

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 204.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190620
Previous Articles Next Articles
XIAO Yuqing1,2,LI Shenhui1,*( ),TANG Jing1,2,XU Jun1,DENG Feng1,*(
),TANG Jing1,2,XU Jun1,DENG Feng1,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-02
Online:2020-02-10
Published:2019-12-31
Contact:
Shenhui LI,Feng DENG
E-mail:lishenhui@wipm.ac.cn;dengf@wipm.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XIAO Yuqing,LI Shenhui,TANG Jing,XU Jun,DENG Feng. Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy Studies on Structure, Dynamics and Host-guest Interaction in Metal-organic Framework Materials †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 204.
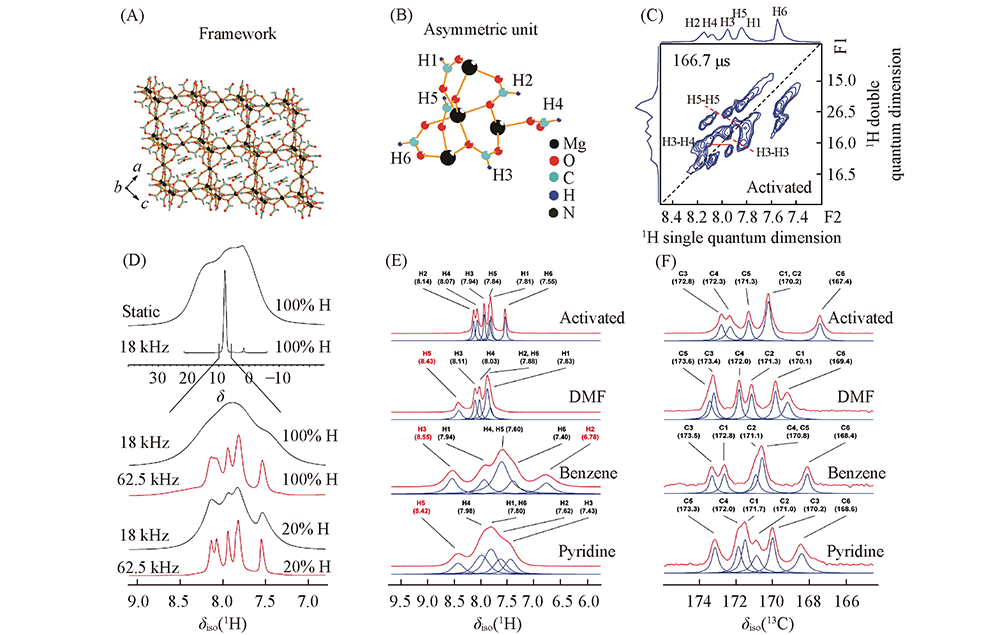
Fig.1 Structural demonstration of α-Mg3(HCOO)6(A), six unequivalent proton and carbon sites in α-Mg3(HCOO)6(B), 2D 1H-1H DQ MAS NMR spectra of α-Mg3(HCOO)6(C), the resolution of 1H MAS NMR spectra of α-Mg3(HCOO)6 largely improved by fast MAS speed and isotopic dilution(D), 1H MAS(E) and 13C CP/MAS(F) NMR spectra of activated α-Mg3(HCOO)6 and α-Mg3(HCOO)6 upon adsorption of DMF, benzene and pyridine[24] Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
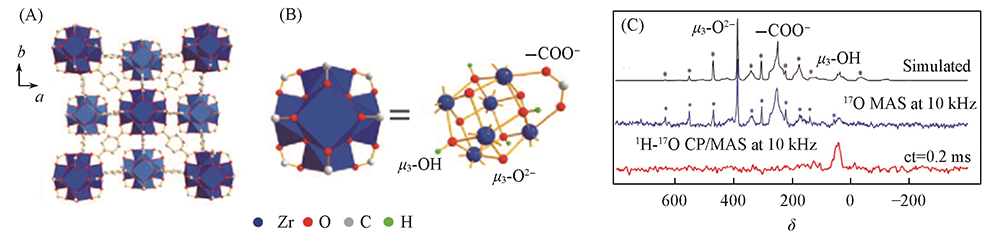
Fig.2 Structural illustration of UiO-66 framework(A), three types of oxygen coordination in UiO-66(B) and 17O MAS and 1H-17O CP/MAS NMR spectra of 17O isotope enriched Zr-UiO-66[33](C) Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
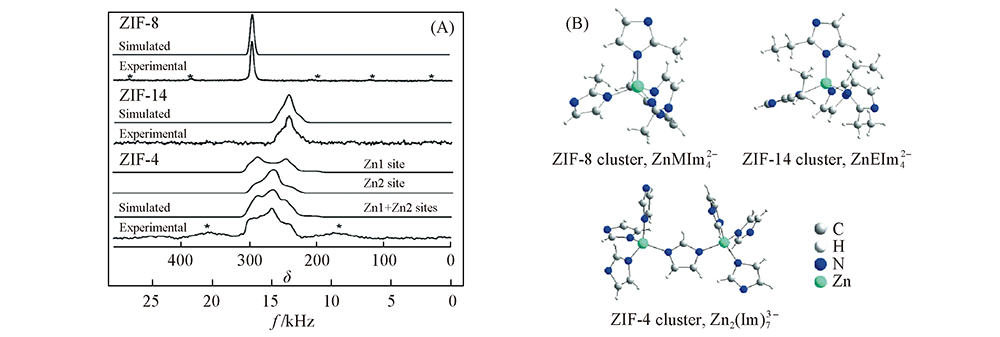
Fig.3 67Zn MAS NMR spectra of ZIF-8, ZIF-14, and ZIF-4 recorded at 21.1 T(A) and model clusters representing the structure of ZIF-8, ZIF-14, and ZIF-4(B)[36] Copyright 2012, John Wiley and sons.
