

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 2061.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170237
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Guanghui1, ZHANG Ya1, ZHANG Yuping1, ZHOU Pengpeng1, LIN Zhihua1, WANG Yuanqiang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2017-04-17
Online:2017-11-10
Published:2017-10-30
Contact:
WANG Yuanqiang
E-mail:wangyqnn@cqut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
TANG Guanghui, ZHANG Ya, ZHANG Yuping, ZHOU Pengpeng, LIN Zhihua, WANG Yuanqiang. Molecular Docking, QSAR and Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Phosphorus Containing Pyrimidines as CDK9 Inhibitors†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2061.
| Method | Parameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Q2 | R2 | SEE | F | r2 | SDEP | |
| CoMFA | 4 | 0.162 | 0.876 | 0.196 | 81.257 | 0.376 | 0.357 |
| CoMSIA-EH | 7 | 0.564 | 0.950 | 0.129 | 115.848 | 0.765 | 0.211 |
| CoMSIA-SEH | 7 | 0.557 | 0.959 | 0.116 | 145.518 | 0.863 | 0.097 |
| T-CoMFA | 11 | 0.719 | 0.964 | 0.629 | 0.344 | ||
Table 1 Summary of 3D-QSAR results*
| Method | Parameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Q2 | R2 | SEE | F | r2 | SDEP | |
| CoMFA | 4 | 0.162 | 0.876 | 0.196 | 81.257 | 0.376 | 0.357 |
| CoMSIA-EH | 7 | 0.564 | 0.950 | 0.129 | 115.848 | 0.765 | 0.211 |
| CoMSIA-SEH | 7 | 0.557 | 0.959 | 0.116 | 145.518 | 0.863 | 0.097 |
| T-CoMFA | 11 | 0.719 | 0.964 | 0.629 | 0.344 | ||
| Compound | R5 | R6 | R7 | Z1 | Z2 | Calculated pIC50 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMSIA-EH | CoMSIA-SEH | T-CoMFA | ||||||
| 64 | H | H | H | H | H | 3.830 | 3.873 | 3.880 |
| 64a | H | Et | H | OCH3 | H | 3.485 | 3.457 | 3.770 |
| 64b | H | H | H | H | Et | 3.378 | 3.349 | 3.880 |
| 64c | H | H | H | BnO | H | 3.680 | 3.568 | 3.820 |
| 64d | H | H | SOOH | H | H | 3.916 | 3.947 | 3.920 |
| 64e | H | H | SOOCH3 | H | H | 3.952 | 3.962 | 3.882 |
| 64f | H | Et | SOOH | H | H | 3.830 | 3.782 | 3.878 |
| 64g | H | Et | SO3CH3 | H | H | 3.988 | 4.012 | 3.860 |
| 64h | H | Et | SOOCH3 | H | H | 3.980 | 3.989 | 3.830 |
| 64i | F | Et | SO3CH3 | H | H | 3.826 | 3.875 | 3.650 |
| 64j | H | H | 4-piperidyl | H | H | 3.825 | 3.869 | 3.890 |
Table 2 Predicted and in vitro activities of new designed compounds*
| Compound | R5 | R6 | R7 | Z1 | Z2 | Calculated pIC50 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMSIA-EH | CoMSIA-SEH | T-CoMFA | ||||||
| 64 | H | H | H | H | H | 3.830 | 3.873 | 3.880 |
| 64a | H | Et | H | OCH3 | H | 3.485 | 3.457 | 3.770 |
| 64b | H | H | H | H | Et | 3.378 | 3.349 | 3.880 |
| 64c | H | H | H | BnO | H | 3.680 | 3.568 | 3.820 |
| 64d | H | H | SOOH | H | H | 3.916 | 3.947 | 3.920 |
| 64e | H | H | SOOCH3 | H | H | 3.952 | 3.962 | 3.882 |
| 64f | H | Et | SOOH | H | H | 3.830 | 3.782 | 3.878 |
