

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 830.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160772
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yong1,2, FU Mao2, WU Deli1, ZHANG Yalei1,*( )
)
Received:2016-11-07
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-04-12
Contact:
ZHANG Yalei
E-mail:zhangyalei@tongji.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Yong, FU Mao, WU Deli, ZHANG Yalei. Removal Performance and Mechanism of Selenite with the Highly Active Ferrous Hydroxyl Complex FHC(Cl-)†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 830.
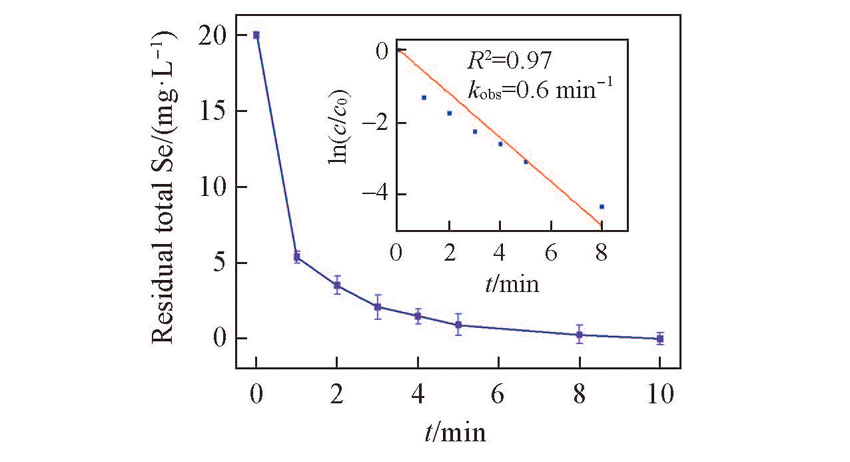
Fig.2 Residual total vs. time of Se(Ⅳ)removal by FHC(Cl-)Inset: fitting results using with first order kinetic model. Initial [Se(Ⅳ)]=20 mg/L, FHC(Cl-) dosage =112 mg/L, pH=7.5.
| Level | Dosage/(mg·L-1) | O2 | pH | c(NaCl)/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56.0 | Aerobic | 5.5 | 0 |
| 2 | 98.0 | Closed | 7.5 | 1 |
| 3 | 140.0 | Anaerobic | 9.5 | 2 |
Table 1 Factor levels based on response surface method(RSM)
| Level | Dosage/(mg·L-1) | O2 | pH | c(NaCl)/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56.0 | Aerobic | 5.5 | 0 |
| 2 | 98.0 | Closed | 7.5 | 1 |
| 3 | 140.0 | Anaerobic | 9.5 | 2 |
| pH | c(NaCl)/ (mmol·L-1) | Dosage/ (mg·L-1) | O2 | c/c0 | pH | c(NaCl)/ (mmol·L-1) | Dosage/ (mg·L-1) | O2 | c/c0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.08 | 7.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.11 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 | 5.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.66 |
| 5.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.52 | 9.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.38 |
| 5.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.88 | 7.5 | 2 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.02 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Aerobic | 0.08 | 5.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.71 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 | 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Aerobic | 0.59 | 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 |
| 7.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.17 | 9.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.14 |
| 9.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.22 | 7.5 | 0 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.48 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 | 5.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.84 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Anaerobic | 0.01 | 7.5 | 2 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.53 |
| 7.5 | 0 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.01 | 5.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.74 |
| 9.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.02 | 9.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.49 |
| 9.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.76 | 7.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.47 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Anaerobic | 0.61 |
Table 2 Designs and results based on RSM
| pH | c(NaCl)/ (mmol·L-1) | Dosage/ (mg·L-1) | O2 | c/c0 | pH | c(NaCl)/ (mmol·L-1) | Dosage/ (mg·L-1) | O2 | c/c0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.08 | 7.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.11 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 | 5.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.66 |
| 5.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.52 | 9.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.38 |