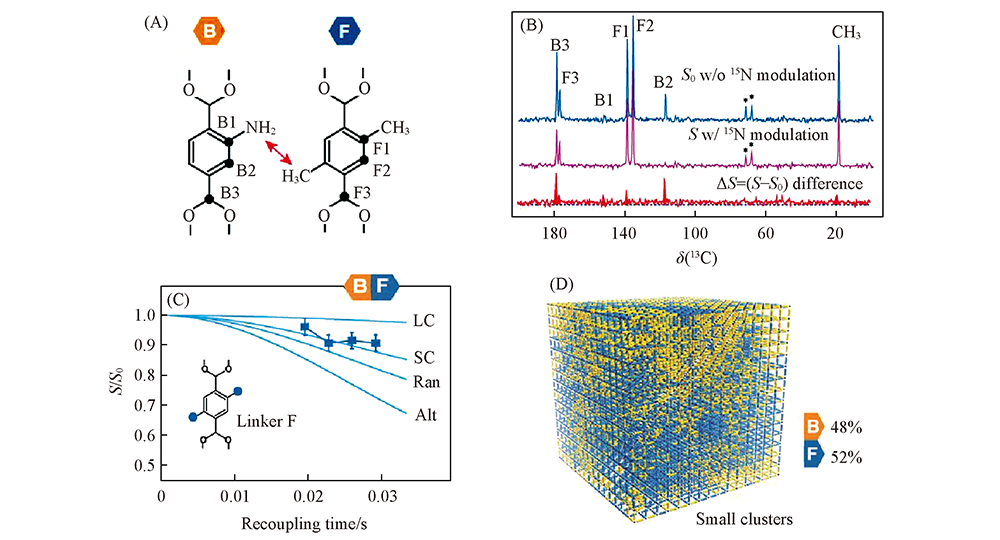
Fig.4 Molecular demostration of MTV-MOF-5-BF(A), 13C NMR spectra extracted from 13C{15N} REDOR experiment(B), 13C{15N} REDOR dephasing ratios and simulation curves using various models(C), and linker apportionment in MTV-MOF-5-BF(D)[45] Copyright 2013, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
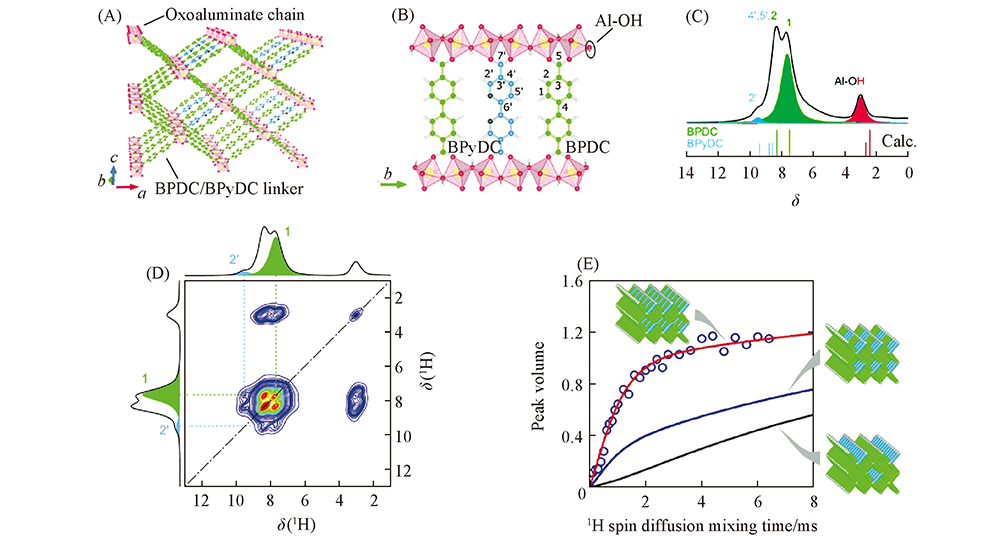
Fig.5 Structure demonstration of ML-DUT-5(A), various proton sites in ML-DUT-5 labled for spectral assignment(B), 1H MAS NMR spectra of ML-DUT-5(C), 1H-1H 2D spin diffusion spectrum of ML-DUT-5(D) and 1H spin diffusion buildup curves of different linker apportionments(E)[47] Copyright 2015, John Wiley and sons.
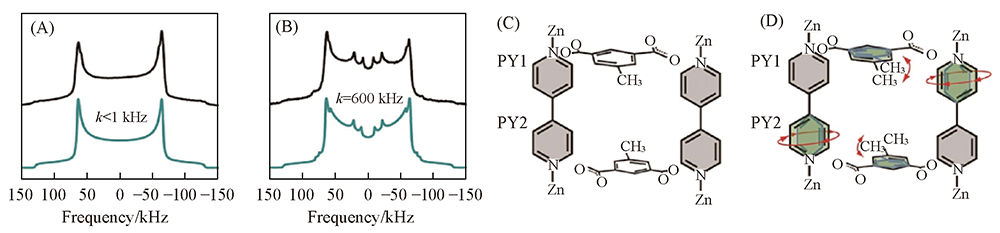
Fig.6 2H NMR spectra of CID-Me at 195 K(A) and 298 K(B) and pore window composed of bpy and 5-Me-ip at 195 K(C) and 296 K(D)[66] Copyright 2018, John Wiley and sons.
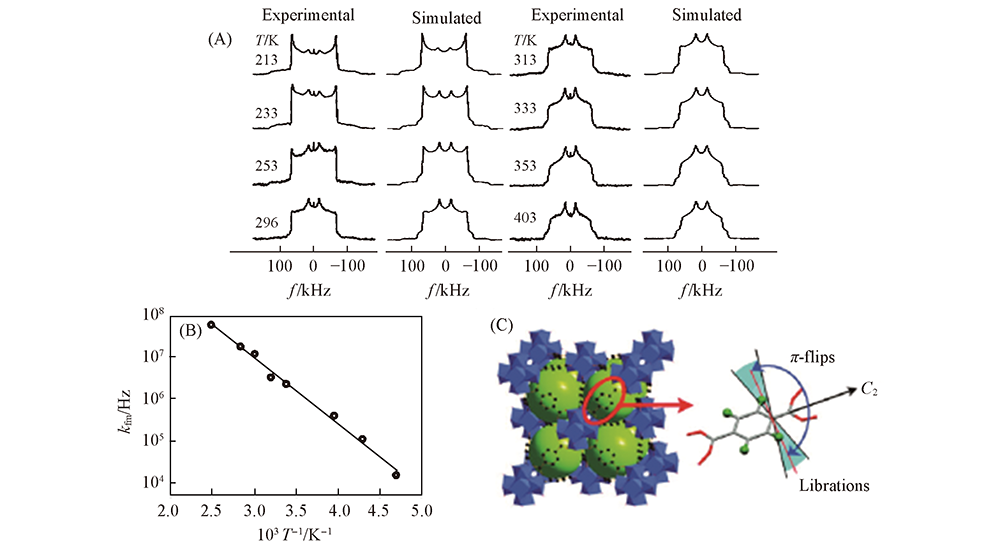
