

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 1761.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140037
收稿日期:2014-01-13
出版日期:2014-08-10
发布日期:2019-08-01
作者简介:联系人简介: 董永春, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事纺织化学与环保技术研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
LI Bing1, DONG Yongchun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2014-01-13
Online:2014-08-10
Published:2019-08-01
Contact:
DONG Yongchun
E-mail:teamdong@sina.cn
Supported by:摘要:
分别使用具有相似羧基含量的海藻纤维、 丙烯酸接枝改性聚四氟乙烯纤维和聚丙烯纤维(PAA-g-PP 和PAA-g-PTFE)3种含羧酸纤维与Fe3+进行配位反应, 研究和比较了反应的动力学特性及影响因素. 将3种含羧酸纤维铁配合物分别作为非均相Fenton反应催化剂应用于染料降解反应中, 分析和评价了其配位结构和表面性能对催化活性的影响. 结果表明, 在所涉及的温度和浓度范围内, 3种含羧酸纤维与Fe3+的反应均很好地符合Langmuir等温吸附模型和Lagergren准二级动力学方程. Fe3+初始浓度的增加会降低反应速率常数, 而反应温度的升高则会增加配合物中Fe3+的配合量. 在相同反应条件下, 海藻纤维比PAA-g-PP和PAA-g-PTFE更容易与Fe3+发生反应, 且反应速率常数和Fe3+配合量按照下列顺序排列: 海藻纤维>PAA-g-PP>PAA-g-PTFE. 3种含羧酸纤维铁配合物都能够在染料氧化降解反应中作为非均相Fenton催化剂, 且紫外光比可见光更能够提高其催化活性. 海藻纤维铁配合物比其它2种含羧酸纤维铁配合物具有更好的催化作用, 这与三者在配位结构和表面性能之间的显著差异有关.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李冰, 董永春. 不同含羧酸纤维与铁离子的配位反应动力学及配合物的催化降解性能. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1761.
LI Bing, DONG Yongchun. Coordination Kinetics of Different Carboxylic Fiber with Fe3+ and Catalytic Degradation Performance of Their Fe3+ Complexes†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1761.
| Carboxylic fiber | ACOOH/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 2.23 | 0.286 | 48.3 |
| PAA-g-PP | 2.27 | 0.251 | 85.8 |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 2.35 | 0.178 | 91.1 |
Table 1 ACOOH values and surface properties of three carboxylic fibers
| Carboxylic fiber | ACOOH/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 2.23 | 0.286 | 48.3 |
| PAA-g-PP | 2.27 | 0.251 | 85.8 |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 2.35 | 0.178 | 91.1 |
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | kL/(L·mmol-1) | Qm/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.4389ce/(1+0.1389ce) | 0.1389 | 3.16 | 0.9877 |
| 35 | Qe=0.2708ce/(1+0.1231ce) | 0.1231 | 2.20 | 0.9856 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1158ce/(1+1.1007ce) | 0.1007 | 1.15 | 0.9898 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.1400ce/(1+0.0625ce) | 0.0625 | 2.24 | 0.9862 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0705ce/(1+0.0538ce) | 0.0538 | 1.31 | 0.9933 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0367ce/(1+0.00448ce) | 0.0448 | 0.82 | 0.9861 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.1195ce/(1+0.0561ce) | 0.0561 | 2.13 | 0.9930 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0489ce/(1+0.0457ce) | 0.0457 | 1.07 | 0.9962 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0212ce/(1+0.0365ce) | 0.0365 | 0.58 | 0.9876 |
Table 2 Parameters and equations for Langmuir adsorption isothermals of Fe3+ onto three carboxylic fibers
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | kL/(L·mmol-1) | Qm/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.4389ce/(1+0.1389ce) | 0.1389 | 3.16 | 0.9877 |
