

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (7): 20240566.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240566
赵莹1,2, 董继程1,2, 方元1,2, 张立军3,4( ), 靳琳3,4, 刘波1,2, 程昉1,2(
), 靳琳3,4, 刘波1,2, 程昉1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-23
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-04-01
通讯作者:
张立军,程昉
E-mail:lijunzhangw@sina.com;ffcheng@dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHAO Ying1,2, DONG Jicheng1,2, FANG Yuan1,2, ZHANG Lijun3,4( ), JIN Lin3,4, LIU Bo1,2, CHENG Fang1,2(
), JIN Lin3,4, LIU Bo1,2, CHENG Fang1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-23
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-04-01
Contact:
ZHANG Lijun, CHENG Fang
E-mail:lijunzhangw@sina.com;ffcheng@dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
报道了一种对聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)及聚酯类材料表面改性的通用方法, 制备了具有广谱性和可持续后续反应活性的抗蛋白抗细菌涂层, 该方法克服了通过引入特定基团用于表面改性的限制. 分别采用一锅法和两步法在PMMA上聚合两性离子单体甲基丙烯酸磺基甜菜碱(SBMA), 元素分析结果表明, 经一锅法制备的PMMA-SBMA改性涂层的SBMA含量最高, 因此选择一锅法进行后续研究. 在聚对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯(PBT)有机玻片、 聚碳酸酯(PC)有机玻片、 聚对苯二甲酸-1,4-环己烷二甲醇酯(PCT)有机玻片和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)有机玻片等聚酯类材料的表面上验证了该方法的广谱性. Ellman’s assay定量研究结果表明, PMMA-SBMA改性涂层表面仍存在乙烯基砜基基团, 表明该涂层具有可持续后续反应活性. 采用石英晶体 微天平(QCM)评价了涂层抗牛血清白蛋白(BSA)吸附的能力, 结果表明, 一锅法涂层显著减少了72.3%的蛋 白质非特异性吸附; 静态涂层抗细菌黏附能力研究结果表明, 对于蜡样芽孢杆菌、 大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄 球菌, 静态下涂层细菌附着面积减少80%以上; 流动池和流场计算结果表明, 该涂层在两种剪切力(0.16和 1.6 dynes/cm2)的流动条件下均可以抵抗细菌附着.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
赵莹, 董继程, 方元, 张立军, 靳琳, 刘波, 程昉. 一锅法对PMMA及聚酯类材料的表面改性及抗生物垢性能评价. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(7): 20240566.
