

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 1.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130691
收稿日期:2013-07-22
出版日期:2014-01-10
发布日期:2013-12-11
作者简介:联系人简介: 祝 莹, 男, 博士, 特聘副研究员, 主要从事液滴微流控和质谱分析方法的研究. E-mail:基金资助:
ZHU Lina, ZHU Ying*( ), FANG Qun*
), FANG Qun*
Received:2013-07-22
Online:2014-01-10
Published:2013-12-11
Contact:
ZHU Ying,FANG Qun
E-mail:yingzhu@zju.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
微流控技术以其高通量、 低消耗和集成化等优点成为蛋白质结晶微型化研究的重要手段. 本文综述了基于微流控技术的蛋白质结晶技术和方法, 主要包括微泵微阀、 液滴(Droplet)、 滑动芯片(SlipChip)以及液滴实验室(DropLab)等技术. 此外, 还针对当前膜蛋白在结构生物学研究中的重要地位, 综述了应用于膜蛋白结晶的微流控技术的研究进展.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
朱丽娜, 祝莹, 方群. 基于微流控技术的蛋白质结晶及其筛选方法的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(1): 1.
ZHU Lina, ZHU Ying, FANG Qun. Recent Progress of Microfluidic Techniques for Protein Crystallization and Screening†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1): 1.
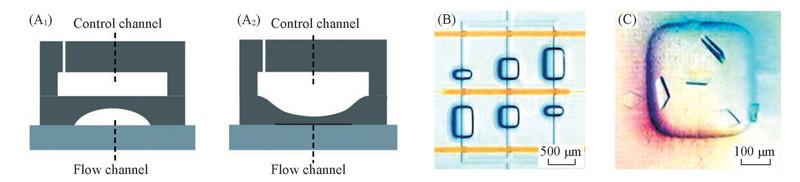
Fig.1 PDMS-based microvalve for protein crystallization under FID mode(A) Schematic illustration of PDMS microvalves under open(A1) and close(A2) states; (B) CCD image of microchip designed to implement three FID assays at three mixing ratios; (C) optical micrographs of crystals grown in the microchamber of FID chip[24].
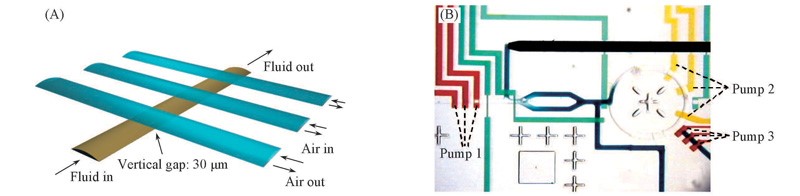
Fig.2 PDMS peristaltic micropump and formulator chip(A)Schematic diagram of an PDMS peristaltic micropump[22]; (B) CCD image of the formulator chip[27].
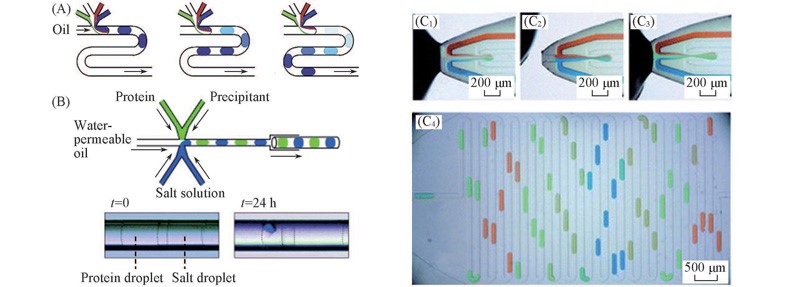
Fig.3 Droplet-based microfluidic system for protein crystallization(A) Schematic diagram showing the procedures of droplet formation in a T junction channel[36]; (B) Protein crystallization with vapor diffusion method in a PDMS/glass-capillary composite microchip[35]; (C) a high throughput screening system using an on-chip integrated sampling probe and a slotted-vial array; (C1)—(C3) sample introduction process; (C4) image of a generated droplet array containing different samples in the chip[20].
