

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1847.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190166
收稿日期:2019-03-20
出版日期:2019-09-10
发布日期:2019-07-16
通讯作者:
金葆康
E-mail:bkjinhf@aliyun.com
基金资助:Received:2019-03-20
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-07-16
Contact:
JIN Baokang
E-mail:bkjinhf@aliyun.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用现场红外光谱电化学技术, 研究了2,6-二氯苯醌(DCBQ)和2,6-二甲氧基苯醌(DMOBQ)在乙腈溶液中对CO2的电化学捕获过程. 结果表明, 2种醌类衍生物在乙腈溶液中的电化学循环伏安(CV)曲线呈现2对氧化还原峰, 遵循连续两步单电子过程. 加入CO2后, 由于取代基亲电性的不同, 2种衍生物发生了不同的变化: DCBQ仍然呈现2对氧化还原峰, 但是第二对还原峰发生了正移动; 而DMOBQ的2对氧化还原峰变成1对峰. 根据现场红外光谱分析结果分别得到了DCBQ和DMOBQ电化学捕获CO2过程的不同机理. DCBQ是二价阴离子发生化学变化的电化学-电化学-化学(EEC)机理, 而DMOBQ则是还原产物一价阴离子自由基参与化学变化的电化学-化学-电化学(ECE)机理. 进一步对CO2捕获过程进行了定量分析, 得出2种反应的化学计量比均为1∶1.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
范慧, 金葆康. 醌类衍生物捕获CO2的红外光谱电化学研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9): 1847.
FAN Hui, JIN Baokang. Investigation on Electrochemical Capture of CO2 by Quinone Derivatives Based on in situ FTIR Spectroelectrochemistry †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1847.
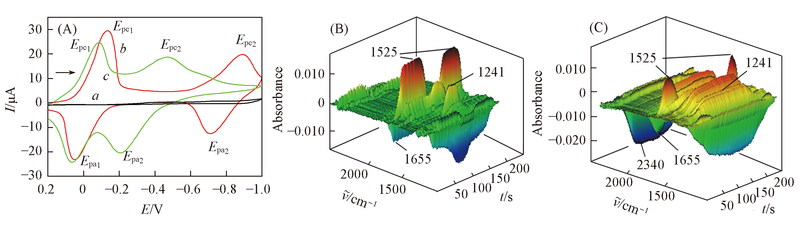
Fig.1 CV curves(A) in acetonitrile with saturated from CO2(a), DCBQ(b) and DCBQ+CO2(c) and the 3D spectra corresponding to curve b(B) and curve c(C) containing 10 mmol/L DCBQ, 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the supporting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
| System | Experimental peak position/cm-1 | Assignation | Calculated peak position/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DCBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1249, 1236 |
| 1525 | νC—C from DCBQ·- | 1521 | |
| 1655 | 1660 | ||
| DMOBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DMOBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1257, 1240 |
| 1627 | 1626, 1641 | ||
| 1697 | 1690 | ||
| CO2 | 2340 | 2346 |
Table 1 Attribution of IR absorption peaks in CH3CN
| System | Experimental peak position/cm-1 | Assignation | Calculated peak position/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DCBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1249, 1236 |
| 1525 | νC—C from DCBQ·- | 1521 | |
| 1655 | 1660 | ||
| DMOBQ in CH3CN | 1241 | νC—C from DMOBQ2-/νC—C from [DMOBQ-CO2]2- | 1257, 1240 |
| 1627 | 1626, 1641 | ||
| 1697 | 1690 | ||
| CO2 | 2340 | 2346 |
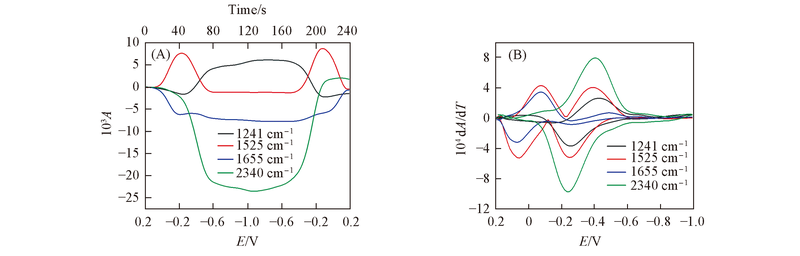
Fig.2 CVA(A) and DCVA(B) curves for DCBQ at 1241, 1525, 1655 and 2340 cm-1 To make the DCVA data readily comparable to CV, the DCVA of 1655 cm-1 and 2340 cm-1 was multiplied by -1, and 1525 cm-1 in the second reduction and first oxidation were multiplied by -1.