ZHAO Ying, DONG Jicheng, FANG Yuan, ZHANG Lijun, JIN Lin, LIU Bo, CHENG Fang. Surface Modification of PMMA and Polyester Materials by One-pot Method and Anti-biofouling Performance Evaluation of the Coatings. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(7): 20240566.
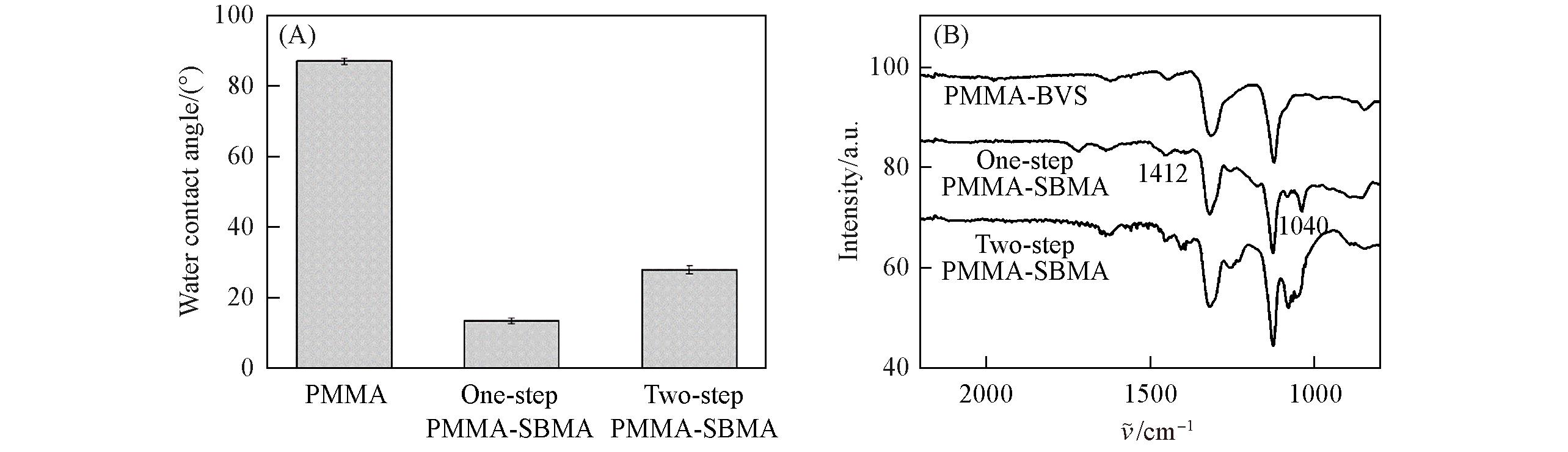
Fig.1 Water contact angles of PMMA surface and PMMA⁃SBMA modified coating prepared by one⁃pot method and two⁃step method(A) and FTIR spectra of PMMA⁃BVS modified coating and PMMA⁃SBMA modified coating prepared by one⁃pot method and two⁃step method(B)
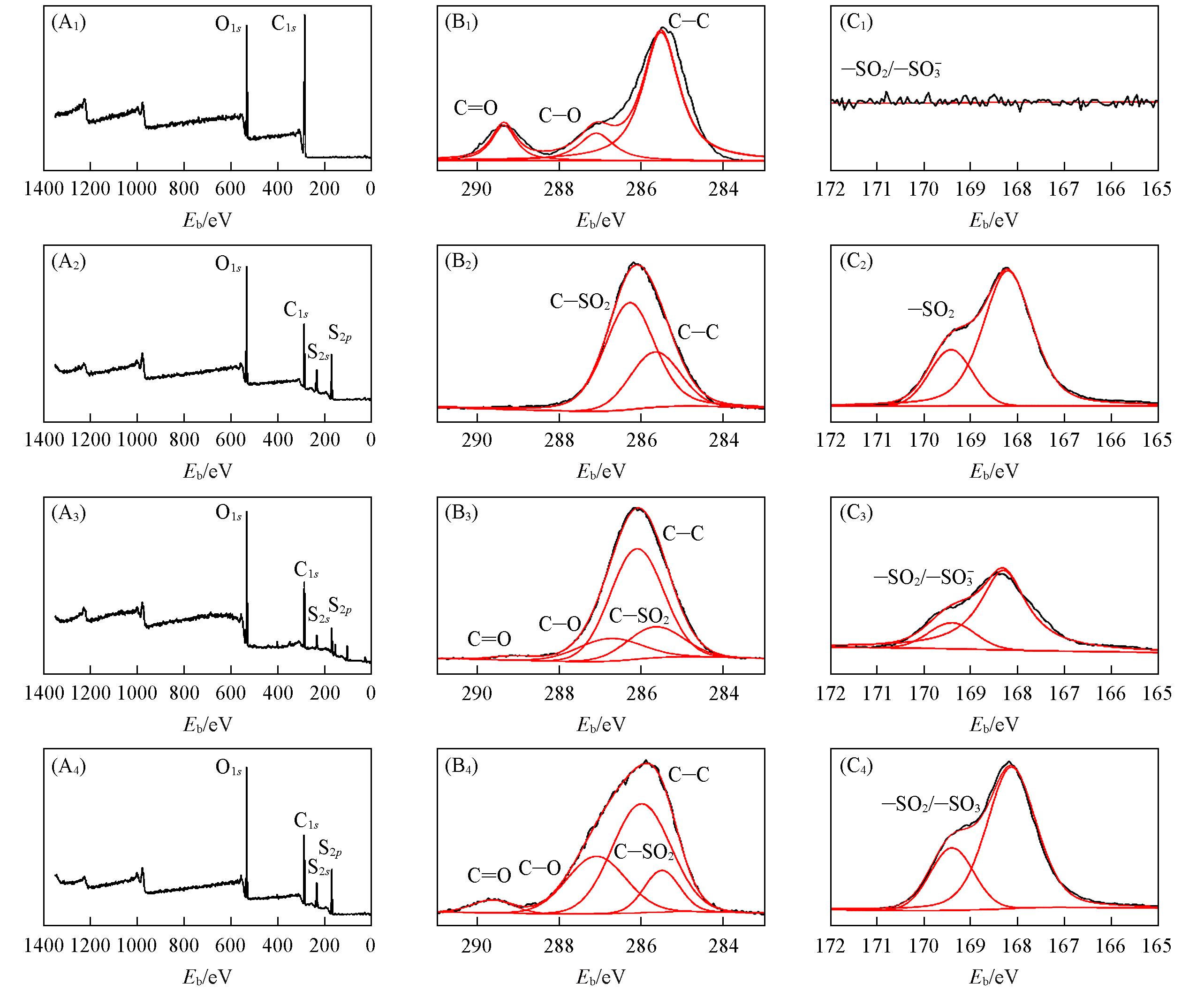
Fig.2 XPS characterization of PMMA surface(A1—C1), PMMA⁃BVS modified coating(A2—C2) and PMMA⁃SBMA modified coating prepared by two⁃step method(A3—C3) and one⁃pot method(A4—C4)(A1—A4) Full scan XPS spectra; (B1—B4) C1s high-resolution spectra; (C1—C4) S2p high-resolution spectra.
| Element(%) | C | O | N | S | Element(%) | C | O | N | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA | 77.4 | 22.4 | 0.2 | ND* | One⁃pot PMMA⁃SBMA | 60. 3 | 26. 7 | 4. 0 | 9. 0 |
| PMMA⁃BVS | 54.9 | 26.7 | 1.4 | 17.0 | Two⁃step PMMA⁃SBMA | 54.6 | 28.5 | 1.4 | 15.5 |
Table 1 Surface element proportion of PMMA surface modified by one-pot method and two-step method
| Element(%) | C | O | N | S | Element(%) | C | O | N | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA | 77.4 | 22.4 | 0.2 | ND* | One⁃pot PMMA⁃SBMA | 60. 3 | 26. 7 | 4. 0 | 9. 0 |
| PMMA⁃BVS | 54.9 | 26.7 | 1.4 | 17.0 | Two⁃step PMMA⁃SBMA | 54.6 | 28.5 | 1.4 | 15.5 |
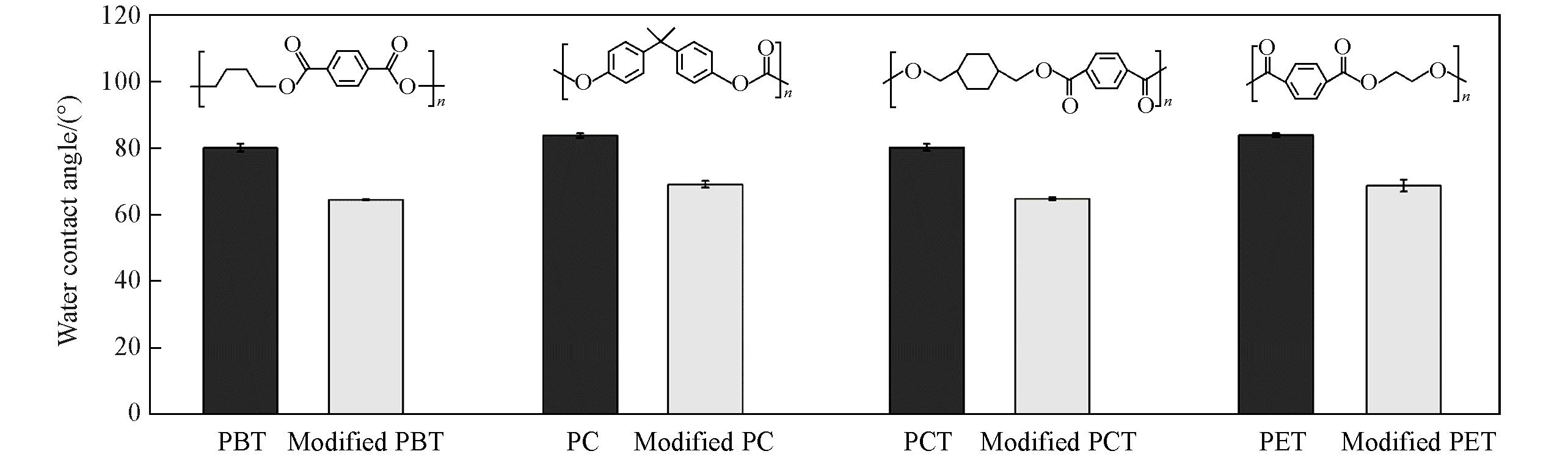
Fig.3 Water contact angle of the original surfaces and the surfaces modified by one⁃pot method of PBT, PC, PCT and PET organic slidesInsets: structures of PBT, PC, PCT and PET organic slides.
