

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 1464.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190057
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Xueyi, CHEN Miaomiao, FANG Yun*( ), FENG Ruiqin, HAN Huihui
), FENG Ruiqin, HAN Huihui
Received:2019-01-18
Online:2019-07-10
Published:2019-07-09
Contact:
FANG Yun
E-mail:yunfang@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HU Xueyi, CHEN Miaomiao, FANG Yun, FENG Ruiqin, HAN Huihui. Investigation on Pseudo-polyanions of Cationic Cellulose-Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1464.

Fig.1 Appearance of JR400(2 g/L)-SDBS(A) and JR400(0.5 g/L)-SDBS(B) with the corresponding turbidity curve(A) cSDBS/(mmol·L-1): a. 0 (clear); b. 2 (clear); c. 4 (turbid); d. 6 (precipitation); e. 8 (precipitation); f. 10 (precipitation); g. 20 (precipitate); h. 30 (clear). (B) cSDBS/(mmol·L-1): a. 0.5 (clear); b. 1 (clear); c. 2 (turbid); d. 4 (precipitation); e. 6 (precipitation); f. 8 (clear); g. 9 (clear).
| ρ/(g·L-1) | cSDBS/(mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation zone | c1 | psp | c2 | |
| 0.05 | 0.4—0.8 | 0.1 | — | 4.0 |
| 0.10 | 0.6—1.0 | 0.2 | — | 6.0 |
| 0.50 | 2.0—6.0 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 8.0 |
Table 1 Concentration thresholds of JR400-SDBS complexes including the corresponding precipitation zone(PZ)*
| ρ/(g·L-1) | cSDBS/(mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation zone | c1 | psp | c2 | |
| 0.05 | 0.4—0.8 | 0.1 | — | 4.0 |
| 0.10 | 0.6—1.0 | 0.2 | — | 6.0 |