| 5.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.88 | 7.5 | 2 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.02 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Aerobic | 0.08 | 5.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.71 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 | 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Aerobic | 0.59 | 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 |
| 7.5 | 0 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.17 | 9.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.14 |
| 9.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.22 | 7.5 | 0 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.48 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.14 | 5.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.84 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Anaerobic | 0.01 | 7.5 | 2 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.53 |
| 7.5 | 0 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.01 | 5.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Closed | 0.74 |
| 9.5 | 1 | 140.0 | Closed | 0.02 | 9.5 | 1 | 98.0 | Aerobic | 0.49 |
| 9.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Closed | 0.76 | 7.5 | 2 | 98.0 | Anaerobic | 0.47 |
| 7.5 | 1 | 56.0 | Anaerobic | 0.61 |
| Soruces of variation | Quadratic sum | Degree of freedom | F | Level of significance, P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 2.18 | 14 | 23.38 | <0.0001 |
| A-pH | 0.46 | 1 | 68.57 | <0.0001 |
| B-c(NaCl) | 0.003 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.4907 |
| C-dosage | 0.85 | 1 | 127.44 | <0.0001 |
| D-DO | 0.004 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.4293 |
| AB | 0.009 | 1 | 1.36 | 0.2636 |
| AC | 0.04 | 1 | 5.43 | 0.0353 |
| AD | 0.07 | 1 | 10.55 | 0.0058 |
| BC | 0.0004 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.8099 |
| BD | 0.03 | 1 | 4.09 | 0.0626 |
| CD | 0.002 | 1 | 0.30 | 0.5899 |
| A2 | 0.69 | 1 | 105.09 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 0.004 | 1 | 0.53 | 0.4783 |
| C2 | 0.06 | 1 | 9.18 | 0.0090 |
| D2 | 0.03 | 1 | 4.07 | 0.0634 |
| Residual error | 0.09 | 14 | 0.007 | |
| Lack of fit | 0.09 | 10 | 0.09 | |
| Pure error | 0 | 4 | 0 | |
| Sum | 2.27 | 28 |
Table 3 Analysis of variance based on RSM
| Soruces of variation | Quadratic sum | Degree of freedom | F | Level of significance, P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 2.18 | 14 | 23.38 | <0.0001 |
| A-pH | 0.46 | 1 | 68.57 | <0.0001 |
| B-c(NaCl) | 0.003 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.4907 |
| C-dosage | 0.85 | 1 | 127.44 | <0.0001 |
| D-DO | 0.004 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.4293 |
| AB | 0.009 | 1 | 1.36 | 0.2636 |
| AC | 0.04 | 1 | 5.43 | 0.0353 |
| AD | 0.07 | 1 | 10.55 | 0.0058 |
| BC | 0.0004 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.8099 |
| BD | 0.03 | 1 | 4.09 | 0.0626 |
| CD | 0.002 | 1 | 0.30 | 0.5899 |
| A2 | 0.69 | 1 | 105.09 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 0.004 | 1 | 0.53 | 0.4783 |
| C2 | 0.06 | 1 | 9.18 | 0.0090 |
| D2 | 0.03 | 1 | 4.07 | 0.0634 |
| Residual error | 0.09 | 14 | 0.007 | |
| Lack of fit | 0.09 | 10 | 0.09 | |
| Pure error | 0 | 4 | 0 | |
| Sum | 2.27 | 28 |
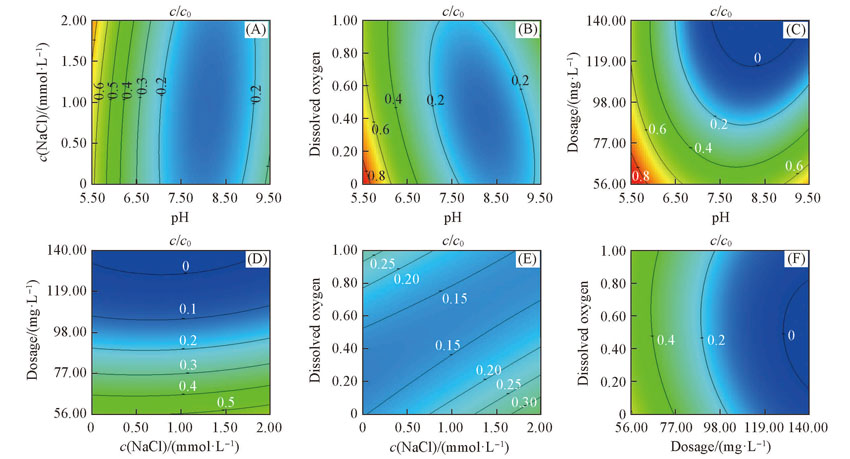
Fig.3 Effects of factors on Se(Ⅳ) removal by FHC(Cl-)(A) Closed system, dosage of FHC(Cl-) =98 mg/L; (B) c(NaCl)=1 mmol/L, dosage of FHC(Cl-) =98 mg/L; (C) closed system, c(NaCl) =1 mmol/L; (D) closed system, pH =7.5; (E) pH =7.5, dosage of FHC(Cl-) =98 mg/L; (F) pH =7.5, c(NaCl)=1 mmol/L.