Fig.7 Variable 2H NMR spectra of deuterated 1,4-benzene-dicarboxylate(BDC) linker fragments of UiO-66(Zr)(A), Arrhenius plot for the mean flipping rate constant in UiO-66(B) and rotation of the BDC aromatic rings in UiO-66(C)[70] Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
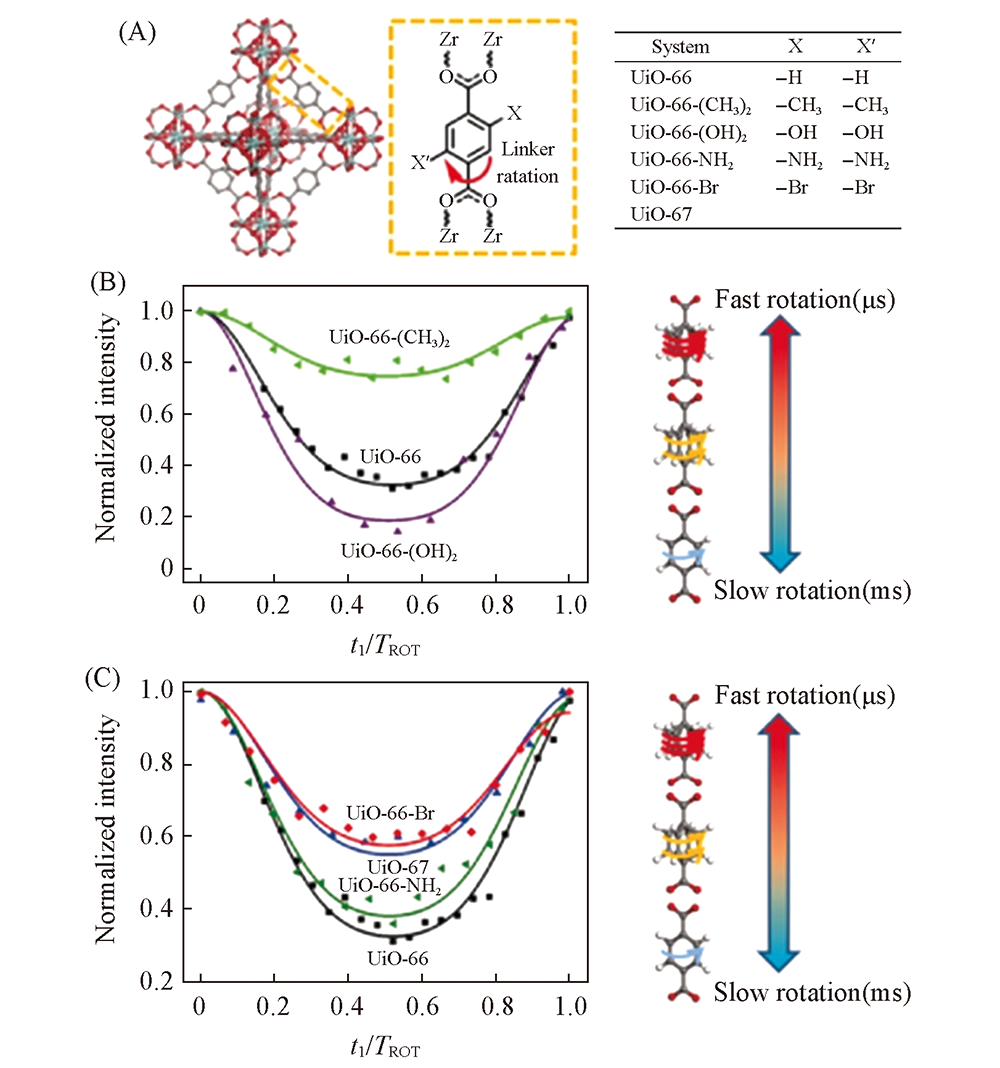
Fig.8 Structural demonstration of UiO-66-X(A), DIPSHIFT dephasing curves and scheme of linker rotation of UiO-66-X(B, C)[78] Copyright 2018, John Wiley and sons.
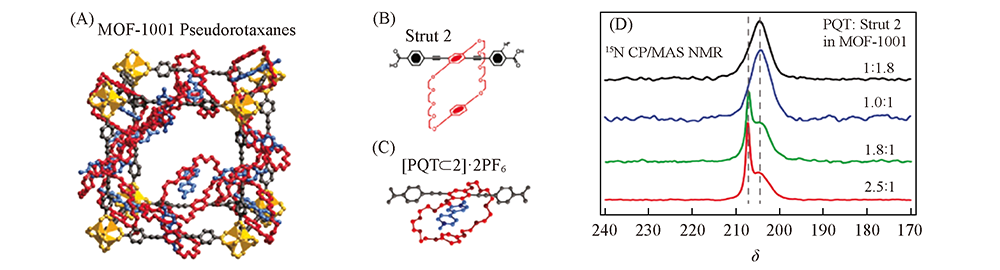
Fig.9 Structural demonstration of MOF-1001 pseudorotaxanes(A), organic linker of MOF-1001(B), PQT2+ adorbed on the organic linker(C) and 15N CP/MAS NMR spectra of MOF-1001 pseudorotaxanes(D)[82] Copyright 2009, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
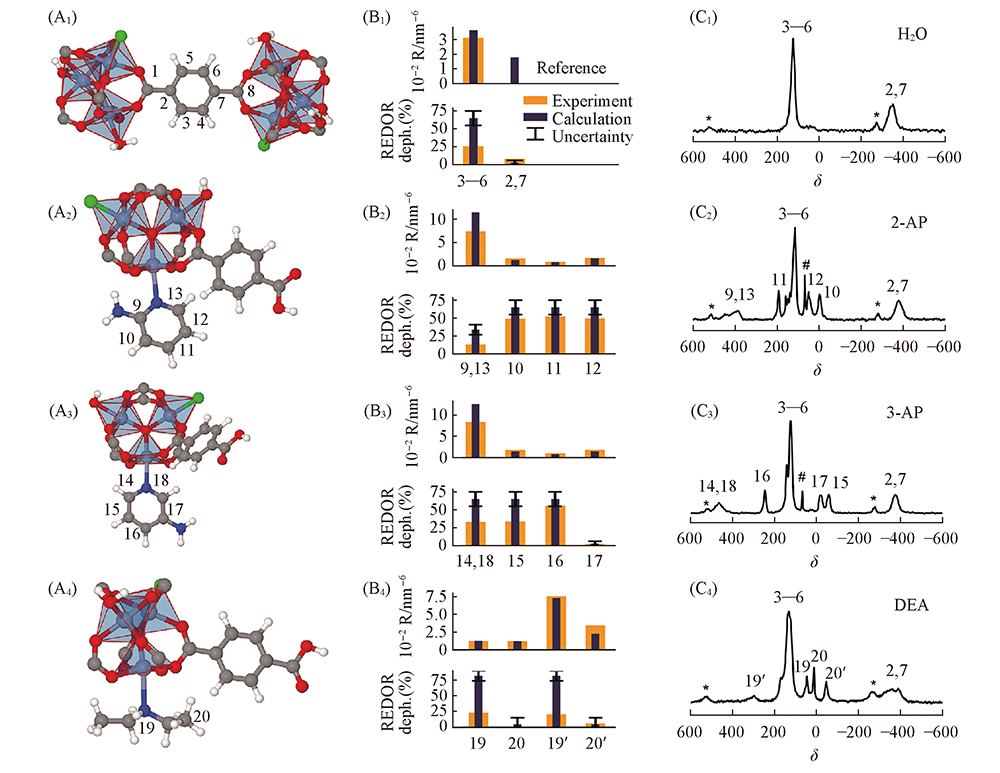
Fig.10 DFT-optimized structural fragments(A1—A4), experimental and calculated distance(B1—B4), 13C MAS NMR spectra(C1—C4) of H2O@Cr-MIL-101(A1—C1), 2-AP@Cr-MIL-101(A2—C2), 3-AP@Cr-MIL-101(A3—C3), and DEA@Cr-MIL-101(A4—C4)[88] Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
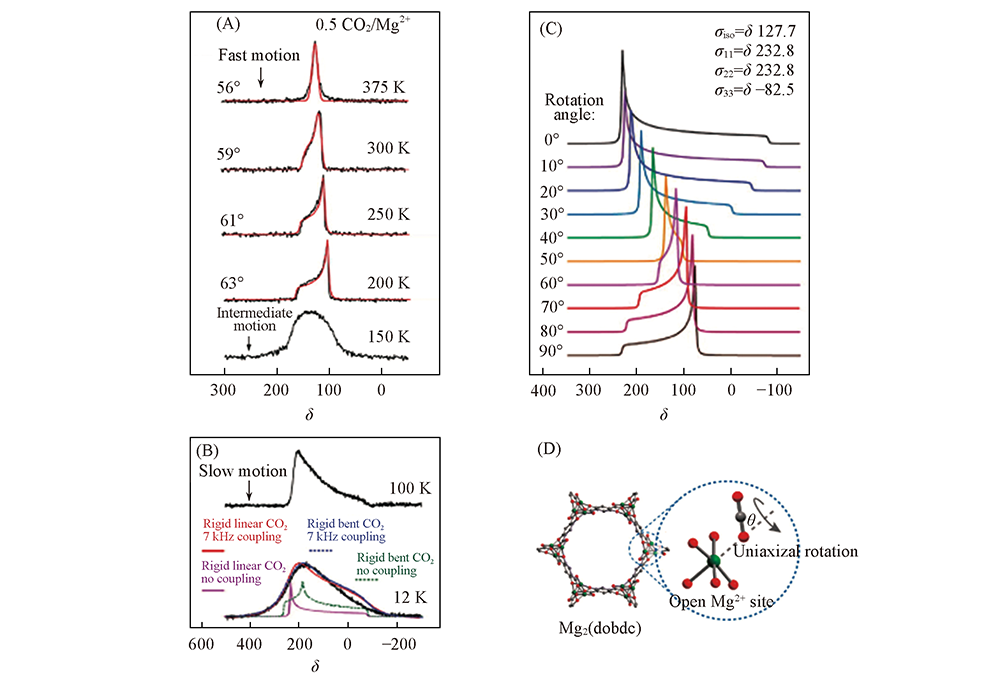