| 35 | Qe=0.2708ce/(1+0.1231ce) | 0.1231 | 2.20 | 0.9856 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1158ce/(1+1.1007ce) | 0.1007 | 1.15 | 0.9898 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.1400ce/(1+0.0625ce) | 0.0625 | 2.24 | 0.9862 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0705ce/(1+0.0538ce) | 0.0538 | 1.31 | 0.9933 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0367ce/(1+0.00448ce) | 0.0448 | 0.82 | 0.9861 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.1195ce/(1+0.0561ce) | 0.0561 | 2.13 | 0.9930 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0489ce/(1+0.0457ce) | 0.0457 | 1.07 | 0.9962 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0212ce/(1+0.0365ce) | 0.0365 | 0.58 | 0.9876 |
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | n | kF | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.8929 | 3.720 | 0.8929 | 0.9258 |
| 35 | Qe=0.6090 | 3.697 | 0.6090 | 0.9579 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.3050 | 3.671 | 0.3050 | 0.9733 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.3707 | 2.664 | 0.3707 | 0.9710 |
| 35 | Qe=0.1998 | 2.656 | 0.1998 | 0.9530 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1051 | 2.460 | 0.1051 | 0.9464 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.3103 | 2.565 | 0.3103 | 0.9682 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0137 | 2.452 | 0.1376 | 0.9750 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0640 | 2.356 | 0.0640 | 0.9465 |
Table 3 Parameters and equations for Freundlich adsorption isothermals of Fe3+ onto three carboxylic fibers
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | n | kF | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.8929 | 3.720 | 0.8929 | 0.9258 |
| 35 | Qe=0.6090 | 3.697 | 0.6090 | 0.9579 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.3050 | 3.671 | 0.3050 | 0.9733 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.3707 | 2.664 | 0.3707 | 0.9710 |
| 35 | Qe=0.1998 | 2.656 | 0.1998 | 0.9530 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1051 | 2.460 | 0.1051 | 0.9464 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.3103 | 2.565 | 0.3103 | 0.9682 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0137 | 2.452 | 0.1376 | 0.9750 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0640 | 2.356 | 0.0640 | 0.9465 |
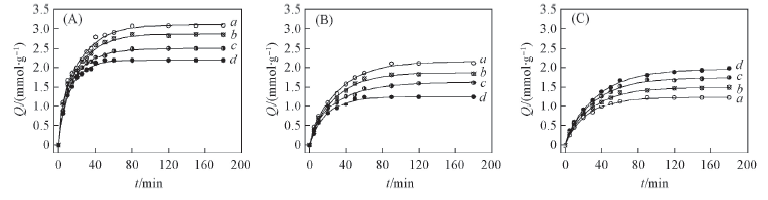
Fig.3 Coordination kinetics curves at different initial concentrations of Fe3+ on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE fibers(C) Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
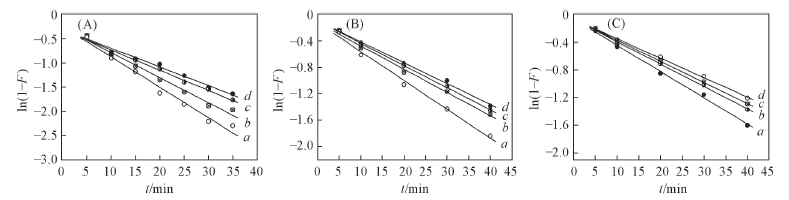
Fig.4 Simulation curves of Lagergren pseudo first-order equation plots on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE fibers(C) Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
| Fiber | c0/(mmol ·L-1) | Rate equation | k1 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0628t | 0.0628 | 0.9807 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0517t | 0.0517 | 0.9833 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0417t | 0.0417 | 0.9907 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0387t | 0.0387 | 0.9852 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0437t | 0.0437 | 0.9916 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0353t | 0.0353 | 0.9940 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0336t | 0.0336 | 0.9975 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0316t | 0.0316 | 0.9962 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0380t | 0.0380 | 0.9967 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0223t | 0.0323 | 0.9989 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0305t | 0.0305 | 0.9989 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0281t | 0.0281 | 0.9984 |