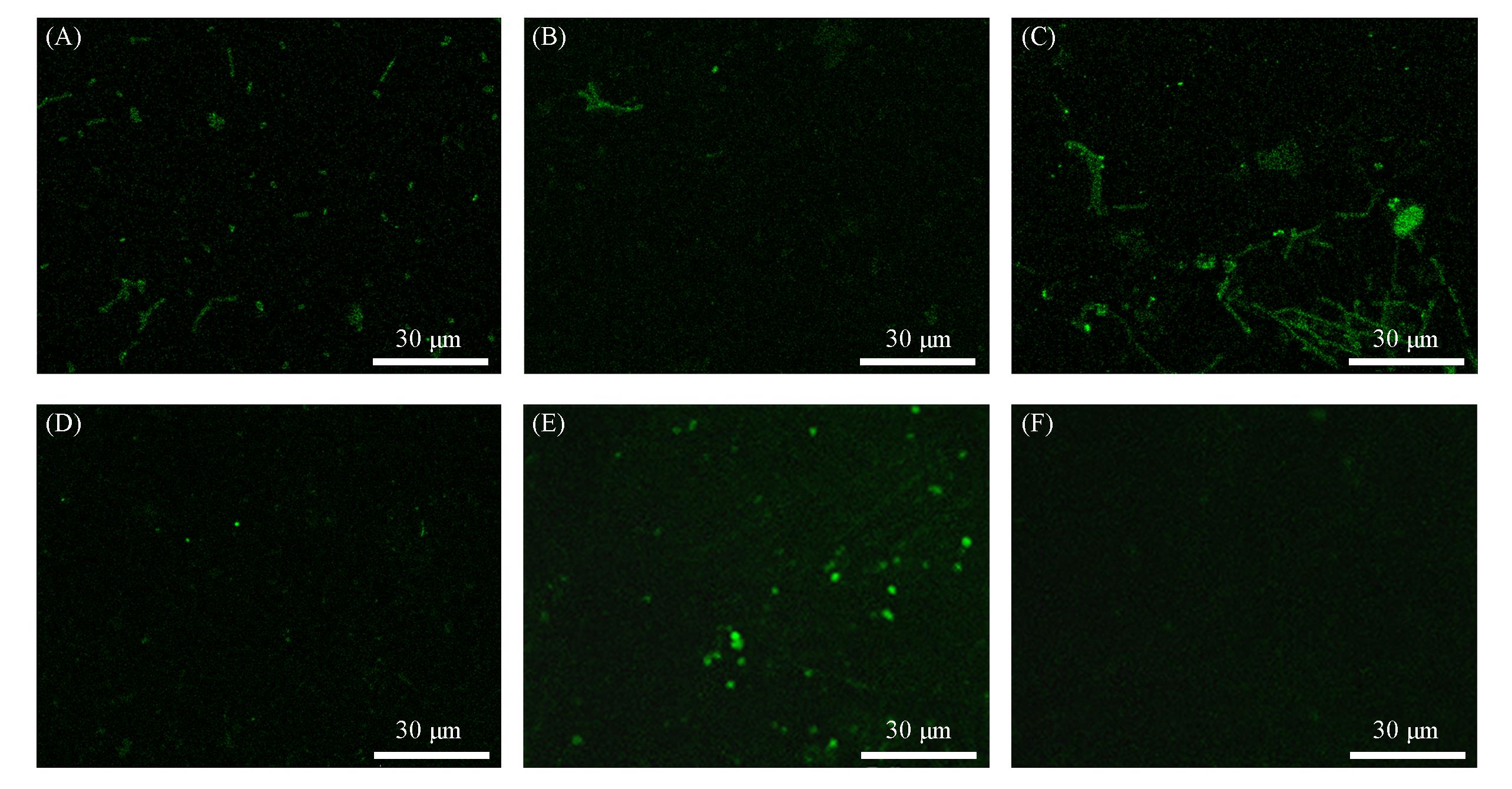
Fig.5 Bacillus cereus(A, B), Escherichia coli(C, D) and Staphylococcus aureus(E, F) attachments on PMMAsurface(A, C, E) and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface(B, D, F) under static conditions
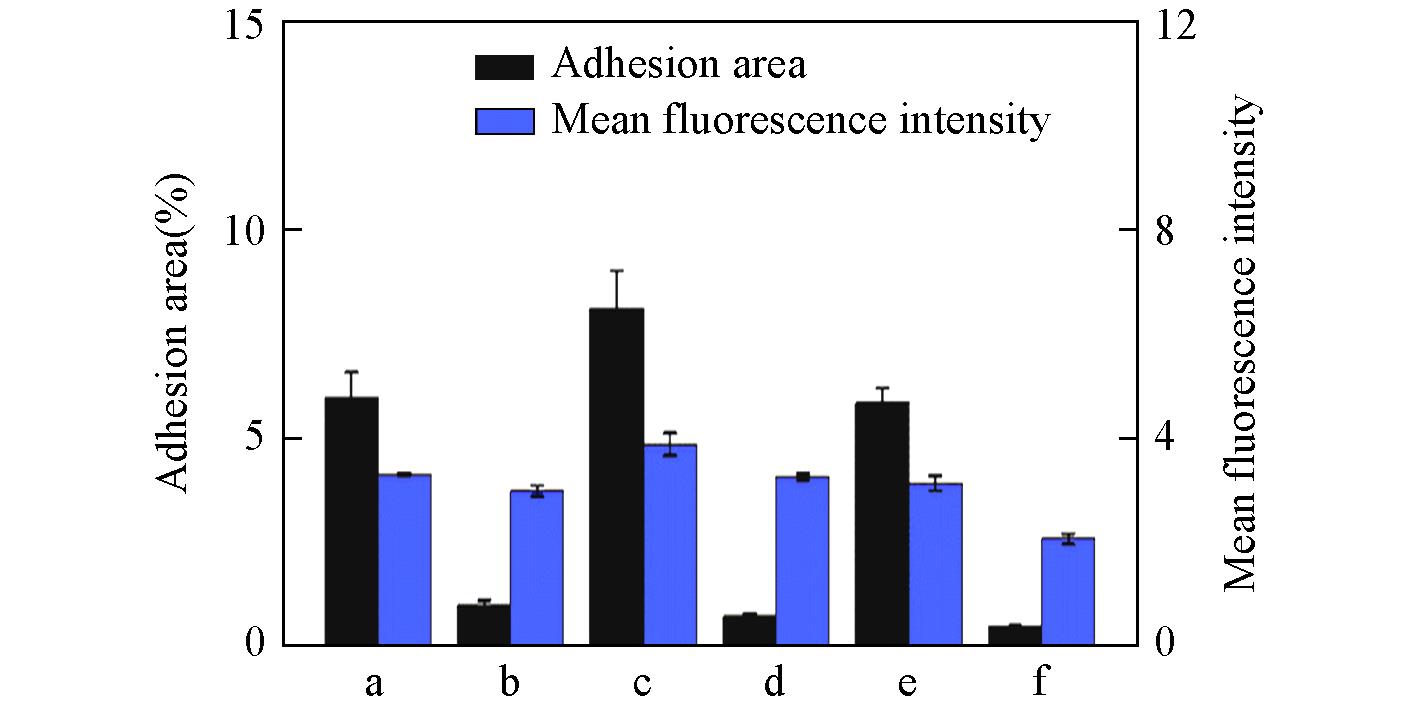
Fig.6 Adhesion area and mean fluorescence intensity of Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus on PMMA surface and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface under static conditionsa. Bacillus cereus on PMMA surface; b. Bacillus cereus on PMMA-SBMA surface; c. Escherichia coli on PMMA surface; d. Escherichia coli on PMMA-SBMA