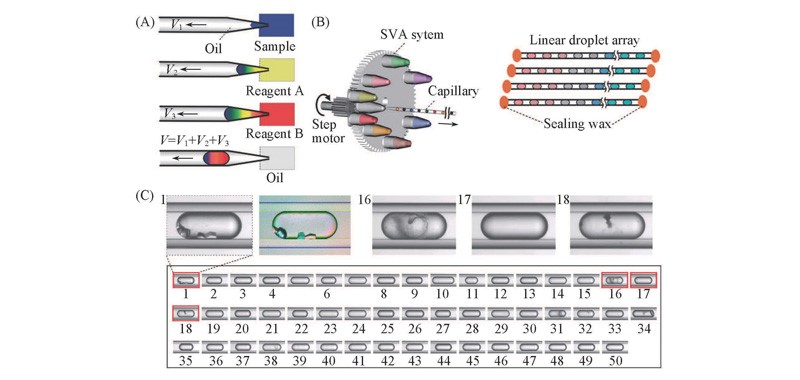
Fig.4 DropLab for protein crystallization[21](A) Principle and procedure of DropLab for droplet generation; (B) setup of the DropLab system with slotted-vial array for sample presentation and microcapillaries for droplet storage; (C) protein crystallization screening result using DropLab.
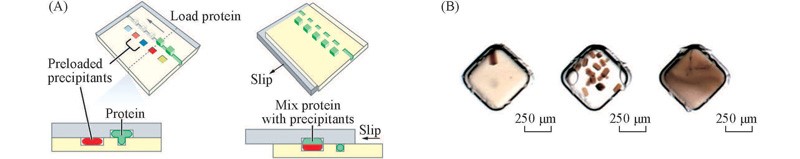
Fig.5 SlipChip-based protein crystallization[46](A) Operation procedures of SlipChip; (B) crystals of the photosynthetic reaction center from Blastochloris viridis obtained with SlipChip.
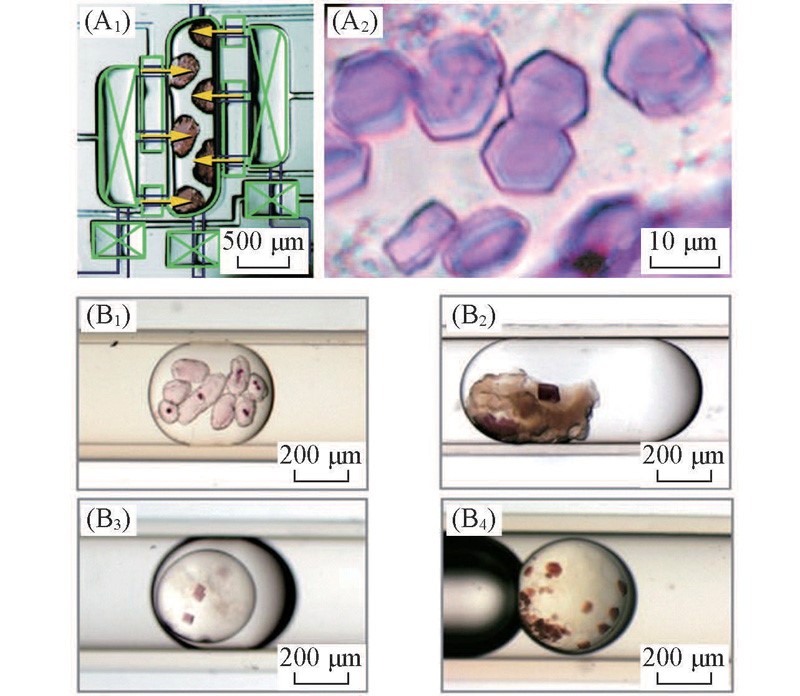
Fig.6 Microfluidic system for membrane protein crystallization within lipidic mesophases(LCP)(A1) CCD image showing the mixing of bacteriorhodopsin solution(left and right chambers) with lipid monoolein(center chamber) in a microfluidic chip[63]; (A2) crystals of bacteriorhodopsin obtained in LCP; (B) membrane protein crystals grown in droplets; (B1) bacteriorhodopsin from Halobacterium salinarum; (B2) caro-tenoid-containing RC from Rhodobacter sphaeroides; (B3) caroteniodless RC from Rhodobacter sphaeroides; (B4) photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodopseudomonas viridis[65].
