

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 1681.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150156
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2015-02-16
Online:2015-09-10
Published:2015-08-17
Contact:
CHEN Yi
E-mail:chenyi@iccas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HU Can, CHEN Yi. Dissolution/diffusion-based Injection for Fast Separation of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine by Short Capillary Electrophoresis†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1681.
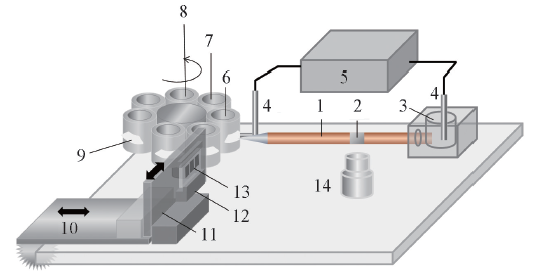
Fig.1 Setup of DDI-CE1. Separation capillary; 2. detection window; 3. grounded electrode reservoir; 4. platinum electrodes; 5. DC power supply; 6. high voltage electrode reservoir; 7. cleaning solution vial; 8. sample vial; 9. slit opening(ca.1 mm); 10. longitudinal slider; 11. cross slider; 12. sample plate and holder; 13. sample solution membrane or dried trace; 14. micro-objective of inverted fluorescence microscope.
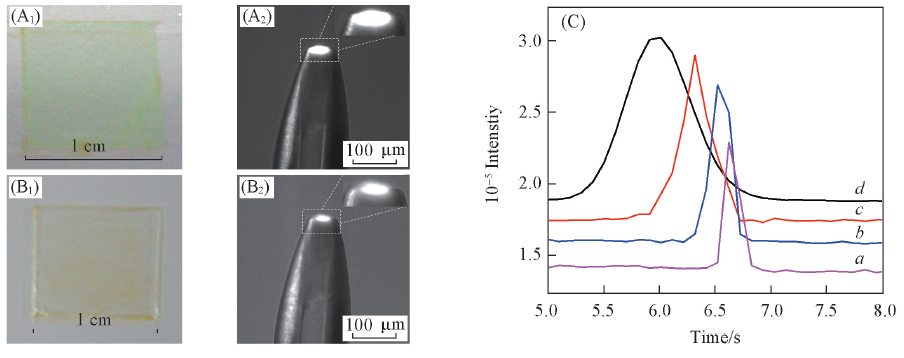
Fig.2 Photos of sample solution(A1, A2) and dried film(B1, B2), and electropherograms via DDI for about 0.2 s(C)(A1) shows a solution film formed in a 1 cm2 well with 1 μL of 0.1 mmol/L FITC,(B1) its dried trace,(A2) and(B2) their corresponding DDI zones, respectively. (C) a. dried film; b. solution film; c. spontaneous injection; d. electrokinetic injection. The electropherograms were obtained after separation at 400 V/cm, through 1 cm capillary filled with 20 mmol/L borax(pH=9.5).
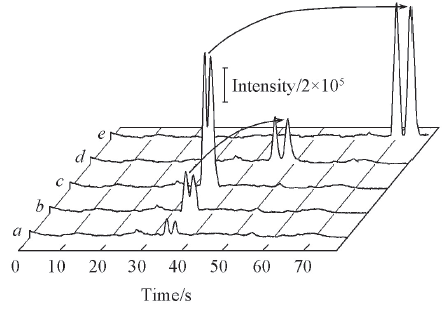
Fig.3 Resolution decreases with initial sample zone length and increases with separation lengthInjection time: a. 0.2 s; b and d. 1 s; c and e. 3 s; capillary: a—c. 50 μm i.d.×3 cm; d. 4 cm; e. 6 cm; sample: 50 μmol/L FITC-labeled E and NE; running buffer: 60 mmol/L borax at pH=10. Other conditions are the same as in Fig.2.
