

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 20220089.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220089
李祎頔1,2, 田晓春1, 李俊鹏1,2, 陈立香1, 赵峰1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-15
出版日期:2022-06-10
发布日期:2022-03-27
通讯作者:
赵峰
E-mail:fzhao@iue.ac.cn
基金资助:
LI Yidi1,2, TIAN Xiaochun1, LI Junpeng1,2, CHEN Lixiang1, ZHAO Feng1( )
)
Received:2022-02-15
Online:2022-06-10
Published:2022-03-27
Contact:
ZHAO Feng
E-mail:fzhao@iue.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
半导体-微生物复合体系在污染物深度降解、 合成有价化学品及元素生物地球化学循环等领域发挥着重要作用, 其界面反应过程的核心是电子转移. 本文重点阐述了微生物/半导体界面上微生物的种类和功能、 半导体的种类及光催化机制, 总结了半导体-微生物界面的直接和间接电子传递途径, 讨论了强化界面电子传递的方法以及半导体与微生物系统的稳定性, 介绍了近年来半导体-微生物复合体系在污染物转化、 化学品合成以及资源循环利用方面的应用现状, 以期为半导体-微生物复合体系的设计及其环境领域应用提供指导.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李祎頔, 田晓春, 李俊鹏, 陈立香, 赵峰. 半导体-微生物界面电子传递及其在环境领域的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220089.
LI Yidi, TIAN Xiaochun, LI Junpeng, CHEN Lixiang, ZHAO Feng. Electron Transfer on the Semiconductor-microbe Interface and Its Environmental Application. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220089.
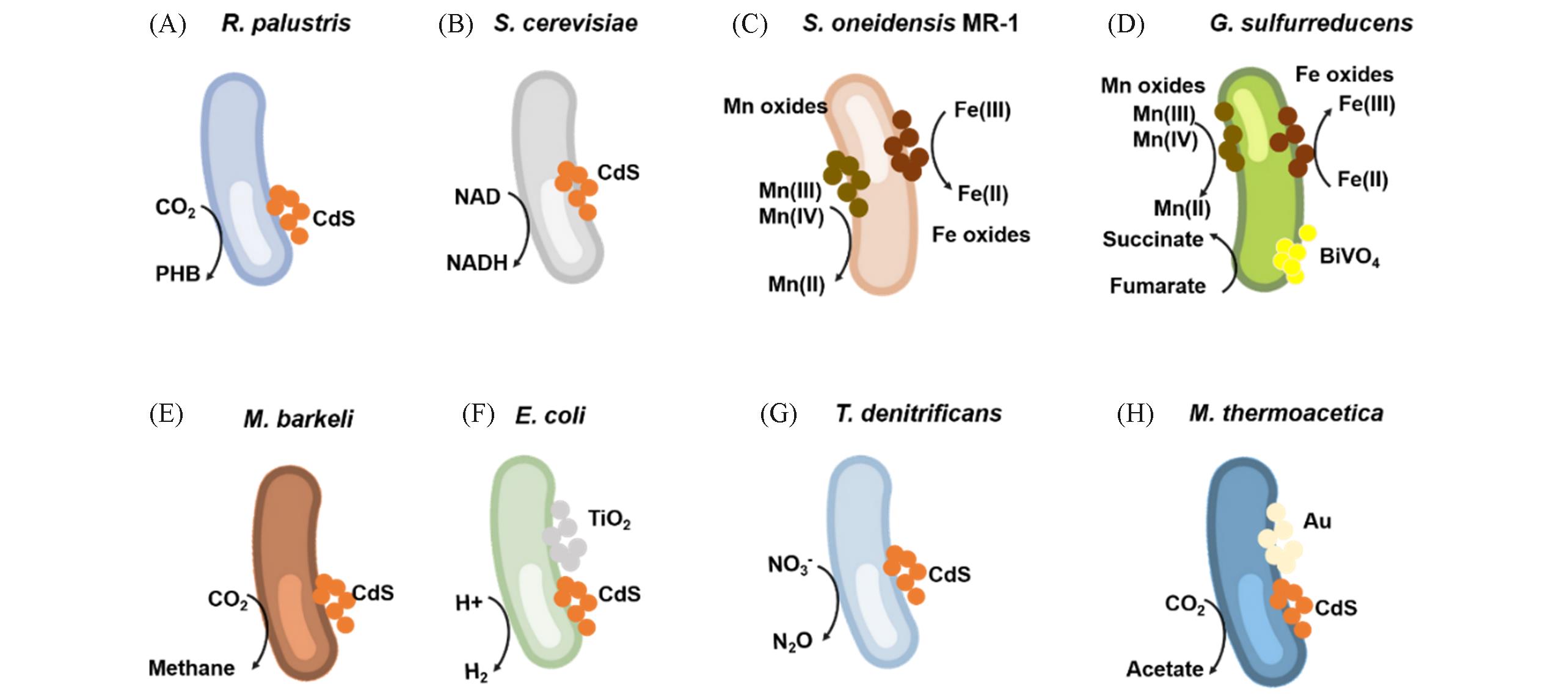
Fig.1 Representative species of functional microorganisms in semiconductor?microbial hybrid systems(A) R. paulustris; (B) S. cerevisiae; (C) S. oneidensis MR-1; (D) G. sulfurreducens; (E) M. barkeli; (F) E. coli; (G) T. denitrificans; (H) M. thermoacetica.
