

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 230.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180562
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Yan, LIAN Huiting, SUN Xiangying, LIU Bin*( )
)
Received:2018-08-10
Online:2019-02-10
Published:2018-12-27
Contact:
LIU Bin
E-mail:bliu@hqu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Yan,LIAN Huiting,SUN Xiangying,LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin Polymeric Membrane Sensor Based on Graphene and Potential Recognition for Histidine Enantiomer†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 230.
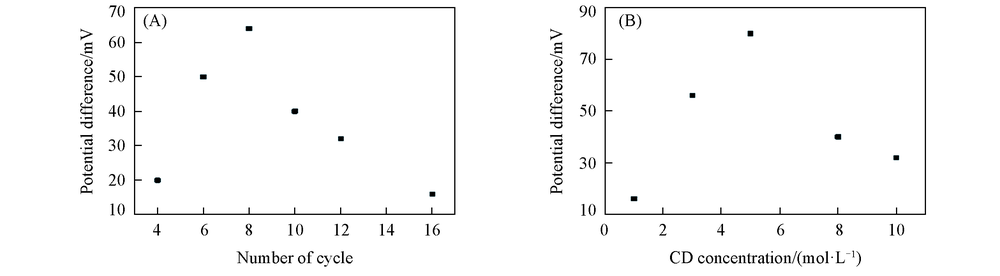
Fig.3 Potential difference of D/L-His on PCD/rGO/GCE with different polymerized cycles of CD(A) and with different concentrations of CD polymerized solution(B)
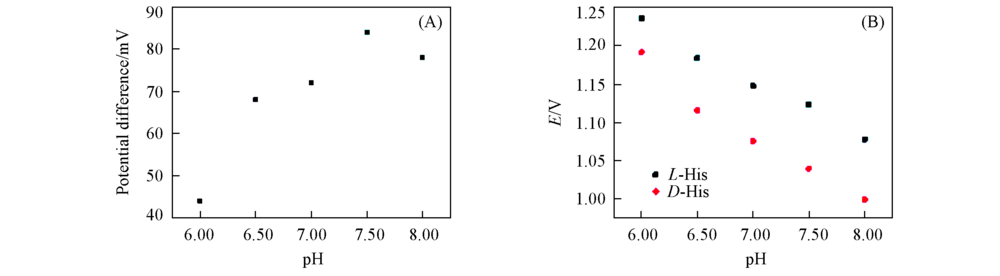
Fig.4 Potential difference of the D/L-His on PCD/rGO/GCE with different pH(A) and the oxidation potential of histidine enantiomer with different pH values(B)
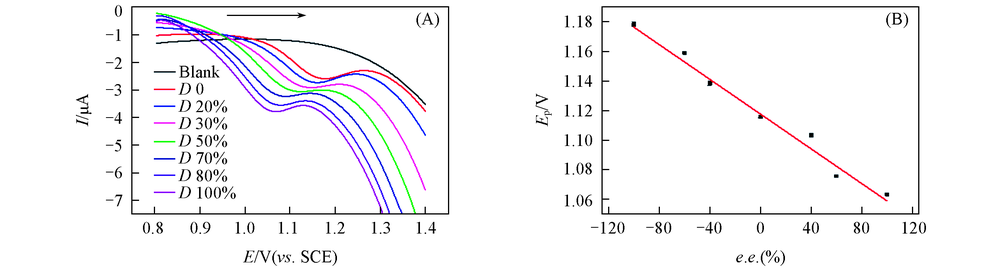
Fig.10 DPV response of PCD/rGO/GCE sensor for different ratio of L/D-His(total concentration 100 μmol/L)(A) and the curve of peak potential Ep to e.e. value(B)The arrow of (A) shows the potential scan direction.
| L-His to D-His ratio | c/(μmol·L-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 50 | 70 | 80 | 100 | 200 | 500 | 800 | 1000 | |
| 5:5 | 1.143 | 1.140 | 1.128 | 1.125 | 1.125 | 1.124 | 1.125 | 1.125 | 1.125 |
| 3:7 | 1.100 | 1.100 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.095 | 1.090 | 1.092 |
| 7:3 | 1.068 | 1.165 | 1.150 | 1.150 | 1.150 | 1.152 | 1.150 | 1.150 | 1.150 |
Table 1 Change of potential(E/V) for the ratios of 5:5, 3:7 and 7:3 between L-His and D-His
| L-His to D-His ratio | c/(μmol·L-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 50 | 70 | 80 | 100 | 200 | 500 | 800 | 1000 | |
| 5:5 | 1.143 | 1.140 | 1.128 | 1.125 | 1.125 | 1.124 | 1.125 | 1.125 | 1.125 |
| 3:7 | 1.100 | 1.100 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.095 | 1.090 | 1.092 |
| 7:3 | 1.068 | 1.165 | 1.150 | 1.150 | 1.150 | 1.152 | 1.150 | 1.150 | 1.150 |
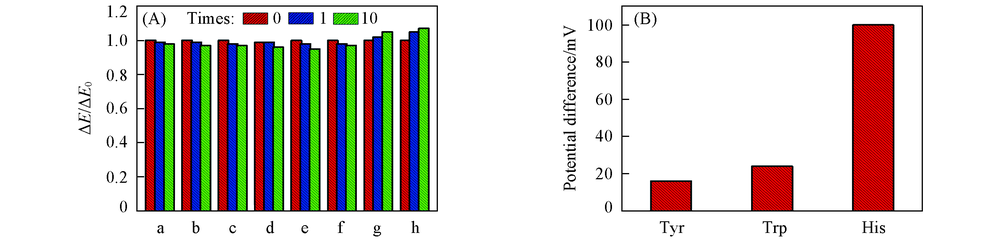
Fig.11 Response ratio(ΔE/ΔE0) of the PD of L/D-His on PCD/rGO/GCE in the presence of 1 and 10 times of the concentration of chiral coexistences(A), recognition of the His, tryptophan and tyrosine on PCD/rGO/GCE(B)(A) a. L-Tyr; b. D-Tyr; c. L-Trp; d. D-Trp; e. L-Pen; f. D-Pen; g. L-Pro; h. D-Pro.
