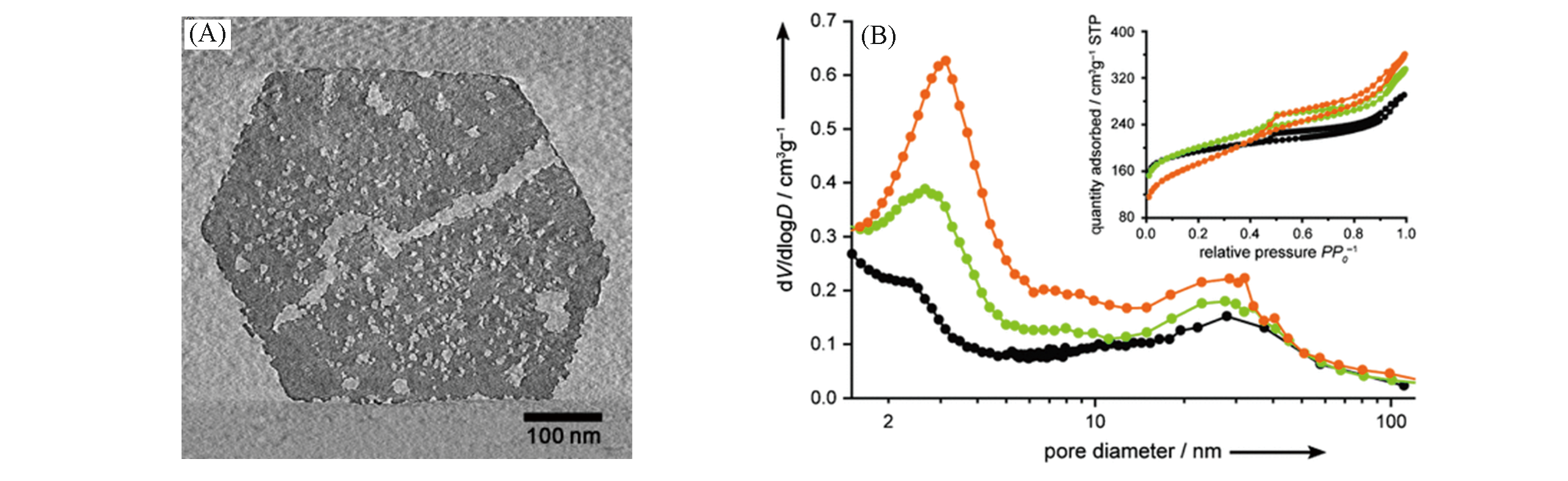
Fig.8 TEM image of desilicated USY(SAR=30) by diluted NaOH solution(0.05 mol/L, 15 min)(A) and the resulting trimodal porosity of the treated zeolite(B)[47]Copyright 2010, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
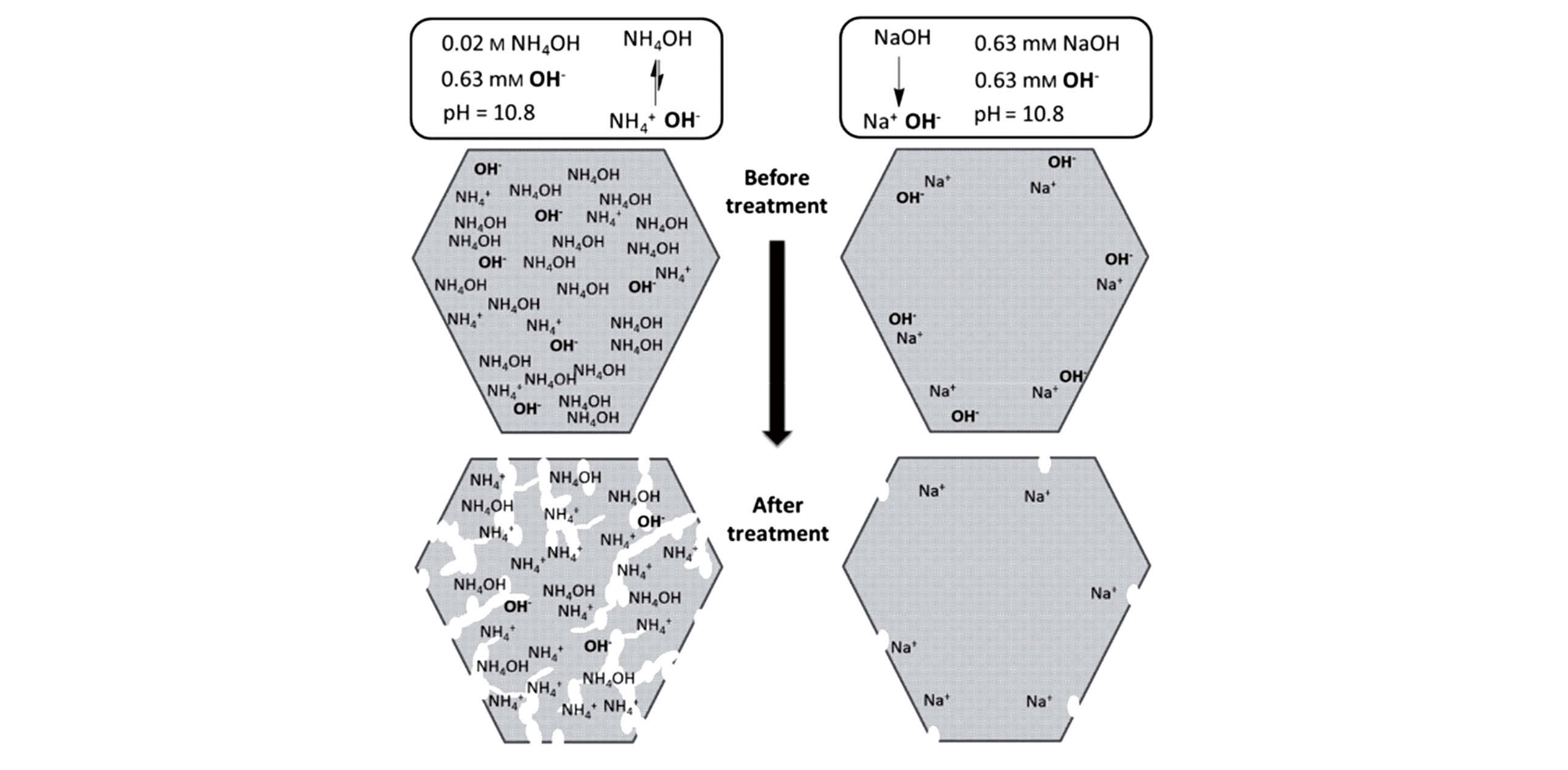
Fig.9 Comparative desilication of USY(SAR=40) by NH4OH and NaOH solutions with the same molar amount of OH-[42]Copyright 2015, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
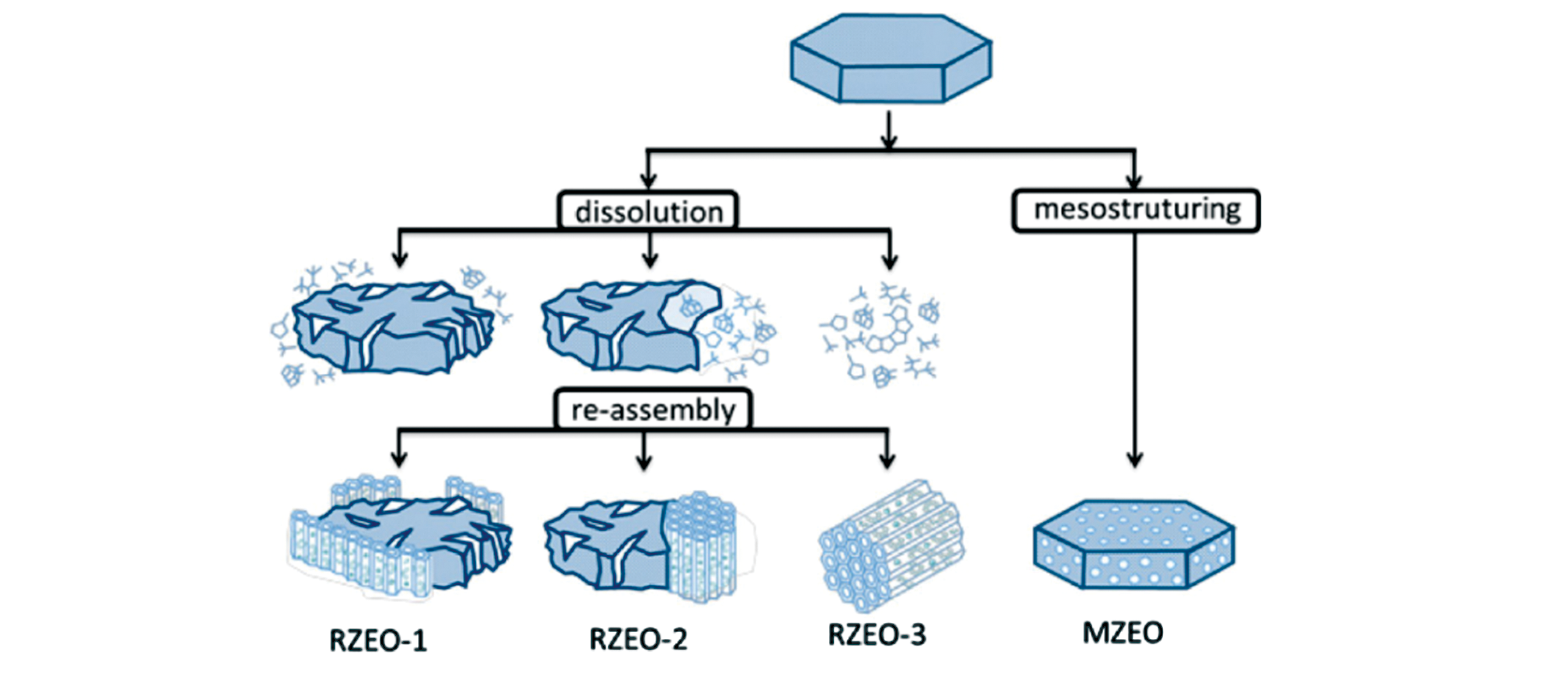
Fig.10 Recrystallisation?induced mesoporous materials RZEO(micro?meso?porous composites) and MZEO(one?phase hybrid single zeolite crystals)[20]Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
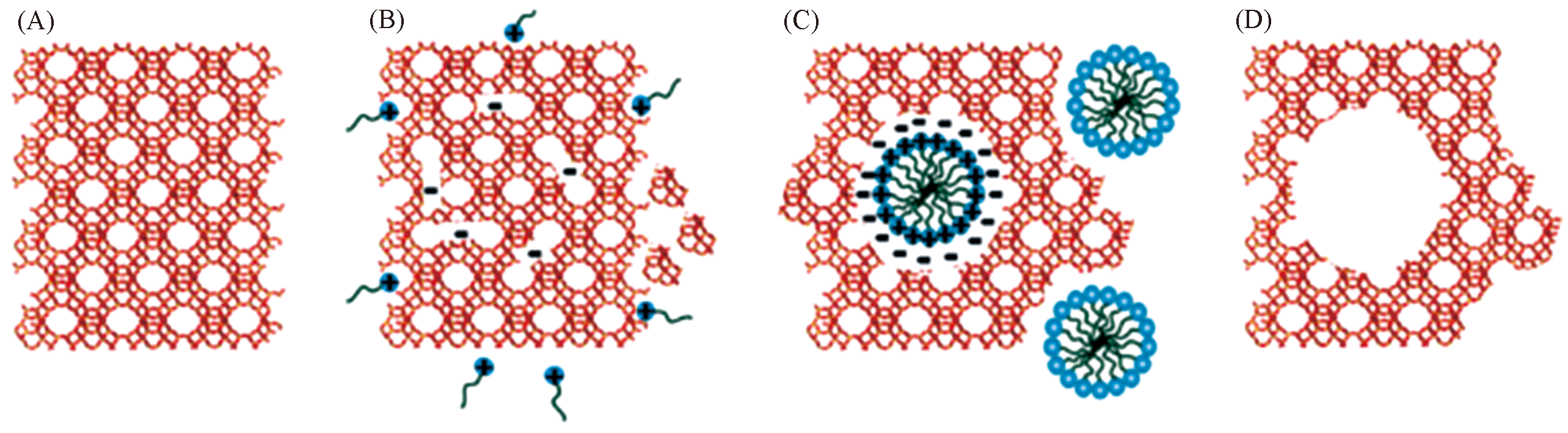
Fig.11 Mesostructuring of USY zeolite by surfactant?templated recrystallisation[46](A) Parent USY zeolites; (B) insertion of surfactants into zeolite framework; (C) rearrangement of crystal structure in USY; (D) template removal by calcination to render mesopores.Copyright 2012, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
| Topology | SAR | Treatment | Vmicro/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmeso/ (cm3·g-1) | Sext./ (m2·g-1) | Dmeso/nm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM?5 | 14 | ―* | 0.12 | 0.14 | 124 | ― | [ |
| 10―11 | Steaming+desilication | 0.1 | 0.32 | 209 | 5 | ||
| ZSM?5 | 15 | ― | 0.14 | 0.15 | 76 | ― | [ |
| ― | Desilication+acid wash(HCl) | 0.15 | 0.4 | 158 | 3 and 35 | ||
| ZSM?5 | 25 | ― | 0.16 | 0.10 | 35 | 7―10 | [ |
| 18 | Desilication | 0.13 | 0.31 | 195 | |||
| ZSM?5 | 40 | ― | 0.16 | 0.14 | 45 | ||
| 29 | Desilication | 0.13 | 0.61 | 225 | |||
| ZSM?5 | 40 | ― | 0.17 | 0.11 | 78 | ― | [ |
| 32 | Desilication(TPA) | 0.12 | 0.36 | 272 | 5 | ||
| Topology | SAR | Treatment | Vmicro/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmeso/ (cm3·g-1) | Sext./ (m2·g-1) | Dmeso/nm | Ref. |
| ZSM?5 | +∞ | 0.16 | 0.25 | 9 | [ | ||
| ― | Desilication(TPA) | 0.1 | 0.42 | 287 | ― | ||
| Y | 2. 6 | ― | 0.3 | 0.04 | 22 | ― | [ |