Table 4 Results from linear regression of Lagergren pseudo first-order equation plots
| Fiber | c0/(mmol ·L-1) | Rate equation | k1 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0628t | 0.0628 | 0.9807 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0517t | 0.0517 | 0.9833 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0417t | 0.0417 | 0.9907 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0387t | 0.0387 | 0.9852 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0437t | 0.0437 | 0.9916 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0353t | 0.0353 | 0.9940 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0336t | 0.0336 | 0.9975 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0316t | 0.0316 | 0.9962 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0380t | 0.0380 | 0.9967 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0223t | 0.0323 | 0.9989 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0305t | 0.0305 | 0.9989 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0281t | 0.0281 | 0.9984 |
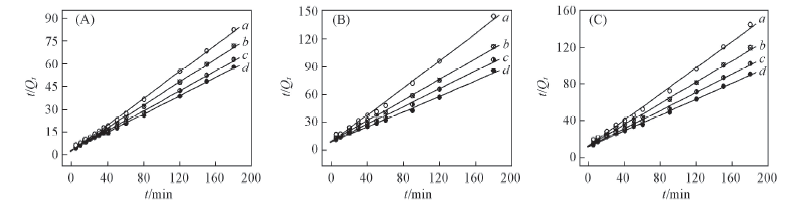
Fig.5 Simulation curves of Lagergren pseudo second-order equation plots on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE fibers(C) Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | k2 | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginatefiber | 30 | t/Qt=2.470+t/2.28 | 0.0781 | 2.28 | 0.9985 |
| 60 | t/Qt=2.943+t/2.64 | 0.0487 | 2.64 | 0.9991 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=2.979+t/3.04 | 0.0364 | 3.04 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=3.096+t/3.32 | 0.0293 | 3.32 | 0.9985 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | t/Qt=8.941+t/1.37 | 0.0598 | 1.37 | 0.9947 |
| 60 | t/Qt=9.936+t/1.80 | 0.0311 | 1.80 | 0.9983 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=9.020+t/2.09 | 0.0255 | 2.09 | 0.9970 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=9.898+t/2.42 | 0.0173 | 2.42 | 0.9976 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | t/Qt=12.665+t/1.40 | 0.0404 | 1.40 | 0.9962 |
| 60 | t/Qt=12.726+t/1.71 | 0.0268 | 1.71 | 0.9968 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=11.838+t/2.01 | 0.0209 | 2.01 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=11.628+t/2.29 | 0.0164 | 2.29 | 0.9984 |
Table 5 Results from linear regression of Lagergren pseudo second-order equation plots
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | k2 | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginatefiber | 30 | t/Qt=2.470+t/2.28 | 0.0781 | 2.28 | 0.9985 |
| 60 | t/Qt=2.943+t/2.64 | 0.0487 | 2.64 | 0.9991 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=2.979+t/3.04 | 0.0364 | 3.04 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=3.096+t/3.32 | 0.0293 | 3.32 | 0.9985 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | t/Qt=8.941+t/1.37 | 0.0598 | 1.37 | 0.9947 |
| 60 | t/Qt=9.936+t/1.80 | 0.0311 | 1.80 | 0.9983 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=9.020+t/2.09 | 0.0255 | 2.09 | 0.9970 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=9.898+t/2.42 | 0.0173 | 2.42 | 0.9976 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | t/Qt=12.665+t/1.40 | 0.0404 | 1.40 | 0.9962 |
