

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 757.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190594
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAO Yan1,2,*( ),YANG Hua2,WANG Xiang2,LI Qingyang2,ZHAO Pan2,TANG Qinghu2,SONG Shili2,XI Guoxi1,2
),YANG Hua2,WANG Xiang2,LI Qingyang2,ZHAO Pan2,TANG Qinghu2,SONG Shili2,XI Guoxi1,2
Received:2019-11-18
Online:2020-04-10
Published:2020-01-15
Contact:
Yan HAO
E-mail:yanhao@htu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HAO Yan, YANG Hua, WANG Xiang, LI Qingyang, ZHAO Pan, TANG Qinghu, SONG Shili, XI Guoxi. Palladium-based Nanocatalysts Supported on Polybenzoxazine for Aromatic Alcohol Oxidation †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 757.
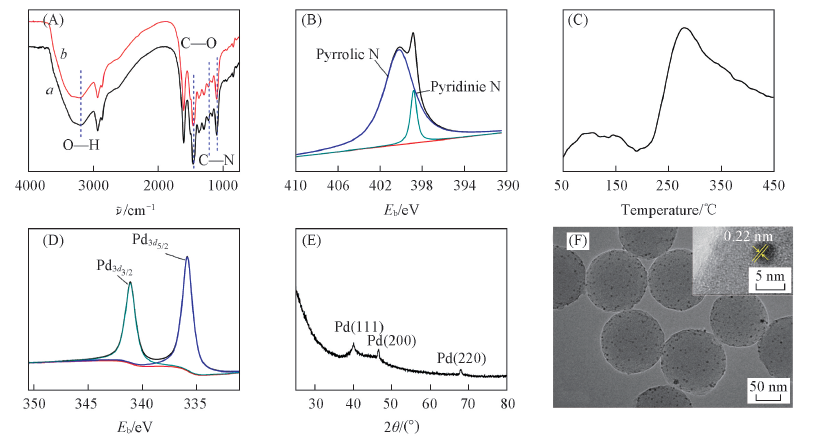
Fig.2 FTIR spectra of polybenzoxazine(a) and Pd/polybenzoxazine(b)(A) , XPS spectra of N1s(B) and CO2-TPD spectrum(C) of carbon support, XPS spectra of Pd3d(D) , XRD pattern(E) , and TEM and HRTEM images(inset)(F) of Pd/C catalyst
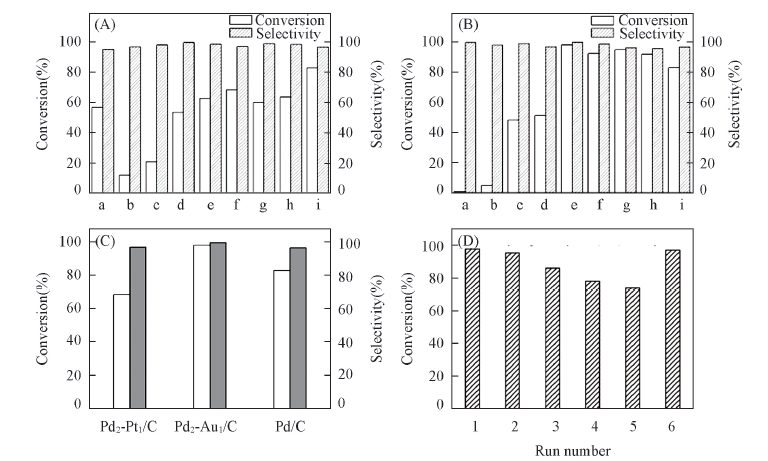
Fig.5 Catalytic activities of various catalysts in the benzyl alcohol oxidation reaction (A) n(Pd)/n(Pd+Pt): a. 0; b. 1/6; c. 1/5; d. 1/3; e. 1/2; f. 2/3; g. 4/5; h. 5/6; i. 1. (B) n(Pd)/n(Pd+Au): a. 0; b. 1/6; c. 1/5; d. 1/3; e. 1/2; f. 2/3; g. 4/5; h. 5/6; i. 1.