| Sample | Mass fraction(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2- | OH- | H2O | OH-+ H2O | |
| FHC(Cl-) | 23.05 | 28.33 | 48.62 | 76.95 |
| pH=5.5 | 22.35 | 29.89 | 47.76 | 77.65 |
| pH=7.5 | 25.09 | 28.18 | 46.73 | 74.91 |
| pH=9.5 | 31.78 | 38.45 | 29.80 | 70.20 |
Table 4 Percentage of different chemical speciation of oxygen
| Sample | Mass fraction(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2- | OH- | H2O | OH-+ H2O | |
| FHC(Cl-) | 23.05 | 28.33 | 48.62 | 76.95 |
| pH=5.5 | 22.35 | 29.89 | 47.76 | 77.65 |
| pH=7.5 | 25.09 | 28.18 | 46.73 | 74.91 |
| pH=9.5 | 31.78 | 38.45 | 29.80 | 70.20 |
| [1] | Fordyce F. M., Essentials of Medical Geology, 2013, 16, 375—416 |
| [2] | Hatfield D.L., Selenium: Its Molecular Biology and Role in Human Health, Springer Publishing Company, NewYork, 2006, 1—326 |
| [3] | Lemly A. D., Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 2004, 59, 44—56 |
| [4] | Cleverley J. S., Bastrakov E. N., Computers & Geosciences, 2005, 31(6), 756—767 |
| [5] | Liang L., Yang W., Guan X. H., Li J., Xu Z., Wu J., Water Research, 2013, 47(15), 5846—5855 |
| [6] | Ling L., Pan B. C., Zhang W. X., Water Research, 2015, 71, 274—281 |
| [7] | Scheinost A. C., Kirsch R., Banerjee D., Fernandez-Martinez A., Zaenker H., Funke H., Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2008, 102(3/4), 228—245 |
| [8] | Naveau A., Monteil-Rivera F., Guillon E., Dumonceau J., Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(15), 5376—5382 |
| [9] | Breynaert E., Bruggeman C., Maes A., Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42, 3595—3601 |
| [10] | Missana T., Alonso U., Scheinost A. C., Granizo N., García-Gutiérrez M., Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(20), 6205—6217 |
| [11] | Loyo R. L. D. A., Nikitenko S. I., Scheinost A. C., Simonoff M., Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(7), 2451—2456 |
| [12] | Myneni S. C. B., Tokunaga T. K., Science, 1997, 278(5340), 1106—1109 |
| [13] | Wu D. L., Feng Y., Ma L. M., Jounal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2011, 39(11), 1657—1662 |
| (吴德礼, 冯勇, 马鲁铭.同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2011,39(11), 1657—1662) | |
| [14] | Liang L. P., Yang W. J., Guan X. H., Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014, 46, 20—24 |
| (梁丽萍, 杨文君, 关小红.哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2014,46(6), 20—24) | |
| [15] | Liang L.P., Magnetic Field Enhanced Se(Ⅳ) and Se(Ⅵ) Removal by Zero-Valent Iron: the Efficiency and Mechanism , Harbin Institute of Technology,Haerbin, 2014 |
| (梁丽萍. 磁场强化零价铁去除水中Se(Ⅳ)和Se(Ⅵ)的效能和机制, 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014) | |
| [16] | Liu Y. Q., Majetich S. A., Tilton R. D., Sholl D. S., Lowry G. V., Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39, 1338—1345 |
| [17] | Kim H. S., Kim T., Ahn J. Y., Hwang K. Y., Park J. Y., Lim T. T., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 197, 16—23 |
| [18] | Lin W. X., Yao X., Zhu X. H., Li Y., He W., Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2016, 2, 269—272 |
| (林伟鑫, 姚曦, 朱秀辉, 李勇, 何伟. 中药新药与临床药理, 2016, 2, 269—272) | |