| 60 | t/Qt=12.726+t/1.71 | 0.0268 | 1.71 | 0.9968 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=11.838+t/2.01 | 0.0209 | 2.01 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=11.628+t/2.29 | 0.0164 | 2.29 | 0.9984 |
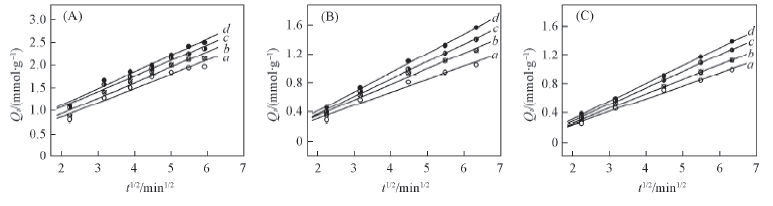
Fig.6 Simulation curves of intra-particle diffusion equation plots on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE(C) fibers Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | kp | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | Qt=0.3121t1/2 | 0.3121 | 0.9486 |
| 60 | Qt=0.3414t1/2 | 0.3415 | 0.9597 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.3428t1/2 | 0.3428 | 0.9787 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.3637t1/2 | 0.3637 | 0.9771 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | Qt=0.1816t1/2 | 0.1816 | 0.9692 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2176t1/2 | 0.2176 | 0.9861 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2436t1/2 | 0.2436 | 0.9957 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2693t1/2 | 0.2693 | 0.9983 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | Qt=0.1767t1/2 | 0.1767 | 0.9943 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2008t1/2 | 0.2008 | 0.9952 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2287t1/2 | 0.2287 | 0.9991 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2466t1/2 | 0.2466 | 0.9995 |
Table 6 Results from linear regression of intra-particle diffusion equation plots
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | kp | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | Qt=0.3121t1/2 | 0.3121 | 0.9486 |
| 60 | Qt=0.3414t1/2 | 0.3415 | 0.9597 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.3428t1/2 | 0.3428 | 0.9787 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.3637t1/2 | 0.3637 | 0.9771 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | Qt=0.1816t1/2 | 0.1816 | 0.9692 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2176t1/2 | 0.2176 | 0.9861 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2436t1/2 | 0.2436 | 0.9957 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2693t1/2 | 0.2693 | 0.9983 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | Qt=0.1767t1/2 | 0.1767 | 0.9943 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2008t1/2 | 0.2008 | 0.9952 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2287t1/2 | 0.2287 | 0.9991 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2466t1/2 | 0.2466 | 0.9995 |
| Complex | Q/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-ALG | 2.32 | 0.248 | 82.1 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PP | 2.37 | 0.263 | 100.3 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PTFE | 2.29 | 0.151 | 104.6 |
Table 7 Q values and surface properties of three carboxylic fiber-Fe(Ⅲ) complexes
| Complex | Q/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-ALG | 2.32 | 0.248 | 82.1 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PP | 2.37 | 0.263 | 100.3 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PTFE | 2.29 | 0.151 | 104.6 |
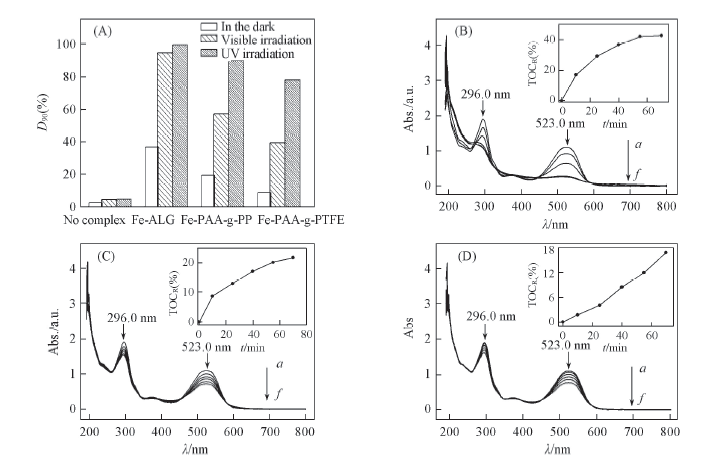
Fig.7 Decoloration rate and mineralization of RR 195 in the presence of different complexes (A) D90 values under different irradiation; (B—D) UV-Vis spectra and TOCR(%) of dye degradation with Fe-ALG(B), Fe-PAA-g-PP(C) and Fe-PAA-g-PTFE(D), respectively. (B—D) t/min: a. 0; b. 10; c. 25; d. 40; e. 55; f. 70.