| < 6 | Dealumination(EDTA)+desilication | 0.2 | 0.46 | 330 | 8 | ||
| Y | 2. 55 | ― | 0.38 | 0.03 | 22 | ― | [ |
| ― | Acid wash+recrystallization(CTAB) | 0.37 | 0.16 | 243 | ― | ||
| USY | 15 | ― | 0.3 | 0.16 | 168 | ― | [ |
| ― | Recrystallization(CTAB) | 0.21 | 0.5 | 704 | 4 | ||
| USY | 15 | ― | 0.28 | 0.23 | 125 | ― | [ |
| ca. 11 | Desilication(TPA) | 0.29 | 0.42 | 253 | 5 | ||
| USY | 30 | ― | 0.33 | 0.28 | 117 | ― | [ |
| ca. 19 | Desilication(TPA) | 0.26 | 0.84 | 500 | 8 | ||
| USY | 30 | ― | 0.21 | 0.16 | 213 | 28 | [ |
| ca. 25 | Mild desilication(NaOH) | 0.16 | 0.25 | 339 | 2.7 and 27 | ||
| USY | 40 | ― | 0.27 | 0.27 | 181 | 6―30 | [ |
| ca. 40 | Mild desilication(NH4OH) | 0.16 | 0.4 | 311 | 2―6 and 6―30 |
Table 2 Porous properties of hierarchical zeolites made by different post-synthetic treatments
| Topology | SAR | Treatment | Vmicro/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmeso/ (cm3·g-1) | Sext./ (m2·g-1) | Dmeso/nm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM?5 | 14 | ―* | 0.12 | 0.14 | 124 | ― | [ |
| 10―11 | Steaming+desilication | 0.1 | 0.32 | 209 | 5 | ||
| ZSM?5 | 15 | ― | 0.14 | 0.15 | 76 | ― | [ |
| ― | Desilication+acid wash(HCl) | 0.15 | 0.4 | 158 | 3 and 35 | ||
| ZSM?5 | 25 | ― | 0.16 | 0.10 | 35 | 7―10 | [ |
| 18 | Desilication | 0.13 | 0.31 | 195 | |||
| ZSM?5 | 40 | ― | 0.16 | 0.14 | 45 | ||
| 29 | Desilication | 0.13 | 0.61 | 225 | |||
| ZSM?5 | 40 | ― | 0.17 | 0.11 | 78 | ― | [ |
| 32 | Desilication(TPA) | 0.12 | 0.36 | 272 | 5 | ||
| Topology | SAR | Treatment | Vmicro/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmeso/ (cm3·g-1) | Sext./ (m2·g-1) | Dmeso/nm | Ref. |
| ZSM?5 | +∞ | 0.16 | 0.25 | 9 | [ | ||
| ― | Desilication(TPA) | 0.1 | 0.42 | 287 | ― | ||
| Y | 2. 6 | ― | 0.3 | 0.04 | 22 | ― | [ |
| < 6 | Dealumination(EDTA)+desilication | 0.2 | 0.46 | 330 | 8 | ||
| Y | 2. 55 | ― | 0.38 | 0.03 | 22 | ― | [ |
| ― | Acid wash+recrystallization(CTAB) | 0.37 | 0.16 | 243 | ― | ||
| USY | 15 | ― | 0.3 | 0.16 | 168 | ― | [ |
| ― | Recrystallization(CTAB) | 0.21 | 0.5 | 704 | 4 | ||
| USY | 15 | ― | 0.28 | 0.23 | 125 | ― | [ |