surface; e. Staphylococcus aureus on PMMA surface; f. Staphylococcus aureus on PMMA-SBMA surface.
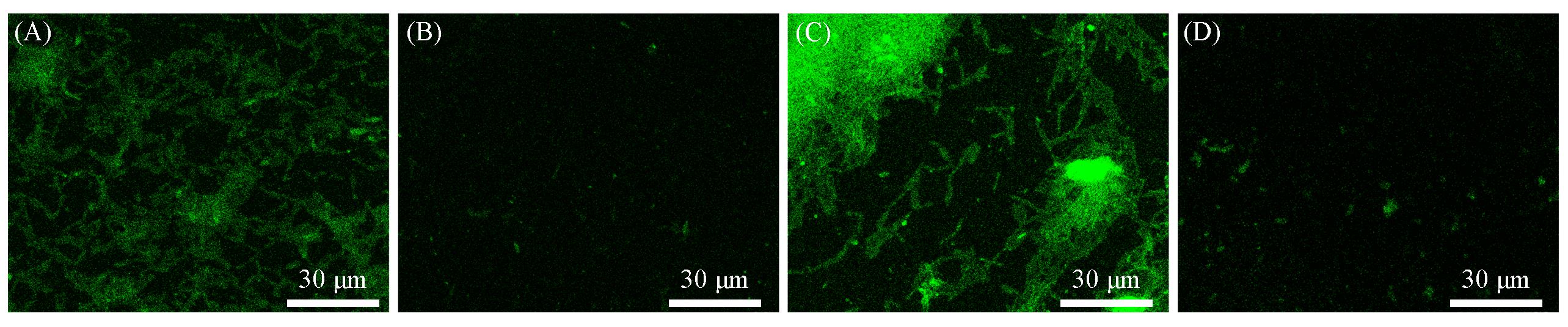
Fig.8 The attachment of Bacillus cereus to PMMA surface(A, C) and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface(B, D) at lower shear forces(A, B) and higher shear forces(C, D)
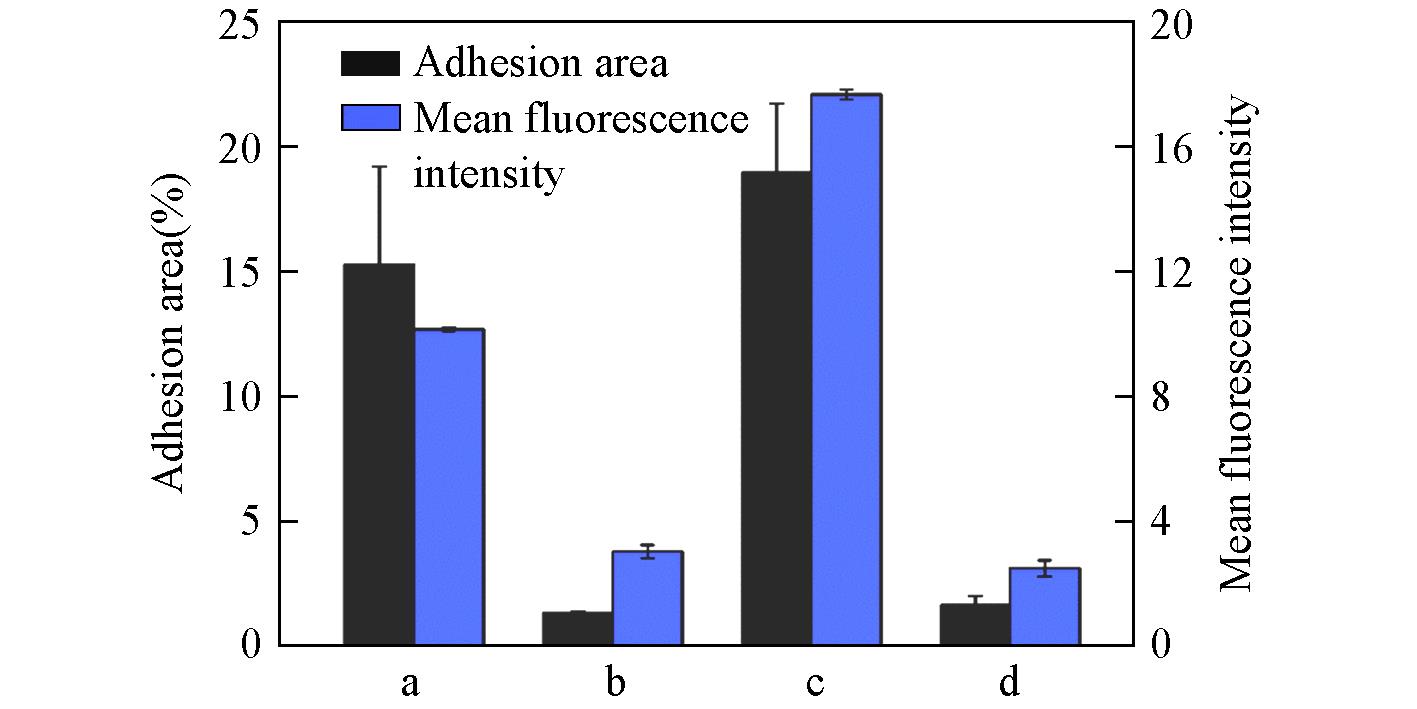
Fig.9 Adhesion area and mean fluorescence intensity of Bacillus cereus on PMMA surface and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface under flow conditiona. PMMA surface with lower shear forces; b. PMMA-SBMA surface with lower shear forces; c. PMMA surface with higher shear forces; d. PMMA-SBMA surface with higher shear forces.