Fig.11 13C CSA powder patterns of 13C-enriched CO2 in Mg2(dobdc) acquried at variable temperature(A, B), 13C lineshapes simulations for CO2 uniaxial rotation(C) and illustration of CO2 uniaxial rotation at the open Mg2+ site in Mg2(dobdc)(D)[94] Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
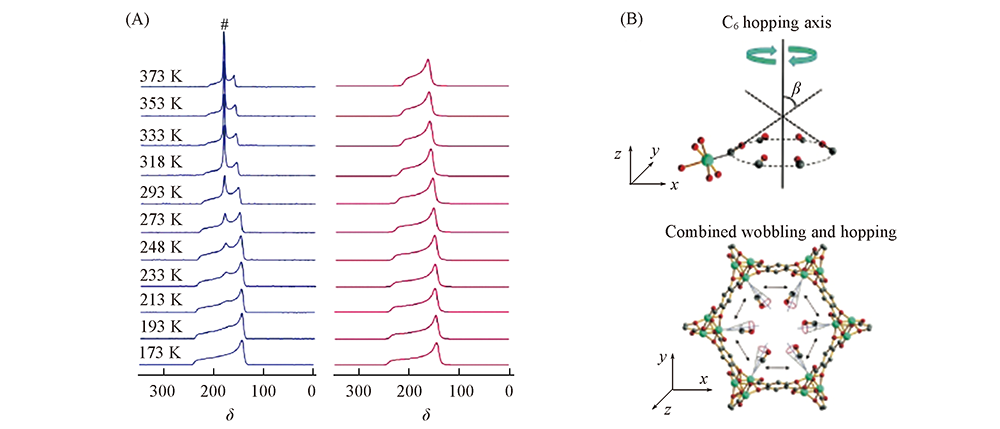
Fig.12 Variable-temperature 13C experimental(left) and simulated(right) NMR spectra of 13CO adsorbed on Mg-MOF-74(A) and schematic diagram illustrating the motions of CO(B) The # symbol denotes the resonance corresponding to mobile, isotropically tumbling CO[105]. Copyright 2016, John Wiley and sons.
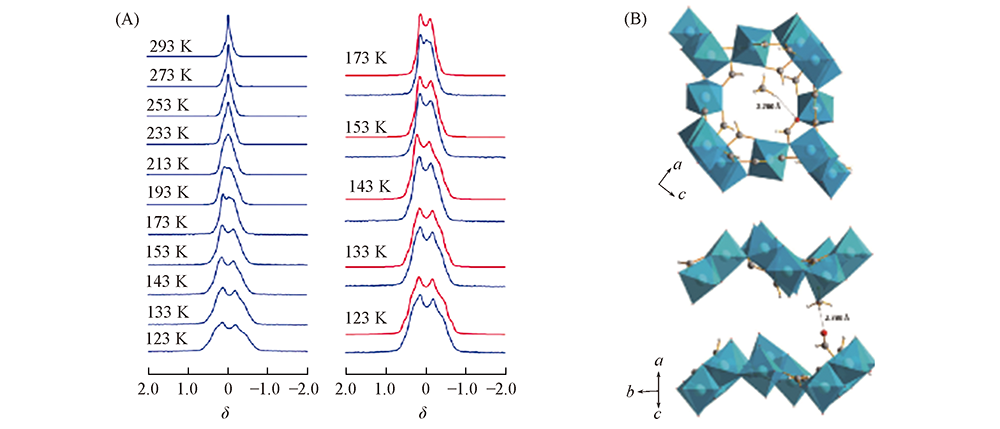
Fig.13 Static variable temperature 2H NMR spectra of CH3D adsorbed within α-Mg3(HCO2)6(A) and DFT-optimized structure of methane-loaded α-Mg3(HCO2)6(B)[109] (A): Left column denotes the experimetal spectra(in blue); right column demonstrates the representive experimental spectra(in blue) and corresponding simulated spectra(in red). Copyright 2018, John Wiley and sons.