| 0.50 | 2.0—6.0 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 8.0 |
| Cationic cellulose | Mass fraction(%) | Viscosity/(mPa·s) | N content(%) | SD/(cation per unit) | CD*/(mmol e·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JR125 | 2 | 75—175 | 1.5—2.2 | 0.42 | 1.33(0.42) |
| JR400 | 2 | 300—500 | 1.5—2.2 | 0.42 | 1.33(0.42) |
| JR30M | 2 | 25000—35000 | 1.5—2.2 | 0.42 | 1.33(0.42) |
| LR400 | 2 | 300—500 | 0.8—1.1 | 0.17 | 0.62(0.17) |
Table 2 Properties of the tested cationic celluloses
| Cationic cellulose | Mass fraction(%) | Viscosity/(mPa·s) | N content(%) | SD/(cation per unit) | CD*/(mmol e·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JR125 | 2 | 75—175 | 1.5—2.2 | 0.42 | 1.33(0.42) |
| JR400 | 2 | 300—500 | 1.5—2.2 | 0.42 | 1.33(0.42) |
| JR30M | 2 | 25000—35000 | 1.5—2.2 | 0.42 | 1.33(0.42) |
| LR400 | 2 | 300—500 | 0.8—1.1 | 0.17 | 0.62(0.17) |
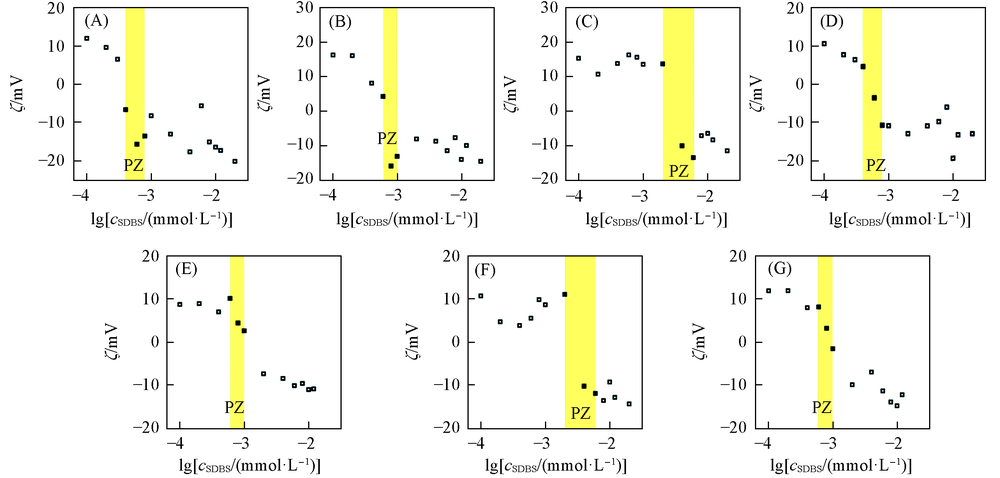
Fig.4 Effects of molecular mass and substitution degrees of cationic celluloses on zeta potential variation of the cationic cellulose-SDBS complexesPZ: precipitation zone. (A) JR125(0.05 g/L)-SDBS; (B) JR125(0.1 g/L)-SDBS; (C) JR125(0.5 g/L)-SDBS; (D) JR30 M(0.05 g/L)-SDBS; (E) JR30M(0.1 g/L)-SDBS; (F) JR30M(0.5 g/L)-SDBS; (G) LR400(0.1 g/L)-SDBS.
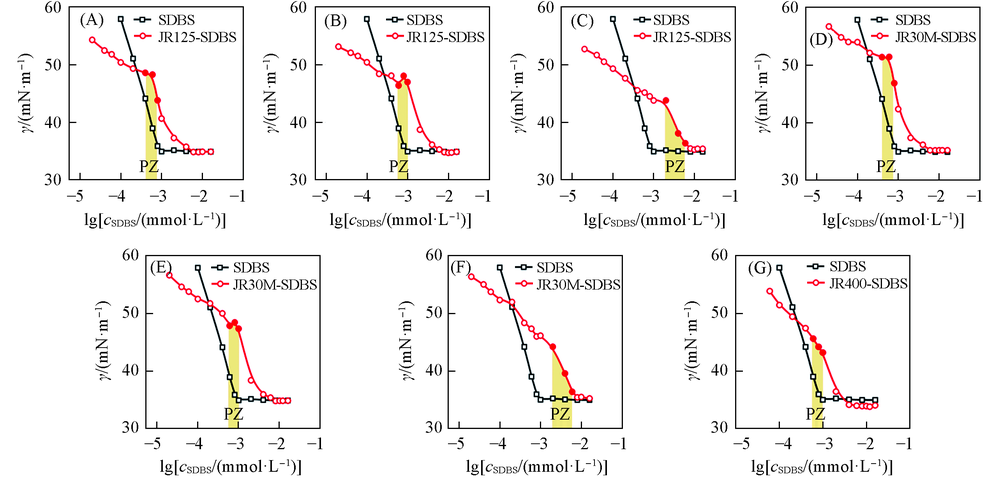
Fig.5 Effect of molecular mass and substitution degrees of cationic celluloses on surface tension variation of the cationic cellulose-SDBS complexesPZ: precipitation zone. ρ/(g·L-1): (A) 0.05; (B) 0.1; (C) 0.5; (D) 0.05; (E) 0.1; (F) 0.5; (G) 0.1.