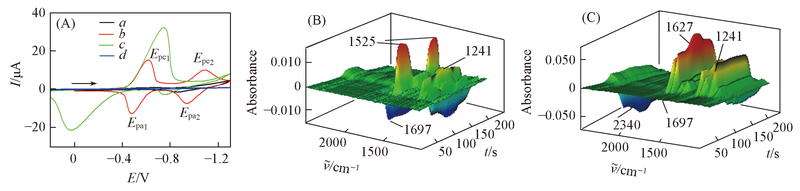
Fig.3 CV curves(A) in acetonitrile saturated from CO2(a), DMOBQ(b), DMOBQ + CO2(c) and the CV curve in acetonitrile without DMOBQ or CO2(d) and the 3D spectra corresponding to curve b(B) and curve c(C) containing 10 mmol/L DMOBQ, 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the suppor-ting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
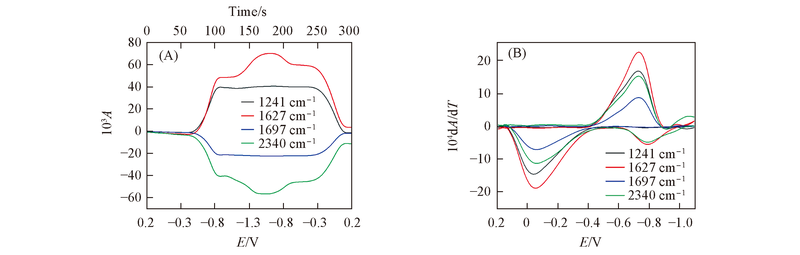
Fig.4 CVA(A) and DCVA(B) curves for DMOBQ at 1241, 1510 and 1697 cm-1 To make the DCVA data readily comparable to CV, the DCVA of 1697 cm-1 was multiplied by -1, and 1510 cm-1 in the second reduction and first oxidation were multiplied by -1.
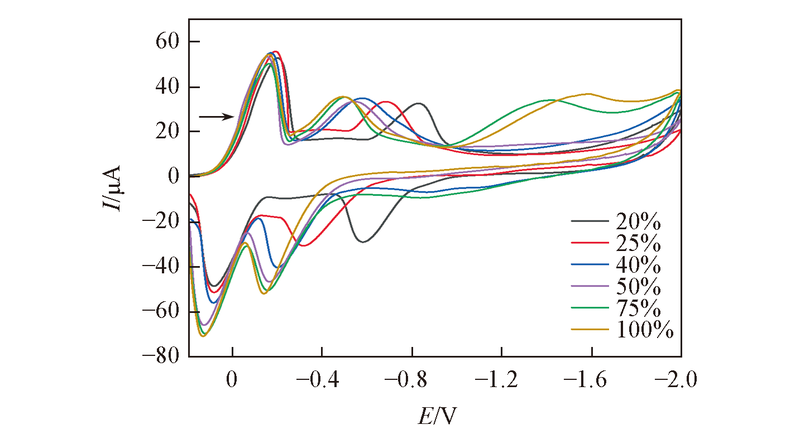
Fig.5 CV curves for DCBQ with varying percentage of saturated CO2 concentration in acetonitrile containing 20 mmol/L DCBQ and 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the supporting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
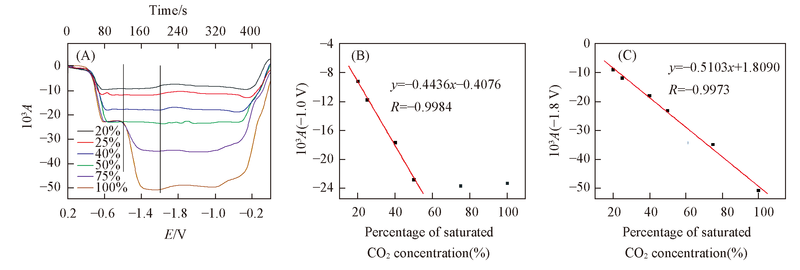
Fig.6 Corresponding CVA curve(A) for DCBQ at 2340 cm-1 and the linear fitting curve of absorbance value at 2340 cm-1 with percentage of saturated CO2 concentration at -1.00 V(B) and -1.80 V(C)
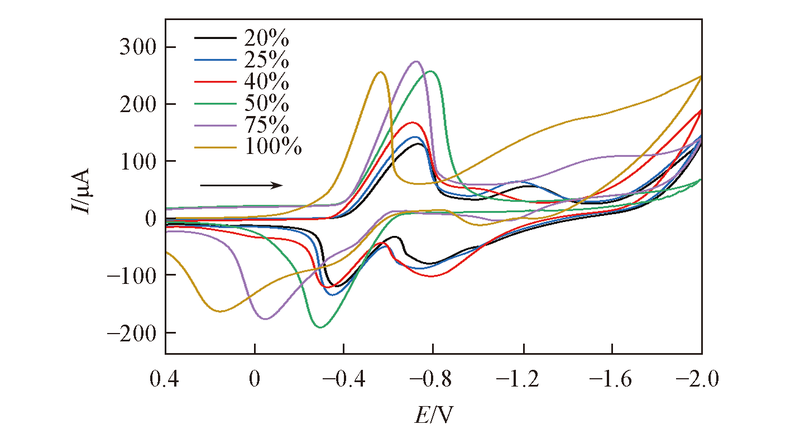
Fig.7 CV curve for DMOBQ with varying percentage of saturated CO2 concentration in acetonitrile containing 20 mmol/L DMOBQ and 0.2 mol/L TBAP as the supporting electrolyte The scan rate was 10 mV/s.
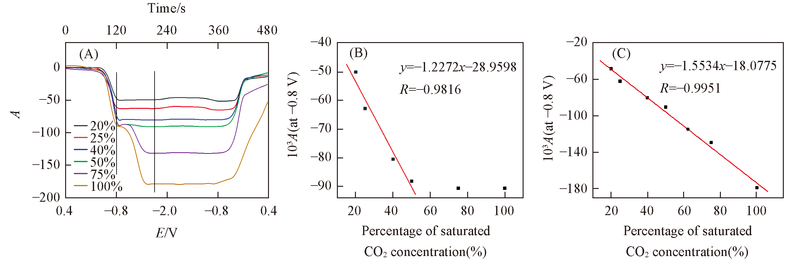
Fig.8 Corresponding CVA curve(A) for DMOBQ at 2340 cm-1 and the linear fitting curve of absorbance value at 2340 cm-1 with percentage of saturated CO2 concentration at -0.80 V(B) and-1.70 V(C)
| [1] | Ge Q. S., Liu Y., Wang F., Zheng J. Y., ,Acta Geographica Sinca, 2018,73( 1), 3— 12 |
| (葛全胜, 刘洋, 王芳, 郑景云.地理学报,2018,73(1), 3— 12) | |
| [2] | Nematollahi M. H., Carvalho P. J ., Current Opinion in Green and SustainableChemistry 2019, 18, 25— 30 |