| [19] | Fu M., Wu D. L., Zhang Y. L., Zhang Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12), 2221—2227 |
| (付茂, 吴德礼, 张亚雷, 张勇.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(12), 2221—2227) | |
| [20] | Liu X. L., Fattahi M., Montavon G., Grambow B., Radiochimica Acta, 2008, 96(8), 473—479 |
| [21] | Jin H., Wang J., Ji Y., Chen M. M., Zhang Y., Wang Q., Cong Y. Q., Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2015, 5, 955—964 |
| (金环, 王娟, 姬云, 陈媚媚, 张轶, 王齐, 丛燕青. 物理化学学报, 2015, 5, 955—964) | |
| [22] | Lu T. C., Huang N. K., Lin L. B., Zhang J., Nuclear Technology, 1996, 6, 332—338 |
| (卢铁城, 黄宁康, 林理彬, 张晋. 核技术, 1996, 6, 332—338) | |
| [23] | Knipe S. W., Mycroft J. R., Pratt A. R., Nesbitt H. W., Bancroff G. M., Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(6), 1079—1090 |
| [24] | Rumble J. R., Bickham D. M., Powell C. J., Surf. & Int. Ana, 1992, 19, 241—246 |
| [25] | Kang M. L., Liu C. L., Chen F. R., Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2013, 43, 536—543 |
| (康明亮, 刘春立, 陈繁荣.中国科学: 化学, 2013,43(5), 536—543) |
| [1] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [2] | WU Yu, LI Xuan, YANG Hengpan, HE Chuanxin. Construction of Cobalt Single Atoms via Double-confinement Strategy for High-performance Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [3] | WANG Xintian, LI Pan, CAO Yue, HONG Wenhao, GENG Zhongxuan, AN Zhiyang, WANG Haoyu, WANG Hua, SUN Bin, ZHU Wenlei, ZHOU Yang. Techno-economic Analysis and Industrial Application Prospects of Single-atom Materials in CO2 Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [4] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [5] | WANG Ruhan, JIA Shunhan, WU Limin, SUN Xiaofu, HAN Buxing. CO2-involved Electrochemical C—N Coupling into Value-added Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220395. |
| [6] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [7] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [8] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [9] | SONG Dewen, WANG Mingwang, WANG Yani, JIAO Zhenmei, NING Hui, WU Mingbo. Progress of CO2 Electroreduction to Oxalic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220248. |
| [10] | ZHAO Runyao, JI Guipeng, LIU Zhimin. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction over Pyrrole Nitrogen-coordinated Single-atom Copper Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| [11] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [12] | CHANG Yunfei, LIAO Mingyi, WEN Jiaming. Reduction Performance and Mechanism of Liquid Terminated-carboxyl Fluoroelastomers Using NaBH4/MCl x Reduction System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210835. |
| [13] | SONG Yingying, HUANG Lin, LI Qingsen, CHEN Limiao. Preparation of CuO/BiVO4 Photocatalyst and Research on Carbon Dioxide Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220126. |
| [14] | TAO Yu, OU Honghui, LEI Yongpeng, XIONG Yu. Research Progress of Single-atom Catalysts in Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220143. |
| [15] | GU Yu, XI Baojuan, LI Jiangxiao, XIONG Shenglin. Structure Regulation of Single-atom Catalysts in Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220036. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||