| ca. 11 | Desilication(TPA) | 0.29 | 0.42 | 253 | 5 | ||
| USY | 30 | ― | 0.33 | 0.28 | 117 | ― | [ |
| ca. 19 | Desilication(TPA) | 0.26 | 0.84 | 500 | 8 | ||
| USY | 30 | ― | 0.21 | 0.16 | 213 | 28 | [ |
| ca. 25 | Mild desilication(NaOH) | 0.16 | 0.25 | 339 | 2.7 and 27 | ||
| USY | 40 | ― | 0.27 | 0.27 | 181 | 6―30 | [ |
| ca. 40 | Mild desilication(NH4OH) | 0.16 | 0.4 | 311 | 2―6 and 6―30 |
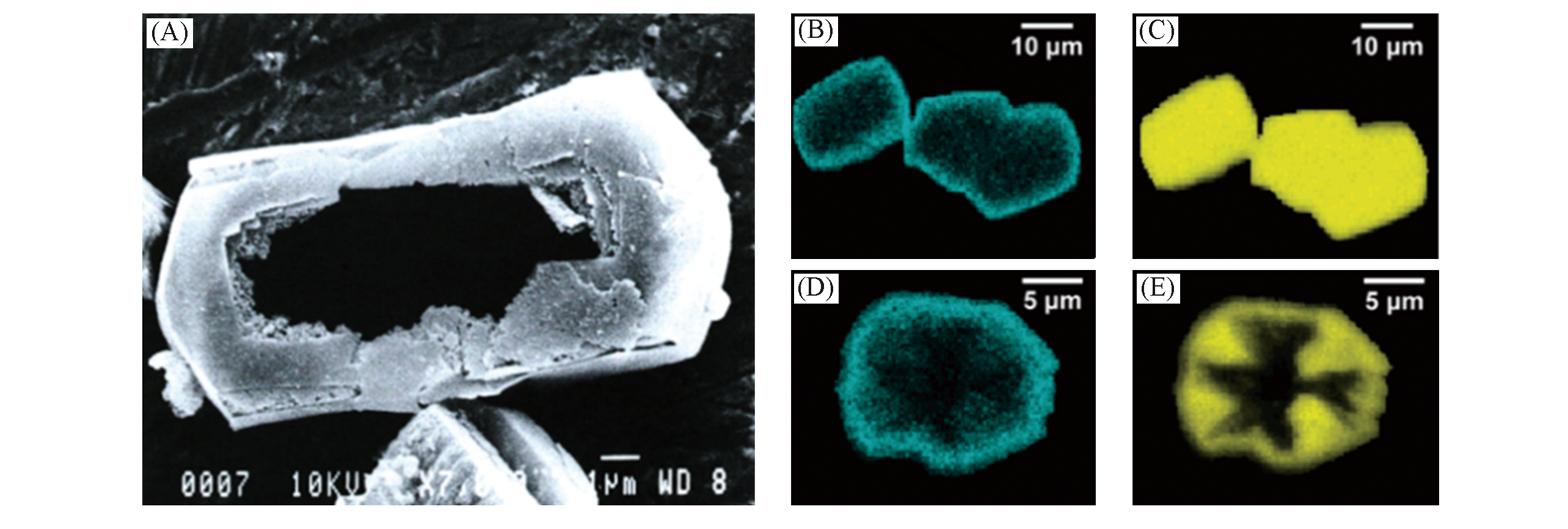
Fig.12 Al?zoned ZSM?5 to form hollow structures after desilication[59](A) SEM graphs of hollow ZSM?5 after alkaline treatment, Si/Al=75, under reflux in 0.5 mol/L Na2CO3 for 16 h; (B, D) SEM?EDX mappings of aluminium in large ZSM?5 crystal before(B) and after(D) alkaline treatment; (C, E) SEM?EDX mappings of silicon in large ZSM?5 crystal before(C) and after(E) alkaline treatment.Copyright 2006, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
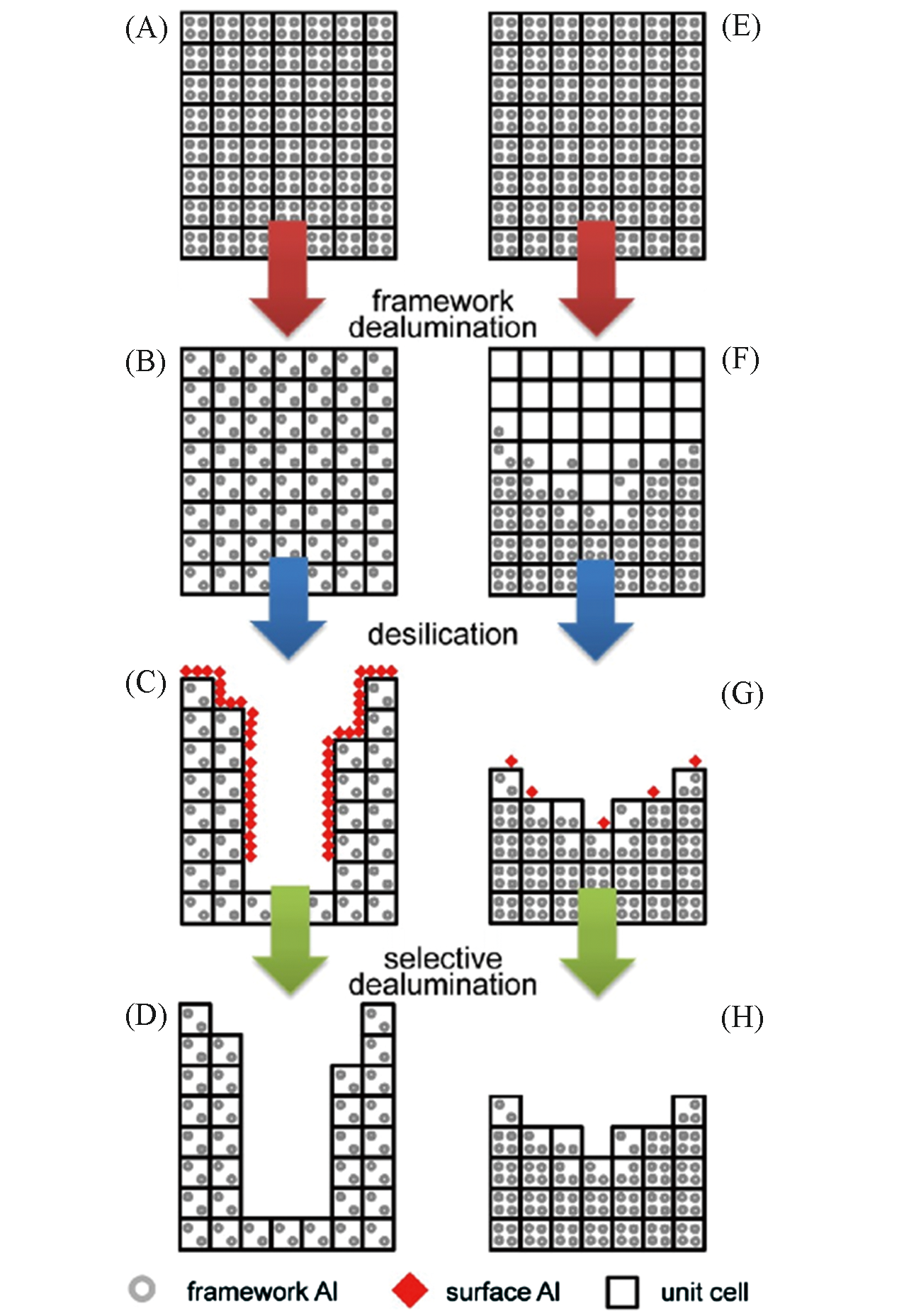
Fig.13 Schematic representation of two different sequential acid?base?acid treatments[105](A, E) parent zeolite; (B) uniform dealumination; (C) uniform dealumination promotes the effective desilication; (D, H) removal of the surface alumina debris by acid washing; (F) uneven dealumination creates Al?zoning; (G) uneven dealumination hinders the subsequent desilication.Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
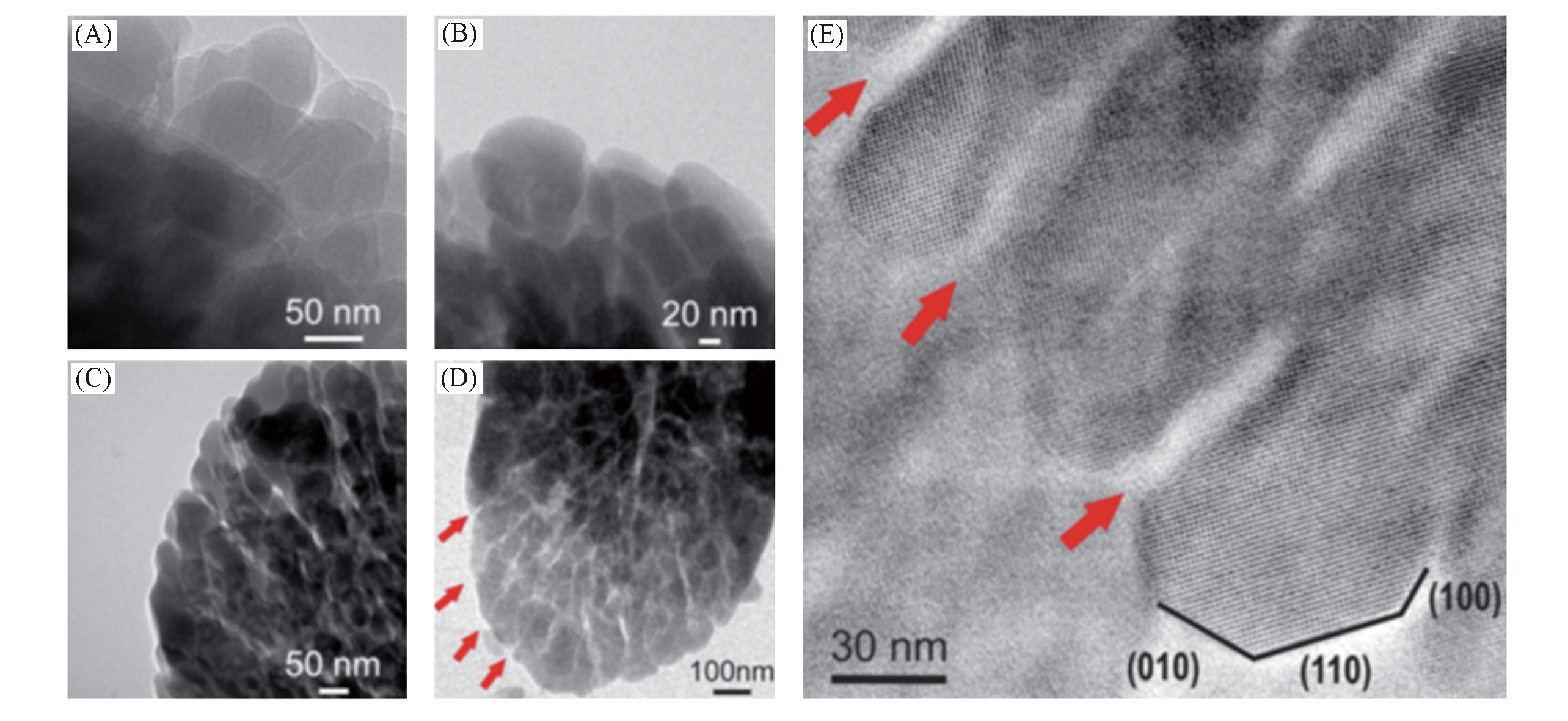
Fig.14 TEM images of MOR zeolite before and after acid and/or chemical treatment[107](A) Parent MOR; (B) MOR treated with oxalic acid; (C) MOR treated with NH4F; (D) MOR treated with oxalic acid and NH4F; (E) larger magnification of (D).Copyright 2020, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
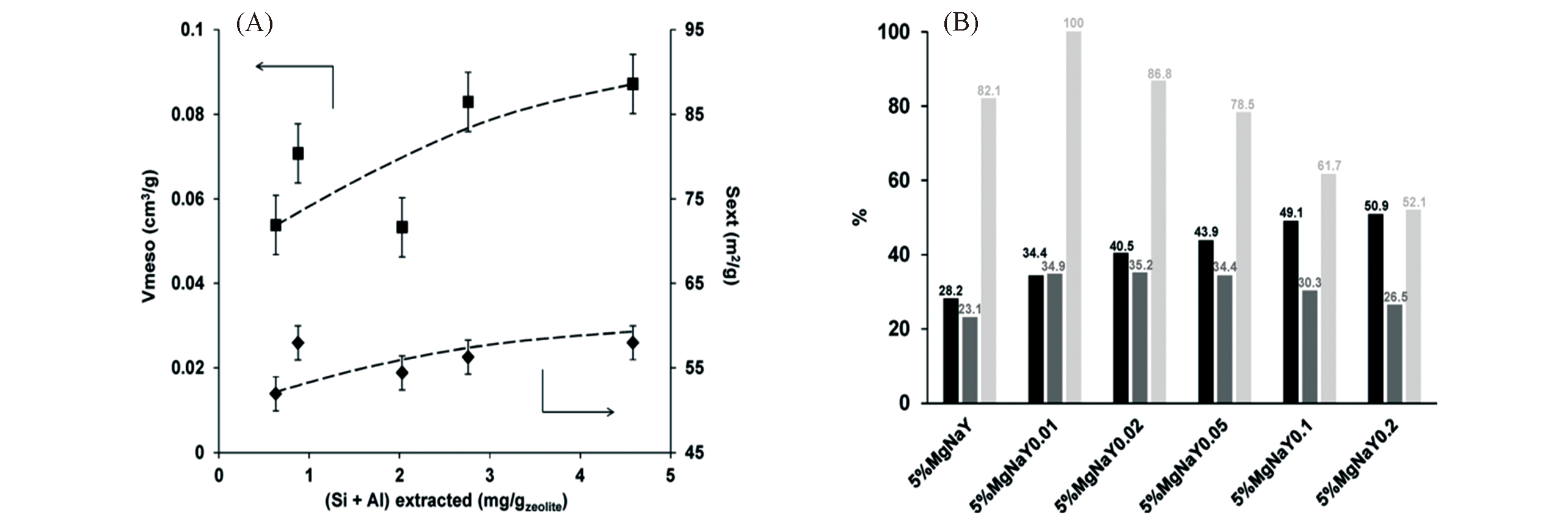
Fig.16 Comparison of mesoporous features(regarding Vmeso and Sext.) of the Na?Y parent zeolite and desilicated Y zeolites(A) and glucose conversion(black), fructose yield(grey) and selectivity to fructose(light grey) from the comparative catalysis over the parent and hierarchical Mg/Na?Y zeolites at 100 °C after 2 h(B)[111]Copyright 2018, Elsevier B. V.