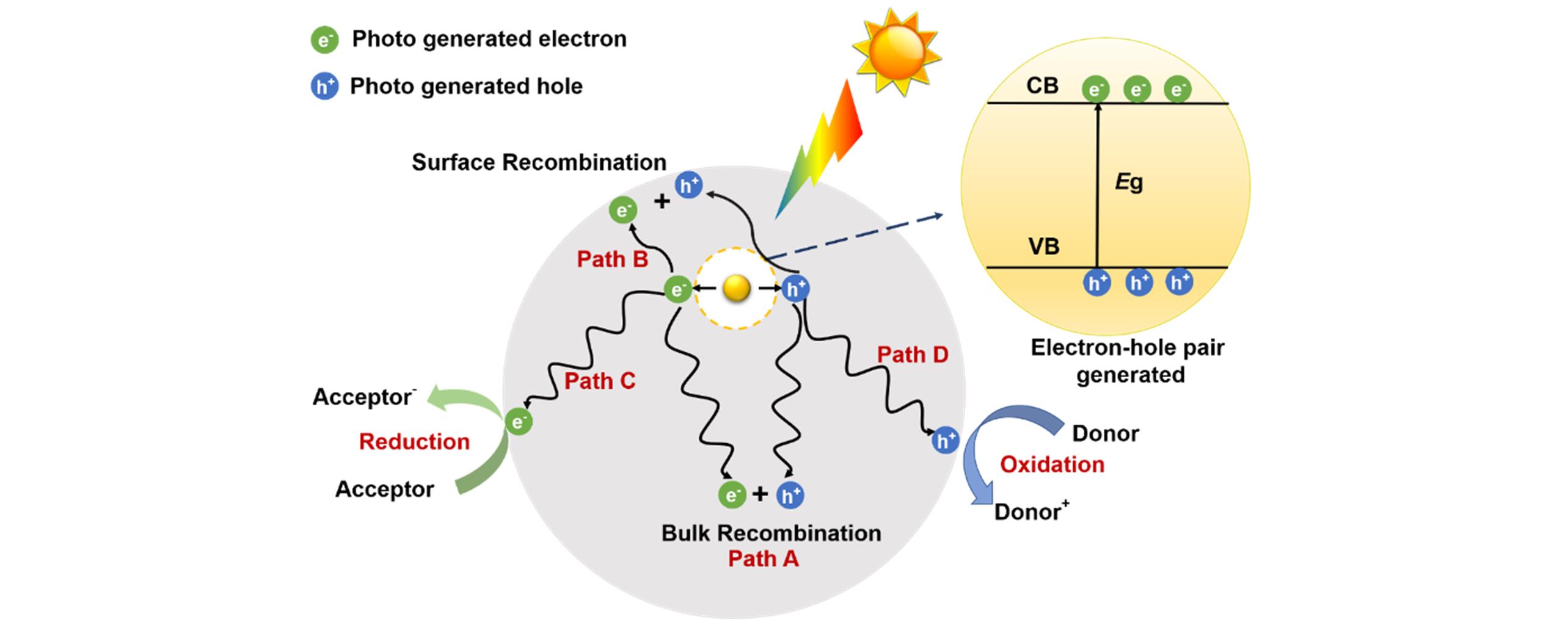
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the photocatalytic redox reactionsSemiconductor is excited by solar energy and the electron?hole pair is generated. VB, valence band; CB, conductive band; Eg, bandgap. Path A: bulk recombination of photo?electrons and holes; path B: photo?electrons and holes recombine on the surface of semiconductor; path C: engagement of electrons and holes in surface reduction reactions; path D: engagement of electrons and holes in surface oxidation reactions.