| [1] | Prasad B. B., Kumar D., Madhuri R., Tiwari M. P., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2011, 28(1), 117-126 |
| [2] | Wade M. A., J. Nutr. Biochem., 1998, 9(6), 308-315 |
| [3] | Zhang C. H., Zhang H. B., Hu Y. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2008, 29(10), 1941-1946 |
| (张朝晖, 张华斌, 胡宇芳. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(10), 1941-1946) | |
| [4] | Gu P., Zhang G., Deng Z., Tang Z., Zhang H., Khusbu F. Y., Wu K., Chen M., Ma C., Spectrochim. Acta A,2018, 203, 195-200 |
| [5] | Kang Y., Oh J., Kim Y., Kim J. S., Kim H., Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(31), 5665-5667 |
| [6] | Han C., Hou X., Zhang H., Guo W., Li. H., Jiang L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(20), 7644-7647 |
| [7] | Nie R., Bo X., Wang H., Zeng L., Guo L., Electrochem. Commun., 2013, 27, 112-115 |
| [8] | Geim A. K., Katsnelson M. I., Novoselov K. S., Nat. Phys., 2006, 2(9), 620-625 |
| [9] | Chang J., Chang K., Hu C., Cheng W., Zen J., Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12(4), 596-599 |
| [10] | Kauppila J., Kunnas P., Damlin P., Electrochimi. Acta,2013, 89, 84-89 |
| [11] | Zhang D., Fang Y., Miao Z., Ma M., Du X., Electrochimi. Acta,2013, 107, 656-663 |
| [12] | Corona-Avendaño S., Ramírez-Silva M. T., Romero-Romo M., Electrochim. Acta,2013, 89, 854-860 |
| [13] | Roa Morales G., Ramírez Silva T., Galicia L., J. Solid State Electrochem.,2003, 7(6), 355-360 |
| [14] | Liu Y. R., Wei M.T., Hu Y., Zhu L. L., Du J. Y., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2018, 255, 544-551 |
| [15] | Wang L., Int. J. Electrochem. Sc., 2018, 13, 1594-1602 |
| [16] | Cheol-Joo Kim. A., Sánchez C., Zack Z., Yui O., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2016, 11(6), 520-525 |
| [17] | Trojanowicz M., Electrochem. Commun., 2014, 38, 47-52 |
| [18] | Liu Y. L., Zhu L. L., Hu Y., Peng X. S., Du J., Food. Chem., 2017, 221, 1128-1134 |
| [19] | Corona-Avendaño S., Ramírez-Silva M. T., Romero-Romo M., Rojas-Hernández A., Palomar-Pardavé M., Electrochim. Acta,2013, 89, 854-860 |
| [20] | Zhao Y., Huang Y., Zhu H., Zhu Q., Xia Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(51), 16645-16654 |
| [21] | Fraschini C., Vignon M. R., Carbohyd. Res., 2000, 328(4), 585-589 |
| [22] | Liu Y. R., Zhu L. L., Hu Y., Peng X. S., Du J. Y., Food. Chem., 2017, 221, 1128-1134 |
| [23] | Ates S., Zor E., Akin I., Bingol H., Alpaydin S., Akgemci E. G., Anal. Chim. Acta,2017, 970, 30-37 |
| [24] | Jung I., Pelton M., Piner R., Dikin D. A., Stankovich S., Watcharotone S., Hausner M., Ruoff R. S., Nano. Lett.,2007, 7(12), 3569-3575 |
| [25] | Ding S., Cao S., Zhu A., Shi G., Anal. Chem., 2016, 88(24), 12219-12226 |
| [26] | Tian F., Mou S. F., J. North Univ. China(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 31(5), 499-503 |
| (田芳, 牟善峰. 中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 31(5), 499-503) | |
| [27] | Liao H., Zhang Z., Nie L., Yao S., J. Biochem. Bioph. Meth., 2004, 59(1), 75-87 |
| [28] | Liu C., Li B., Xu C., Microchim. Acta,2014, 181(11/12), 1407-1413 |
| [1] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [2] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [3] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [4] | ZHENG Xuelian, YANG Cuicui, TIAN Weiquan. The Second Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Azulene-defect Graphene Nanosheets with Full Armchair Edge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [5] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [7] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [8] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [9] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [10] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [11] | WEI Zheyu, WU Zhikang, RU Shi, NI Lubin, WEI Yongge. Research Progress of Polyoxometalates-Cyclodextrin Supramolecular System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210665. |
| [12] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [13] | ZHU Deshuai, ZHAO Jianying, YANG Zhenghui, GUO Haiquan, GAO Lianxun. Graphene Oxide/Polyimide Composites with High Energy Storage Density Based on Multilayer Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2694. |
| [14] | HUANG Shan, YAO Jiandong, NING Gan, XIAO Qi, LIU Yi. Efficient Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2412. |
| [15] | LIU Yang, LI Qingbo, SUN Jie, ZHAO Xian. Direct Synthesis of Graphene on AlN Substrates via Ga Remote Catalyzation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||