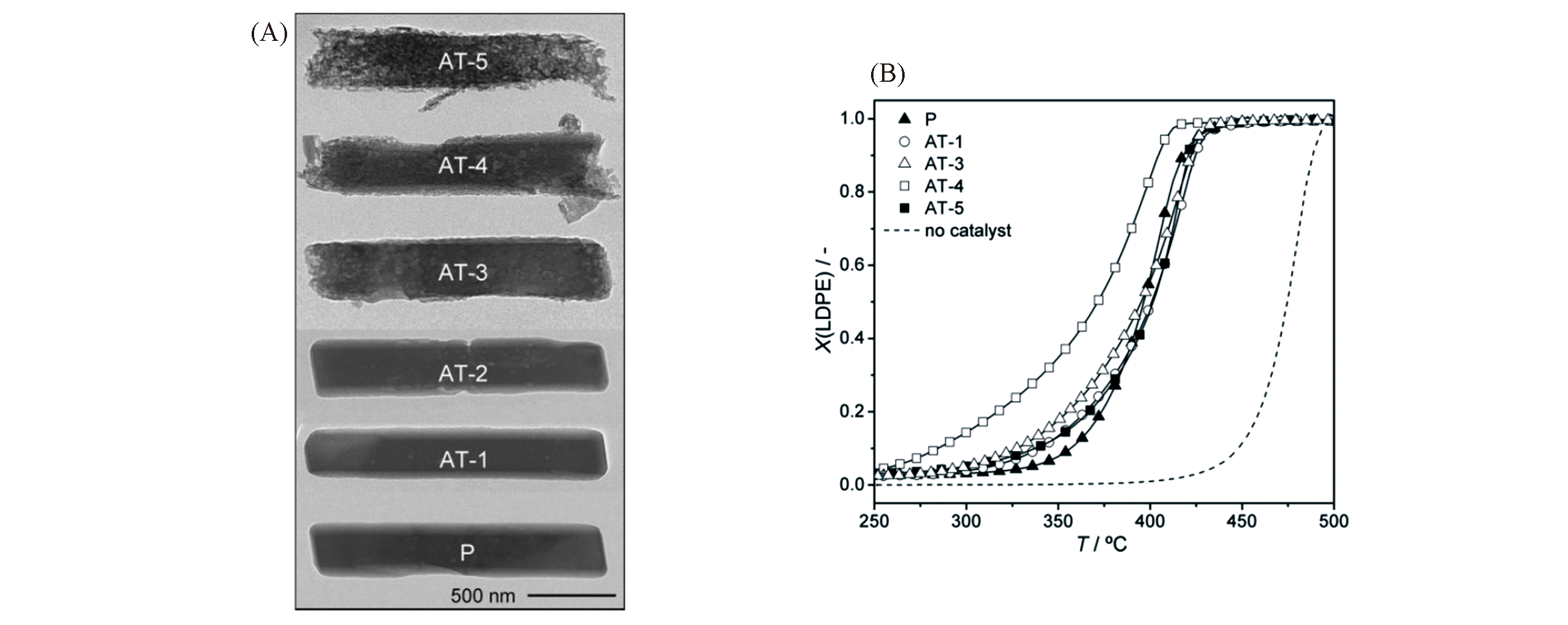
Fig.17 TEM images of the parent(P) and alkaline?treated(AT) ITQ?4 zeolites(A) and conversion(X) of LDPE as a function of reaction temperature in catalytic pyrolysis over the ITQ?4 zeolites(B)[112]Copyright 2010, Wiley?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
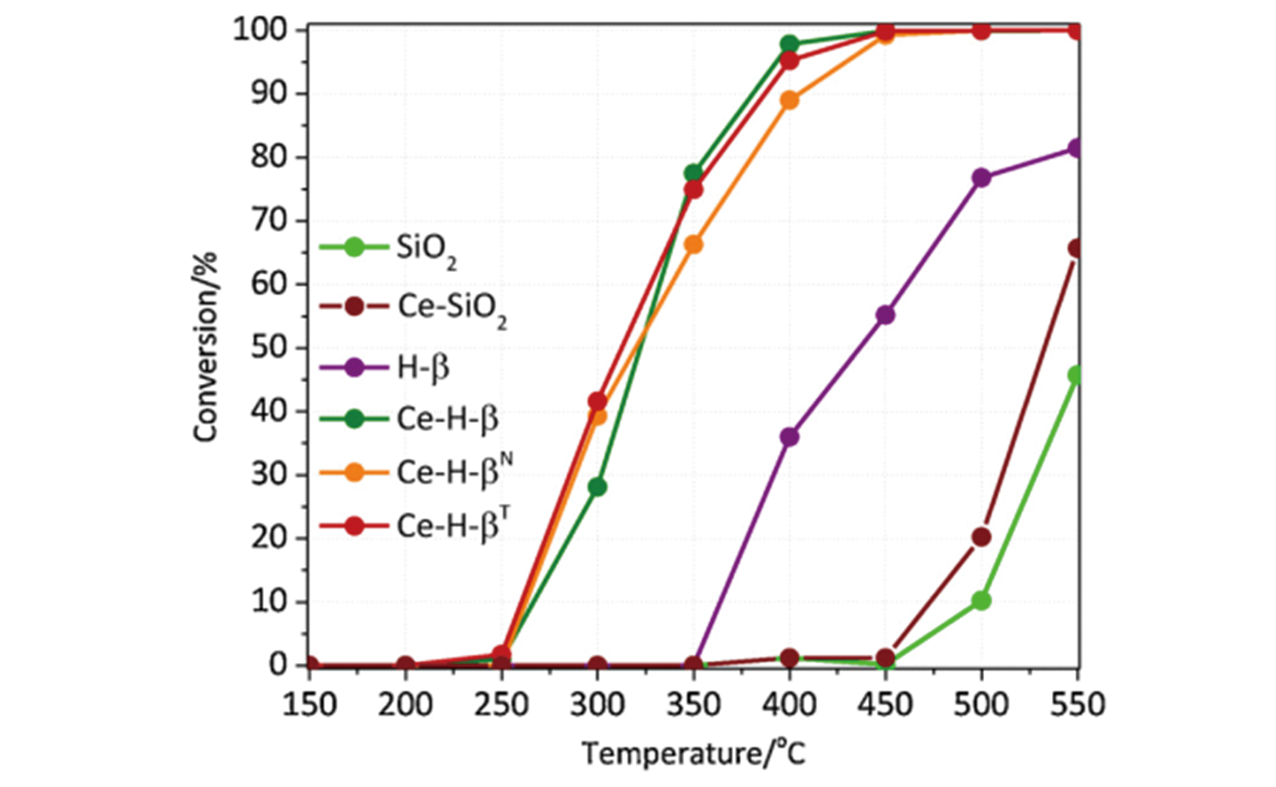
Fig.18 Trichloroethylene conversion as a function of temperature over the Ce supported on silica and beta zeolite catalysts[113]Copyright 2019, Elsevier B. V.