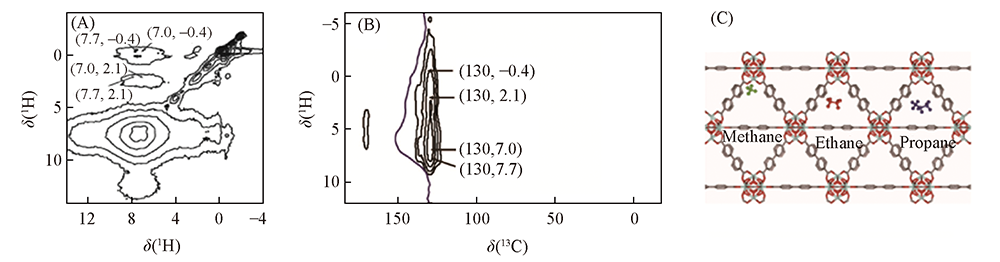
Fig.14 2D 1H-1H spin diffusion HOMCOR NMR spectra(A), 1H-13C HETCOR NMR spectra of UiO-67 upon methane adsorption with a spin diffusion mixing time of 36 ms(B) and schematic model of host-guest interaction between UiO-67 and light alkane(C)[110] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
| [1] | Furukawa H., Cordova K. E., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2013,341(6149), 974— 989 |
| [2] | Ferey G., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008,37(1), 191— 214 |
| [3] |
Liu C., Li F., Ma L. P., Cheng H. M., Adv. Mater., 2010,22(8), E28— E62
doi: 10.1002/adma.v22:8 URL |
| [4] | Sumida K., Rogow D. L., Mason J. A., McDonald T. M., Bloch E. D., Herm Z. R., Bae T. H., Long J. R., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 724— 781 |
| [5] |
Kreno L. E., Leong K., Farha O. K., Allendorf M., van Duyne R. P., Hupp J. T., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 1105— 1125
doi: 10.1021/cr200324t URL |
| [6] |
Li J. R., Sculley J., Zhou H. C., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 869— 932
doi: 10.1021/cr200190s URL |
| [7] |
Han Q., Wang Z., Chen X., Mao C., Li H., Yu R., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2019,35(4), 564— 569
doi: 10.1007/s40242-019-8415-z URL |
| [8] | Mu X., Jiang S. S., Zhang S. H., Ren H., Sun F. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(9), 1818— 1824 |
| ( 穆鑫, 姜双双, 张舒皓, 任浩, 孙福兴 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(9), 1818— 1824) | |
| [9] | Hou J. Y., Hao J. J., Wang Y. Y., Liu J. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(9), 1926— 1931 |
| ( 侯俊英, 郝建军, 王雅雅, 刘敬春 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(9), 1926— 1931) | |
| [10] |
Horcajada P., Gref R., Baati T., Allan P. K., Maurin G., Couvreur P., Ferey G., Morris R. E., Serre C., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 1232— 1268
doi: 10.1021/cr200256v URL |
| [11] |
Lee J., Farha O. K., Roberts J., Scheidt K. A., Nguyen S. T., Hupp J. T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009,38(5), 1450— 1459
doi: 10.1039/b807080f URL |
| [12] |
Hou J., Hao J., Wang Y., Liu J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2019,35(5), 860— 865
doi: 10.1007/s40242-019-9133-2 URL |
| [13] |
Zhang Y., Zhang F., Zhang X., Xu Y., Qi X., Quan C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2018,34(4), 655— 660
doi: 10.1007/s40242-018-7361-5 URL |
| [14] | Wang P. C., Shan L., Fan Y., Wang L., Xu J. N., Wu S. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(8), 1655— 1661 |
| ( 王鹏程, 单梁, 范勇, 王莉, 徐家宁, 吴淑杰 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(8), 1655— 1661) | |
| [15] |
Brown S. P., Spiess H. W., Chem. Rev., 2001,101(12), 4125— 4155
doi: 10.1021/cr990132e URL |
| [16] |
Laws D. D., Bitter H. M. L., Jerschow A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2002,41(17), 3096— 3129
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020902)41:17<>1.0.CO;2-C URL |
| [17] |
Li S., Deng F., Annu. Rep. NMR Spectro., 2013,78, 1— 54
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-404716-7.00001-8 URL |
| [18] |
Lucier B. E. G., Chen S., Huang Y., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018,51(2), 319— 330
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00357 URL |
| [19] | Sutrisno A., Huang Y ., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2013, 49—50, 1— 11 |
| [20] |
Witherspoon V. J., Xu J., Reimer J. A., Chem. Rev., 2018,118(20), 10033— 10048
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00695 URL |
| [21] |
Marchetti A., Chen J., Pang Z., Li S., Ling D., Deng F., Kong X., Adv. Mater., 2017,29(14), 1605895
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.14 URL |
| [22] |
Ding S. Y., Dong M., Wang Y. W., Chen Y. T., Wang H. Z., Su C. Y., Wang W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(9), 3031— 3037
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10754 URL |
| [23] |
Ben T., Ren H., Ma S., Cao D., Lan J., Jing X., Wang W., Xu J., Deng F., Simmons J. M., Qiu S., Zhu G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009,48(50), 9457— 9460
doi: 10.1002/anie.200904637 URL |
| [24] |
Xu J., Terskikh V. V., Chu Y., Zheng A., Huang Y., Chem. Mater., 2015,27(9), 3306— 3316
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b00360 URL |
| [25] |
Devautour-Vinot S., Maurin G., Serre C., Horcajada P., da Cunha D. P., Guillerm V., Costa E. d. S., Taulelle F., Martineau C., Chem. Mater., 2012,24(11), 2168— 2177
doi: 10.1021/cm300863c URL |
| [26] |
Loiseau T., Serre C., Huguenard C., Fink G., Taulelle F., Henry M., Bataille T., Ferey G., Chem. Eur. J., 2004,10(6), 1373— 1382
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3765 URL |
| [27] |
Dawson D. M., Jamieson L. E., Mohideen M. I. H., McKinlay A. C., Smellie I. A., Cadou R., Keddie N. S., Morris R. E., Ashbrook S. E., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013,15(3), 919— 929
doi: 10.1039/C2CP43445H URL |
| [28] |
Tong Y. B., Liu S. X., Zou Y., Xue C., Duan H. B., Liu J. L., Ren X. M., Inorg. Chem., 2016,55(22), 11716— 11726
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b01759 URL |
| [29] |
Li Y., Wu X. P., Jiang N., Lin M., Shen L., Sun H., Wang Y., Wang M., Ke X., Yu Z., Gao F., Dong L., Guo X., Hou W., Ding W., Gong X. Q., Grey C. P., Peng L., Nat. Commun., 2017,8, 581
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00603-7 URL |
| [30] |
Wang M., Wu X. P., Zheng S., Zhao L., Li L., Shen L., Gao Y., Xue N., Guo X., Huang W., Gan Z., Blanc F., Yu Z., Ke X., Ding W., Gong X. Q., Grey C. P., Peng L., Sci. Adv., 2015,1(1), e1400133
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1400133 URL |
| [31] |
Peng L. M., Liu Y., Kim N. J., Readman J. E., Grey C. P., Nat. Mater., 2005,4(3), 216— 219
doi: 10.1038/nmat1332 URL |
| [32] |
Peng L., Stebbins J. F., J. Non-Crys. Solids, 2008,354(27), 3120— 3128
doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.01.026 URL |
| [33] |
He P., Xu J., Terskikh V. V., Sutrisno A., Nie H. Y., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013,117(33), 16953— 16960
doi: 10.1021/jp403512m URL |
| [34] |
Bignami G. P. M., Davis Z. H., Dawson D. M., Morris S. A., Russell S. E., McKay D., Parke R. E., Iuga D., Morris R. E., Ashbrook S. E., Chem. Sci., 2018,9(4), 850— 859
doi: 10.1039/C7SC04649A URL |
| [35] |
Mueller M., Hermes S., Kaehler K., van den Berg M. W. E., Muhler M., Fischer R. A., Chem. Mater., 2008,20(14), 4576— 4587
