

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 2301.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190233
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Chunyan,JIANG Xiaoqing,ZHOU Bo( )
)
Received:2019-04-22
Online:2019-11-10
Published:2019-08-20
Contact:
ZHOU Bo
E-mail:zhoubo@njnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Chunyan,JIANG Xiaoqing,ZHOU Bo. An Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Cu-TPA for Determination of Aflatoxin B1 †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2301.
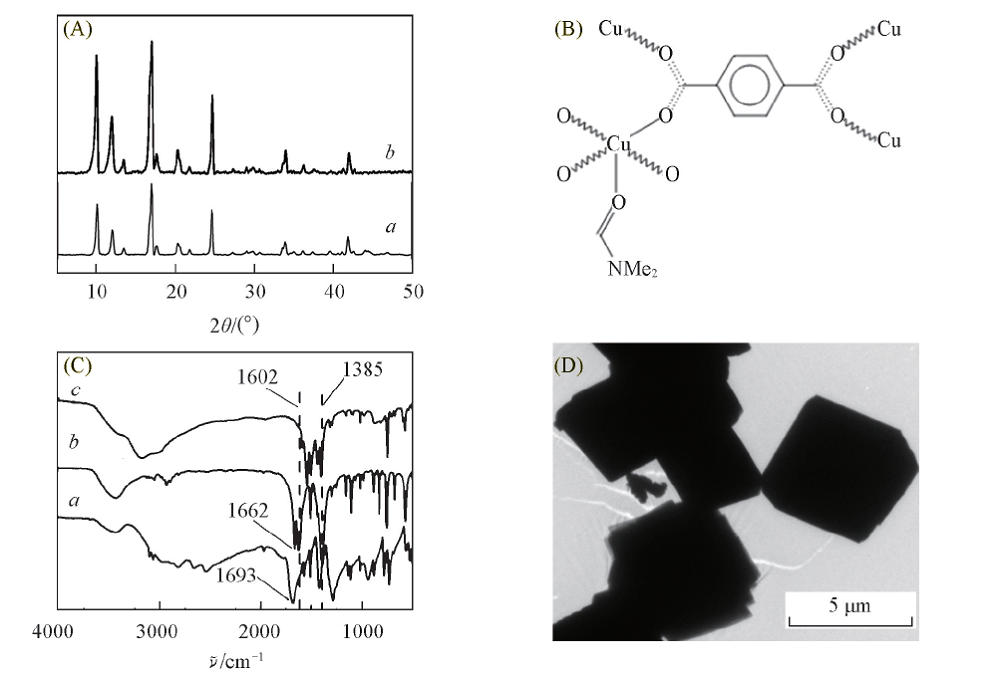
Fig.1 XRD patterns of CuTPA×DMF(CCDC-687690)(a) and Cu-TPA(b)(A), chemical structure of Cu-TPA(B), IR spectra of HTPA(a), Cu-TPA(b) and Cu-TPA/AuNPs(C) and TEM image of Cu-TPA(D)
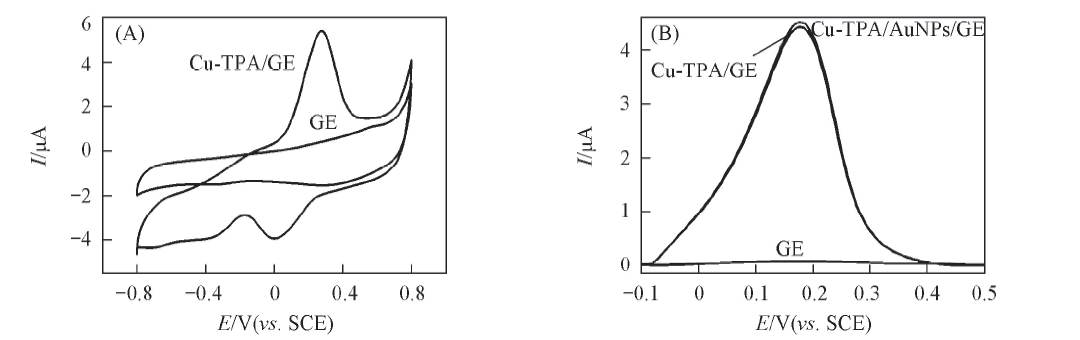
Fig.2 CV responses of the electrodes GE and Cu-TPA/GE in the scan range of -0.8—0.8 V(A) and DPV responses of the electrodes GE, Cu-TPA/GE and Cu-TPA/AuNPs/GE in Tris-HCl(pH=7.4) with a scan rate of 100 mV/s in the scan range of -0.1—0.5 V(B)