| Catalyst | Metal loading(%) | Reaction time/h | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd-Au/C | 2 | 2 | 98 | 95 | This work |
| Pd/Fe@C | 1 | 25 | 93 | 99 | [29] |
| Au/ZnCuO | 4 | 5 | 93 | 99 | [30] |
| Pd/CeO2 | 3 | 2 | 93 | 99 | [31] |
| Pd/FMOF | 3 | 12 | 89 | 99 | [32] |
| Au-Pd/Fe-Gr | 5 | 4 | 96.2 | 89.9 | [33] |
| Catalyst | Metal loading(%) | Reaction time/h | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd-Au/C | 2 | 2 | 98 | 95 | This work |
| Pd/Fe@C | 1 | 25 | 93 | 99 | [29] |
| Au/ZnCuO | 4 | 5 | 93 | 99 | [30] |
| Pd/CeO2 | 3 | 2 | 93 | 99 | [31] |
| Pd/FMOF | 3 | 12 | 89 | 99 | [32] |
| Au-Pd/Fe-Gr | 5 | 4 | 96.2 | 89.9 | [33] |
| Substrate | Product | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Methylbenzyl alcohol | 4-Methylbenzaldehyde | 32 | >99 |
| 4-Methoxybenzyl alcohol | 4-Methoxybenzaldehyde | 37 | >99 |
| 2-Methylbenzyl alcohol | 2-Methylbenzaldehyde | 13 | >99 |
| 4-Nitrobenzyl alcohol | 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde | 4 | >99 |
| Substrate | Product | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Methylbenzyl alcohol | 4-Methylbenzaldehyde | 32 | >99 |
| 4-Methoxybenzyl alcohol | 4-Methoxybenzaldehyde | 37 | >99 |
| 2-Methylbenzyl alcohol | 2-Methylbenzaldehyde | 13 | >99 |
| 4-Nitrobenzyl alcohol | 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde | 4 | >99 |
| [1] | Song Y. C., Ding X. S., Yan Y. H., Wang S. F., Wang Y. J., J. Chem. Industry Engin., 2019, 70 4), 1401— 1408 |
| ( 宋宇淙,丁晓墅,闫亚辉,王淑芳,王延吉.化工学报, 2019, 70(4), 1401— 1408) | |
| [2] | Chen Z. Y., Mao J. X., Zhou R. X., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 465, 25— 22 |
| [3] | Cui W. H., Li S. D., Wang D. D., Deng Y. Z., Chen Y. F., Catal. Commun., 2019, 119, 86— 90 |
| [4] | Lin Z. C., Huang Q. X., Lei M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40 5), 1013— 1018 |
| ( 林周晨,黄巧茜,雷鸣.高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(5), 1013— 1018) | |
| [5] | Liu J. J., Zou S. H., Wu J. C., Kobayashi H., Zhao H. T., Fan J., Chinese J. Catal., 2018, 39( 6), 1081— 1089 |
| [6] | Li J. W., Li P. P., Li J. B., Tian Z. Q., Yu F ., Catalysts, 2019, 9( 6), 1— 12 |
| [8] | Naik G. K., Majhi S. M., Jeong K. U., Lee I. H., Yu Y. T., J. Alloy. Compd., 2019, 771, 505— 512 |
| Li T. J., Lin H. F., Ouyang X. P., Qu X. Q., Wan Z. C., ACS Catal., 2019, 9( 7), 5828— 5836 | |
| [9] | Li Y., Yao L., Zhang L. Q., Liu A. R., Zhang Y. J., Liu S. Q., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2014, 730, 65— 68 |
| [10] | Lv Q., Si W. Y., He J. J., Sun L., Zhang C. F., Wang N., Yang Z., Li X. D., Wang X., Deng W. Q., Long Y. Z., Huang C. S., Li Y. L., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 3376— 3386 |
| [11] | Zhou J., Wu K., Wang W. J., Xu Z. Y., Wan H. Q., Zheng S. R., Appl. Catal. A-Gen, 2017, 470, 336— 343 |
| [12] | Ravat V., Nongwe I., Meijboom R., Bepete G., Coville N. J., J. Catal., 2013, 305, 36— 45 |
| [13] | Ma X. B., Feng Y. Y., Li Y., Han Y. S., Lu G. P., Yang H. F., Kong D. S., Chinese J. Catal., 2015, 36( 7), 943— 951 |
| [14] | Wang S., Li W. C., Hao G. P., Hao Y., Sun Q., Zhang X. Q., Lu A. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 15304— 15307 |
| [15] | Luo J., Peng F., Wang H. J., Yu H., Catal. Commun., 2013, 39, 44— 49 |
| [16] | Huang C. L., Zhong W., Wen J. J., Zhang M. Y., Huang H. M., Fu M. L., Wu J. L., Ye D. Q., Chen L. M., Acta Scien. Circum., 2019, 39 6), 1942— 1951 |
| ( 黄春蕾,钟雯,文进军,张明远,黄皓旻,付名利,吴军良,叶代启,陈礼敏.环境科学学报, 2019, 39(6), 1942— 1951) | |
| [17] | Liu J., Zhou W. Y., Wu Z., Sun F. A., He M. Y., Chen Q., Chinese J. Appl. Chem., 2015, 32 9), 1033— 1039 |
| ( 刘杰,周维友,吴中,孙富安,何明阳,陈群.应用化学, 2015, 32(9), 1033— 1039) | |
| [18] | Lu A H., . Li W . C., Hou Z . S, Schüth F. Chem. Commun., 2007, ( 10), 1038— 1040 |
| [19] | Ruiz-García C., Heras F., Calvo L., Alonso-Morales N., Rodriguez J. J., Gilarranz M. A., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58, 4355— 4363 |
| [20] | Yan X. H., Ge X., Zhang L., Qi L. J., Li Y., Wei S. H., Zhu X. S., Tang Y. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38 9), 1619— 1626 |
| ( 闫晓红,葛霞,张琳,齐丽娟,刘洋,魏少华,朱晓舒,唐亚文.高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(9), 1619— 1626) | |
| [21] | Han F. Y., Xia J. W., Zhang X. L., Fu Y. S., RSC Advances, 2019, 9, 17812— 17823 |
| [22] | Nassiri H., Hayes R. E., Semagina N., Chem. Eng. Sci., 2018, 186, 44— 51 |
| [23] | Hong W., Wang J., Wang E. K., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2014, 6, 9481— 9487 |