doi: 10.1021/cm703339h URL |
| [36] |
Sutrisno A., Terskikh V. V., Shi Q., Song Z., Dong J., Ding S. Y., Wang W., Provost B. R., Daff T. D., Woo T. K., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2012,18(39), 12251— 12259
doi: 10.1002/chem.201201563 URL |
| [37] |
Xu J., Lucier B. E. G., Sinelnikov R., Terskikh V. V., Staroverov V. N., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2015,21(41), 14348— 14361
doi: 10.1002/chem.201501954 URL |
| [38] |
He P., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Shi Q., Dong J., Chu Y., Zheng A., Sutrisno A., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(41), 23728— 23744
doi: 10.1021/jp5063868 URL |
| [39] |
Xu J., Blaakrneer E. S. M., Lipton A. S., McDonald T. M., Liu Y. M., Smit B., Long J. R., Kentgens A. P. M., Reimert J. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017,121(36), 19938— 19945
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07809 URL |
| [40] |
Chen S., Lucier B. E. G., Chen M., Terskikh V. V., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2018,24(35), 8732— 8736
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.35 URL |
| [41] | Jiang Y., Huang J., Marx S., Kleist W., Hunger M., Baiker A ., J. vPhys. Chem. Lett., 2010,1(19), 2886— 2890 |
| [42] | Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Zheng R., Huang Y., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2017,84, 118— 131 |
| [43] | Deng H., Doonan C. J., Furukawa H., Ferreira R. B., Towne J., Knobler C. B., Wang B., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2010,327(5967), 846— 850 |
| [44] |
Abednatanzi S., Gohari Derakhshandeh P., Depauw H., Coudert F. X., Vrielinck H., van Der Voort P., Leus K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019,48(9), 2535— 2565
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00337H URL |
| [45] |
Kong X., Deng H., Yan F., Kim J., Swisher J. A., Smit B., Yaghi O. M., Reimer J. A., Science, 2013,341(6148), 882— 885
doi: 10.1126/science.1241606 URL |
| [46] | Giovine R., Volkringer C., Trebosc J., Amoureux J. P., Loiseau T., Lafon O., Pourpoint F., Acta Crystallog. C, 2017,73, 176— 183 |
| [47] |
Krajnc A., Kos T., Logar N. Z., Mali G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015,54(36), 10535— 10538
doi: 10.1002/anie.201504426 URL |
| [48] |
Bueken B van Velthoven N., Krajnc A., Smolders S., Taulelle F., Mellot-Draznieks C., Mali G., Bennett T. D., de Vos D., ., Chem. Mater., 2017,29(24), 10478— 10486
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04128 URL |
| [49] |
Krajnc A., Bueken B., De Vos D., Mali G ., J. Magn. Reson., 2017,279, 22— 28
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.04.008 URL |
| [50] |
Jayachandrababu K. C., Verploegh R. J., Leisen J., Nieuwendaal R. C., Sholl D. S., Nair S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(23), 7325— 7336
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b02754 URL |
| [51] |
Jayachandrababu K. C., Sholl D. S., Nair S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017,139(16), 5906— 5915
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01660 URL |
| [52] |
Springuel-Huet M. A., Nossov A., Adem Z., Guenneau F., Volkringer C., Loiseau T., Ferey G., Gedeon A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010,132(33), 11599— 11607
doi: 10.1021/ja103105y URL |
| [53] |
Springuel-Huet M. A., Nossov A., Guenneau F., Gedeon A., Chem. Commun., 2013,49(67), 7403— 7405
doi: 10.1039/c3cc43119c URL |
| [54] |
Chen Y. Z., Gu B., Uchida T., Liu J., Liu X., Ye B. J., Xu Q., Jiang H. L., Nat. Commun., 2019,10, 3462
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11449-6 URL |
| [55] |
Cao W., Wang W. D., Xu H. S., Sergeyev I. V., Struppe J., Wang X., Mentink-Vigier F., Gan Z., Xiao M. X., Wang L. Y., Chen G. P., Ding S. Y., Bai S., Wang W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(22), 6969— 6977
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b02839 URL |
| [56] | Rossini A. J., Zagdoun A., Lelli M., Canivet J., Aguado S., Ouari O., Tordo P., Rosay M., Maas W. E., Coperet C., Farrusseng D., Emsley L., Lesage A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012,51(1), 123— 127 |
| [57] |
Todorova T. K., Rozanska X., Gervais C., Legrand A., Ho L. N., Berruyer P., Lesage A., Emsley L., Farrusseng D., Canivet J., Mellot-Draznieks C., Chem. Eur. J., 2016,22(46), 16531— 16538
doi: 10.1002/chem.201603255 URL |
| [58] |
Guo Z., Kobayashi T., Wang L. L., Goh T. W., Xiao C., Caporini M. A., Rosay M., Johnson D. D., Pruski M., Huang W., Chem. Eur. J., 2014,20(49), 16308— 16313
doi: 10.1002/chem.v20.49 URL |
| [59] |
Kobayashi T., Perras F. A., Goh T. W., Metz T. L., Huang W., Pruski M., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016,7(13), 2322— 2327
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00860 URL |
| [60] |
Pourpoint F., Thankamony A. S. L., Volkringer C., Loiseau T., Trebosc J., Aussenac F., Carnevale D., Bodenhausen G., Vezin H., Lafon O., Amoureux J. P., Chem. Commun., 2014,50(8), 933— 935
doi: 10.1039/C3CC47208F URL |
| [61] |
Hong M., Zhang Y., Hu F. H., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2012,63, 1— 24
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-032511-143731 URL |
| [62] |
Rapp A., Schnell I., Sebastiani D., Brown S. P., Percec V., Spiess H. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003,125(43), 13284— 13297
doi: 10.1021/ja035127d URL |
| [63] |
Fu D. W., Cai H. L., Li S. H., Ye Q., Zhou L., Zhang W., Zhang Y., Deng F., Xiong R. G., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2013,110(25), 257601
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.257601 URL |
| [64] |
Ye H. Y., Li S. H., Zhang Y., Zhou L., Deng F., Xiong R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014,136(28), 10033— 10040
doi: 10.1021/ja503344b URL |
| [65] |
Ji C., Li S., Deng F., Sun Z., Li L., Zhao S., Luo J ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016,120(48), 27571— 27576
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b09890 URL |
| [66] |
Ferey G., Serre C., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009,38(5), 1380— 1399
doi: 10.1039/b804302g URL |
| [67] |
Ott L. S., Cline M. L., Deetlefs M., Seddon K. R., Finke R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005,127(16), 5758— 5759
doi: 10.1021/ja0423320 URL |
| [68] |
Gonzalez-Nelson A., Coudert F. X., van der Veen M. A., Nanomaterials, 2019,9(3), 330— 365