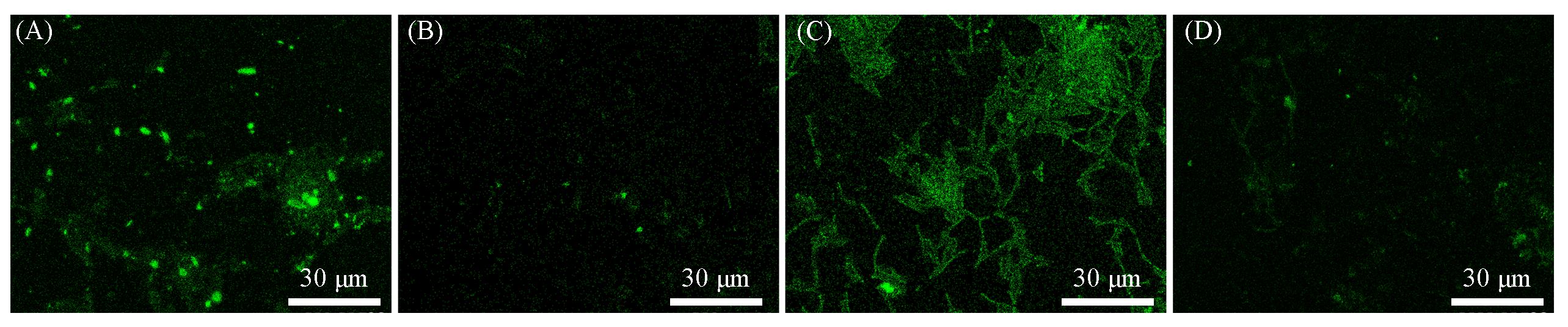
Fig.10 The attachment of Escherichia coli to PMMA surface(A, C) and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface(B, D) at lower shear force(A, B) and higher shear force(C, D)
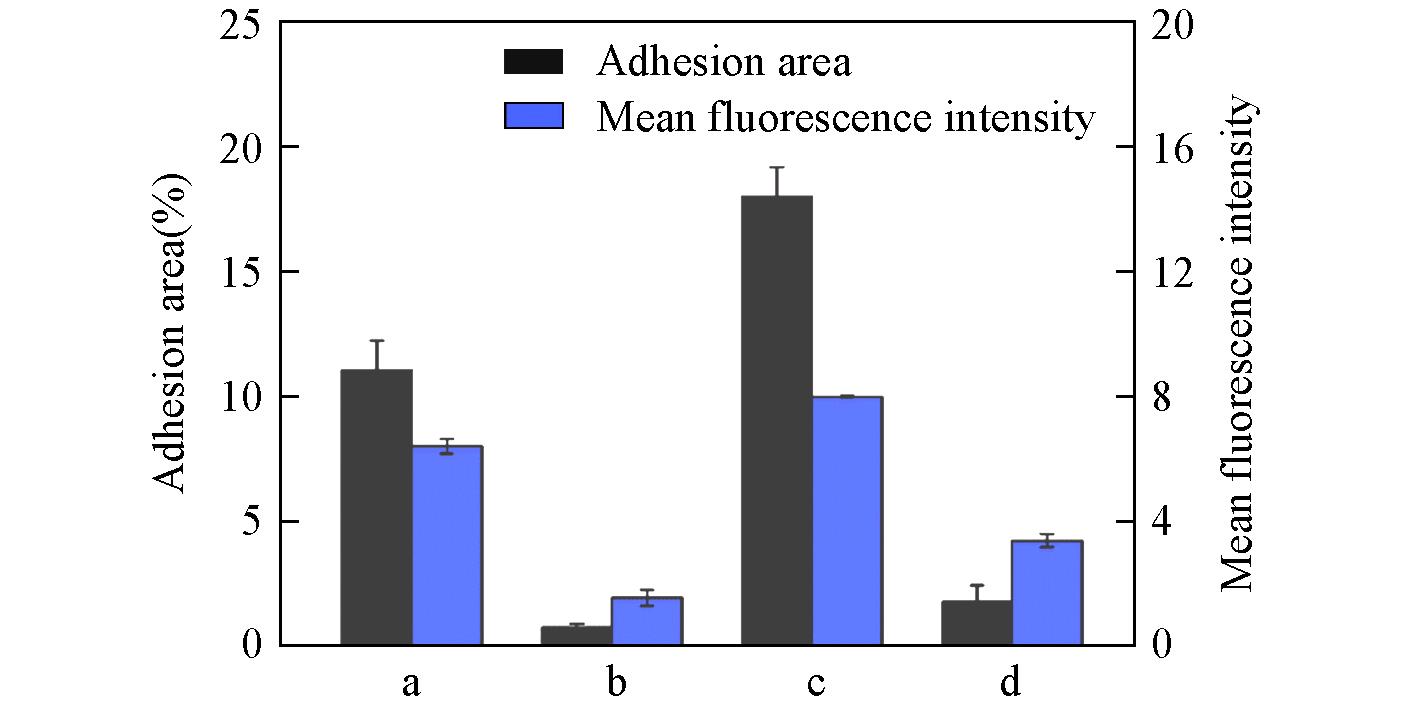
Fig.11 Adhesion area and mean fluorescence intensity of Escherichia coli on PMMA surface and PMMA⁃ SBMA modified surface under flow conditiona. PMMA surface with lower shear forces; b. PMMA-SBMA surface with lower shear forces; c. PMMA surface with higher shear forces; d. PMMA-SBMA surface with higher shear forces.