| Complex | ρ/(g·L-1) | cSDBS/(mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation zone | c1 | psp | c2 | ||
| JR125-SDBS | 0.05 | 0.4—0.8(6.0—12.0) | 0.2 | — | 4.0 |
| 0.10 | 0.6—1.0(4.5—7.5) | 0.2 | — | 6.0 | |
| 0.50 | 2.0—6.0(3.0—9.0) | 0.4 | 2.0 | 8.0 | |
| JR30M-SDBS | 0.05 | 0.4—0.8(6.0—12.0) | 0.2 | — | 4.0 |
| 0.10 | 0.6—1.0(4.5—7.5) | 0.4 | — | 6.0 | |
| 0.50 | 2.0—6.0(3.0—9.0) | 0.4 | 2.0 | 8.0 | |
| LR400-SDBS | 0.10 | 0.6—1.0(9.7—16.1) | 0.2 | — | 6.0 |
Table 3 More concentration thresholds of various cationic cellulose-SDBS complexes including the corresponding precipitation zone*
| Complex | ρ/(g·L-1) | cSDBS/(mmol·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation zone | c1 | psp | c2 | ||
| JR125-SDBS | 0.05 | 0.4—0.8(6.0—12.0) | 0.2 | — | 4.0 |
| 0.10 | 0.6—1.0(4.5—7.5) | 0.2 | — | 6.0 | |
| 0.50 | 2.0—6.0(3.0—9.0) | 0.4 | 2.0 | 8.0 | |
| JR30M-SDBS | 0.05 | 0.4—0.8(6.0—12.0) | 0.2 | — | 4.0 |
| 0.10 | 0.6—1.0(4.5—7.5) | 0.4 | — | 6.0 | |
| 0.50 | 2.0—6.0(3.0—9.0) | 0.4 | 2.0 | 8.0 | |
| LR400-SDBS | 0.10 | 0.6—1.0(9.7—16.1) | 0.2 | — | 6.0 |
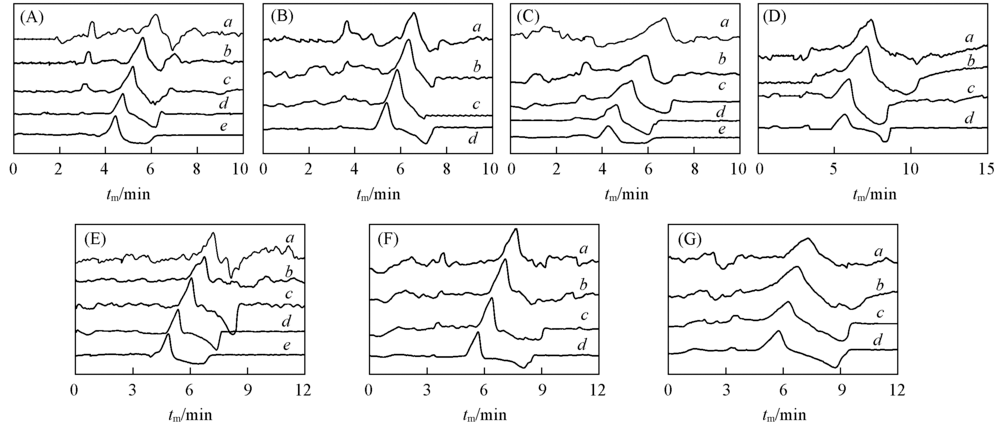
Fig.6 Electropherograms of various cationic cellulose-SDBS complexes(A) JR125(0.05 g/L)-SDBS; (B) JR125(0.1 g/L)-SDBS; (C) JR400(0.05 g/L)-SDBS; (D) JR400(0.1 g/L)-SDBS; (E) JR400(0.05 g/L)-SDBS; (F) JR400(0.1 g/L)-SDBS; (G) JR400(0.1 g/L)-SDBS.cSDBS/(mmol·L-1): a. 8; b. 6; c. 4; d. 2; e. 1.