| [3] | Liang X., Chen L. F., Zhang L., Su C. Y., ,Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018,63( 3), 248— 265 |
| (梁祥, 陈莲芬, 张利, 苏成勇, 科学通报.2018, 63(3), 248— 265) | |
| [4] | Lackner K. S., Brennan S., Matter J. M., Park A. H., Wright A., Zwaan B ., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109(33) 13156— 13162 |
| [5] | Haszeldine R. S ., Science 2009, 325( 5948), 1647— 1652 |
| [6] | Li P., Zhang J., Wang H., Hua J., Xu J., Sui X., Hu H., Yin H., ,. Catalysis Science & Technology 2014, 4( 4), 1070— 1077 |
| [7] | Li P., Wang H., Xu J., Jing H., Zhang J., Han H., Lu F ., Nanoscale 2013, 5( 23), 11748— 11754 |
| [8] | Rochelle G. T ., Science 2009, 325( 5948), 1652— 1654 |
| [9] | Wang M., Lawal A., Stephenson P., Sidders J., Ramshaw C ., Chemical Engineering Research & Design 2011, 89( 9), 1609— 1624 |
| [10] | Lu W., Ying Y., Shen W., Kong X., Ping L., Yu J., ,. Chemical Engineering Science 2013, 101( 14), 615— 619 |
| [11] | Du Y., Yuan Y., Rochelle G. T ., International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2017, 58, 1— 9 |
| [12] | Miedaner A., Curtis C. J., ,. Inorganic Chemistry 1994, 33( 24), 5482— 5490 |
| [13] | Durand W. J., Petrson A. A., Studt F., Abild-Pedersen F., Nϕrskow J. K., ,. Surface Science 2011, 605( 15), 1354— 1359 |
| [14] | Gattrell M., Gupta N., Co A., ,. Energy Conversion & Management 2007, 48( 4), 1255— 1265 |
| [15] | Li Q., Fu J., Zhu W., Chen Z., Shen B., Wu L., Xi Z., Wang T., Lu G., Zhu J. J ., Journal of the American Chemical Society 2017, 139( 12), 4290— 4293 |
| [16] | Yang D., Zhu Q., Sun X., Chen C., Han B., ,. Green Chemistry 2018, 20( 16), 3705— 3710 |
| [17] | Cao J., Lu H. Y., Chen C. F ., Tetrahedron 2009, 65( 39), 8104— 8112 |
| [18] | Buffinton G. D., Ollinger K., Brunmark A., Cadenas E., ,. Biochemical Journal 1989, 257( 2), 561— 571 |
| [19] | Chambers J. Q., ,. The Quinonoid Compounds 1988, 1, 719— 757 |
| [20] | Daves G. D., ,. Journal of Chemical Education 1975, 52( 7), A359— A360 |