| 64g | H | Et | SO3CH3 | H | H | 3.988 | 4.012 | 3.860 |
| 64h | H | Et | SOOCH3 | H | H | 3.980 | 3.989 | 3.830 |
| 64i | F | Et | SO3CH3 | H | H | 3.826 | 3.875 | 3.650 |
| 64j | H | H | 4-piperidyl | H | H | 3.825 | 3.869 | 3.890 |
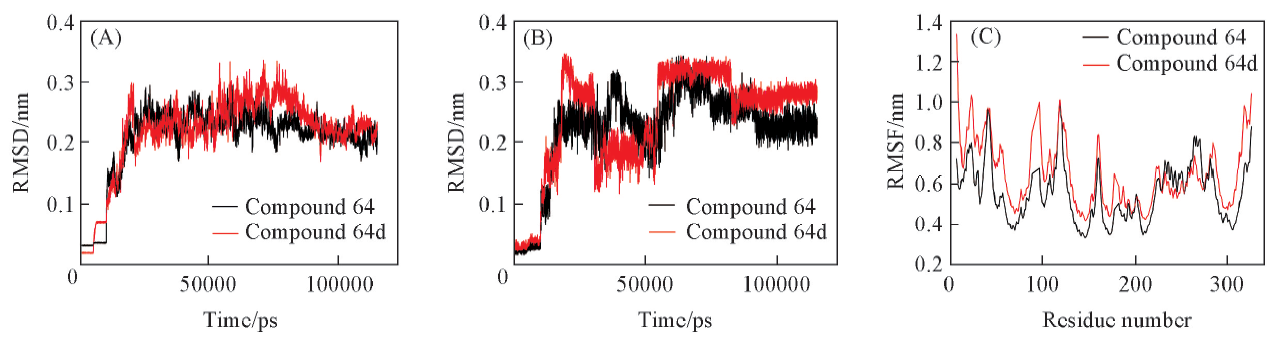
Fig.6 RMSDs(A) of backbone Cα atoms for CDK9-analogs complex systems, RMSDs(B) of heavy atoms for ligands and RMSF(C) of each residue for CDK9-analogs complex systems
| Method | Compound | ΔGvdW/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGele/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGepb/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGenp/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGedi/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGpred/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBSA | 64 | -235.92 | -169.07 | 294.49 | -156.05 | 282.81 | 16.16 |
| 64d | -247.77 | -226.50 | 342.00 | -179.54 | 313.70 | 1.88 | |
| Method | Compound | ΔGvdW/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGele/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGele,sol/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGnonpol,sol/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGpred/ (kJ·mol-1) | |
| GBSA | 64 | -235.92 | -169.07 | 237.72 | -28.30 | -195.61 | |
| 64d | -247.77 | -226.50 | 277.82 | -33.74 | -23.23 |
Table 3 Predicted activities of new designed compounds*
| Method | Compound | ΔGvdW/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGele/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGepb/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGenp/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGedi/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGpred/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBSA | 64 | -235.92 | -169.07 | 294.49 | -156.05 | 282.81 | 16.16 |
| 64d | -247.77 | -226.50 | 342.00 | -179.54 | 313.70 | 1.88 | |
| Method | Compound | ΔGvdW/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGele/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGele,sol/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGnonpol,sol/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGpred/ (kJ·mol-1) | |
| GBSA | 64 | -235.92 | -169.07 | 237.72 | -28.30 | -195.61 | |
| 64d | -247.77 | -226.50 | 277.82 | -33.74 | -23.23 |
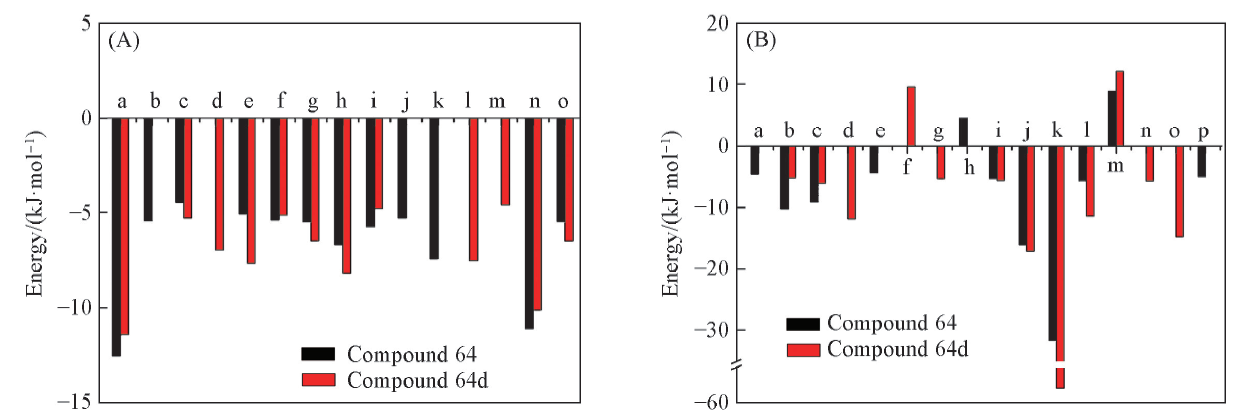
Fig.7 Comparison of per-residue energy decomposition for key residues of two systems in GBSA model(A) The van der Waals energy. a. I25, b. G26, c. Q27, d. F30, e. V33, f. A46, g. F103, h. F105, i. C106, j. H108, k. D109, l. A153, m. N154, n. L156, o. D167; (B) the electrostatic energy. a. K24, b. I25, c. G26, d. Q27, e. K35, f. K48, g. E66, h. D104, i. F105, j. C106, k. D109, l. D149, m. K151, n. A153, o. D167, p. E221.