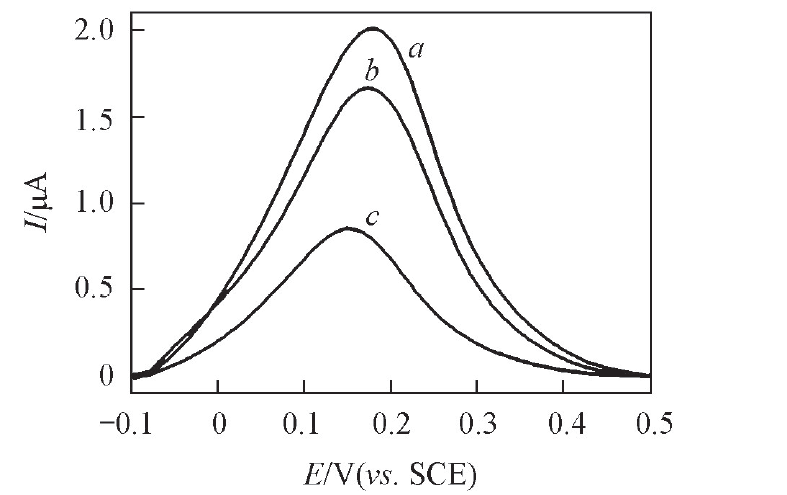
Fig.3 DPV responses of the CuTPA/AuNPs/S1/S3/S2/GE electrode to different concentrations of AFB1 in Tris-HCl(pH=7.4) with a scan rate of 100 mV/s and scan range of -0.1—0.5 V Concentration of AFB1/(ng·mL-1): a. 0; b. 0.001; c. 10.

Fig.4 CV(A) and EIS(B) results of the electrodes in different modification steps in 5.0 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6]/K4[Fe(CN)6] with a scan rate of 100 mV/s and in a scan range of -0.2—0.6 V a. Bare gold electrode; b. S2 immobilized on the electrode; c. S3 and S2 complementary paired on the electrode; d. S1 and S3 complementary paired on the electrode; e. adding 10 ng/mL AFB1 on the electrode.
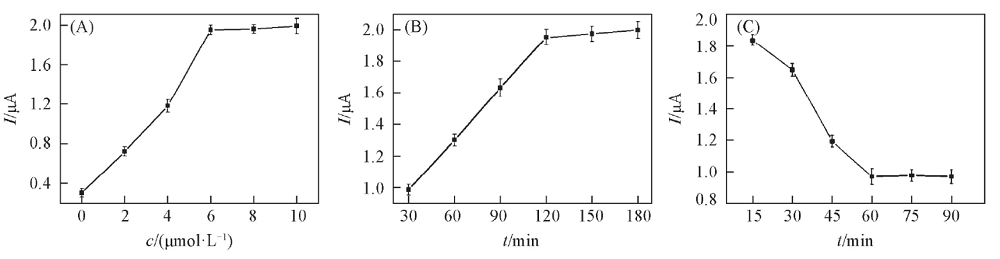
Fig.5 Optimization of experimental parameters during the experiment (A) Concentration optimization of S3 binding to the electrode; (B) binding time of Cu-TPA/AuNPs/S1 to S3/S2/GE electrode; (C) combination time after the addition of AFB1 and S3. The concentration of AFB1 is 10 ng/mL.