| 1 | Tang X. W., Tang R. D., Xiong S., Zheng J. F., Li L., Zhou Z. P., Gong D. X., Deng Y. C., Su L., Liao C. J., Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 812, 152434 |
| 2 | Lu A. H., Li Y., Ding H. R., Wang C. Q., Xu X. M., Liu F. F., Liu Y. W., Zhu Y., Li Y. Z., Earth Sci. Front., 2020, 27(5), 179—194 |
| 鲁安怀, 李艳, 丁竑瑞, 王长秋, 许晓明, 刘菲菲, 刘雨薇, 朱莹, 黎晏彰. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(5), 179—194 | |
| 3 | Sakimoto K. K., Wong A. B., Yang P. D., Science, 2016, 351(6268), 74—77 |
| 4 | Sakimoto K. K., Kornienko N., Cestellos⁃Blanco S., Lim J., Liu C., Yang P. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(6), 1978—1985 |
| 5 | Wang W., Chen X., Sci. China Chem., 2018, 61(7), 792—796 |
| 6 | Lu A. H., Li Y., Ding H. R., Wang C. Q., Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochemistry, 2018, 37(1), 1—15 |
| 7 | Xiong H. F., Dong S. S., Zhang J., Zhou D. D., Rittmann B. E., Water Res., 2018, 136, 75—83 |
| 8 | Zhu G. L., Yang Y., Liu J., Liu F., Lu A. H., He W. D., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 94, 227—234 |
| 9 | Fang X., Kalathil S., Reisner E., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(14), 4926—4952 |
| 10 | Ramos F. C., Nottoli M., Cupellini L., Mennucci B., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(42), 9650—9662 |
| 11 | Wang B., Jiang Z. F., Yu J. C., Wang J. F., Wong P. K., Nanoscale, 2019, 11(19), 9296—9301 |
| 12 | Wu R. R., Wang C., Shen J. S., Zhao F., Process Biochem., 2015, 50(12), 2061—2065 |
| 13 | Fang X., Kalathil S., Divitini G., Wang Q., Reisner E., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2020, 117(9), 5074—5080 |
| 14 | Ye J., Yu J., Zhang Y. Y., Chen M., Liu X., Zhou S. G., He Z., Appl. Catal. B, 2019, 257, 117916 |
| 15 | Honda Y., Hagiwara H., Ida S., Ishihara T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(28), 8045—8048 |
| 16 | Chen M., Zhou X. F., Yu Y. Q., Liu X., Zeng R. J. X., Zhou S. G., He Z., Environ. Int., 2019, 127, 353—360 |
| 17 | Sakimoto K. K., Zhang S. J., Yang P. D., Nano Lett., 2016, 16(9), 5883—5887 |
| 18 | Zhang H., Liu H., Tian Z. Q., Lu D., Yu Y., Cestellos-Blanco S., Sakimoto K. K., Yang P. D., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13(10), 900—905 |
| 19 | Gassler T., Sauer M., Gasser B., Egermeier M., Troyer C., Causon T., Hann S., Mattanovich D., Steiger M. G., Nat. Biotechnol., 2020, 38(2), 210—216 |
| 20 | Zou M. Z., Wu Y. C., Redmile⁃Gordon M., Wang D. J., Liu J., Huang Q. Y., Cai P., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 608, 2955— 2963 |
| 21 | Liu J., Liu X., Ding H. R., Ren G. P., Sun Y., Liu Y., Ji X., Ma L. Y. Z., Li Y., Lu A. H., Bioelectrochemistry, 2021, 141, 107849 |
| 22 | Feng Y. H., Xu M. Y., Tremblay P. L., Zhang T., Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2021, 46(42), 21901—21911 |
| 23 | Chellamuthu P., Naughton K., Pirbadian S., Silva K. P. T., Chavez M. S., El⁃Naggar M. Y., Boedicker J., Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10, 938 |
| 24 | Xu M. Y., Tremblay P. L., Ding R., Xiao J. X., Wang J. T., Kang Y., Zhang T., Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 753, 142050 |
| 25 | Tremblay P. L., Xu M. Y., Chen Y. M., Zhang T., iScience, 2020, 23(1), 100784 |
| 26 | Kowshik M., Vogel W., Urban J., Kulkarni S. K., Paknikar K. M., Adv. Mater., 2002, 14(11), 815—818 |
| 27 | Su Y. L., Du Q. Q., Qu X. C., Wan D. Y., Liu Y. H., Wang C., Yan Z. Y., Wu S. M., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(34), 28187—28193 |