doi: 10.3390/nano9030330 URL |
| [69] | Inukai M., Tamura M., Horike S., Higuchi M., Kitagawa S., Nakamura K., Angew. Chem. Int.Ed., 2018,57(28), 8687— 8690 |
| [70] |
Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Guillerm V., Serre C., Frick B., Jobic H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012,116(22), 12131— 12136
doi: 10.1021/jp3029193 URL |
| [71] |
Kolokolov D. I., Jobic H., Stepanov A. G., Guillerm V., Devic T., Serre C., Ferey G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010,49(28), 4791— 4794
doi: 10.1002/anie.201001238 URL |
| [72] |
Gonzalez J., Devi R. N., Tunstall D. P., Cox P. A., Wright P. A., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2005,84(1—3), 97— 104
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.04.019 URL |
| [73] |
Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Guillerm V., Serre C., Frick B., Jobic H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012,116(22), 12131— 12136
doi: 10.1021/jp3029193 URL |
| [74] |
Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Jobic H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(29), 15978— 15984
doi: 10.1021/jp506010p URL |
| [75] |
Inukai M., Fukushima T., Hijikata Y., Ogiwara N., Horike S., Kitagawa S ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015,137(38), 12183— 12186
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b05413 URL |
| [76] |
Eddaoudi M., Kim J., Rosi N., Vodak D., Wachter J., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2002,295(5554), 469— 472
doi: 10.1126/science.1067208 URL |
| [77] |
Deria P., Mondloch J. E., Karagiaridi O., Bury W., Hupp J. T., Farha O. K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43(16), 5896— 5912
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00067F URL |
| [78] |
Damron J. T., Ma J., Kurz R., Saalwaechter K., Matzger A. J., Ramamoorthy A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,57(28), 8678— 8681
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.28 URL |
| [79] |
Li S. H., Pourpoint F., Trebosc J., Zhou L., Lafon O., Shen M., Zheng A. M., Wang Q., Amoureux J. P., Deng F., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014,5(17), 3068— 3072
doi: 10.1021/jz501389z URL |
| [80] |
Xu J., Wang Q., Deng F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2019,52(8), 2179— 2189
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00125 URL |
| [81] |
Zheng A., Li S., Liu S. B., Deng F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2016,49(4), 655— 663
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00007 URL |
| [82] |
Li Q., Zhang W., Miljanic O. S., Sue C. H., Zhao Y. L., Liu L., Knobler C. B., Stoddart J. F., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2009,325(5942), 855— 859
doi: 10.1126/science.1175441 URL |
| [83] |
Xu X., Li S., Liu Q., Liu Z., Yan W., Zhao L., Zhang W., Zhang L., Deng F., Cong H., Deng H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019,11(1), 973— 981
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b19211 URL |
| [84] |
Nandy A., Forse A. C., Witherspoon V. J., Reimer J. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018,122(15), 8295— 8305
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12628 URL |
| [85] | Tang J., Li S., Chui Y., Xiao Y., Xu J., Deng F., Magn. Reson. Chem., 2020, DOI: 10.1002/mrc.4923 |
| [86] |
Wack J., Siegel R., Ahnfeldt T., Stock N., Mafra L., Senker J ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013,117(39), 19991— 20001
doi: 10.1021/jp4063252 URL |
| [87] |
Li S., Li J., Tang J., Deng F ., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2018,90, 1— 6
doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2017.12.004 URL |
| [88] |
Wittmann T., Mondal A., Tschense C. B. L., Wittmann J. J., Klimm O., Siegel R., Corzilius B., Weber B., Kaupp M., Senker J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(6), 2135— 2144
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b10148 URL |
| [89] |
Tang J., Li S., Chu Y., Xiao Y., Xu J., Deng F ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(39), 24062— 24070
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b06332 URL |
| [90] |
Khan A. H., Peikert K., Hoffmann F., Fröba M., Bertmer M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(7), 4299— 4307
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11919 URL |
| [91] |
Gul-E-Noor F Jee B., Pöppl A., Hartmann M., Himsl D., Bertmer M., ., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13(17), 7783— 7788
doi: 10.1039/c0cp02848g URL |
| [92] |
Gul-E-Noor F., Michel D., Krautscheid H., Haase J., Bertmer M., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2013,180, 8— 13
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.06.033 URL |
| [93] |
Fu Y., Kang Z. Z., Yin J. L., Cao W. C., Tu Y. Q., Wang Q., Kong X. Q., Nano Lett., 2019,19(3), 1618— 1624
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04518 URL |
| [94] |
Kong X., Scott E., Ding W., Mason J. A., Long J. R., Reimer J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012,134(35), 14341— 14344
doi: 10.1021/ja306822p URL |
| [95] |
Chen M., Chen S., Chen W., Lucier B. E. G., Zhang Y., Zheng A., Huang Y., Chem. Mater., 2018,30(11), 3613— 3617
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00681 URL |
| [96] |
Wang W. D., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Wang W., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014,5(19), 3360— 3365
doi: 10.1021/jz501729d URL |
| [97] |
Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., Huang Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18(12), 8327— 8341
doi: 10.1039/C5CP04984A URL |
| [98] |
Chen S., Lucier B. E. G., Boyle P. D., Huang Y., Chem. Mater., 2016,28(16), 5829— 5846
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b02239 URL |
| [99] |
Lu Y., Lucier B. E. G., Zhang Y., Ren P., Zheng A., Huang Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19(8), 6130— 6141
doi: 10.1039/C7CP00199A URL |
| [100] |
Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., McKenzie S. M., Arhangelskis M., Morris A. J., Friscic T., Reid J. W., Terskikh V. V., Chen M., Huang Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(34), 28582— 28596
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b08562 URL |
| [101] |
Desveaux B. E., Wong Y. T. A., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Boyle P. D., Jiang S., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(29), 17798— 17807