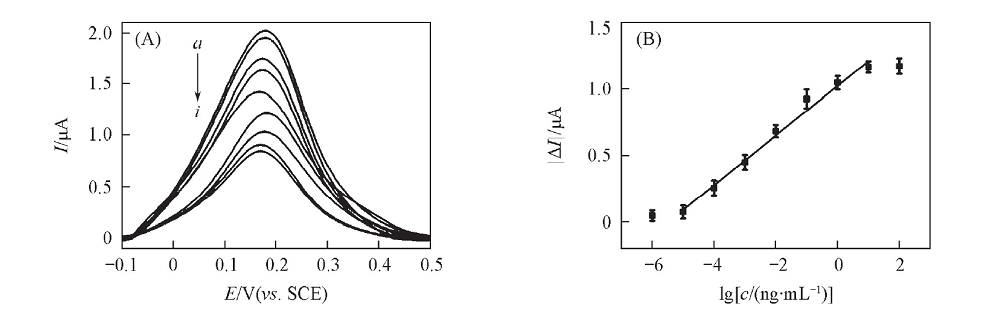
Fig.6 DPV responses of the electrochemical biosensor to different concentrations of AFB1 under optimal experimental conditions(A) and the calibration curve between the peak current change and logarithm of AFB1 concentration(B) Concentration of AFBI/(ng·mL-1) from a to i: 10-6, 10-5, 10-4, 10-3, 10-2, 10-1, 1, 10, 100. The error bars in (B) are the standard deviations of the three experiments.
| Analytical method | Material | Linear range/(ng·mL-1) | Detection limit/(ng·mL-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical immunosensor | AFB1-BSA/Cu-apatite | 10-3—100 | 2.0×10-4 | [ |
| Electrochemiluminoscence | DNA2/HRP/AuNR | 5.0×10-6—10 | 4.3×10-7 | [ |
| Electrochemiluminescence | luminol-AgNPs @MC | 10-4—50 | 5.0×10-5 | [ |
| Electrochemicalsensors | MIP-based polymer/AuNPs | 10-6—1000 | 3.0×10-7 | [ |
| Electrochemicalsensors | MIPOPD-Au/PtNP-MCNT | 10-4—10 | 3.1×10-5 | [ |
| Electrochemical biosensor | Cu-TPA/AuNPs/S1 | 10-5—10 | 4.2×10-6 | This work |
| Analytical method | Material | Linear range/(ng·mL-1) | Detection limit/(ng·mL-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical immunosensor | AFB1-BSA/Cu-apatite | 10-3—100 | 2.0×10-4 | [ |
| Electrochemiluminoscence | DNA2/HRP/AuNR | 5.0×10-6—10 | 4.3×10-7 | [ |
| Electrochemiluminescence | luminol-AgNPs @MC | 10-4—50 | 5.0×10-5 | [ |
| Electrochemicalsensors | MIP-based polymer/AuNPs | 10-6—1000 | 3.0×10-7 | [ |
| Electrochemicalsensors | MIPOPD-Au/PtNP-MCNT | 10-4—10 | 3.1×10-5 | [ |
| Electrochemical biosensor | Cu-TPA/AuNPs/S1 | 10-5—10 | 4.2×10-6 | This work |
| Spiked AFB1/(ng·mL-1) | Detected AFB1/(ng·mL-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10.6 | 106 | 2.33 |
| 1 | 0.99 | 99 | 2.90 |
| 0.1 | 0.095 | 95 | 4.41 |
| Spiked AFB1/(ng·mL-1) | Detected AFB1/(ng·mL-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10.6 | 106 | 2.33 |
| 1 | 0.99 | 99 | 2.90 |
| 0.1 | 0.095 | 95 | 4.41 |
| [1] | Carson C. G., Hardcastle K., Schwartz J., Liu X., Hoffmann C., Gerhardt R. A., Tannenbaum R., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2009,2009(16), 2338— 2343 |
| [2] | Acheson R. J., Galwey A. K., J. Chem. Soc. A, 1967, 1174— 1178 |
| [3] | Sherif F. G ., Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 1970,9(3), 408— 412 |
| [4] | Cueto S., Gramlich V., Petter W., Rys F. S., Rys P ., Acta Cryst., 1991,47(1), 75— 78 |
| [5] | Chen Z., Xiang S., Zhao D., Chen B., Cryst. Growth Des., 2009,9(12), 5293— 5296 |
| [6] | Cheng Y., Wang X., Jia C., Wang Y., Zhai L., Wang Q., Zhao D ., J. Membr. Sci., 2017,539, 213— 223 |
| [7] | Elder A. C., Bhattacharyya S., Nair S., Orlando T. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018,122(19), 10413— 10422 |
| [8] | Zhang X., Dong W., Luan Y., Yang M., Tan L., Guo Y., Gao H., Tang Y., Dang R., Li J ., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015,3(8), 4266— 4273 |
| [9] | Brondani D., Zapp E., Heying R. S., De Souza B., Vieira I. C., Electroanalysis, 2017,29(12), 2810— 2817 |
| [10] | Bai R. Y., Zhang K. L., Li D. L., Zhang Q., Liu T. Z., Liu Y., Hu R., Yang Y. H., Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 2017,45(1), 48— 55 |