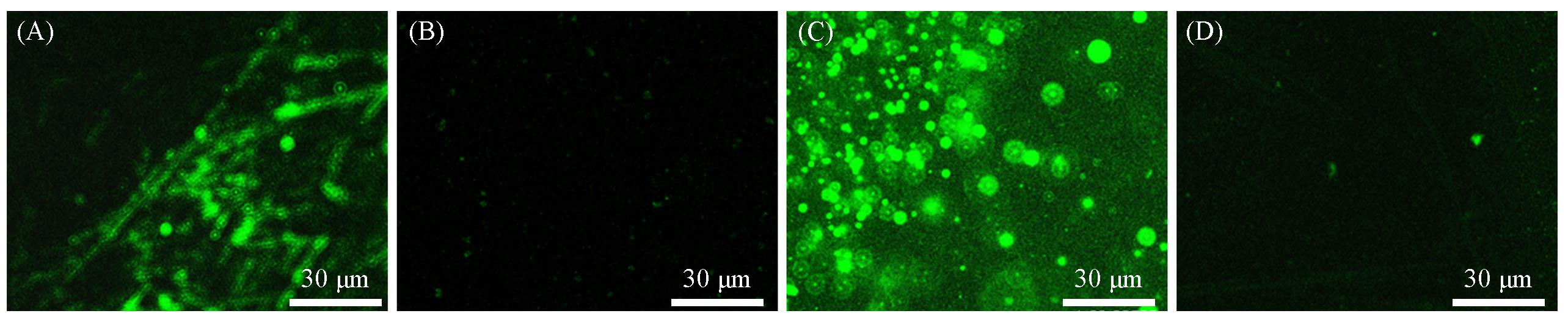
Fig.12 The attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to PMMA surface(A, C) and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface(B, D) at lower shear force(A, B) and higher shear force(C, D)
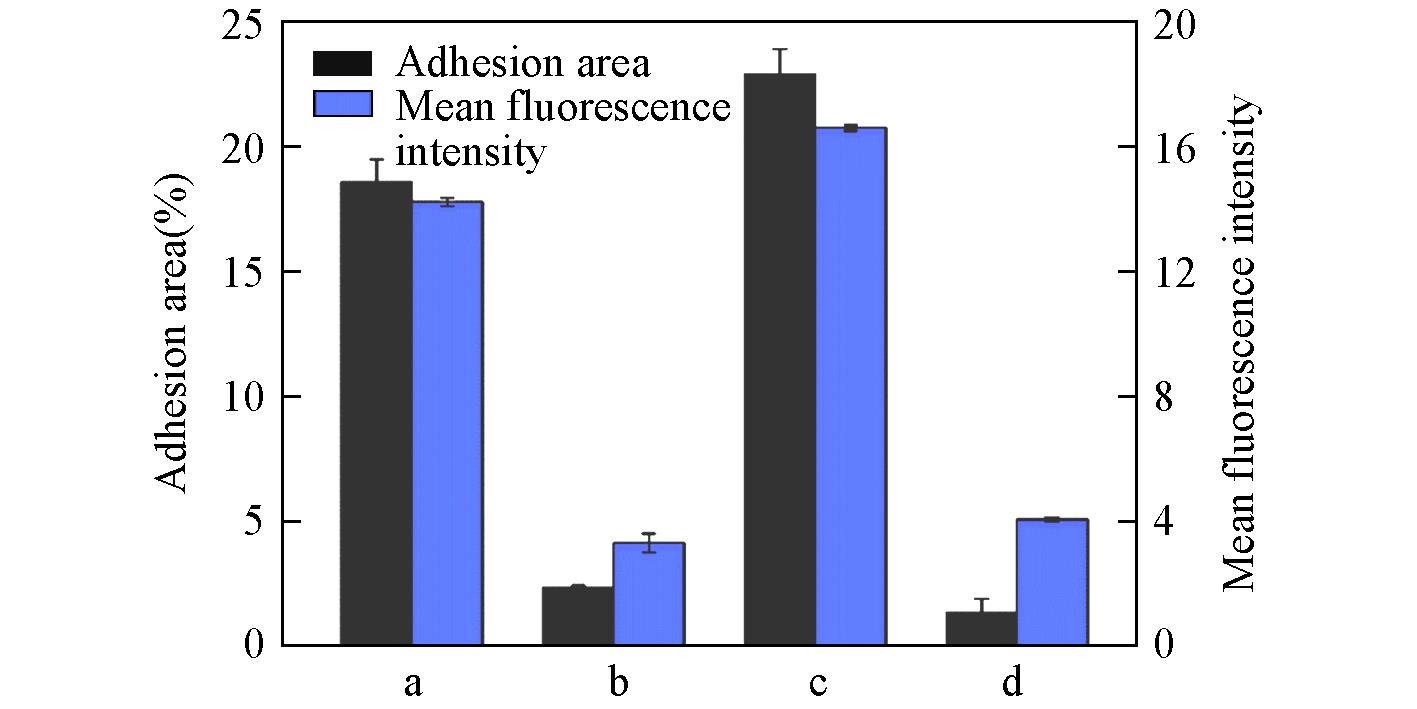
Fig.13 Adhesion area and mean fluorescence intensity of Staphylococcus aureus on PMMA surface and PMMA⁃SBMA modified surface under flow conditiona. PMMA surface with lower shear forces; b. SBMA surface with lower shear forces; c. PMMA surface with higher shear forces; d. SBMA surface with higher shear forces.