| [1] | Cicenas J., Kalyan K., Sorokinas A., Jatulyte A., Valiunas D., Kaupinis A., Valius M., Cancers,2014, 6, 2224-2234 |
| [2] | Asghar U., Witkiewicz A. K., Turner N. C., Knudsen E. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 130-146 |
| [3] | Lim S., Kaldis P., Development,2013, 140, 3079-3087 |
| [4] | Liao Y., Feng Y., Shen J., Hornicek F. J., Duan Z., Cancer and Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 151-163 |
| [5] | Kim M. S., Ji H. K., Jin M. K., Hong S. H., Lee K., Choi H. S., Sang M. W., Chang J. Y., Tai Y. K., Ko S. G. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 3522-3522 |
| [6] | Wang S., Fischer P. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 302-313 |
| [7] | Barrière C., Santamaría D., Cerqueira A., Galán J., Martín A., Ortega S., Malumbres M., Dubus P., Barbacid M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 72-81 |
| [8] | Berthet C., Aleem E., Coppola V., Tessarollo L., Kaldis P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 1775-1785 |
| [9] | Malumbres M., Sotillo R. O., Santamarí A. D., Galán J., Cerezo A., Ortega S., Dubus P., Barbacid M., Cell,2004, 118, 493-504 |
| [10] | Santamaría D., Barrière C., Cerqueira A., Hunt S., Tardy C., Newton K., Cáceres J. F., Dubus P., Malumbres M., Barbacid M., Nature,2007, 448, 811-815 |
| [11] | Shao H., Shi S., Huang S., Hole A., Abbas A. Y., Baumli S., Liu X., Lam F., Foley D., Fischer P. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 640-659 |
| [12] | Sansó M., Levin R. S., Lipp J. J., Wang V. Y., Greifenberg A. K., Quezada E. M., Ali A., Ghosh A., Larochelle S., Rana T. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 117-129 |
| [13] | Huang C. H., Lujambio A., Zuber J., Tschaharganeh D. F., Doran M. G., Evans M. J., Kitzing T., Zhu N., De S. E., Sawyers C. L., Genes Dev., 2014, 28, 1800-1813 |
| [14] | Walsby E., Pratt G., Shao H., Abbas A. Y., Fischer P. M., Bradshaw T. D., Brennan P., Fegan C., Wang S., Pepper C., Oncotarget,2014, 5, 375-382 |
| [15] | Mariaule G., Belmont P., Molecules,2014, 19, 14366-14382 |
| [16] | Manohar S. M., Rathos M. J., Sonawane V., Rao S. V., Joshi K. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 821-833 |
| [17] | Heathcote D. A., Patel H., Kroll S. H., Hazel P., Periyasamy M., Alikian M., Kanneganti S. K., Jogalekar A. S., Scheiper B., Barbazanges M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 8508-8522 |
| [18] | Conroy A., Stockett D. E., Walker D., Arkin M. R., Hoch U., Fox J. A., Hawtin R. E., Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacolog,2009, 64, 723-732 |
| [19] | Wu Y., Chen C., Sun X., Shi X., Jin B., Ding K., Yeung S.C., Pan J., Clin. Cancer Res., 2012, 18, 1966-1978 |
| [20] | Bettayeb K., Tirado O. M., Marionneaulambot S., Ferandin Y., Lozach O., Morris J. C., Mateolozano S., Drueckes P., Schächtele C., Kubbutat M. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 8325-8334 |
| [21] | Albert T. K., Rigault C., Eickhoff J., Baumgart K., Antrecht C., Klebl B., Mittler G., Meisterernst M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 55-68 |
| [22] | Sawant R. R., Jhaveri A. M., Koshkaryev A., Lin Z., Qureshi F., Torchilin V. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 375-388 |
| [23] | Sonawane Y.A., Taylor M. A., Napoleon J. V., Rana S., Contreras J. I.,Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2016, 59-67 |
| [24] | Kryštof V., Baumli S., Fürst R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 2883-2890 |
| [25] | Lu H., Xue Y., Xue Y., Yu G. K., Arias C., Lin J., Fong S., Faure M., Weisburd B., Ji X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31 |
| [26] | Wu S. Y., Mcnae I., Kontopidis G., Mcclue S. J., Mcinnes C., Stewart K. J., Wang S., Zheleva D. I., Marriage H., Lane D. P., Struct., 2003, 11, 399-410 |
| [27] | Wang S., Meades C., Wood G., Osnowski A., Anderson S., Yuill R., Thomas M., Mezna M., Jackson W., Midgley C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 1662-1670 |
| [28] | Wang S., Griffiths G., Midgley C. A., Barnett A. L., Cooper M., Grabarek J., Ingram L., Jackson W., Kontopidis G., Mcclue S. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 1111-1121 |