| [1] | Espenson J.H., Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanisms, 2nd Ed., McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, 1995 |
| [2] | Xu Y., Chemical Reaction Kinetics, Press of Chemical Industry, Beijing, 2005 |
| (许越. 化学反应动力学. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005) | |
| [3] | Song X. P., Huang M. Y., Jiang Y. Y., Journal of Functional Polymers, 1994, 7(2), 136—141 |
| (宋啸平, 黄美玉, 江英彦. 功能高分子学报, 1994, 7(2), 136—141) | |
| [4] | Ishtchenko V. V., Huddsman K. D., Vitkovskaya R. F., Appl. Catal. A., 2003, 242, 123—137 |
| [5] | Tao T. X., Wu Z. C., Wang X. Q., Li M. S., Zhang J. H., Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2006, 3, 387—390 |
| (陶庭先, 吴之传, 汪学骞, 李梅生, 张俊华. 高分子学报, 2006, 3, 387—390) | |
| [6] | Dong Y. C., Du F., Han Z. B., Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2008, 24(11), 2114—2121 |
| (董永春, 杜芳, 韩振邦. 物理化学学报, 2008, 24(11), 2114—2121) | |
| [7] | Dong Y. C., Zhao J. Z., Hou C. Y., Wu D. Z., Journal of Sichuan University(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 41(4), 125—131 |
| (董永春, 赵娟芝, 侯春燕, 吴多智, 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2009, 41(4), 125—131) | |
| [8] | Zhang Y., Wu Z. C., Tao T. X., Tong W., Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 25(7), 1299—1303 |
| (张勇, 吴之传, 陶庭先, 童伟, 无机化学学报, 2009, 25(7), 1299—1303) | |
| [9] | Liu X., Tang R., He Q., Liao X., Shi B., J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 174, 687—693 |
| [10] | Dong Y., Han Z., Liu C., Du F., Sci. Total Environ., 2010, 408, 2245—2253 |
| [11] | Dong Y., Han Z., Dong S., Wu J., Ding Z., Catal. Today, 2011, 175, 299—309 |
| [12] | Li B., Dong Y., Ding Z., Color. Technol., 2013, 129, 403—411 |
| [13] | Ding Z. Z., Dong Y. C., Li B., Li M., Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2013, 29(1), 157—166 |
| (丁志忠, 董永春, 李冰, 李淼.物理化学学报, 2013, 29(1), 157—166) | |
| [14] | Han Z. B., Dong Y. C., Liu C. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 5(11), 986—993 |
| (韩振邦, 董永春, 刘春燕. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 5(11), 986—993) | |
| [15] | Ding Y. Y., Wang C. Z., Wen X. F., Zhang X. P., Ye L., Zhang A. Y., Feng Z. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7), 1758—1764 |
| (丁耀莹, 王成志, 问县芳, 张鑫鹏, 叶霖, 张爱英, 冯增国. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(7), 1758—1764) | |
| [16] | Yang X.W., Luo Y. Y., Textbook of Chemical Products: Dyestuffs, Press of Chemical Industry, Beijing, 2005 |
| (杨新玮, 罗钰言. 化工产品手册: 染料. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005) | |
| [17] | Dong Y. C., Zhang B. H., Water Cooled Temperature Controlling Photoreaction System, CN03275610.0, 2003-07-11) |
| (董永春, 张宝华. 水冷式控温光反应器, CN03275610.0, 2003-07-11) | |
| [18] | Xiong C., Yao C., J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 170, 541—542 |
| [19] | Wei J. F., Wang Z. P., Zhang J., Wu Y. Y., Zhang Z. P., Xiong C. H., React. Funct. Polym., 2005, 65, 127—134 |