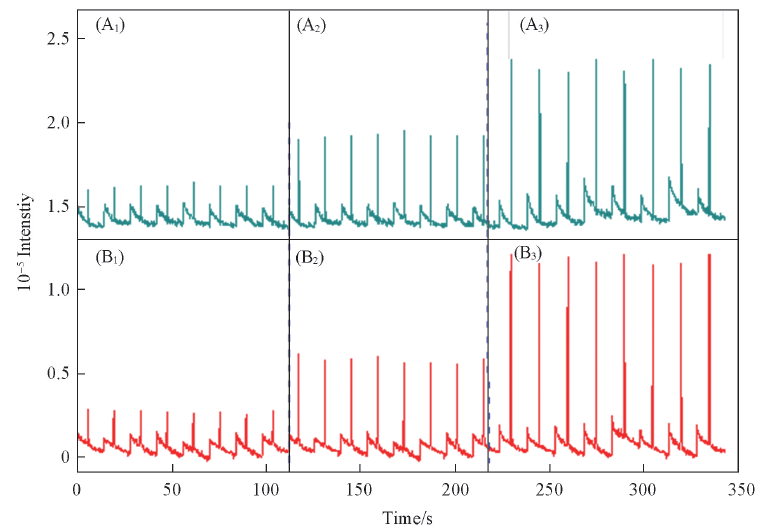
Fig.4 Successive DDI-CE of FITC dryness(A1—A3) and solution(B1—B3) membranes, respectivelyOther conditions are the same as in Fig.2. c(FITC)/( μmol·L-1): (A1), (B1) 20; (A2), (B2) 50; (A3), (B3) 100.
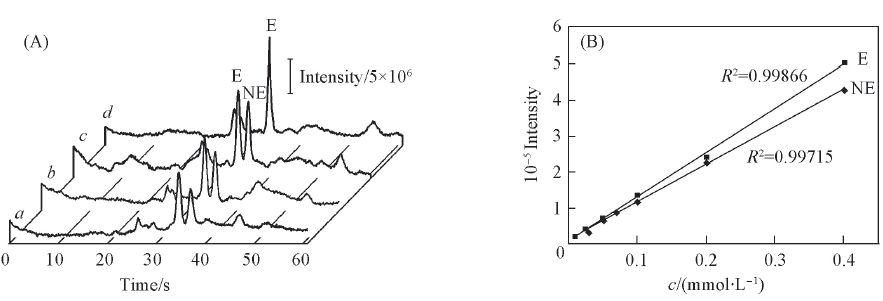
Fig.5 DDI-CE of standard and real samples(A) together with their working curves(B)(A) Sample state: a. solution film, b. film dried for 1 h, c. film dried for >1 d, d. real sample, all analytes were prepared at 50 μmol/L; (B) injection diluted for 100 times, and labeled by FITC; DDI injection time: 0.2 s; separation distance: 3 cm. Other conditions are the same as in Fig.2.
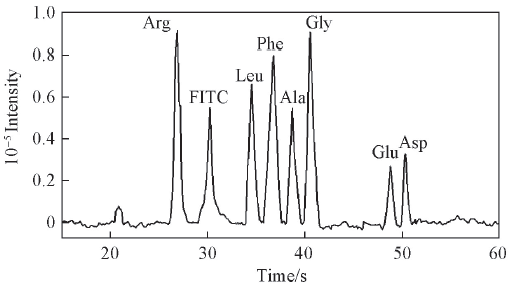
Fig.6 DDI-CE of amino acid mixturesSample: 50 μmol/L FITC-labled Arg, Leu, Phe, Ala, Gly, Glu and Asp. Capillary: 50 μm(i.d.)×6 cm;buffer: 20 mmol/L borax at pH=9.2. Other conditions are the same as in Fig.2.
| [1] | Haeberle S., Zengerle R., Lab Chip, 2007, 7, 1094—1110 |
| [2] | Glatz Z., Electrophoresis, 2013, 34, 631—642 |
| [3] | Liao T., Guo Z. P., Li J. C., Liu M. R., Chen Y., Lab Chip, 2013, 13, 706—713 |
| [4] | Shintaku H., Nishikii H., Marshall L.A., Kotera H., Santiago J. G., Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 1953—1957 |
| [5] | Alarie J. P., Jacobson S. C., Culbertson C. T., Ramsey J. M., Electrophoresis, 2000, 21, 100—106 |
| [6] | Matysik F. M., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2010, 397, 961—965 |
| [7] | Skoog D.A., Holler F. J., Crouch S. R., Principles of Instrumental Analysis, Thomson Brooks/Cole Publishing, Belmont, 2007, 867—874 |
| [8] | Monnig C. A., Jorgenson J. W., Anal. Chem., 1991, 63, 802—807 |
| [9] | Plenert M. L., Shear J. B., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2003, 100, 3853—3857 |
| [10] | Lemmo A. V., Jorgenson J. W., Anal. Chem., 1993, 65, 1576—1581 |
| [11] | Yang P. L., Whelan R. J., Mao Y. W., Lee A W. M., Carter-Su C., Kennedy R. T., Anal. Chem., 2007, 79, 1690—1695 |
| [12] | Wang H. L., Lu M. L., Le X. C., Anal. Chem., 2005, 77, 4985—4990 |
| [13] | Zhang T., Fang Q., Du W. B., Fu J. L., Anal. Chem, 2009, 81, 3693—3698 |
| [14] | Zhang T., Fu J. L., Fang Q., Electrophoresis, 2014, 35, 2361—2369 |
| [15] | Chen Y., Zhu A., Chin. J. Chromatogr., 1991,9, 353—356 |
| (陈义, 竺安. 色谱, 1991,9, 353—356) | |
| [16] | Diao P., Yuan H., Huo F., Chen L., Xiao D., Paau M. C., Choi M. M. F., Talanta, 2011, 85, 1279—1284 |
| [17] | Lu X., Chen Y., J. Chromatogr. A, 2002, 955, 133—140 |
| [18] | Yin Q. M., Ye J. M., Zhou Y. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(8), 1647—1649 |
| (阴启明, 叶嘉明, 周勇亮. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(8), 1647—1649 ) | |
| [19] | Zhang H., Li Z., Zhang J., Zhang Y., Ye J., Chu Q., Zhang M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(5), 850—853 |
| [20] | Xu H., Wang X., Chen R., Yu Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(2), 205—210 |
| [1] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [2] | TIAN Xueqin, MO Zheng, DING Xin, WU Pengyan, WANG Yu, WANG Jian. A Squaramide-containing Luminescent Metal-organic Framework as a High Selective Sensor for Histidine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210589. |