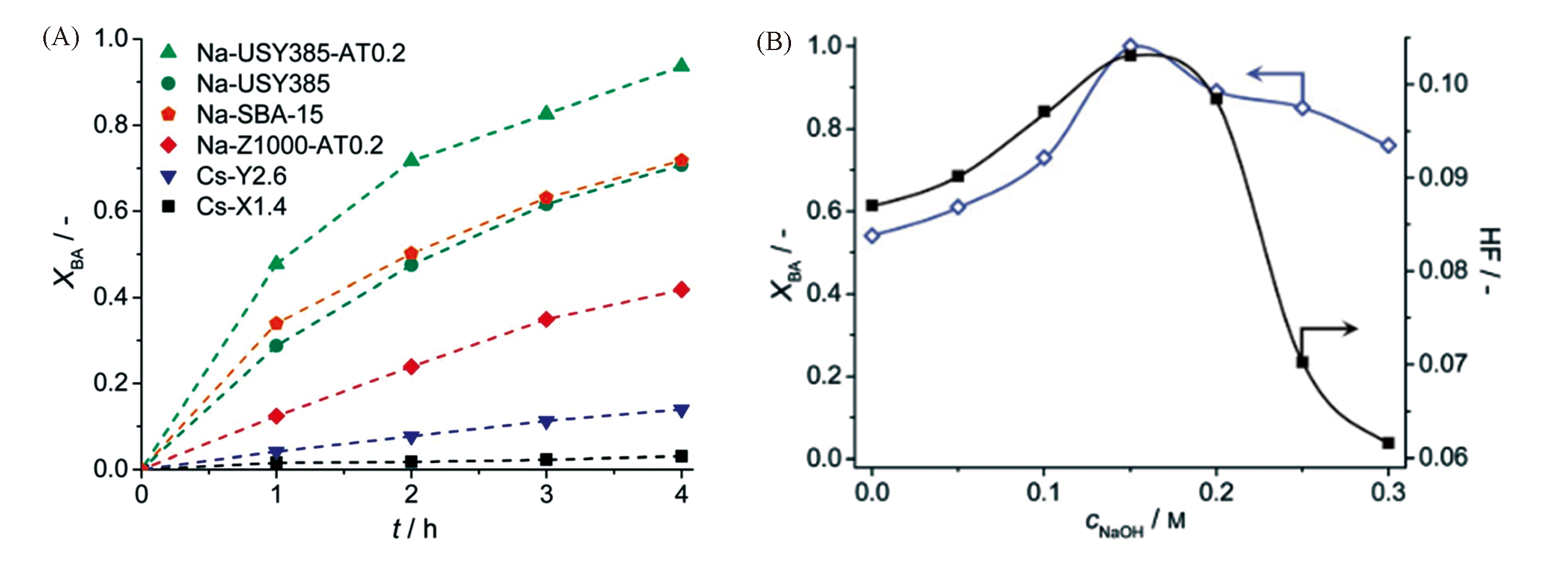
Fig.19 Benzaldehyde conversion(XBA) in the Knoevenagel condensation over different catalysts as a function of reaction time(A) and effect of NaOH concentration in desilication on XBA and hierarchy factor(HF) for desilicated USY385 zeolites(B)[114]Copyright 2014, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
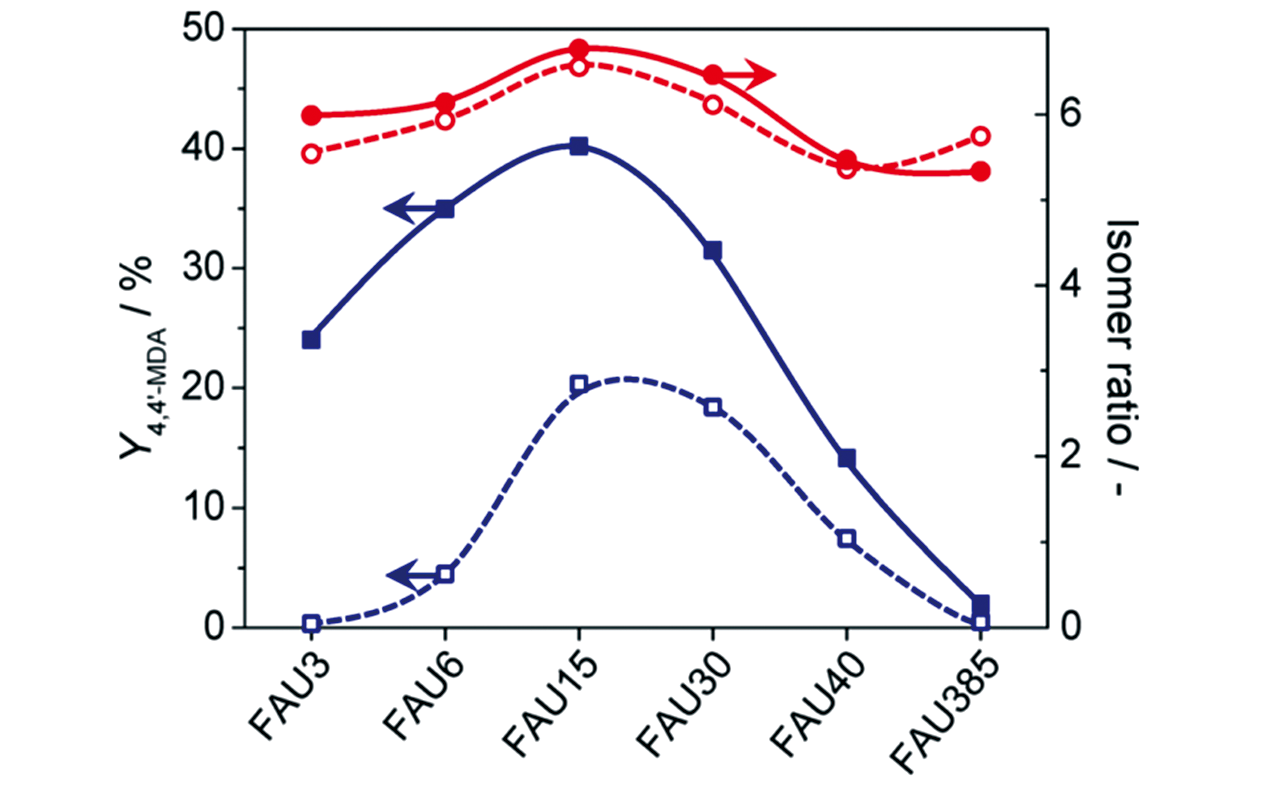
Fig.20 Yield of 4,4′?MDA(blue squares) and isomer ratio(red circles) over the parent(open symbols) and relevant hierarchical(full symbols) FAU zeolites[100]Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society.
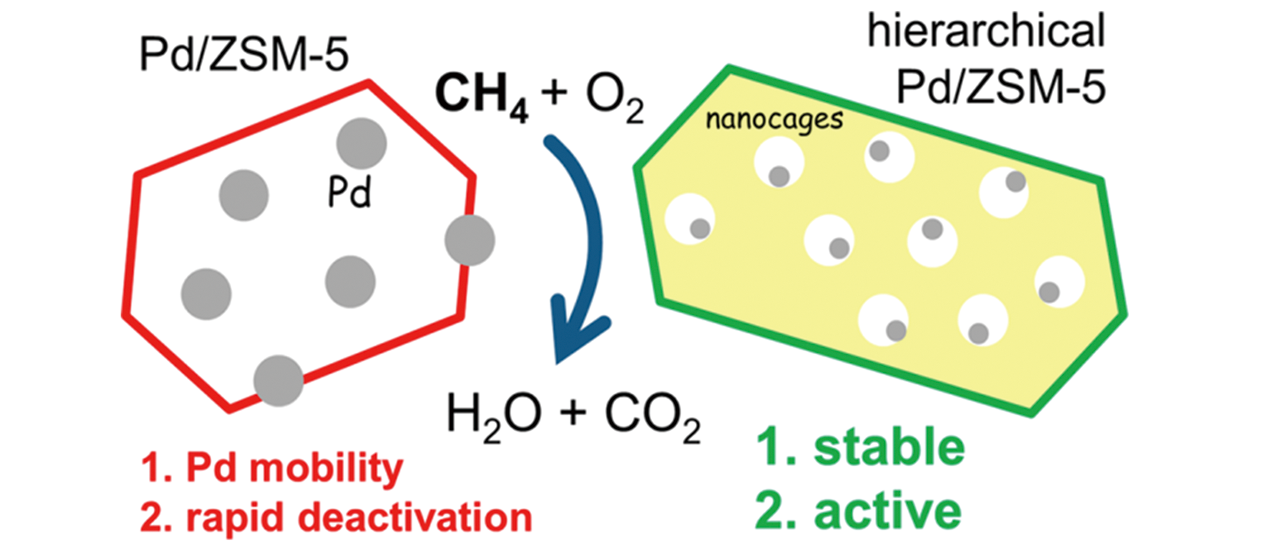
Fig.21 Schematic illustration of improving the stability of Pd nanoparticles supported on hierarchical ZSM?5 zeolites[49]Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
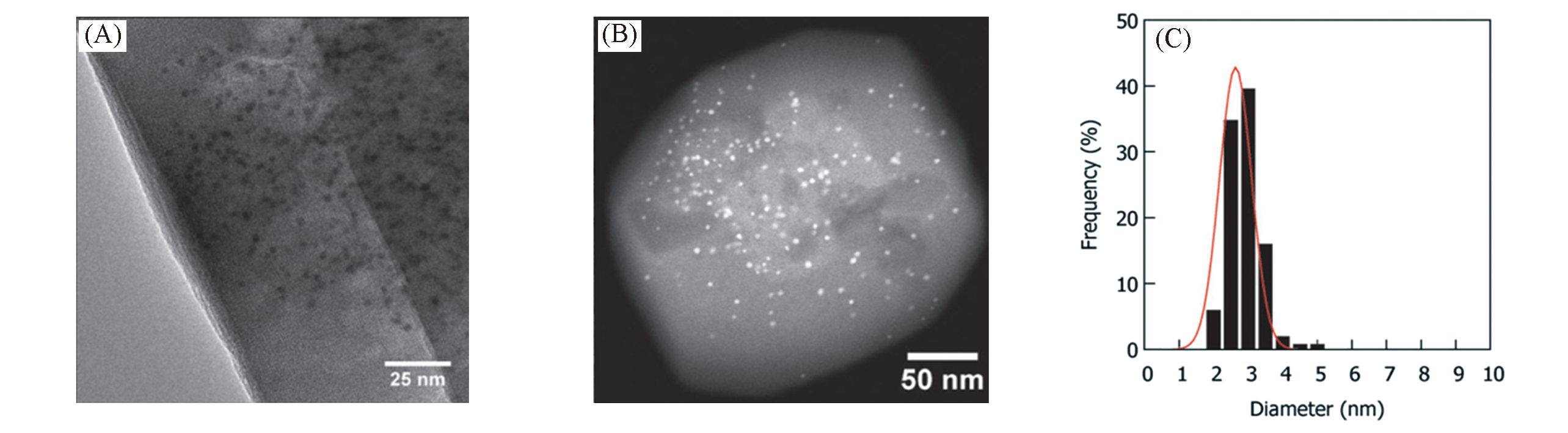
Fig.22 TEM(A) and STEM(B) images of Au/Recryst?S1 and size distribution of Au nanoparticles based on measurements of approximately 250 nanoparticles by TEM(C)[116]Copyright 2014, WILEY?VCH Verlay GmbH&Co. kGaA, Weinheim.