| ( 白茹燕, 张坤蕾, 李德蕾, 张茜, 刘婷知, 刘仪, 胡蓉, 杨云慧 , 分析化学, 2017,45(1), 48— 55) | |
| [11] | Mak A. C., Osterfeld S. J., Yu H., Wang S. X., Davis R. W., Jejelowo O., Pourmand N ., Biosensors Bioelectron., 2010,25(7), 1635— 1639 |
| [12] | Zheng W., Teng J., Cheng L., Ye Y., Pan D., Wu J., Xue F., Liu G., Chen W., Biosensors Bioelectron., 2016,80, 574— 581 |
| [13] | Li X., Li P., Zhang Q., Li R., Zhang W., Zhang Z., Ding X., Tang X., Biosensors Bioelectron., 2013,49, 426— 432 |
| [14] | Zhang J., Li Z., Zhao S., Lu Y ., Analyst, 2016,141(13), 4029— 4034 |
| [15] | Wang Z., Li J., Xu L., Feng Y., Lu X ., J. Solid State Electrochem., 2014,18(9), 2487— 2496 |
| [16] | Kuang H., Chen W., Xu D., Xu L., Zhu Y., Liu L., Chu H., Peng C., Xu C., Zhu S., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2011,26(2), 710— 716 |
| [17] | Ge L., Wang W., Li F., Anal. Chem., 2017,89(21), 11560— 11567 |
| [18] | Li Q., Lu Z., Tan X., Xiao X., Wang P., Wu L., Shao K., Yin W., Han H., Biosens Bioelectron., 2017,97, 59— 64 |
| [19] | Wu L., Ding F., Yin W., Ma J., Wang B., Nie A., Han H., Anal. Chem., 2017,89(14), 7578— 7585 |
| [20] | Adams R., Carson C., Ward J., Tannenbaum R., Koros W., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2010,131(1), 13— 20 |
| [21] | Bai R., Zhang K., Delei L. I., Zhang X., Liu T., Liu Y., Rong H. U., Yang Y., Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017,45(1), 48— 55 |
| [22] | Ji X., Song X., Li J., Bai Y., Yang W., Peng X ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007,129(45), 13939— 13948 |
| [23] | Zhang J., Song S., Wang L., Pan D., Fan C., Nat. Protoc., 2007,2(11), 2888— 2895 |
| [24] | Goud K. Y., Catanante G., Hayat A., Satyanarayana M., Gobi K. V., Marty J. L., Sens. Actuators,B, 2016,235, 466— 473 |
| [25] | Kubica P., Wolinska Grabczyk A., Grabiec E., Libera M., Wojtyniak M., Czajkowska S., Domański M., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2016,235, 120— 134 |
| [26] | Elder A. C., Aleksandrov A. B., Nair S., Orlando T. M., Langmuir, 2017,33(39), 10153— 10160 |
| [27] | Feijani E. A., Mahdavi H., Tavasoli A ., Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2015,96, 87— 102 |
| [28] | Yadav D. K., Ganesan V., Sonkar P. K., Gupta R., Rastogi P. K., Electrochim. Acta, 2016,200, 276— 282 |
| [29] | Iqbal M., Ali S., Tahir M. N., Muhammad N., Shah N. A., Journal of Molecular Structure., 2015,1093, 135— 143 |
| [30] | Wang H., Zhang Y., Chu Y., Ma H., Li Y., Wu D., Du B., Wei Q ., Talanta, 2016,147, 556— 560 |
| [31] | Lv X., Li Y., Cao W., Yan T., Li Y., Du B., Wei Q., Sens. Actuators, B, 2014,202, 53— 59 |
| [32] | Jiang M., Braiek M., Florea A., Chrouda A., Farre C., Bonhomme A., Bessueille F., Vocanson F., Zhang A., Jaffrezic R. N., Toxins, 2015,7(9), 3540— 3553 |
| [1] | WU Yangyi, CHEN Jianping, Ai Yijing, WANG Qingxiang, GAO Fei, GAO Feng. Synthesis of 2-(2-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-C60 and Its Application for Sensing of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promotor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1754. |