| 28 | Nakamura R., Kai F., Okamoto A., Newton G. J., Hashimoto K., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(3), 508—511 |
| 29 | Liu P. C., Ma X. L., Li T. T., Yan F., Wu L. J., Xiao X., Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2020, 151, 104969 |
| 30 | Xie Q. Q., Lu Y., Tang L., Zeng G. M., Yang Z. H., Fan C. Z., Wang J. J., Atashgahi S., Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec., 2020, 51(17), 1924—1969 |
| 31 | Yang C. H., Aslan H., Zhang P., Zhu S. J., Xiao Y., Chen L. X., Khan N., Boesen T., Wang Y. L., Liu Y., Wang L., Sun Y., Feng Y. J., Besenbacher F., Zhao F., Yu M., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 1379 |
| 32 | Yu S. S., Chen J. J., Cheng R. F., Min Y., Yu H. Q., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2021, 55(16), 11424—11433 |
| 33 | Zhang B., Cheng H. Y., Wang A. J., Bioelectrochemistry, 2021, 138, 107683 |
| 34 | Song B., Zeng Z. T., Zeng G. M., Gong J. L., Xiao R., Ye S. J., Chen M., Lai C., Xu P., Tang X., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 272, 101999 |
| 35 | Ong W. J., Tan L. L., Ng Y. H., Yong S. T., Chai S. P., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(12), 7159—7329 |
| 36 | Liu D. X., Chen X. B., Yang X., Zhang J., Chen C. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4), 742—749 |
| 刘东旭, 陈雪冰, 杨霞, 张静, 陈常东. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4), 742—749 | |
| 37 | Luo B., Liu G., Wang L. Z., Nanoscale, 2016, 8(13), 6904—6920 |
| 38 | Wang Y. S., Li X., Yan L., Xu H. Y., Zhu Y. X., Song Y. H., Cui Y. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12), 3722—3730 |
| 王乙舒, 李雪, 闫丽, 徐红赟, 祝玉鑫, 宋艳华, 崔言娟. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(12), 3722—3730 | |
| 39 | Xia P. F., Zhu B. C., Yu J. G., Cao S. W., Jaroniec M., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(7), 3230—3238 |
| 40 | Yin T., Su L., Li H., Lin X. X., Dong L., Du H. X., Fu D. G., Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 258, 1072—1080 |
| 41 | Bian R. X., Jiang Y., Wang Y., Sun J. K., Hu J. S., Jiang L., Liu H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(19), 1707408 |
| 42 | Kamat P. V., Jin S., ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3(3), 622—623 |
| 43 | Lin Z. Q., Yuan S. J., Li W. W., Chen J. J., Sheng G. P., Yu H. Q., Water Res., 2017, 109, 88—93 |
| 44 | Zhang R. T., He Y., Yi J., Zhang L. J., Shen C. P., Liu S. J., Liu L. F., Liu B. H., Qiao L., Chem, 2020, 6(1), 234—249 |
| 45 | Wu S., Xiao Y., Song P. P., Wang C., Yang Z. H., Slade R. C. T., Zhao F., Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 210, 117—121 |
| 46 | Van Trump J. I., Sun Y., Coates J. D., Adv. Appl. Microbiol., 2006, 60, 55—96 |
| 47 | Zhu W. H., Shi M. R., Yu D., Liu C. X., Huang T. L., Wu F. C., Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 23718 |
| 48 | Marsili E., Baron D. B., Shikhare I. D., Coursolle D., Gralnick J. A., Bond D. R., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, 105(10), 3968—3973 |
| 49 | Pan Q., Tian X. C., Li J. P., Wu X. E., Zhao F., Appl. Energy, 2021, 292, 116885 |
| 50 | Ren G. P., Sun Y., Ding Y., Lu A. H., Li Y., Wang C. Q., Ding H. R., Bioelectrochemistry, 2018, 123, 233—240 |
| 51 | Tashiro Y., Hirano S., Matson M. M., Atsumi S., Kondo A., Metab. Eng., 2018, 47, 211—218 |