| [1] | Drury J. L., Mooney D. J., Biomater., 2003, 24, 4337—4351 |
| [2] | Nair L. S., Laurencin C. T., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2007, 32, 762—798 |
| [3] | Rezwan K., Chen Q. Z., Blaker J. J., Boccaccini A. R., Biomater., 2006, 27, 3413—3431 |
| [4] | Yu L., Wei M., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 944 |
| [5] | Souza J. C., Sordi M. B., Kanazawa M., Ravindran S., Henriques B., Silva F. S., Aparicio C., Cooper L. F., Acta Biomater., 2019, 94, 112—131 |
| [6] | Zafar M. S., Amin F., Fareed M. A., Ghabbani H., Riaz S., Khurshid Z., Kumar N., Biomimetics, 2020, 5(3), 34 |
| [7] | Chen S., Jiang S., Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 335—338 |
| [8] | Bu Y., Ma J., Bei J., Wang S., Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 2019, 7, 98 |
| [9] | Dahms H. U., Dobretsov S., Mar. Drugs., 2017, 15, 265 |
| [10] | Yousefi S. Z., Tabatabaei⁃Panah P., Seyfi J., Colloids Surf. B Biointerf., 2018, 167, 492—498 |
| [11] | Becker M. L., Burdick J. A., Chem. Rev., 2021, 121(18), 10789—10791 |
| [12] | Mishra S., Shah H., Patel A., Tripathi S. M., Malviya R., Prajapati B. G., ACS Omega, 2024, 9(1), 81—96 |
| [13] | Balaji A., Jaganathan S. K., Vellayappan M. V., John A. A., Subramanian A. P., Selvakumar M., Mohandas H., Raj S. M., Supriyanto E., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(85), 69660—69679 |
| [14] | Wang Y. Q., Qu X., Lu J., Zhu C. F., Wan L. J., Yang J. L., Bei J. Z., Wang S. G., Biomat., 2004, 25(19), 4777—4783 |
| [15] | Zhen S. J., Radiat. Phys. Chem., 2001, 60(4), 445—451 |
| [16] | Ko J., Cho K., Han S. W., Flan S. W., Sung H. K., Baek S. W., Koh W., Yoon J. S., Colloi. Surf. B Biointerf., 2017, 158, 287—294 |
| [17] | Zhang Y., Wang Z., Lin W., Sun H., Wu L., Chen S., J. Membr. Sci., 2013, 446, 164—170 |
| [18] | Song Q., Zhao R., Liu T., Gao L., Su C., Ye Y., Chan S. Y., Liu X., Wang K., Li P., Huang W., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 418, 129368 |
| [19] | Pereira C., Da Moura C. S., Carrado A., Falentin⁃Daudre C., Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp., 2022. 655, 130295 |
| [20] | Li D., Wei Q., Wu C., Zhang X., Xue Q., Zheng T., Cao M., Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2020, 278, 102141 |
| [21] | Zhang Z., Finlay J. A., Wang L., Gao Y., Callow J. A., Callow M. E., Jiang S., Langmuir, 2009, 25(23), 13516—13521 |
| [22] | Cao Y. Y., Ma J., Wu B. M., Xia M. S., Cheng S. F., J. Chem. Eng. Chinese Univ., 2020, 34(2), 512—518 |
| 曹耀匀, 马骏, 吴碧梅, 夏枚生, 陈圣福. 高校化学工程学报, 2020, 34(2), 512—518 | |
| [23] | Xin X., Jin X., Wang Y., Yuan J., Shen J., Mater. Lett., 2018, 218, 186—189 |
| [24] | Zhang J., Shen B., Chen L., Chen L., Mo J., Feng J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2019, 11(35), 31594—31604 |
| [25] | Zhang J., Qian S., Chen L., Chen L., Zhao L., Feng J., J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 85, 235—244 |
| [26] | Fang K., Wang R., Zhang H., Zhou L., Xu T., Xiao Y., Zhou Y., Gao G., Chen J., Liu D., ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2020, 12(47), 52307—52318 |
| [27] | Xu C., Liu L., Renneckar S., Jiang F., Ind. Crops Prod., 2021, 170, 113759 |
| [28] | Lin Y., Ting Y., Chen B., Cheng Y., Liu T., Surf. Coat. Technol., 2020, 391, 125663 |
| [29] | Sui X., Guo H., Chen P., Zhu Y., Wen C., Gao Y., Yang J., Zhang X., Zhang L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(7), 1907986 |
| [30] | Carr L., Cheng G., Xue H., Jiang S., Langmuir, 2010, 26(18), 14793—14798 |
| [31] | Ye Q., He B., Zhang Y., Zhang Y., Zhang J., Liu S., Zhou F., ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2019, 11(42), 39171—39178 |
| [32] | Liu Y., Zhang D., Ren B., Gong X., Xu L., Feng Z., Chang Y., He Y., Zheng J., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8(17), 3814—3828 |
| [33] | Guelses A., Lopar A., Es⁃Souni M., Emmert M., Es⁃Souni M., Behrens E., Naujokat H., Liedtke K. R., Acil Y., Wiltfang J., Florke C., Materials, 2021, 14(12), 3303 |
| [34] | Gu Y., Liu H., Dong X., Ma Z., Li Y., Li L., Gan D., Liu P., Shen J., Rare Met., 2022, 41(2), 700—712 |
| [35] | Cheng G., Zhang Z., Chen S., Bryers J. D., Jiang S., Biomaterials, 2007, 28(29), 4192—4199 |
| [36] | Zhu Z., Gao Q., Long Z., Huo Q., Ge Y., Vianney N., Daliko N. A., Meng Y., Qu J., Chen H., Bioact. Mater., 2021, 6(8), 2546—2556 |