| [2] | HUANG Ling, ZHUANG Zijian, LI Xiang, SHI Muling, LIU Gaoqiang. Advances in Molecular Recognition of Exosomes Based on Aptamers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3493. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaorong, CHEN Lanlan, HU Shanwen. Advances in Bacteria Biosensing Based on Molecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3468. |
| [4] | JI Cailing, CHENG Xing, TAN Jie, YUAN Quan. Selection of Functionalized Aptamers and Their Applications in Molecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3457. |
| [5] | LIU Ke, JIN Yu, LIANG Jiangong, WU Yuan. Research Progress on Improving the Binding Affinity of Aptamers through Chemical Modification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3477. |
| [6] | XIE Chen, CHEN Na, YANG Yanbing, YUAN Quan. Recent Progress of Aptamer Functionalized Two-dimensional Materials Field Effect Transistor Sensors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3406. |
| [7] | ZHAO Zhuo, WANG Xueqiang. Investigations upon the Bioconjugation-based Construction Technologies and Applications of Aptamer-drug Conjugates [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3367. |
| [8] | LIU Xuejiao, YANG Fan, LIU Shuang, ZHANG Chunjuan, LIU Qiaoling. Progress in Aptamer-targeted Membrane Protein Recognition and Functional Regulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3277. |
| [9] | REN Yushuang, GUO Yuanyuan, LIU Xueyi, SONG Jie, ZHANG Chuan. Platinum(Ⅳ) Prodrug-grafted Phosphorothioate DNA and Its Self-assembled Nanostructure for Targeted Drug Delivery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1721. |
| [10] | DU Xianchao, HAO Hongxia, QIN Anjun, TANG Benzhong. Detection of Cocaine Based on the System of AIEgen, Aptamer and Exonuclease Ⅰ † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 411. |
| [11] | DONG Qian, LI Zhaoqian, PENG Tianhuan, CHEN Zhuo, TAN Weihong. Progress on Aptamer for Cancer Theranostics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2648. |
| [12] | Zhiqing ZHANG,Shanshan WANG,Zichen ZHANG,Jie MA,Xiufeng WANG,Ting ZHOU,Fang WANG,Guodong ZHANG. Rolling Circle Amplification-based Polyvalent Molecular Beacon Probe for Signal-amplifying and Sensitive-Detection of Thrombin † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2465. |
| [13] | LIU Zhongcheng, LIU Shifang, ZHANG Su, YANG Yanlei, LI Fei, ZHANG Nan, YUAN Xin, ZHANG Yanfen. Structure Prediction and Screening of Oligonucleotide Aptamers Target Cε3-Cε4 Protein† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 83. |
| [14] | DU Shanshan, LI Yang, GUO Lei, LI Pengyu, CHAI Zhilong, WANG Tao, QUAN Dongqin, HE Junlin. Modification of Aptamer TBA with Extra Functional Groups and the Biological Activities† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2445. |
| [15] | LIU Renzhi, LI Xiaoyan. Preparation of MoS2 Hollow Nanospheres and Application in Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Biosensing Platform for Micro-RNA Detection† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||