| [21] | Jacq J., ,. Electrochimica Acta 1967, 12( 9), 1345— 1361 |
| [22] | Pourbaix M., Staehle R W. ., Electrochemical Kinetics, Plenum Press,New York, 1973 |
| [23] | Macías-Ruvalcaba N., Cuevas G., González I., Aguilar-Martínez M., ,. Journal of Organic Chemistry 2002, 67( 11), 3673— 3681 |
| [24] | Izumi Y., Sawada H., Sakka N., Yamamoto N., Kume T., Katsuki H., Shimohama S., Akaike A., ,. Journal of Neuroscience Research 2005, 79( 6), 849— 860 |
| [25] | Meganathan R., ,. Vitamins & Hormones 2001, 61( 1), 173— 218 |
| [26] | Verma C., Olasunkanmi L. O., Ebenso E. E., Quraishi M. A., ,. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2018, 251, 100— 118 |
| [27] | Mizen M. B., Wrighton M. S ., Journal of the Electrochemical Society 1989, 136( 4), 941— 946 |
| [28] | Versteeg P., Rubin E S ., Energy Procedia, 2011, 4, 1957— 1964 |
| [29] | Stern M. C., Simeon F., Hammer T., Landes H., Herzog H. J., Hatton T. A., ,. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 860— 867 |
| [30] | Ganesh K., Satheshkumar A., Balraj C., Elango K. P ., Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular & Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2013, 107( 15), 156— 166 |
| [31] | Jin B., Liu P., Wang Y., Zhang Z., Tian Y., Yang J., Zhang S., Cheng F ., The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2007, 111( 7), 1517— 1522 |
| [32] | Kvarnström C., Neugebauer H., Kuzmany H., Sitter H., Sariciftci N. S., ,. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 2001, 511( 1/2), 13— 19 |
| [33] | Gurkan B., Simeon F., Hatton T. A ., ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2015, 3( 7), 1394— 1405 |
| [34] | Becke A. D ., The Journal of Chemical Physics 1993, 98( 7), 5648— 5652 |
| [35] | Hahn S., Lee H., Cho M ., The Journal of Chemical Physics 2004, 121( 4), 1849— 1865 |
| [36] | Fabian J., Hartmann H ., Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry 2004, 17( 5), 359— 369 |