| [1] | Mcpherson A., Methods, 2004, 34(3), 254—265 |
| [2] | Chayen N. E., Curr. Opin. Struct., 2004, 14(5), 577—583 |
| [3] | Chayen N. E., Trends Biotechnol., 2002, 20(3), 98 |
| [4] | Berman H. M., Bhat T. N., Bourne P. E., Feng Z., Gilliland G., Weissig H., Westbrook J., Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2000, 7, 957—959 |
| [5] | Chayen N. E., J. Cryst. Growth, 1999, 198, 649—655 |
| [6] | Kuhn P., Wilson K., Patch M. G., Stevens R. C., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2002, 6(5), 704—710 |
| [7] | Stevens R. C., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2000, 10(5), 558—563 |
| [8] | Chayen N.E., Protein Crystallization Strategies for Structural Genomics, International University Line, California, 2007, 36—40 |
| [9] | Nakanishi K., Sakiyama T., Imamura K., J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2001, 91(3), 233—244 |
| [10] | Thudi L., Jasti L. S., Swarnalatha Y., Fadnavis N. W., Mulani K., Deokar S., Ponrathnam S., Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2012, 90, 184—190 |
| [11] | Juárez-Martínez G., Steinmann P., Roszak A. W., Isaacs N. W., Cooper J. M., Anal. Chem., 2002, 74(14), 3505—3510 |
| [12] | Sanjoh A., Tsukihara T., J. Cryst. Growth, 1999, 196(2), 691—702 |
| [13] | Li L., Ismagilov R. F., Annu. Rev. Biophys., 2010, 39, 139—158 |
| [14] | Bian T. B., Yin X. F., Liu J. H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2010, 26(4), 522—526 |
| [15] | Hansen C., Quake S. R., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2003, 13(5), 538—544 |
| [16] | Sauter C., Dhouib K., Lorber B., Cryst. Growth Des., 2007, 7(11), 2247—2250 |
| [17] | Li J. J., Chen Q., Li G., Zhao J. L., Zhu Z. Q., Prog. Chem., 2009, 21(5), 1034—1039 |
| (李俊君, 陈强, 李刚, 赵建龙, 朱自强.化学进展, 2009,21(5), 1034—1039) | |
| [18] | Chen D. L., Ismagilov R. F., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2006, 10(3), 226—231 |
| [19] | Zheng B., Gerdts C. J., Ismagilov R. F., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2005, 15(5), 548—555 |
| [20] | Sun M., Fang Q., Lab Chip, 2010, 10(21), 2864—2868 |
| [21] | Du W. B., Sun M., Gu S. Q., Zhu Y., Fang Q., Anal. Chem., 2010, 82(23), 9941—9947 |
| [22] | Unger M. A., Chou H. P., Thorsen T., Scherer A., Quake S. R., Science, 2000, 288(5463), 113—116 |
| [23] | Mcpherson A., Crystallization of Biological Macromolecules, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1999, 455—460 |
| [24] | Hansen C. L., Skordalakes E., Berger J. M., Quake S. R., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002, 99(26), 16531—16536 |
| [25] | Bird R. B., Stewart W. E., Lightfoot E. N., Transport Phenomena, Wiley, New York ,1960, 138, 148 |
| [26] | Hansen C. L., Classen S., Berger J. M., Quake S. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(10), 3142—3143 |
| [27] | Hansen C. L., Sommer M. O., Quake S. R., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, 101(40), 14431—14436 |
| [28] | Anderson M. J., Hansen C. L., Quake S. R., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006, 103(45), 16746—16751 |
| [29] | Thorsen T., Roberts R. W., Arnold F. H., Quake S. R., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2001, 86(18), 4163—4166 |