| 52 | Tian S. H., Wang H. Q., Dong Z. W., Yang Y., Yuan H., Huang Q., Song T. S., Xie J. J., Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2019, 12, 71 |
| 53 | Hrenovic J., Milenkovic J., Ivankovic T., Rajic N., J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 201, 260—264 |
| 54 | Wang Y., Zhao Y. N., Wu J. L., Li M., Tan J., Fu W. S., Tang H., Zhang P., Nano Lett., 2021, 21(22), 9433—9441 |
| 55 | Nosaka Y., Nosaka A. Y., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(17), 11302—11336 |
| 56 | Yang R. Q., Yu X., Liu H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5), 1340—1356 |
| 杨瑞琪, 于欣, 刘宏. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5), 1340—1356 | |
| 57 | Chen X. Y., Feng Q. Y., Cai Q. H., Huang S. F., Yu Y. Q., Zeng R. J., Chen M., Zhou S. G., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2020, 54(17), 10820—10830 |
| 58 | Yang F., Zheng Y., Tian X. C., Liu Y., Li J. H., Shao Z. Z., Zhao F., Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 375, 137963 |
| 59 | Ji Z., Zhang H., Liu H., Yaghi O. M., Yang P. D., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2018, 115(42), 10582—10587 |
| 60 | Cornejo J. A., Sheng H., Edri E., Ajo⁃Franklin C. M., Frei H., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 2263 |
| 61 | Li Y. D., Chen L. X., Tian X. C., Lin L. F., Ding R., Yan W. F., Zhao F., Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 784, 147049 |
| 62 | Li G. Z., Park S., Kang D. W., Krajmalnik⁃Brown R., Rittmann B. E., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, 45(19), 8359—8367 |
| 63 | Xing Z. P., Zhou W., Du F., Qu Y., Tian G. H., Pan K., Tian C. G., Fu H. G., Dalton Trans., 2014, 43(2), 790—798 |
| 64 | Akbarzadeh R., Fung C. S. L., Rather R. A., Lo I. M. C., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 341, 248—261 |
| 65 | Liu M. H., Tao R., Li B., Li X. H., Han C. H., Li X. W., Shao C. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11), 2367—2374 |
| 刘美宏, 陶然, 李冰, 李兴华, 韩朝翰, 李晓伟, 邵长路. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(11), 2367—2374 | |
| 66 | Yu M. L., Wang J. J., Tang L., Feng C. Y., Liu H. Y., Zhang H., Peng B., Chen Z. M., Xie Q. Q., Water Res., 2020, 175, 115673 |
| 67 | Xiong H. F., Zou D. L., Zhou D. D., Dong S. S., Wang J. W., Rittmann B. E., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 316, 7—14 |
| 68 | Ding R., Yan W. F., Wu Y., Xiao Y., Gang H. Y., Wang S. H., Chen L. X., Zhao F., Water Research, 2018, 143, 589—598 |
| 69 | Zhang C. F., Fu L., Xu Z. X., Xiong H. F., Zhou D. D., Huo M. X., Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2017, 24(31), 24725—24731 |
| 70 | Zhou D. D., Xu Z. X., Dong S. S., Huo M. X., Dong S. S., Tian X. D., Cui B., Xiong H. F., Li T. T., Ma D. M., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(13), 7776—7783 |
| 71 | Zhou D. D., Dong S. S., Shi J. L., Cui X. C., Ki D. W., Torres C. I., Rittmann B. E., Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 317, 882—889 |
| 72 | Yan N., Chang L., Gan L., Zhang Y. M., Liu R., Rittmann B. E., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, 97(24), 10555—10561 |
| 73 | Shi H. F., Jiang X. B., Chen D., Li Y., Hou C., Wang L. J., Shen J. Y., Water Res., 2020, 187, 116464 |
| 74 | Liang Y. N., Jiao C. L., Pan L. S., Zhao T. Y., Liang J. X., Xiong J. H., Wang S. F., Zhu H. X., Chen G. N., Lu L. H., Song H. N., Yang Q. F., Zhou Q. Y., Environ. Res., 2021, 195, 110840 |