| [29] | Lukasik P. M., Elabar S., Lam F., Shao H., Liu X., Abbas A. Y., Wang S., European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2012, 57, 311-322 |
| [30] | Shao H., Shi S., Foley D. W., Lam F., Abbas A. Y., Liu X., Huang S., Jiang X., Baharin N., Fischer P. M., European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2013, 70, 447-455 |
| [31] | Németh G., Varga Z., Greff Z., Bencze G., Sipos A., Szántaikis C., Baska F., Gyuris A., Kelemenics K., Szathmáry Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 342-358 |
| [32] | Nemeth G., Greff Z., Sipos A., Varga Z., Szekely R., Sebestyen M., Jaszay Z., Beni S., Nemes Z., Pirat J. L., Volle J. N., Virieux D., Gyuris A., Kelemenics K., Ay E., Minarovits J., Szathmary S., Keri G., Orfi L., J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57, 3939-3965 |
| [33] | Zhang Q. Q., Yao Q. Z., Zhang S. P., Bi L. M., Zhou Z. G., Zhang J., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30, 371-381 |
| (张青青, 姚其正, 张生平, 毕乐明, 周之光, 张骥. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30, 371-381) | |
| [34] | Liu B. G., Liu J. W., Li J. Q., Geng S., Mo H. Z., Liang G. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities., 2017, 38(1), 41-46 |
| (刘本国, 刘江伟, 李嘉琪, 耿升, 莫海珍, 梁桂兆. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(1), 41-46) | |
| [35] | Chen W. Y., Wang S. S., Li D. L., Peng W., Zhao J. F., Duan H. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities., 2013, 34(12), 2798-2805 |
| 陈文雅, 王珊珊, 李冬玲, 彭炜, 赵静馥, 段红霞. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(12), 2798-2805 | |
| [36] | Chen Y., Cai X., Jiang L., Li Y., Ecotoxicology and Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 202-215 |
| [37] | Li B., Zhou R., He G., Guo L., Huang W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 1396-1403 |
| (李博, 周锐, 何谷, 郭丽, 黄维. 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1396-1403) | |
| [38] | Czudnochowski N., Bösken C. A., Geyer M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 842-854 |
| [39] | Hole A. J., Baumli S., Shao H., Shi S., Huang S., Pepper C., Fischer P. M., Wang S., Endicott J. A., Noble M. E., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 660-670 |
| [40] | Baumli S., Hole A. J., Noble M. E., Endicott J. A., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 811-822 |
| [41] | Li X., Ye L., Wang X., Shi W., Qian X., Zhu Y., Yu H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 357-367 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [3] | CHEN Hanxiang, BIAN Shaoju, HU Bin, LI Wu. Molecular Simulation of the Osmotic Pressures for LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O Solution System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [4] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [5] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [7] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [8] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [9] | LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling, LIU Chengbu. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pulsed Electric Field O/W Emulsion Demulsification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| [10] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [11] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [12] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [13] | HE Jinlu, LONG Run, FANG Weihai. A-site Cation Effects on Hot Carrier Relaxation in Perovskites by Nonadiabatic Molecular Dynamics Simulations † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 439. |
| [14] | ZHU Yuquan, ZHAO Xiaojie, ZHONG Yuan, CHEN Ziru, YAN Hong, DUAN Xue. Theoretical Study on the Construction and Characteristics of the Host-guest Intercalated Structure of Layered Double Hydroxides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2287. |
| [15] | QU Siying, XU Qin. Different Roles of Some Key Residues in the S4 Pocket of Coagulation Factor Xa for Rivaroxaban Binding † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||