| [30] | Chen J. S., Jiang J. H., Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 2012, 40(8), 1293—1300 |
| (陈九生, 蒋稼欢.分析化学, 2012,40(8), 1293—1300) | |
| [31] | Velev O. D., Prevo B. G., Bhatt K. H., Nature, 2003, 426(6966), 515—516 |
| [32] | Burns M. A., Johnson B. N., Brahmasandra S. N., Handique K., Webster J. R., Krishnan M., Sammarco T. S., Man P. M., Jones D., Heldsinger D., Mastrangelo C. H., Burke D. T., Science, 1998, 282(5388), 484—487 |
| [33] | Song H., Tice J. D., Ismagilov R. F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2003, 42(7), 768—772 |
| [34] | Roach L. S., Song H., Ismagilov R. F., Anal. Chem., 2005, 77(3), 785—796 |
| [35] | Zheng B., Tice J. D., Roach L. S., Ismagilov R. F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2004, 43(19), 2508—2511 |
| [36] | Zheng B., Roach L. S., Ismagilov R. F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(37), 11170—11171 |
| [37] | Zheng B., Tice J. D., Ismagilov R. F., Anal. Chem., 2004, 76(17), 4977—4982 |
| [38] | Srinivasan V., Pamula V. K., Fair R. B., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2004, 507(1), 145—150 |
| [39] | Shestopalov I., Tice J. D., Ismagilov R. F., Lab Chip, 2004, 4(4), 316—321 |
| [40] | Dolega M. E., Jakiela S., Razew M., Rakszewska A., Cybulski O., Garsteckil P., Lab Chip, 2012, 12(20), 4022—4025 |
| [41] | Yadav M. K., Gerdts C. J., Sanishvili R., Smith W. W., Roach L. S., Ismagilov R. F., Kuhn P., Stevens R. C., J. Appl. Cryst., 2005, 38(6), 900—905 |
| [42] | Zheng B., Ismagilov R. F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(17), 2520—2523 |
| [43] | Garstecki P., Gitlin I., Diluzio W., Whitesides G. M., Kumacheva E., Stone H. A., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85(13), 2649—2651 |
| [44] | Lau B. T. C., Baitz C. A., Dong X. P., Hansen C. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 129(3), 454—455 |
| [45] | Shim J. U., Cristobal G., Link D. R., Thorsen T., Jia Y., Piattelli K., Fraden S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(28), 8825—8835 |
| [46] | Du W. B., Li L., Nichols K. P., Ismagilov R. F., Lab Chip, 2009, 9(16), 2286—2292 |
| [47] | Li L., Du W. B., Ismagilov R. F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(1), 106—111 |
| [48] | Li L., Du W. B., Ismagilov R. F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(1), 112—119 |
| [49] | Dhouib K., Malek C. K., Pfleging W., Gauthier-Manuel B., Duffait R. , Thuillier G., Ferrigno R., Jacquamet L., Ohana J., Ferrer J. L., Theobald-Dietrich A., Giege R., Lorber B., Sauter C., Lab Chip, 2009, 9(10), 1412—1421 |
| [50] | Pinker F., Brun M., Morin P., Deman A. L., Chateaux J. F., Olieéric V., Stirnimann C., Lorber B., Terrier N., Ferrigno R., Sauter C., Cryst. Growth Des., 2013, 13(8), 3333—3340 |
| [51] | Ng J. D., Gavira J. A., García-Ruíz J. M., J. Struct. Biol., 2003, 142(1), 218—231 |
| [52] | Li G., Chen Q., Li J., Hu X., Zhao J., Anal. Chem., 2010, 82(11), 4362—4369 |
| [53] | Luo Y. H., Li G., Chen Q., Zhao J. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10), 2178—2183 |
| (罗娅慧, 李刚, 陈强, 赵建龙.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(10), 2178—2183) | |