| [37] | And S. W. R., Yoo K. P., Lee J. S., Nam S. C., And J. E. S., Min B. M ., Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 1997, 42( 6), 1161— 1164 |
| [38] | Costentin C., Robert M., Saveant J. M., ,. Chemical Society Reviews 2013, 42( 6), 2423— 2436 |
| [1] | 杨静怡, 施思齐, 彭怀涛, 杨其浩, 陈亮. Ga-C3N4单原子催化剂高效光驱动CO2环加成[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220349. |
| [2] | 葛怡聪, 聂万丽, 孙国峰, 陈稼轩, 田冲. 银催化2-烯基苯胺与苯并异噁唑的[5+1]环化反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220142. |
| [3] | 姜胜寒, 曹长林, 肖荔人, 杨唐, 钱庆荣, 陈庆华. 基于紫外屏蔽性能的云母/MnO2/TiO2复合半导体微米片的制备及在聚丙烯中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [4] | 谭彦, 余申, 吕佳敏, 刘湛, 孙明慧, 陈丽华, 苏宝连. 介孔γ-Al2O3微球的高效制备及负载Pd催化剂的性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [5] | 夏雾, 任颖异, 刘京, 王锋. 壳聚糖包裹CdSe量子点组装体的水相可见光催化CO2还原[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [6] | 周雷雷, 程海洋, 赵凤玉. Pd基多相催化剂上CO2加氢反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [7] | 杨丹, 刘旭, 戴翼虎, 祝艳, 杨艳辉. 金团簇电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [8] | 赵盈喆, 张建玲. 金属-有机框架基材料在二氧化碳光催化转化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [9] | 丁杨, 王万辉, 包明. 多孔骨架固定分子催化剂催化CO2加氢制备甲酸研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [10] | 王茹涵, 贾顺涵, 吴丽敏, 孙晓甫, 韩布兴. CO2参与电化学构筑C—N键制备重要化学品[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220395. |
| [11] | 蒋小康, 周琦, 周恒为. Gd2ZnTiO6∶Dy3+, Eu3+单基质白光荧光粉的制备与发光性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220029. |
| [12] | 冯丽, 邵兰兴, 李思骏, 全文选, 庄金亮. 超薄Sm-MOF纳米片的合成及可见光催化降解芥子气模拟剂性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210867. |
| [13] | 王明智, 郑燕萍, 翁维正. CeO2负载的PdO与Ce1‒x Pd x O2‒δ 物种的甲烷催化燃烧性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210816. |
| [14] | 曹磊, 陈美君, 袁刚, 常钢, 张修华, 王升富, 何汉平. 冠醚功能化的栅控石墨烯场效应晶体管的制备及对汞离子的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [15] | 李华, 杨科, 黄俊峰, 陈凤娟. UiO-66-NH2/wood的设计构筑及高效去除水中微量重金属离子性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210701. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