| [24] | Hong W., Shang C. S., Wang J., Wang E. K., Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8, 2910— 2915 |
| [25] | Wang Z. T., Song Y. X., Zou J. H., Li L. Y., Yu Y., Wu L., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 8, 268— 275 |
| [26] | Hao Y., Hao G. P., Guo D. C., Guo C. Z., Li W. C., Li M. Y., Lu A. H ., ChemCatChem, 2012, 4, 1595— 1602 |
| [27] | Zhu X. J., Guo Q. S., Sun Y. F., Chen S. J., Wang J. Q., Wu M. M., Fu W. Z., Tang Y. Q., Duan X. Z., Chen D., Wan Y., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1428— 1438 |
| [28] | Yan Y. B., Jia X. L., Yang Y. H., Catal. Today, 2016, 259, 292— 302 |
| [29] | Zhang H., Liu Y., Zhang X. G., Chinese J. Catal., 2011, 32, 1693— 1701 |
| [30] | Wang W., Xie Y., Zhang S.H ., Liu X., Zhang L. Y.,Zhang B. S, Haruta M., Huang J. H ., Chin. J. Catal.,2019, 40, 1924— 1933 |
| [31] | Zheng H., Wei Z. H., Hu X. Q., Xu J., Xue B., Chemistry Select, 2019, 4, 5470— 5475 |
| [32] | Liu J. Y., Yu H. J., Wang L., Deng Z., Vatsadze S. Z., J. Mol. Struc., 2019, 1198, 126895 |
| [33] | Sun J. Y., Tong X. L., Liu Z. H., Liao S. Y., Zhuang X. L., Xue S., Catal. Commun., 2016, 85, 70— 74 |
| [34] | Tang Q. H., Liu T., Yang Y. H., Catal. Commun., 2008, 9( 15), 2570— 2573 |
| [1] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [2] | WEI Chunhong, JIANG Qian, WANG Panpan, JIANG Chengfa, LIU Yuefeng. Atomic Scale Investigation of Pt Atoms/clusters Promoted Co-catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220074. |
| [3] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [4] | XU Siran, YIN Hengbo, XUE Dongping, XIA Huicong, ZHAO Shuyan, YAN Wenfu, MU Shichun, ZHANG Jianan. Atomically Dispersed Metal-Nitrogen-Carbon Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220028. |
| [5] | WANG Mingzhi, ZHENG Yanping, WENG Weizheng. Catalytic Methane Combustion over CeO2 Supported PdO and Ce1‒x Pd x O2‒δ Species [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210816. |
| [6] | ZHAO Wanjun, LI Xiao, Dang Hui, WANG Yongzhao, ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation of Supported Pd-Cu Catalyst and Its Preferential Oxidation of CO Under Hydrogen-rich Atmosphere [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210754. |
| [7] | JIANG Shan, SHEN Qianqian, LI Qi, JIA Husheng, XUE Jinbo. Pd-loaded Defective TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220206. |
| [8] | GUO Yang, LIN Kai, XIE Kaiqiang, LIU Sheng. Novel Approach to Isatins via Pd-Cu Catalyzed Oxidative Transformation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2798. |
| [9] | XU Yan, YANG Hongguo, NIU Huibin, TIAN Hailin, PIAO Hongguang, HUANG Yingping, FANG Yanfen. Preparation Mechanism and Application of Alcohol⁃modified Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2564. |
| [10] | WEN Wei, HUANG Dading, BAO Jingxiao, ZHANG John Z. H.. Residue Specific Binding Mechanisms of PD-1 to Its Monoclonal Antibodies by Computational Alanine Scanning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2161. |
| [11] | WANG Yuxiang, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LYU Jiamin, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. One-step Synthesis of Amorphous Silica Aluminum Support Materials with Controllable Acidity and Porosity and Catalytic Performance of Their Pd-based Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1826. |
| [12] | REN Ying, LI Changhua, WANG Tao, XUE Shanshan, ZHANG Tingting, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Studies on Pd-catalyzed Oxidative N─H Carbonylation to Synthesis of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-2(3H)-one Heterocyclic Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1793. |
| [13] | LI Boxin, YANG Junge, YIN Dezhong, GAO Chengqian, ZHANG Qiuyu. Preparation of Large-sized Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials Through Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Monodisperse Polymer Microspheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2085. |
| [14] | LI Xiao,XING Lisha,ZHAO Wanjun,WANG Yongzhao,ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation and Characterization of Pd-Cu/hydroxyapatite Catalyst and Its Catalytic Performance for Room-temperature CO Oxidation in Humid Circumstances† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1600. |
| [15] | LU Man,SONG Chunmei,WAN Bo. Thixotropic Behavior of Hydrophobically Modified Ethoxylated Urethane-thickened Waterborne Latex † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||