| [37] | Yang L., Wu H., Liu Y., Xia Q., Yang Y., Chen N., Yang M., Luo R., Liu G., Wang Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 427, 130910 |
| [38] | Xu X., Wang K., Guo H., Sun G., Chen R., Yu J., Liu J., Lin C., Wang J., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2021, 588, 9—18 |
| [39] | Fromel M., Pester C. W., Macromolecules, 2022, 55(12), 4907—4915 |
| [40] | Li C., Li X., Tao C., Ren L., Zhao Y., Bai S., Yuan X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2017, 9(27), 22959—22969 |
| [41] | Aguiar A. O., Yi H., Asatekin A., J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 669, 121253 |
| [42] | Wang Y., Chen C., Wu X., Wang Z., Wen S., Yu J., Yan C., Cong W., Prog. Org. Coat., 2020, 144, 105666 |
| [43] | Lee S. Y., Lee Y., Thi P. L., Oh D. H., Park K. D., Biomater. Res., 2018, 22(1), 3 |
| [44] | Li M., Zhang W., Li J., Qi Y., Peng C., Wang N., Fan H., Li Y., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2023, 34(11), 108177 |
| [45] | Jin Q., Chen Y., Wang Y., Ji J., Colloids Surf. B Biointerf., 2014, 124, 80—86 |
| [46] | Liu B., Liu H., Cheng F., Liu C., Shao F., Li C., Cheng G., Wang H., Prog. Org. Coat., 2022, 172, 107081 |
| [47] | Ma X. C., Construction and Characterization of Controllable Surface Density Gradients on Silicon Materials, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, 2020 |
| 马晓春. 硅材料表面密度梯度的可控构建及表征, 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020 | |
| [48] | Cheng F., Ma X., Feng Q., Wang H., Yin M., He W., Biointerphases, 2019, 14(6), 61003 |
| [49] | Qin K., Xiang C., Cao L., Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol., 2011, 10(5), 743—754 |
| [50] | Xu G., Qin K. R., Liu Z. R., Chinese Quart. Mech., 2000, 1, 45—51 |
| 徐刚, 覃开蓉, 柳兆荣. 力学季刊, 2000, 1, 45—51 | |
| [51] | Liu C., Cheng F., He W., Acta Polym. Sin., 2023, 54(9), 1320—1332 |
| 刘冲, 程昉, 何炜. 高分子学报, 2023, 54(9), 1320—1332 | |
| [52] | Yang B., Wang C., Zhang Y., Ye L., Qian Y., Shu Y., Wang J., Li J., Yao F., Polym. Chem., 2015, 6(18), 3431—3442 |
| [53] | Riener C. K., Kada G., Gruber H. J., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2002, 373(4/5), 266—276 |
| [54] | Zhang Y., Silva D. M., Young P., Traini D., Li M., Ong H. X., Cheng S., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2022, 119(6), 1483—1497 |
| [55] | Moreira J. M. R., Araujo J. D. P., Miranda J. M., Simoes M., Melo L. F., Mergulhao F. J., Colloids Surf. B Biointerf., 2014, 123, 1—7 |
| [1] | 张兴红, 耿鹏, 向娟娟, 晏佳莹, 毛妙付, 肖述章. 一锅法合成可印刷室温磷光二氟化硼衍生物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(1): 20230432. |
| [2] | 冯瑞沁, 方云, 樊晔, 夏咏梅. 金纳米花的简易合成及催化硼氢化钠还原对硝基酚性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230027. |
| [3] | 刘玲, 姬发, 余林玲, 孙彦. 高效黏膜穿透的近红外光驱动的黏惰性纳米马达[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(6): 20220759. |
| [4] | 郝清海, 杨帆, 卿澈, 谭红革. 静电强度和反离子价态诱导的聚两性离子刷表面形貌[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230279. |
| [5] | 姬发, 刘玲, 余林玲, 孙彦. 黏惰化及酸敏感修饰对纳米粒子黏膜穿透的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20210837. |
| [6] | 杨兆华, 成鸿静, 杨弋, 刘辉, 杜飞鹏, 张云飞. 聚乙烯醇载银海绵的制备及界面光热驱动水蒸发性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220181. |
| [7] | 罗磊, 穆晓清, 吴涛, 聂尧, 徐岩. 一锅法合成去甲基麻黄素[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2458. |
| [8] | 韩一秀, 吴殿国, 李宏谱, 殷鸿尧, 梅拥军, 冯玉军, 钟祖勤. 低温非水环境中疏水缔合聚丙烯酸钠与两性离子表面活性剂的相互作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2056. |
| [9] | 彭新艳, 刘云鸿, 李嘉文, 冯乙胧, 王汉春. 单宁酸/两性离子改性油-水分离膜的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1337. |
| [10] | 曹锰, 柳阳, 张尚玺, 王振希, 徐胜. 壳聚糖钴配合物的合成及光催化产氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4): 735. |
| [11] | 崔思乾, 卢俊瑞, 谢志强, 卢博为, 刘金彪, 刘梅, 马瑶, 胡新龙, 李贾东. 吡唑并[2,3-c]吡喃酮衍生物的一锅法熔融合成[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(4): 688. |
| [12] | 张金, 史天彩, 罗力文, 刘佳, 刘荣, 刘乐, 梁明, 马养民. 纳米氧化铜催化一锅法合成β-咔啉类化合物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2411. |
| [13] | 刘豫龙, 路芳, 路萍. 基于芘并咪唑的电致发光材料的合成与表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(4): 583. |
| [14] | 张金, 刘佳, 马养民, 杨秀芳, 程佩, 范超, 卢萍. 纳米TiO2催化一锅法合成喹唑啉酮并酞嗪酮及3-酰胺基异吲哚酮并喹唑啉酮类化合物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(9): 1629. |
| [15] | 陈杰, 李小舟, 田华雨, 朱筱娟, 陈学思. 两性离子聚合物在恶性肿瘤治疗中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(11): 2148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||