| [3] | WANG Shoubai, WU Xiuming, SHU Chen, ZHONG Min, HUANG Wei, YAN Deyue. Gas Separation Performance of Polyimide Homogeneous MembranesContaining tert-Butyl Groups [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220357. |
| [4] | TANG Yuanhui, LI Chunyu, LIN Yakai, ZHANG Chunhui, LIU Ze, YU Lixin, WANG Haihui, WANG Xiaolin. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of the Effect of Polymer Chain Rigidity on Membranes Formation by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220169. |
| [5] | LIU Xueguang, YANG Xiaoshan, MA Jingjing, LIU Weisheng. Separating Methyl Blue Selectively from the Mixture of Dyes by Europium Metal-organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210715. |
| [6] | ZHAO Yangyang, LIU Qiyong, CHEN Boxin, ZHAO Bin, ZHOU Haimei, LI Xinxin, ZHENG Dan, FENG Fei. Silicon-based Micro Gas Chromatographic Column Using Metal-Organic Framework Material ZIF-8 as Stationary Phase [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1736. |
| [7] | GAO Yifei, XIAO Changfa, JI Dawei, HUANG Yangzheng. Preparation of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes via Melt Spinning-stretching Method and Its Oil-water Separation Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2065. |
| [8] | WANG Longjie, FAN Hongchuan, QIN Yu, CAO Qiue, ZHENG Liyan. Research Progress of Metal-organic Frameworks in the Field of Chemical Separation and Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [9] | LIU Pengchang, LAI Hua, CHENG Zhongjun, LIU Yuyan. Fabrication of Superwetting Porous Shape Memory Sponge and Its Application in Oil-water Separation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 894. |
| [10] | YAN Yanhong, WU Simin, YAN Yilun, TANG Xihao, CAI Songliang, ZHENG Shengrun, ZHANG Weiguang, GU Fenglong. Sulfonic Acid-functionalized Spherical Covalent Organic Framework with Ultrahigh Capacity for the Removal of Cationic Dyes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 956. |
| [11] | LIN Ningqin, YAO Ke, CHEN Xiangjun. Research Progress of Molecular Recognition and Interaction of Crystallins Linking Cataract [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3379. |
| [12] | LIU Yi, LIU Yi. Research Progress on Zeolite Layer Preparation via Oriented Seeded Growth [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 117. |
| [13] | SONG Hongling, PENG Yuan, YANG Weishen. Two-dimensional Nanosheets for Ultra-permeable Membrane-Based Gas Separation with High Efficiency [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 248. |
| [14] | LIU Shanshan, CHAI Yuchao, GUAN Naijia, LI Landong. Small Molecule Adsorption and Separation on Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 268. |
| [15] | YAN Yilun, HUANG Xiaoling, FAN Jun, CAI Songliang, ZHENG Shengrun, ZHANG Weiguang. Synthesis of a β-Ketoenamine-linked Chiral Covalent Organic Framework and Its Application in Capillary Gas Chromatography [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1996. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