| Complex | ρ/(g·L-1) | μe/(cm2·kV-1·s-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mmol/L SDBS | 2 mmol/L SDBS | 4 mmol/L SDBS | 6 mmol/L SDBS | 8 mmol/L SDBS | ||
| JR125 | 0.05 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.37 |
| 0.10 | -0.35 | -0.36 | -0.36 | -0.37 | ||
| JR400 | 0.05 | -0.33 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.39 |
| 0.10 | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.38 | ||
| JR30M | 0.05 | -0.34 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.37 | -0.37 |
| 0.10 | -0.36 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.37 | ||
| LR400 | 0.10 | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.38 | |
Table 4 Effective electrophoretic mobility(μe) of various cationic cellulose-SDBS complexes
| Complex | ρ/(g·L-1) | μe/(cm2·kV-1·s-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mmol/L SDBS | 2 mmol/L SDBS | 4 mmol/L SDBS | 6 mmol/L SDBS | 8 mmol/L SDBS | ||
| JR125 | 0.05 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.37 |
| 0.10 | -0.35 | -0.36 | -0.36 | -0.37 | ||
| JR400 | 0.05 | -0.33 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.39 |
| 0.10 | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.38 | ||
| JR30M | 0.05 | -0.34 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.37 | -0.37 |
| 0.10 | -0.36 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.37 | ||
| LR400 | 0.10 | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.38 | -0.38 | |
| [1] | Senra T. D. A., Campana-Filho S. P., Desbrièresb J., European Polymer Journal, 2018, 104, 128—135 |
| [2] | Cao Y., Li H.L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(2), 312—316 |
| (曹亚, 李惠林. 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22(2), 312—316 | |
| [3] | Deshpande T., M , Shi H., Pietryka J., Stephen W. H., Medek A., Mol. Pharm., 2018, 15(3), 962—974 |
| [4] | Qi L., Li J., Ma J., Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(14), 300—303 |
| [5] | Nilsson S., Goldraich M., Lindman B., TalmonL Y., Langmuir, 2000, 16(17), 6825—6832 |
| [6] | Mel’Nikov S. M., Sergeyev V. G., Yoshikawa K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117(40), 9951—9956 |
| [7] | Taylor D. J. F., Thomas R. K., Hines J. D., Humphreys K., Langmuir, 2002, 18(25), 9783—9791 |
| [8] | Wang R.J., Yan H. T., Ma W. W., Li Y. H., Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 509, 293—300 |
| [9] | Chatterjee S., Prajapati R., Bhattacharya A., Mukherjee T. K., Langmuir, 2014, 30(32), 9859—9865 |
| [10] | Liu Q., Li J., Tao W., Zhu Y. D., Yao S. Z., Bioelectrochem., 2007, 70(2), 301—307 |
| [11] | Lafitte G., Thuresson K., Soderman O., Langmuir, 2005, 21(16), 7097—7104 |
| [12] | Taylor D.J., Thomas R. K., Penfold J., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 132(2), 69—110 |
| [13] | Liu Y., Chen G., Zhu J. T., Chen W. J., Hu W., Liu Y. Y., Fang Z. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10), 2298—2303 |
| (刘宇, 陈港, 朱家添, 陈文锦, 胡稳, 刘映尧, 方志强. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10), 2298—2303 | |
| [14] | Wang W. L., Shi Y. J., Wang S. H., Dang Z. P., Li X. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5), 964—970 |
| (王文亮, 时宇杰, 王少华, 党泽攀, 李新平. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(5), 964—970 | |
| [15] | Chakraborty I., Chakraborty T., Moulik S. P. J., Colloid and Polymer Science, 2013, 291(8), 1939—1948 |
| [16] | Han J., Jiang X. D., Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology, 2015, 23(1), 36—42 |
| (韩晶, 江笑单. 纤维素科学与技术, 2015, 23(1), 36—42 | |
| [17] | Goddard E. D., J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 1994, 71(1), 1—16 |
| [18] | Han J., Cheng F., Wang X. G., Wei Y. P., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 88(1), 139—145 |
| [19] | Goddard E. D., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2002, 256(1), 228—235 |
| [20] | Feng W. Y., Qiao J., Qi L., Li Z. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8), 1640—1646 |
| (冯文雅, 乔娟, 齐莉, 李志伟. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(8), 1640—1646 | |
| [21] | Wu Y.F., Chen J., Fang Y., Zhu M., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2016, 479, 34—42 |