| [20] | Park H. J., Na C. K., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2006, 301, 46—54 |
| [21] | Park H. J., Na C. K., J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 166, 1201—1209 |
| [22] | Ibrahim N. A., Abo-Shosha H., Elnagdy E. I., Gaffari M. A., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 84, 2243—2253 |
| [23] | Park B. H., Lee M., Kim S. B., Jo Y. M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, 3709—3716 |
| [24] | Dong Y., Dong W., Cao Y., Han Z., Ding Z., Catal. Today, 2011, 175, 346—355 |
| [25] | Qin Y., Text. Res. J., 2005, 75, 165—168 |
| [26] | Lv F., Zhu P., Wang C., Zheng L. J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 126, 383—388 |
| [27] | Naeem M., El-Sawy Z. I. A., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2007, 103, 4065—4071 |
| [28] | Kong Q., Wang B., Ji Q., Xia Y., Guo Z., Yu J., Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2009, 27, 807—812 |
| [29] | Cheng X. S., Guan H. M., Su Y. C., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2000, 58, 407—413 |
| [30] | Cheng M., Song W., Ma W., Chen C., Zhao J., Lin J., Zhu H., Appl. Catal. B., 2008, 77, 355—363 |
| [31] | Ma W., Huang Y., Li J., Chen M., Song W., Zhao J.,Chem. Commun., 2003, 1582—1583 |
| (Ed.: V, Z ) |
| [1] | 张振, 邓煜, 张琴芳, 余达刚. 可见光促进二氧化碳参与的羧基化反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220255. |
| [2] | 常云飞, 廖明义, 温佳明. NaBH4/MCl x 体系对液体端羧基氟橡胶的还原及还原机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20210835. |
| [3] | 张文梦, 李梦琴, 侯震, 陈栋阳. 羧基化含氟聚芳醚的合成及涂层性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210604. |
| [4] | 常书晴, 辛旭, 黄雅琦, 张信聪, 傅仰河, 朱伟东, 张富民, 李晓娜. Zr基金属有机框架材料的冷热驱动热释电催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2558. |
| [5] | 王阿强, 朱玉长, 靳健. 羧基甜菜碱型两性离子聚氨酯水凝胶的制备及水下抗原油黏附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1246. |
| [6] | 李琛, 李悦生. 吡啶基有机碱催化O-羧基酐的活性开环聚合[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3203. |
| [7] | 高霞,潘会宾,乔成芳,陈凤英,周元,杨文华. 基于多级孔金属有机骨架构筑HRP固定化酶反应器及其染料降解应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(7): 1591. |
| [8] | 韩志英,李佑稷,陈飞台,汤森培,王鹏. 同轴静电纺丝法制备ZnO/Ag2O纳米纤维材料及其光电催化性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 308. |
| [9] | 任向荣,周琦. 纳米多孔Ni和NiO的制备及电催化析氧性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(1): 162. |
| [10] | 李晓莉, 黄亮, 段红娟, 张力, 张海军. 石墨烯负载Pt/Co双金属纳米颗粒催化剂的制备及催化制氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1662. |
| [11] | 甘露,董永春. 不同结构二元羧酸改性棉纤维铁配合物的制备和光催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(10): 2205. |
| [12] | 张春燕, 罗建新, 李文军, 欧丽娟, 喻桂朋, 潘春跃. 单分散键合型含铕聚苯乙烯微球的制备与荧光传感性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 153. |
| [13] | 刘千榕, 蔡会武, 关明, 乔娟, 齐莉. 基于金纳米簇探针的荧光猝灭检测铁离子[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 55. |
| [14] | 方镭, 夏盛杰, 薛继龙, 孟跃, 钱梦丹, 罗伟, 张晓锋, 倪哲明. 金基二元合金团簇Au12M(M=Cu,Pt,Ni)催化水煤气变换反应的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(8): 1721. |
| [15] | 王斌, 乌英嘎, 刘哲林, 王晓红, 安智华, 曾俊, 杨鹏, 刘宗瑞. Keggin型多酸XW12 |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||