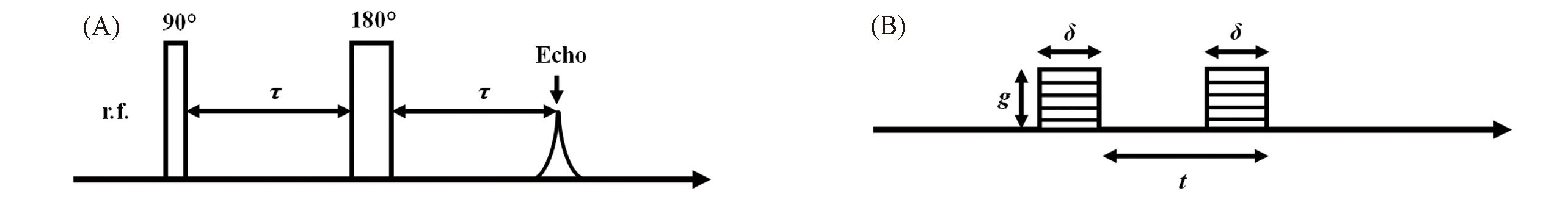
Fig.23 RF pulses for generating Hahn echo (A) and the field gradient pulses applied for self?diffusion measurement(B)(A) Thin and thick bars represent 90° and 180° RF pulses, respectively; (B) δ, pulse duration; g, magnitude of the gradient pulse; t, the time interval between the two gradient pulses.Ψ=S/S0=exp[-Dγ2g2δ2t] (1)
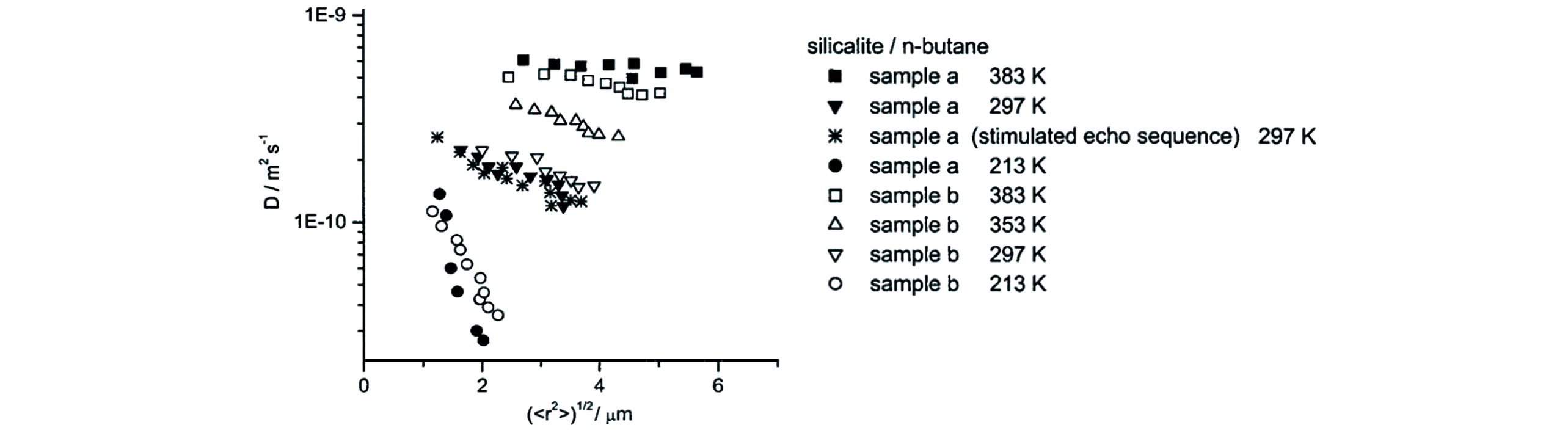
Fig.24 Diffusivity of n?butane in silicalite?1 as a function of RMSD measured at different temperatures by the PFG NMR[134]Copyright 2001, American Chemical Society.
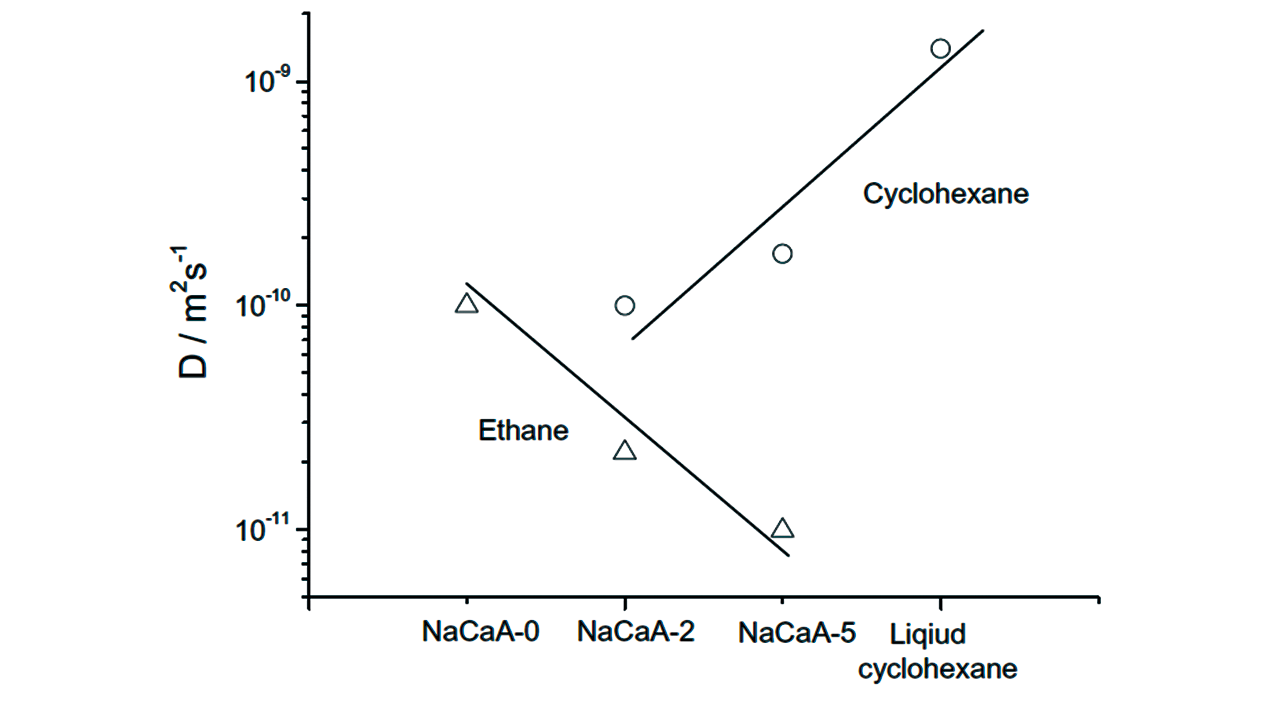
Fig.26 Comparison of the diffusivity in the space of micropores(probed with ethane) and mesopores(cyclohexane) of the LTA zeolites at room temperature[138]Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc.