| [22] | Wu Y. F., Chen M. M.,Fang Y, Wang W. S., RSC Adv., 2017, 7(15), 9338—9346 |
| [23] | Wu Y.F., Chen M. M., Fang Y., Zhu M., J. Chromatogr. A, 2017, 1489, 134—142 |
| [24] | Wu Y.F., Wang W. S., Fang Y., Chen M. M., Feng R. Q., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2019, 832, 105—111 |
| [25] | Jones M.N., J Colloid Interface Sci., 1967, 23(1), 36—42 |
| [1] | QIN Gaizhao, TANG Minghua, LAI Yalin, YUAN Liming. Chiral Metal-organic Cage MOC-PA as a Chiral Stationary Phase for Capillary Electrophoresis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220417. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xiaotao,WANG Yan’an,HUI Jia,SHI Yan,FU Zhifeng,YANG Wantai. Reversible-deactivation Radical Solution Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate Catalyzed by Tetrabutylammonium Iodide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 366. |
| [3] | CAO Xiaoqiang, YAN Bingqi, WANG Qian, WANG Yaping, QIU Jun, HUANG Yongqing, LI Lin, ZHANG Yan, HU Shugang, KANG Ling, LÜ Xianjun. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) from Aqueous Solutions on Organic Modified Laponite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 173. |
| [4] | ZOU Haimin, ZHOU Chen, SUN Chengjun, LI Yongxin, YANG Xiaosong, WEN Jun, ZENG Hongyan. Simultaneous Determination of 7 Components in Functional Food for Anti-hangover and Hepatoprotection by Capillary Electrophoresis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1276. |
| [5] | HU Can, CHEN Yi. Dissolution/diffusion-based Injection for Fast Separation of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine by Short Capillary Electrophoresis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1681. |
| [6] | WEI Yu, CHEN Yufu, ZHOU Qiang, YUAN Qiuyue, TAN Fengyu, XIE Tianyao. Enantioseparation of Underivatized D,L-Serine in Biological Matrices by Capillary Electrophoresis with Contactless Conductivity Detection† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1409. |
| [7] | YANG Jiao-Mei, REN Jie, LIU Hui-Qing, WANG Yong-Le, XU Zhong-Qi. Separation and Detection of Neurotransmitter-related Substances in Urine Sample by Capillary Electrophoresis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(12): 2699. |
| [8] | HUANG Jia-Hua, GONG Zhen-Bin, LIN Ji-Jun, DUAN Hua-Ling. Measurement of Complexation Stability Constant and Coordinating Number of Poly(ethylenimine) with Metals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12): 2633. |
| [9] | QIU Chang-Gui, WANG Xiao-Yu, GUO Zhen-Peng, SONG Li-Juan, CHEN Yi. Chiral Ligand-exchange Capillary Electrophoretic Assay of L-Dopa Tablets Using a Non-analyte Chiral Ligand [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(03): 470. |
| [10] | GUO Kai, SUN Liang, WU Meng-Chun, WANG Shao-Dan, WANG Li-Yan*. Effects of Inclusion Complexation and Degree of Protonation on Cloud Point of Poly(N-acryloyl-N′-propylpiperazine) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9): 2223. |
| [11] | LI Yu-Rong, CHEN Chang-Bao, ZHOU Jie*. Separation of DNA Fragments with a Broad Range of Molecular Weight by Capillary Electrophoresis with Sieving Matrix of Poly(ethylene oxide) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(4): 844. |
| [12] | XIA Zhi-Ning*, LI Li-Xian, CHEN Hua, XIONG Cai-Qiao, YANG Feng-Qing. Kinetic Parameters of Interaction Between Cell Membrane and Drug by ppKCE [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(4): 851. |
| [13] | WANG Xiao-Yu, CHEN Yi*. Online Base Barrage Focusing and Capillary Electrophoresis of Aromatic Amines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(8): 1506. |
| [14] | XU Zhang-Run*, LI Na, ZHANG Hui-Dan, FAN Xiao-Feng, FANG Jin*. On-chip Temperature Gradient Capillary Electrophoresis with Thermal Resistance Gradient Heating System for DNA Mutation Detection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(4): 667. |
| [15] | XIE Ming-Yi, GUO Zhen-Peng, CHEN Yi*. Inspection into the Interaction of Bovine Serum Albumin with Gold Nanoparticles by Capillary Electrophoresis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(11): 2162. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||