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b03221 URL |
| [102] |
Sin M., Kavoosi N., Rauche M., Pallmann J., Paasch S., Senkovska I., Kaskel S., Brunner E ., Langmuir, 2019,35(8), 3162— 3170
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03554 URL |
| [103] |
McDonald T. M., Mason J. A., Kong X., Bloch E. D., Gygi D., Dani A., Crocella V., Giordanino F., Odoh S. O., Drisdell W. S., Vlaisavljevich B., Dzubak A. L., Poloni R., Schnell S. K., Planas N., Lee K., Pascal T., Wan L. F., Prendergast D., Neaton J. B., Smit B., Kortright J. B., Gagliardi L., Bordiga S., Reimer J. A., Long J. R., Nature, 2015,519(7543), 303— 308
doi: 10.1038/nature14327 URL |
| [104] |
Forse A. C., Milner P. J., Lee J. H., Redfearn H. N., Oktawiec J., Siegelman R. L., Martell J. D., Dinakar B., Porter-Zasada L. B., Gonzalez M. I., Neaton J. B., Long J. R., Reimer J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(51), 18016— 18031
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b10203 URL |
| [105] | Lucier B. E. G., Chan H., Zhang Y., Huang Y., Eur.J. Inorg. Chem., 2016,2016(13/14), 2017— 2024 |
| [106] |
Gul-E-Noor F Mendt M., Michel D., Poeppl A., Krautscheid H., Haase J., Bertmer M., ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013,117(15), 7703— 7712
doi: 10.1021/jp400869f URL |
| [107] |
Wong Y. T. A., Babcock T. K., Chen S., Lucier B. E. G., Huang Y., Langmuir, 2018,34(51), 15640— 15649
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02205 URL |
| [108] |
He Y. B., Zhou W., Qian G. D., Chen B. L., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43(16), 5657— 5678
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00032C URL |
| [109] |
Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., Fischer M., Gan Z., Boyle P. D., Desveaux B., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2018,24(31), 7866— 7881
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.31 URL |
| [110] |
Li J., Li S., Zheng A., Liu X., Yu N., Deng F ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017,121(26), 14261— 14268
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b04611 URL |
| [111] |
Wehring M., Gascon J., Dubbeldam D., Kapteijn F., Snurr R. Q., Stallmach F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010,114(23), 10527— 10534
doi: 10.1021/jp102212w URL |
| [112] |
Chmelik C., Freude D., Bux H., Haase J., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2012,147(1), 135— 141
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.06.009 URL |
| [113] |
Freude D., Dvoyashkina N., Arzumanov S. S., Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Chmelik C., Jin H., Li Y., Kaerger J., Haase J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(3), 1904— 1912
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11673 URL |
| [114] |
Pantatosaki E., Megariotis G., Pusch A. K., Chmelik C., Stallmach F., Papadopoulos G. K., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012,116(1), 201— 207
doi: 10.1021/jp207771s URL |
| [115] |
Ramsahye N. A., Gao J., Jobic H., Llewellyn P. L., Yang Q., Wiersum A. D., Koza M. M., Guillerm V., Serre C., Zhong C. L., Maurin G., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(47), 27470— 27482
doi: 10.1021/jp509672c URL |
| [116] |
Berens S., Chmelik C., Hillman F., Kaerger J., Jeong H. K., Vasenkov S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018,20(37), 23967— 23975
doi: 10.1039/C8CP04889D URL |
| [1] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [2] | LU Cong, LI Zhenhua, LIU Jinlu, HUA Jia, LI Guanghua, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescence Detection Properties of a New Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220037. |
| [3] | TIAN Xueqin, MO Zheng, DING Xin, WU Pengyan, WANG Yu, WANG Jian. A Squaramide-containing Luminescent Metal-organic Framework as a High Selective Sensor for Histidine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210589. |
| [4] | XING Peiqi, LU Tong, LI Guanghua, WANG Liyan. Controllable Syntheses of Two Cd(II) Metal-organic Frameworks Possessing Related Structures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220218. |
| [5] | LIU Xueguang, YANG Xiaoshan, MA Jingjing, LIU Weisheng. Separating Methyl Blue Selectively from the Mixture of Dyes by Europium Metal-organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210715. |
| [6] | SHI Xiaofan, ZHU Jian, BAI Tianyu, FU Zixuan, ZHANG Jijie, BU Xianhe. Research Status and Progress of MOFs with Application in Photoelectrochemical Water-splitting [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210613. |
| [7] | WU Ji, ZHANG Hao, LUO Yuhui, GENG Wuyue, LAN Yaqian. A Microporous Cationic Ga(III)-MOF with Fluorescence Properties for Selective sensing Fe3+ Ion and Nitroaromatic Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210617. |
| [8] | LI Wen, QIAO Junyi, LIU Xinyao, LIU Yunling. Zirconium-based Metal-Organic Framework with Naphthalene for Fluorescent Detection of Nitroaromatic Explosives in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210654. |
| [9] | WANG Jie, HUO Haiyan, WANG Yang, ZHANG Zhong, LIU Shuxia. General Strategy for In situ Synthesis of NENU-n Series Polyoxometalate-based MOFs on Copper Foil [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210557. |
| [10] | HAN Zongsu, YU Xiaoyong, MIN Hui, SHI Wei, CHENG Peng. A Rare Earth Metal-Organic Framework with H6TTAB Ligand [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210342. |
| [11] | MO Zongwen, ZHANG Xuewen, ZHOU Haolong, ZHOU Dongdong, ZHANG Jiepeng. Guest-responses of A Porous Coordination Polymer Based on Synergistic Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210576. |
| [12] | LI Shurong, WANG Lin, CHEN Yuzhen, JIANG Hailong. Research Progress of Metal⁃organic Frameworks on Liquid Phase Catalytic Chemical Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [14] | ZHANG Renli, WANG Yao, YU Zhiquan, SUN Zhichao, WANG Anjie, LIU Yingya. Molybdenum Peroxide Anchored on Fluoronated UiO-66 as Catalyst in the Oxidation of Sulfur Containing Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1914. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yangyang, LIU Qiyong, CHEN Boxin, ZHAO Bin, ZHOU Haimei, LI Xinxin, ZHENG Dan, FENG Fei. Silicon-based Micro Gas Chromatographic Column Using Metal-Organic Framework Material ZIF-8 as Stationary Phase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1736. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||