| 1 | Weckhuysen B. M., Yu J. H, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(20), 7022—7024 |
| 2 | Coronas J., Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 156(2), 236—242 |
| 3 | Liang J., Liang Z., Zou R. Q., Zhao Y. L., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(30), 1701139 |
| 4 | Gueudré L., Quoineaud A. A., Pirngruber G., Leflaive P., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 10899—10908 |
| 5 | Frising T., Leflaive P., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2008, 114(1—3), 27—63 |
| 6 | Feliczak⁃Guzik A., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2018, 259, 33—45 |
| 7 | Holm M. S., Taarning E., Egeblad K., Christensen C. H., Catal. Today, 2011, 168(1), 3—16 |
| 8 | Moliner M., Martínez C., Corma A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(12), 3560—3579 |
| 9 | Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Christensen C. H., Egeblad K., Christensen C. H., Groen J. C., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37(11), 2530—2542 |
| 10 | Corma A., Díaz⁃Cabañas M. J., Jordá J. L., Martínez C., Moliner M., Nature, 2006, 443(7113), 842—845 |
| 11 | Mintova S., Gilson J. P., Valtchev V., Nanoscale, 2013, 5(15), 6693—6703 |
| 12 | Roth W. J., Nachtigall P., Morris R. E., Čejka J., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(9), 4807—4837 |
| 13 | Tang K., Wang Y. G., Song L. J., Duan L. H., Zhang X. T., Sun Z. L., Mater. Lett., 2006, 60(17/18), 2158—2160 |
| 14 | Schwieger W., Machoke A. G., Weissenberger T., Inayat A., Selvam T., Klumpp M., Inayat A., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(12), 3353—3376 |
| 15 | Zhao S. F., Wang W. D., Wang L. Z., Schwieger W., Wang W., Huang J., ACS Catal., 2019, 10(2), 1185—1194 |
| 16 | Zhang D. Z., Jin C. Z., Zou M. M., Huang S. J., Chemistry, 2019, 25(11), 2675—2683 |
| 17 | Issa H., Chaouati N., Toufaily J., Hamieh T., Sachse A., Pinard L., ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(18), 4581—4592 |
| 18 | Srivastava R., Catal. Today, 2018, 309, 172—188 |
| 19 | Masoumifard N., Guillet⁃Nicolas R., Kleitz F., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(16), 1704439 |
| 20 | Sachse A., García⁃Martínez J., Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(9), 3827—3853 |
| 21 | Zhang K., Ostraat M. L., Catal. Today, 2016, 264, 3—15 |
| 22 | Verboekend D., Nuttens N., Locus R., Aelst J. V., Verolme P., Groen J. C., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Sels B. F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(12), 3331—3352 |
| 23 | Wei Y., Parmentier T. E., de Jong K. P., Zečević J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(20), 7234—7261 |
| 24 | Javdani A., Ahmadpour J., Yaripour F., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2019, 284, 443—458 |
| 25 | Čejka J., Millini R., Opanasenko M., Serrano D. P., Roth W. J., Catal. Today, 2019, 345, 2—13 |
| 26 | Yang X. Y., Chen L. H., Li Y., Rooke J. C., Sanchez C., Su B. L., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(2), 481—558 |
| 27 | Gallego E. M., Paris C., Díaz⁃Rey M. R., Martínez⁃Armero M. E., Martínez⁃Triguero J., Martínez C., Moliner M., Corma A., Chem. Sci., 2017, 8(12), 8138—8149 |
| 28 | Sun M. H., Huang S. Z., Chen L. H., Li Y., Yang X. Y., Yuan Z. Y., Su B. L., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(12), 3479—3563 |
| 29 | Hartmann M., Machoke A. G., Schwieger W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(12), 3313—3330 |
| 30 | Verboekend D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(3), 753—764 |
| 31 | Verboekend D., Mitchell S., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Chimia, 2013, 67(5), 327—332 |
| 32 | Chal R., Gérardin C., Bulut M., Donk S. V., ChemCatChem, 2011, 3(1), 67—81 |
| 33 | Choi M., Cho H. S., Srivastava R., Venkatesan C., Choi D. H., Ryoo R., Nat. Mater., 2006, 5(9), 718—723 |
| 34 | Zhang R. X., Zhong P. N., Arandiyan H., Guan Y. N., Liu J. N., Wang N., Jiao Y. L., Fan X. L., Front. Chem. Sci. Eng., 2020, 14(2), 275—287 |
| 35 | Zhang R. X., Xu S. J, Raja D., Khusni N. B., Liu J. M., Zhang J. Y., Abdulridha S., Xiang H., Jiang S. S., Guan Y. N., Jiao Y. L., Fan X. L., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2019, 278, 297—306 |
| 36 | Verboekend D., Keller T. C., Mitchell S., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(15), 1923—1934 |
| 37 | Verboekend D., Vilé G., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22(5), 916—928 |
| 38 | Datka J., Kolidziejski W., Klinowski J., Sulikowski B., Catal. Lett., 1993, 19, 159—165 |
| 39 | Lee S., Kim H., Choi M., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(39), 12096—12102 |
| 40 | Peng C., Liu Z. D., Yonezawa Y., Linares N., Yanaba Y., Trujillo C. A., Okubo T., Matsumoto T., García⁃Martínez J., Wakihara T., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(2), 735—742 |
| 41 | Mehlhorn D., Rodriguez J., Cacciaguerra T., Andrei R. D., Cammarano C., Guenneau F., Gedeon A., Coasne B., Thommes M., Minoux D., Aquino C., Dath J. P., Fajula F., Galarneau A., Langmuir, 2018, 34(38), 11414—11423 |
| 42 | Aelst J. V., Verboekend D., Philippaerts A., Nuttens N., Kurttepeli M., Gobechiya E., Haouas M., Sree S. P., Denayer J. F. M., Martens J. A., Kirschhock C. E. A., Taulelle F., Bals S., Baron G. V., Jacobs P. A., Sels B. F., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(46), 7130—7144 |
| 43 | Nuttens N., Verboekend D., Deneyer A., Aelst J. V., Sels B. F., ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(7), 1197—1205 |
| 44 | Aelst J. V., Haouas M., Gobechiya E., Houthoofd K., Philippaerts A., Sree S. P., Kirschhock C. E. A., Jacobs P., Martens J. A., Sels B. F., Taulelle F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(39), 22573—22582 |
| 45 | García⁃Martínez J., Li K. H., Krishnaiah G., Chem. Commun., 2012, 48(97), 11841—11843 |
| 46 | García⁃Martínez J., Johnson M., Valla J., Li K. H., Ying J. Y., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, 2(5), 987—994 |
| 47 | de Jong K. P., Zečević J., Friedrich H., de Jongh P. E., Bulut M., Donk S. V., Kenmogne R., Finiels A., Hulea V., Fajula F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49(52), 10074—10078 |
| 48 | Silva B. J. B., Sousa L. V., Sarmento L. R. A., Alencar S. L., Quintela P. H. L., Silva A. O. S., Appl. Catal. B, 2020, 267, 118699 |
| 49 | Petrov A. W., Ferri D., Kröcher O., van Bokhoven J. A., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(3), 2303—2312 |
| 50 | Li T., Ihli J., Wennmacher J. T. C., Krumeich F., van Bokhoven J. A., Chemistry, 2019, 25(32), 7689—7694 |
| 51 | Yang S. T., Yu C. X., Yu L. L., Miao S., Zou M. M., Jin C. Z., Zhang D. Z., Xu L. Y., Huang S. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(41), 12553—12556 |
| 52 | Yu L. L., Huang S. J., Miao S., Chen F. C., Zhang S., Liu Z. N., Xie S. J., Xu L. Y., Chemistry, 2015, 21(3), 1048—1054 |
| 53 | You S. J., Park E. D., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2014, 186, 121—129 |
| 54 | Ahn J. H., Kolvenbach R., Neudeck C., Al⁃Khattaf S. S., Jentys A., Lercher J. A., J. Catal., 2014, 311, 271—280 |
| 55 | Sazama P., Sobalik Z., Dedecek J., Jakubec I., Parvulescu V., Bastl Z., Rathousky J., Jirglova H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(7), 2038—2041 |
| 56 | Dapsens P. Y., Mondelli C., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(5), 831—839 |
| 57 | Verboekend D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Chemistry, 2011, 17(4), 1137—1147 |
| 58 | Verboekend D., Mitchell S., Milina M., Groen J. C., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(29), 14193—14203 |
| 59 | Groen J. C., Moulijn J. A., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Mater. Chem., 2006, 16(22), 2121—2131 |
| 60 | Groen J. C., Bruckner A., Berrier E., Maldonado L., Moulijn J., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Catal., 2006, 243(1), 212—216 |
| 61 | Groen J. C., Zhu W. D., Brouwer S., Huynink S. J., Kapteijn F., Moulijn J. A., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 355—360 |
| 62 | Tao Y. S., Hattori Y., Matumoto A, Kanoh H., Kaneko K., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 194—199 |
| 63 | Schmidt I., Boisen A., Gustavsson E., Ståhl K., Pehrson S., Dahl S., Carlsson A., Jacobsen C. J. H., Chem. Mater., 2001, 13, 4416—4418 |
| 64 | Fan W., Snyder M. A., Kumar S., Lee P. S., Yoo W. C., McCormick A. V., Penn R. L., Stein A., Tsapatsis M., Nat. Mater., 2008, 7(12), 984—991 |
| 65 | Sun M. H., Chen L. H., Yu S., Li Y., Zhou X. G., Hu Z. Y., Sun Y. H., Xu Y., Su B. L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 2—12 |
| 66 | Zhu H. B., Liu Z. C., Wang Y. D., Kong D. J., Yuan X. H., Xie Z. K., Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 1134—1139 |
| 67 | Rhodes K. H., Davis H. A., Caruso F., Zhang B. J., Mann S., Chem. Mater., 2000, 12, 2832—2834 |
| 68 | Yue M. B., Sun M. N., Xie F., Ren D. D., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2014, 183, 177—184 |
| 69 | Abdulridha S., Jiang J. X., Xu S. J., Zhou Z. X., Liang H., Mao B. Y., Zhou Y. T., Garforth A. A., Jiao Y. L., Fan X. L., Green Chem., 2020, 22, 5115—5122 |
| 70 | Zhang B., Li X. R., Wu Q. F., Zhang C., Yu Y. C., Lan M. L., Wei X., Ying Z., Liu T., Liang G. F., Zhao F. Y., Green Chem., 2016, 18(11), 3315—3323 |
| 71 | Dong A. G., Wang Y., Tang Y., Ren N., Zhang Y. H., Yue Y. H., Gao Z., Adv. Mater., 2002, 14, 926—929 |
| 72 | Xiao F. S., Wang L. F., Yin C. Y., Lin K. F., Di Y., Li J. X., Xu R. R., Su D. S., Schlögl R., Yokoi T., Tatsumi T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45(19), 3090—3093 |
| 73 | Serrano D. P., Aguado J., Escola J. M., Rodriguez J. M., Peral A., J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18(35), 4210—4218 |
| 74 | Aguado J., Serrano D. P., Rodríguez J. M., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2008, 115(3), 504—513 |
| 75 | Serrano D. P., Aguado J., Escola J. M., Rodríguez J. M., Peral A., Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 2462—2464 |
| 76 | Yang G. Y., Han J., Qiu Z. Y., Chen X. X., Feng Z. C., Yu J. H., Inorg. Chem. Front., 2020, 7(10), 1975—1980 |