| [54] | Zhou X. X., Lau L. N., Lam W. W. L., Au S. W. N., Zheng B., Anal. Chem., 2007, 79(13), 4924—4930 |
| [55] | Drews J., Science, 2000, 287(5460), 1960—1964 |
| [56] | Sanders C. R., Myers J. K., Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 2004, 33, 25—51 |
| [57] | Deisenhofer J., Epp O., Miki K., Huber R., Michel H., Nature, 1985, 318(6047), 618—624 |
| [58] | Loll P. J., J. Struct. Biol., 2003, 142(1), 144—153 |
| [59] | Chang G., Spencer R. H., Lee A. T., Barclay M. T., Rees D. C., Science, 1998, 282(5397), 2220—2226 |
| [60] | Nollert P., Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol., 2005, 88(3), 339—357 |
| [61] | Li L., Mustafi D., Fu Q., Tereshko V., Chen D. L. L., Tice J. D., Ismagilov R. F., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006, 103(51), 19243—19248 |
| [62] | Caffrey M., Cherezov V., Nat. Protoc., 2009, 4(5), 706—731 |
| [63] | Perry S. L., Roberts G. W., Tice J. D., Gennis R. B., Kenis P. J., Cryst. Growth Des., 2009, 9(6), 2566—2569 |
| [64] | Khvostichenko D. S., Kondrashkina E., Perry S. L., Pawate A. S., Brister K., Kenis P. J. A., Analyst, 2013, 138(18), 5384—5395 |
| [65] | Li L., Fu Q., Kors C. A., Stewart L., Nollert P., Laible P. D., Ismagilov R. F., Microfluid. Nanofluid., 2010, 8(6), 789—798 |
| [1] | 刘学娇, 杨帆, 刘爽, 张春娟, 刘巧玲. 核酸适体靶向的膜蛋白识别与功能调控研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3277. |
| [2] | 匡小军, 伊京伟, 方晓霞, 赖东梅, 徐宏. 水溶性香豆素荧光底物的制备及在液滴数字式检测中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3537. |
| [3] | 黄辉龙, 黄汉雄. 注压成型纳米结构PP/POE共混物表面的液滴低温冲击行为[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3195. |
| [4] | 彭伙, 高则航, 廖承悦, 王晓冬, 周洪波, 赵建龙. 一种用于核酸绝对定量检测的高鲁棒性液滴式数字PCR芯片[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(8): 1760. |
| [5] | 戴浩宇,董智超,江雷. 电控液滴移动的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(1): 1. |
| [6] | 林玉才, 裴文乐, 孙若璇, 高春雷, 陈基棚, 郑咏梅. 特殊浸润性表面的液滴凝结[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(6): 1236. |
| [7] | 孟秀峰, 翟志伟, 郭爱军. 自组装单分子层对多巴黏附能力的可控性研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10): 2245. |
| [8] | 李丹, 郑咏梅. 微纳米复合的各向异性结构表面的液滴驱动[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(1): 109. |
| [9] | 袁浩钧, 郜晚蕾, 景奉香, 刘松生, 周洪波, 贾春平, 金庆辉, 赵建龙. 一种用于核酸高灵敏检测的液滴式数字聚合酶链式反应芯片[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(7): 1140. |
| [10] | 曹婷婷, 杜寿文, 许汪, 邢彬, 赵飞, 王茂鹏, 朱羿龙, 白杰英, 田宇飞, 刘立明, 赵翠青, 周义发, 李昌, 金宁一. 基于Tet-On 3G的IFITM3诱导表达MDCK细胞系的建立及功能分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(5): 770. |
| [11] | 黄兆亮, 高方园, 王伯良, 张维冰. 电喷雾离子源(ESI)中带电液滴的形成与碎裂模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(4): 633. |
| [12] | 郭兰磊, 李静, 祝仰文, 马宝东, 徐志成, 王武宁, 张磊, 张路. 模拟乳状液中微小液滴间的相互作用力[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2): 361. |
| [13] | 熊文, 权春善, 王丽娜, 张旭宁, 赵晶, 郑维, 范圣第. 不同电性脂质体对金黄色葡萄球菌组氨酸激酶AgrC跨膜镶嵌效率的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(9): 1901. |
| [14] | 张永建, 刘正堂, 钱一梦, 栗志广, 臧渡洋. 含盐胶体液滴的蒸发图案形成机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(6): 1258. |
| [15] | 田飞, 安俊超, 曹宏梅, 郭世珍, 孙景. 毫秒激光烧蚀镍靶高效率制备NiO纳米立方体[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(8): 1965. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||