| 75 | Xiong J. H., Guo S. C., Zhao T. Y., Liang Y. N., Liang J. X., Wang S. F., Zhu H. X., Zhang L. M., Zhao J. R., Chen G. N., Cellulose, 2020, 27(6), 3391—3404 |
| 76 | Ding R., Wu Y., Yang F., Xiao X. F., Li Y. D., Tian X. C., Zhao F., J. Hazard. Mater., 2021, 416, 125857 |
| 77 | Liu C., Gallagher J. J., Sakimoto K. K., Nichols E. M., Chang C. J., Chang M. C. Y., Yang P. D., Nano Lett., 2015, 15(5), 3634—3639 |
| 78 | Xiao K. M., Liang J., Wang X. Y., Hou T. F., Ren X. N., Yin P. Q., Ma Z. P., Zeng C. P., Gao X., Yu T., Si T., Wang B., Zhong C., Jiang Z. F., Lee C. S., Yu J. C. M., Wong P. K., Energ. Environ. Sci., 2022, 15(2), 529—549 |
| 79 | Cui S., Tian L. J., Li J., Wang X. M., Liu H. Q., Fu X. Z., He R. L., Lam P. K. S., Huang T. Y., Li W. W., Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 428, 131254 |
| 80 | Huang S. F., Jing X. Y., Chen M., Zhou S. G., Sci. Sin. Tech., 2021, 51(4), 435—445 |
| 黄绍福,靖宪月, 陈曼, 周顺桂. 中国科学; 技术科学, 2021, 51(4), 435—445 | |
| 81 | Shi L., Dong H. L., Reguera G., Beyenal H., Lu A. H., Liu J., Yu H. Q., Fredrickson J. K., Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2016, 14(10), 651—662 |
| 82 | Baars O., Morel F. M. M., Zhang X. N., Environ. Microbiol., 2018, 20(5), 1667—1676 |
| 83 | Zhou X. X., Pan Y. J., Wang Y. B., Li W. F., J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 2007, 8(9), 686—692 |
| 84 | Soldatova A. V., Tao L. Z., Romano C. A., Stich T. A., Casey W. H., Britt R. D., Tebo B. M., Spiro T. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(33), 11369—11380 |
| 85 | Ren G. P., Yan Y. C., Nie Y., Lu A. H., Wu X. L., Li Y., Wang C. Q., Ding H. R., Front. Microbiol., 2019, 10, 293 |
| [1] | 王剑桥, 马於光. 有机半导体非平衡态HOMO和LUMO能量位移规律与OLED中“热激子”形成的唯象理解[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210856. |
| [2] | 田晓康, 张青松, 杨舒淋, 白洁, 陈冰洁, 潘杰, 陈莉, 危岩. 微生物发酵诱导多孔材料: 制备方法和应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [3] | 高晓乐, 王家信, 李志芳, 李艳春, 杨冬花. 复合材料NiOx-ZSM-5的制备及微生物电解池催化析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2886. |
| [4] | 梁雪静, 赵付来, 王宇, 张义超, 王亚玲, 冯奕钰, 封伟. 硫硒化亚锗光电探测器的制备及光电性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2661. |
| [5] | 林城策, 彭博宇, 李寒莹. 有机单晶电路的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1672. |
| [6] | 余丽莎, 李丹, 肖丽萍, 范杰. 沸石与蛋白质的相互作用及生物医用功能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(1): 311. |
| [7] | 孙辉, 赖小勇. 中空多壳层结构材料的制备及气体传感应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(5): 855. |
| [8] | 潘国勇,荔雅文,马立军,马宇帆,艾文婷,王振国,侯欣慧,戈里戈瑞·齐格亚诺夫,王卓. 基于正电荷和光热协同效应的新型半导体聚合物纳米抗菌材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4): 670. |
| [9] | 华涛, 李胜男, 李凤祥, 王浩楠. 生物电化学系统降解多环芳烃萘及微生物群落研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9): 1964. |
| [10] | 代红艳, 杨慧敏, 刘宪, 简选, 郭敏敏, 曹乐乐, 梁镇海. MoS2/石墨烯复合阴极材料的制备及微生物电解池催化产氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(2): 351. |
| [11] | 朱磊, 韩军燕, 常海珍, 邱宇渊, 张雅楠, 彭丹妮, 胡伟, MiaoShaobin. 二胺与二酮环聚合反应的不同途径与产物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(12): 2686. |
| [12] | 韩瑞霞, 吕继涛, 张淑贞. 一种适用于复杂异相体系中羟基自由基定量检测的探针分子—香豆素[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(12): 2658. |
| [13] | 刘阳, 付现伟, 赵天宇, 廉刚, 董宁, 宋思德, 王琪珑, 崔得良. 利用原位红外光谱研究钙钛矿复合半导体CH3NH3PbI3的稳定性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(9): 1605. |
| [14] | 马晓丹, 张志明, 于良民. 天然海水中聚吡咯膜的防微生物附着及防腐蚀性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2): 373. |
| [15] | 陈九菊. 有机半导体Terazulene单晶双极电荷传输性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(1): 121. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||