| 77 | Zhang Q., Mayoral A., Terasaki O., Zhang Q., Ma B., Zhao C., Yang G. J., Yu J. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(9), 3772—3776 |
| 78 | Zhang J., Chen Z. W., Wang Y. D., Zheng G. C., Zheng H. R., Cai F. Y., Hong M., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2017, 252, 79—89 |
| 79 | Zhang J., Bai S., Chen Z. W., Wang Y. D., Dong L., Zheng H. R., Cai F. Y., Hong M., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(39), 20757—20764 |
| 80 | Feng R., Wang X. X., Lin J. W., Li Z., Hou K., Yan X. L., Hu X. Y., Yan Z. F., Rood M. J., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2018, 270, 57—66 |
| 81 | Zhang M. R., Liu X. M., Yan Z. F., Mater. Lett., 2016, 164, 543—546 |
| 82 | Choi M., Na K., Kim J., Sakamoto Y., Terasaki O., Ryoo R., Nature, 2009, 461(7261), 246—249 |
| 83 | Park D. H., Kim S. S., Wang H., Pinnavaia T. J., Papapetrou M. C., Lappas A. A., Triantafyllidis K. S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(41), 7645—7648 |
| 84 | Wang H., Pinnavaia T. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45(45), 7603—7606 |
| 85 | Lucas A. D., Canizares P., Durán A., Carrero A., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 1997, 154, 221—240 |
| 86 | Williams B. A., Babitz S. M., Miller J. T., Snurr R. Q., Kung H. H., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 1999, 177, 161—175 |
| 87 | Janssen A. H., Koster A. J., de Jong K. P., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 106, 11905—11909 |
| 88 | Janssen A. H., Koster A. J., de Jong K. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2001, 40, 1102—1104 |
| 89 | Kortunov P., Vasenkov S., Kärger J., Valiullin R., Gottschalk P., Fé Elía M., Perez M., Stöcker M., Drescher B., McElhiney G., Berger C., Gläser R., Weitkamp J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 13055—13059 |
| 90 | Triantafillidis C. S., Vlessidis A. G., Nalbandian L., Evmiridis N. P., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2001, 47, 369—388 |
| 91 | Inagaki S., Shinoda S., Kaneko Y., Takechi K., Komatsu R., Tsuboi Y., Yamazaki H., Kondo J. N., Kubota Y., ACS Catal., 2012, 3(1), 74—78 |
| 92 | Kerr G. T., J. Phys. Chem. C, 1968, 72, 2594—2596 |
| 93 | Akira Y., Hiromi N., Kazuhito O., Tatsuro T., Hiroshi T., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 1982, 55, 581—586 |
| 94 | Ogura M., Shin⁃ya S., Tateno J., Nara Y., Eiichi K., Masahiko M., Chem. Lett., 2000, 29, 882—883 |
| 95 | Groen J. C., Jansen J. C., Moulijn J. A., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 13062—13065 |
| 96 | Groen J. C., Peffer L. A., Moulijn J. A., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Chemistry, 2005, 11(17), 4983—4994 |
| 97 | Verboekend D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2011, 1(6), 879—890 |
| 98 | Milina M., Mitchell S., Crivelli P., Cooke D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 3922 |
| 99 | Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Verboekend D., Bonilla A., Abelló s., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2009, 19(24), 3972—3979 |
| 100 | Keller T. C., Arras J., Wershofen S., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., ACS Catal., 2014, 5(2), 734—743 |
| 101 | Ivanova I. I., Kasyanov I. A., Maerle A. A., Zaikovskii V. I., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2014, 189, 163—172 |
| 102 | Ivanova I. I, Knyazeva E. E., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42 (9), 3671—3688 |
| 103 | Dessau R. M., Valyocsik E. W., Goeke N. H., Zeolites, 1992, 12, 776—779 |
| 104 | Groen J. C., Bach T., Ziese U., Donk A. M. P., de Jong K. P., Moulijn J. A., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 10792—10793 |
| 105 | Verboekend D., Keller T. C., Milina M., Hauert R., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Chem. Mater., 2013, 25(9), 1947—1959 |
| 106 | Li S. H., Zheng A. M., Su Y. C., Zhang H. L., Chen L., Yang J., Ye C. H., Deng F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 11161—11171 |
| 107 | Qin Z. X., Hafiz L., Shen Y. F., Daele S. V., Boullay P., Ruaux V., Mintova S., Gilson J. P., Valtchev V., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(7), 3621—3631 |
| 108 | Qin Z. X, Shen B. J., Yu Z. W., Deng F., Zhao L., Zhou S. G., Yuan D. L., Gao X. H., Wang B. J., Zhao H. J., Liu H. H., J. Catal., 2013, 298, 102—111 |
| 109 | Svelle S., Sommer L., Barbera K., Vennestrøm P. N. R., Olsbye U., Lillerud K. P., Bordiga S., Pan Y. H., Beato P., Catal. Today, 2011, 168(1), 38—47 |
| 110 | Wu S. M., Yang X. Y., Janiak C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(36), 12340—12354 |
| 111 | Graça I., Bacariza M. C., Fernandes A., Chadwick D., Appl. Catal. B, 2018, 224, 660—670 |
| 112 | Verboekend D., Groen J. C., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20(9), 1441—1450 |
| 113 | Gołąbek K., Palomares A. E., Martínez⁃Triguero J., Tarach K. A., Kruczała K., Girman V., Góra⁃Marek K., Appl. Catal. B, 2019, 259, 118022 |
| 114 | Keller T. C., Isabettini S., Verboekend D., Rodrigues E. G., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Chem. Sci., 2014, 5(2), 677—684 |
| 115 | Losch P., Huang W. X., Vozniuk O., Goodman E. D., Schmidt W., Cargnello M., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(6), 4742—4753 |
| 116 | Mielby J., Abildstrom J. O., Wang F., Kasama T., Weidenthaler C., Kegnaes S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(46), 12513—12516 |
| 117 | Schneider D., Mehlhorn D., Zeigermann P., Kärger J., Valiullin R., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2016, 45, 3439—3467 |
| 118 | Randall Q. Snurr K., J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1997, 101, 6469—6473 |
| 119 | Hoang V. T., Huang Q., Malekian A., Eić M., Do T. O., Kaliaguine S., Adsorption, 2005, 11, 421—426 |
| 120 | Ruthven D. M., Brandani S., Recent Advances in Gas Separation by Microporous Ceramic Membranes,Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2000, 187—212 |
| 121 | Ruthven D., Derrah, R., Can. J. Chem. Eng., 1972, 50(6), 743—747 |
| 122 | Jobic H., Theodorou D. N., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2007, 102(1—3), 21—50 |
| 123 | Jobic H., Schmidt W., Krause C. B., Kärger J., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2006, 90(1—3), 299—306 |
| 124 | Ito T., Fraissard J., J. Chem. Phys., 1982, 76(11), 5225—5229 |
| 125 | Hwang S., Parditka B., Cserháti C., Erdélyi Z., Gläser R., Haase J., Kärger J., Schmidt W., Chmelik C., Chem. Ing. Tech., 2017, 89(12), 1686—1693 |
| 126 | Kirchner T., Shakhov A., Zeigermann P., Valiullin R., Kärger J., Carbon, 2012, 50(13), 4804—4808 |
| 127 | Tanner J. E., Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1965, 36(8), 1086—1087 |
| 128 | Bingre R., Losch P., Megias⁃Sayago C., Vincent B., Pale P., Nguyen P., Louis B., ChemPhysChem, 2019, 20(21), 2874—2880 |
| 129 | Gunther J. P., Majer G., Fischer P., J. Chem. Phys., 2019, 150(12), 124201 |
| 130 | Mehlhorn D., Valiullin R., Kärger J., Cho K., Ryoo R., Materials, 2012, 5(4), 699—720 |
| 131 | Freeman R., Spin choreography, Oxford University Press Oxford, 1998 |
| 132 | Kärger J., Valiullin R., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42 (9), 4172—4197 |
| 133 | Mehlhorn D., Valiullin R., Kärger J., Cho K., Ryoo R., ChemPhysChem, 2012, 13(6), 1495—1499 |
| 134 | Vasenkov S., Böhlmann W., Galvosas P., Geier O., Liu H., Kärger J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105(25), 5922—5927 |
| 135 | Jobic H., Ernst H., Heink W., Kärger J., Tuel A., Bée M., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 1998, 26, 67—75 |
| 136 | Geier O., Vasenkov S., Kärger J., J. Chem. Phys., 2002, 117(5), 1935—1938 |
| 137 | Kärger J., Vasenkov S., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2005, 85(3), 195—206 |
| 138 | Mehlhorn D., Valiullin R., Kärger J., Cho K., Ryoo R., Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2012, 164, 273—279 |
| 139 | Jiao Y. L., Forster L., Xu S. J., Chen H. H., Han J. F., Liu X. Q., Zhou Y. T., Liu J. M., Zhang J. S., Yu J. H., D'Agostino C., Fan X. L., Angew. Chem.Int. Ed., 2020, 132, 2—11 |
| [1] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [2] | YAO Qing, YU Zhiyong, HUANG Xiaoqing. Progress in Synthesis and Energy-related Electrocatalysis of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [3] | LIN Zhi, PENG Zhiming, HE Weiqing, SHEN Shaohua. Single-atom and Cluster Photocatalysis: Competition and Cooperation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| [4] | TANG Quanjun, LIU Yingxin, MENG Rongwei, ZHANG Ruotian, LING Guowei, ZHANG Chen. Application of Single-atom Catalysis in Marine Energy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220324. |
| [5] | YANG Jingyi, LI Qinghe, QIAO Botao. Synergistic Catalysis Between Ir Single Atoms and Nanoparticles for N2O Decomposition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220388. |
| [6] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [7] | WANG Sicong, PANG Beibei, LIU Xiaokang, DING Tao, YAO Tao. Application of XAFS Technique in Single-atom Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [8] | TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325. |
| [9] | YANG Jingyi, SHI Siqi, PENG Huaitao, YANG Qihao, CHEN Liang. Integration of Atomically Dispersed Ga Sites with C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Photo-driven CO2 Cycloaddition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220349. |
| [10] | WANG Ruyue, WEI Hehe, HUANG Kai, WU Hui. Freezing Synthesis for Single Atom Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220428. |
| [11] | WANG Xintian, LI Pan, CAO Yue, HONG Wenhao, GENG Zhongxuan, AN Zhiyang, WANG Haoyu, WANG Hua, SUN Bin, ZHU Wenlei, ZHOU Yang. Techno-economic Analysis and Industrial Application Prospects of Single-atom Materials in CO2 Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [12] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [13] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [14] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [15] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||